Abstract
Coriobacterium glomerans Haas and König 1988, is the only species of the genus Coriobacterium, family Coriobacteriaceae, order Coriobacteriales, phylum Actinobacteria. The bacterium thrives as an endosymbiont of pyrrhocorid bugs, i.e. the red fire bug Pyrrhocoris apterus L. The rationale for sequencing the genome of strain PW2T is its endosymbiotic life style which is rare among members of Actinobacteria. Here we describe the features of this symbiont, together with the complete genome sequence and its annotation. This is the first complete genome sequence of a member of the genus Coriobacterium and the sixth member of the order Coriobacteriales for which complete genome sequences are now available. The 2,115,681 bp long single replicon genome with its 1,804 protein-coding and 54 RNA genes is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: Gram-positive, non-motile, non-sporulating, obligatory anaerobic, chemoorganotroph, mesophile, endosymbiont, insect intestinal tract, Coriobacteriaceae, Actinobacteria, GEBA
Introduction
Strain PW2T (= DSM 20642 = ATCC 49209 = JCM 10262) is the type strain of Coriobacterium glomerans [1]. The absence of sequence data in the original description excluded determination of the phylogenetic position of the genus Coriobacterium, but taxonomic evidence also excluded an affiliation with Bifidobacterium, Eubacterium or Lachnospira. The 16S rRNA gene sequence [2] revealed that Coriobacterium and Atopobium [3] are phylogenetic neighbors. Based upon phylogenetic position within the class Actinobacteria and a unique set of 16S rRNA gene signature nucleotides both genera were placed in the family Coriobacteriaceae, order Coriobacterales, subclass Coriobacteridae [4]. The family was expanded by the description of several new genera which at the time of writing encompasses 13 genera and 29 species [5]. In the 2nd edition of Bergey’s Manual the class Actinobacteria was elevated to phylum rank [6] and subsequently the subclass Coriobacteridae was elevated to class rank [7]. The suborder rank ‘Coriobacterineae’ has been introduced by Garrity and collaborators [8]. Coriobacterium is a phylogenetic neighbor of Collinsella [9] and both genera form one of four sister clades of Coriobacteriaceae. Besides the type strain a few other closely related strains (e.g. accession numbers FJ554833, FJ554832, FJ554836, FJ554835) were isolated from Pyrrhocoris apterus L. and a related pyrrhocorid host. Their localization in the midgut, the rectum and feces of the red firebug and the vertical transmission route via application of the symbiont to the surface of the eggs was determined via PCR amplification and FISH hybridization. Horizontal transmission also occurred via symbiont-containing material [10]. BLAST re-analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences of other strains and clones (e.g. accession numbers AJ131149, AJ131150, AJ245921) reported to be members of Coriobacterium [11] revealed that they are actually members of Collinsella.
Here we present a summary classification and a set of features for C. glomerans PW2T together with the description of the complete genomic sequencing and annotation.
Features of the organism
16S rRNA gene sequence analysis
A representative genomic 16S rRNA gene sequence of C. glomerans PW2T was compared using NCBI BLAST [12,13] under default settings (e.g., considering only the high-scoring segment pairs (HSPs) from the best 250 hits) with the most recent release of the Greengenes database [14] and the relative frequencies of taxa and keywords (reduced to their stem [15]) were determined, weighted by BLAST scores. The most frequently occurring genera were Collinsella (61.9%) and Coriobacterium (38.1%) (29 hits in total). Regarding the five hits to sequences from members of the species, the average identity within HSPs was 97.8%, whereas the average coverage by HSPs was 93.4%. Among all other species, the one yielding the highest score was Collinsella tanakaei (AB490807), which corresponded to an identity of 93.4% and an HSP coverage of 99.4%. (Note that the Greengenes database uses the INSDC (= EMBL/NCBI/DDBJ) annotation, which is not an authoritative source for nomenclature or classification.) The highest-scoring environmental sequence was EF399657 (Greengenes short name 'human fecal clone SJTU E 01 75'), which showed an identity of 93.5% and an HSP coverage of 98.4%. The most frequently occurring keywords within the labels of all environmental samples which yielded hits were 'human' (20.6%), 'fecal' (19.8%), 'fece' (10.6%), 'lion' (4.7%) and 'intestin' (1.9%) (221 hits in total). Environmental samples which yielded hits of a higher score than the highest scoring species were not found, indicating that C. glomerans is rarely found in environmental samples.
