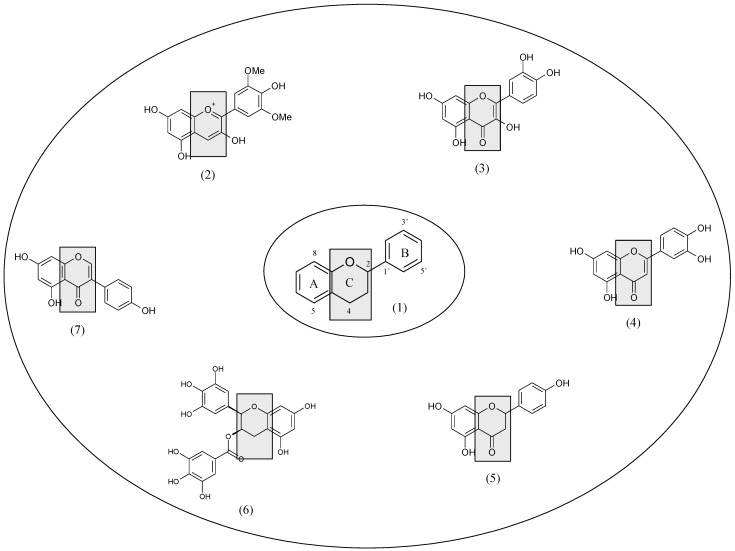
Figure 1.
The flavan nucleus (1) is the basic structure of flavonoids, which include anthocyanidins (e.g., malvidin) (2), flavonols (e.g., quercetin) (3), flavones (e.g., luteolin) (4), flavanones (e.g., naringenin) (5), flavan-3-ols (e.g., epigallocatechin gallate) (6) and isoflavones (e.g., genistein) (7) differing in the level of oxidation and saturation of the C ring.