Abstract
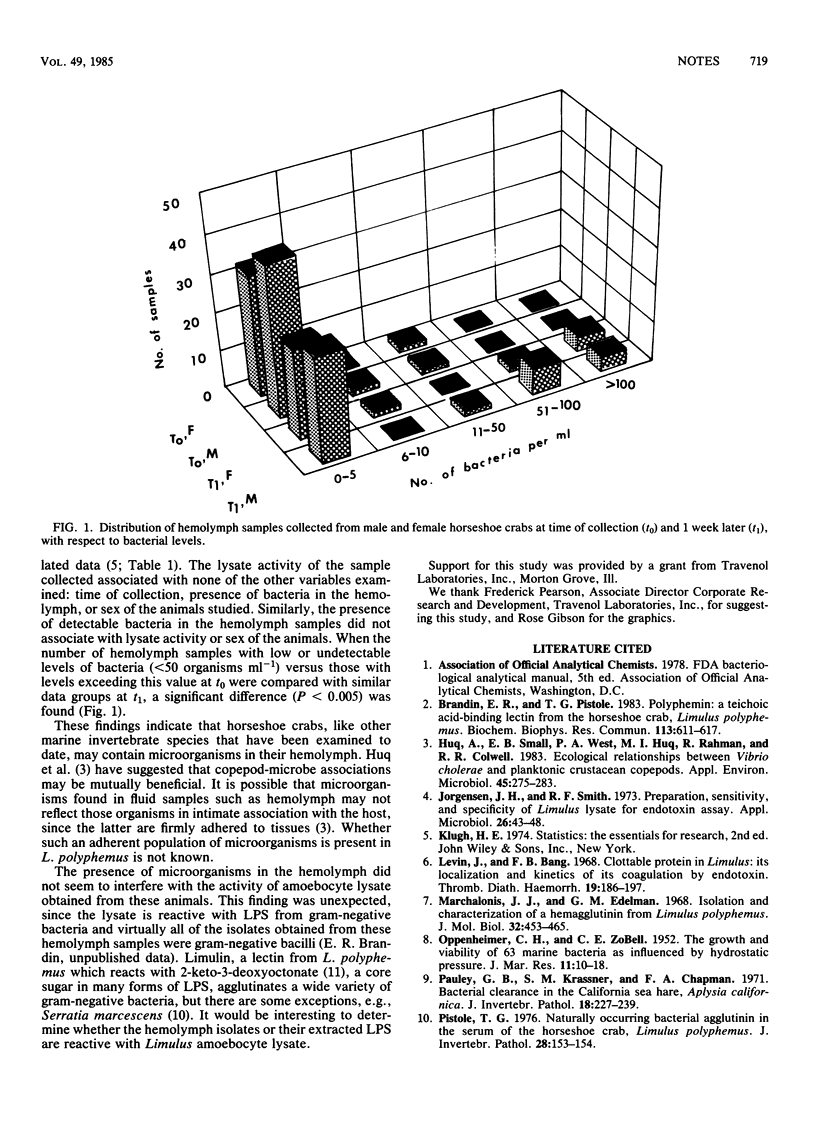
Hemolymph samples obtained from Limulus polyphemus at the time of collection and after a 1-week holding period exhibited a significant increase in bacterial levels. No differences were observed in the ability of amoebocyte lysate, prepared from these same samples, to gel in the presence of lipopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandin E. R., Pistole T. G. Polyphemin: a teichoic acid-binding lectin from the horseshoe crab, Limulus Polyphemus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):611–617. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91770-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huq A., Small E. B., West P. A., Huq M. I., Rahman R., Colwell R. R. Ecological relationships between Vibrio cholerae and planktonic crustacean copepods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.275-283.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Smith R. F. Preparation, sensitivity, and specificity of Limulus lysate for endotoxin assay. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.43-48.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Bang F. B. Clottable protein in Limulus; its localization and kinetics of its coagulation by endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchialonis J. J., Edelman G. M. Isolation and characterization of a hemagglutinin from Limulus polyphemus. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):453–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauley G. B., Krassner S. M., Chapman F. A. Bacterial clearance in the California sea hare, Aplysia californica. J Invertebr Pathol. 1971 Sep;18(2):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(71)90150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistole T. G. Naturally occurring bacterial agglutinin in the serum of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. J Invertebr Pathol. 1976 Jul;28(1):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(76)90084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostam-Abadi H., Pistole T. G. Lipopolysaccharide-binding lectin from the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, with specificity for 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate (KDO). Dev Comp Immunol. 1982 Spring;6(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(82)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubiash H. S., Sizemore R. K., Colwell R. R. Bacterial flora of the hemolymph of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus: most probable numbers. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):388–392. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.388-392.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Galanos C., Kinsky S., Bradshaw R. A., Wessler S., Lüderitz O., Sarmiento M. E. Picogram-sensitive assay for endotoxin: gelation of Limulus polyphemus blood cell lysate induced by purified lipopolysaccharides and lipid A from Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 28;261(1):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