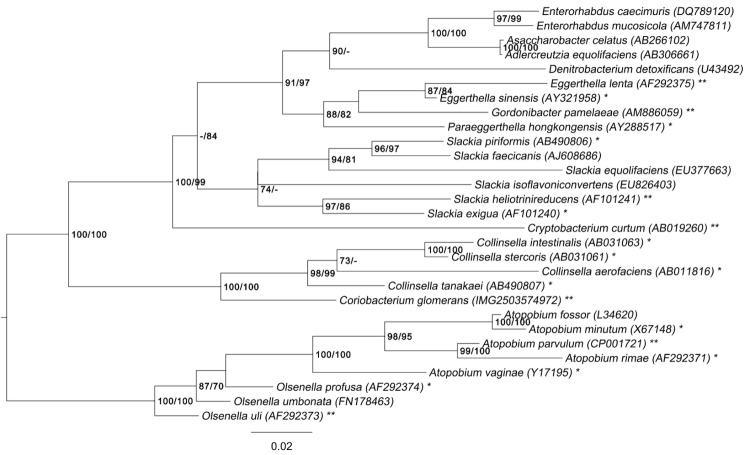
Figure 1 shows the phylogenetic neighborhood of C. glomerans PW2T in a 16S rRNA based tree. The sequences of the two identical 16S rRNA gene copies in the genome differ by six nucleotides from the previously published 16S rRNA sequence (X79048), which contains three ambiguous base calls.
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of C. glomerans relative to the type strains of the other species within the family Coriobacteriaceae. The tree was inferred from 1,401 aligned characters [16,17] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood (ML) criterion [18]. Rooting was done initially using the midpoint method [19] and then checked for its agreement with the current classification (Table 1). The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers adjacent to the branches are support values from 300 ML bootstrap replicates [20] (left) and from 1,000 maximum-parsimony bootstrap replicates [21] (right) if larger than 60%. Lineages with type strain genome sequencing projects registered in GOLD [22] are labeled with one asterisk, those also listed as 'Complete and Published' with two asterisks ([23-27], see FP929047 for Gordonibacter pamelaeae).
Table 1. Classification and general features of C. glomerans PW2T according to the MIGS recommendations [28].
| MIGS ID | Property | Term | Evidence code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current classification | Domain Bacteria | TAS [29] | |
| Phylum Actinobacteria | TAS [30] | ||
| Class Actinobacteria | TAS [4] | ||
| Subclass Coriobacteridae | TAS [4,31] | ||
| Order Coriobacteriales | TAS [4,31] | ||
| Suborder Coriobacterineae | TAS [32] | ||
| Family Coriobacteriaceae | TAS [4,31] | ||
| Genus Coriobacterium | TAS [1] | ||
| Species Coriobacterium glomerans | TAS [1] | ||
| MIGS-7 | Subspecific genetic lineage (strain) | PW2T | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-12 | Reference for biomaterial | Haas and König 1988 | TAS [1] |
| Gram stain | positive | TAS [1] | |
| Cell shape | rod-shaped | TAS [1] | |
| Motility | non-motile | TAS [1] | |
| Sporulation | non-sporulating | TAS [1] | |
| Temperature range | mesophile | TAS [1] | |
| Optimum temperature | 30°C | TAS [1] | |
| Salinity | not reported | ||
| MIGS-22 | Relationship to oxygen | obligate anaerobe | TAS [1] |
| Carbon source | not reported | ||
| Energy metabolism | chemoorganotroph | TAS [1] | |
| MIGS-6 | Habitat | host, intestinal tract | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-6.2 | pH | not reported | |
| MIGS-15 | Biotic relationship | unknown | |
| MIGS-14 | Known pathogenicity | none | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-16 | Specific host | Pyrrhocoris apterus L. | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-18 | Health status of Host | unknown | |
| Biosafety level | 1 | TAS [33] | |
| MIGS-19 | Trophic level | unknown | |
| MIGS-23.1 | Isolation | intestinal tract of the red soldier bug | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-4 | Geographic location | Bavaria, Germany | TAS [1] |
| MIGS-5 | Time of sample collection | December 1981 | NAS |
| MIGS-4.1 | Latitude | not reported | |
| MIGS-4.2 | Longitude | not reported | |
| MIGS-4.3 | Depth | not reported | |
| MIGS-4.4 | Altitude | not reported |
Evidence codes - TAS: Traceable Author Statement (i.e., a direct report exists in the literature); NAS: Non-traceable Author Statement (i.e., not directly observed for the living, isolated sample, but based on a generally accepted property for the species, or anecdotal evidence). Evidence codes are from the Gene Ontology project [34].
Morphology and physiology
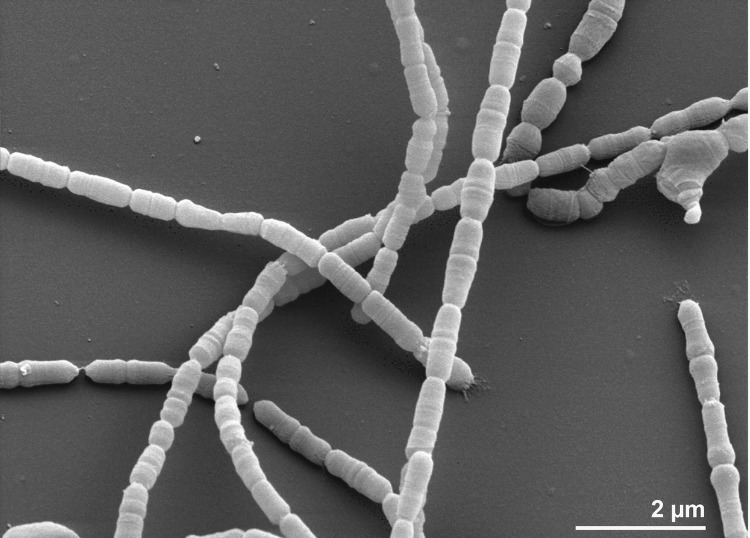
Cells of C. glomerans PW2T stain Gram-positive which is consistent with an electron-dense cell wall, 40 nm wide [35]. The cells are pear-shaped to irregularly shaped rods with length that varies from 0.44 to 1.80 µm (Figure 2). Spherical involution forms are common. When attached to the epithelia of the intestines, the bacteria form chains which may reach more than 150 µm in length. Flagella are absent. Colonies, grown anaerobically in an atmosphere of N2-CO2 (80:20) on blood agar (Columbia agar base, BBL), supplemented Schaedler agar (BBL), and TPY agar at 25 and 30°C are about 0.6 mm in diameter and consist of long filamentous chains, bent into hairpins, curls, and loops. A flocculent, wooly sediment with a clear supernatant is formed in fluid media. The bacteria are strictly anaerobic. In TPY medium glucose is fermented to acetic acid, L-lactic acid, and ethanol in a molar ratio of 1.16:1.00:0.95. CO2 and H2 also are produced [1] but D-lactic acid, formic acid, volatile short-chain alcohols, or other volatile fatty acids are not formed. Under more stringent anaerobic conditions with N2-CO2 (80:20) as the gas phase, but lacking H2, the formation of ethanol occurs only at a lower concentration. C. glomerans PW2T ferments glucose, L-arabinose, D-xylose, D-ribose, mannose, sucrose, maltose, cellobiose, mannitol, and salicin but not lactose, melibiose, raffinose, inulin, starch, and inositol [1].
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrograph of C. glomerans PW2T
Chemotaxonomy
The peptidoglycan of stain PW2T contains lysine as the diagnostic amino acid in position 3 of the peptide subunit with the interpeptide bridge containing aspartic acid (Lys-Asp type; A4α according to [36]; A11.31 according to [37]). Information on major cell wall sugars, fatty acids, menaquinones and polar lipids is not available. The mol% G+C of DNA was reported to be about 61, and is here confirmed by the genome sequence.
Genome sequencing and annotation
Genome project history
This organism was selected for sequencing on the basis of its phylogenetic position [38], and is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project [39]. The genome project is deposited in the Genomes OnLine Database [22] and the complete genome sequence is deposited in GenBank. Sequencing, finishing and annotation were performed by the DOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI) using state of the art sequencing technology [40]. A summary of the project information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Genome sequencing project information.
| MIGS ID | Property | Term |
|---|---|---|
| MIGS-31 | Finishing quality | Finished |
| MIGS-28 | Libraries used | Three genomic libraries: one 454 pyrosequence standard library, one 454 PE library (6.7 kb insert size), one Illumina library |
| MIGS-29 | Sequencing platforms | Illumina GAii, 454 GS FLX Titanium |
| MIGS-31.2 | Sequencing coverage | 35.8 × Illumina; 68.3 × pyrosequence |
| MIGS-30 | Assemblers | Newbler version 2.3, Velvet, Phrap version SPS - 4.24 |
| MIGS-32 | Gene calling method | Prodigal 1.4, GenePRIMP |
| INSDC ID | CP002628 | |
| GenBank Date of Release | October 11, 2011 | |
| GOLD ID | Gc01723 | |
| NCBI project ID | 42699 | |
| Database: IMG-GEBA | 2503538010 | |
| MIGS-13 | Source material identifier | DSM 20642 |
| Project relevance | Tree of Life, GEBA |
Growth conditions and DNA isolation
C. glomerans strain PW2T, DSM 20642, was grown anaerobically in an atmosphere of N2-CO2 (80:20) in DSMZ medium 104 (modified PYG medium) at 30°C. DNA was isolated from 1-1.5 g of cell paste using MasterPure Gram-positive DNA purification kit (Epicentre MGP04100) following the standard protocol as recommended by the manufacturer with modification st/LALM for cell lysis as described in Wu et al. 2009 [39]. DNA is available through the DNA Bank Network [41].
Genome sequencing and assembly
The genome was sequenced using a combination of Illumina and 454 sequencing platforms. All general aspects of library construction and sequencing can be found at the JGI website [42]. Pyrosequencing reads were assembled using the Newbler assembler (Roche). The initial Newbler assembly consisting of 14 contigs in one scaffold was converted into a phrap [43] assembly by making fake reads from the consensus, to collect the read pairs in the 454 paired end library. Illumina GAii sequencing data (75.8 Mb) was assembled with Velvet [44] and the consensus sequences were shredded into 1.5 kb overlapped fake reads and assembled together with the 454 data. The 454 draft assembly was based on 128.4 Mb 454 draft data and all of the 454 paired end data. Newbler parameters are -consed -a 50 -l 350 -g -m -ml 20. The Phred/Phrap/Consed software package [43] was used for sequence assembly and quality assessment in the subsequent finishing process. After the shotgun stage, reads were assembled with parallel phrap (High Performance Software, LLC). Possible mis-assemblies were corrected with gapResolution [42], Dupfinisher [45], or sequencing cloned bridging PCR fragments with subcloning. Gaps between contigs were closed by editing in Consed, by PCR and by Bubble PCR primer walks (J.-F. Chang, unpublished). A total of 40 additional reactions were necessary to close gaps and to raise the quality of the finished sequence. Illumina reads were also used to correct potential base errors and increase consensus quality using a software Polisher developed at JGI [46]. The error rate of the completed genome sequence is less than 1 in 100,000. Together, the combination of the Illumina and 454 sequencing platforms provided 104.1 × coverage of the genome. The final assembly contained 456,305 pyrosequence and 2,106,317 Illumina reads.
Genome annotation
Genes were identified using Prodigal [47] as part of the DOE-JGI genome annotation pipeline [48], followed by a round of manual curation using the JGI GenePRIMP pipeline [49]. The predicted CDSs were translated and used to search the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nonredundant database, UniProt, TIGR-Fam, Pfam, PRIAM, KEGG, COG, and InterPro databases. Additional gene prediction analysis and functional annotation was performed within the Integrated Microbial Genomes – Expert Review (IMG-ER) platform [50].
Genome properties
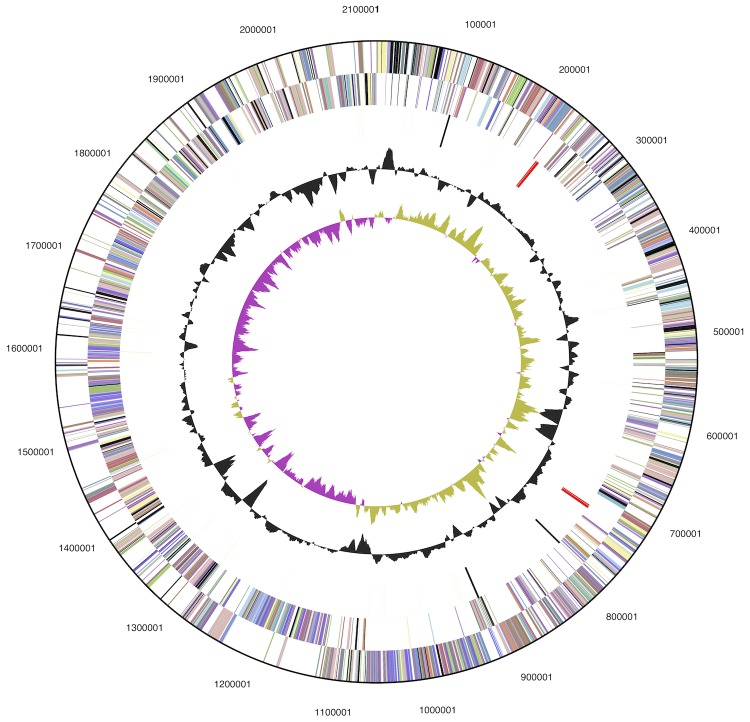
The genome statistics are provided in Table 3 and Figure 3. The genome consists of one chromosome with a total length of 2,115,681 bp and a G+C content of 60.4%. Of the 1,858 genes predicted, 1,804 were protein-coding genes, and 54 RNAs; 36 pseudogenes were also identified. The majority of the protein-coding genes (74.2%) were assigned a putative function while the remaining ones were annotated as hypothetical proteins. The distribution of genes into COGs functional categories is presented in Table 4.
Table 3. Genome Statistics.
| MIGS ID | Attribute | Number | % of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 2,115,681 | 100.00 | |
| DNA coding region (bp) | 1,879,452 | 88.83 | |
| DNA G+C content (bp) | 1,277,733 | 60.39 | |
| MIGS-9 | Number of replicons | 1 | |
| MIGS-10 | Extrachromosomal elements | 0 | |
| Total genes | 1,858 | 100.00 | |
| RNA genes | 54 | 2.91 | |
| rRNA operons | 2 | ||
| tRNA genes | 45 | 2.42 | |
| Protein-coding genes | 1,804 | 97.09 | |
| Pseudo genes | 36 | 1.94 | |
| Genes with function prediction | 1,378 | 74.17 | |
| Genes in paralog clusters | 828 | 44.56 | |
| Genes assigned to COGs | 1,500 | 80.73 | |
| Genes assigned Pfam domains | 1,551 | 83.48 | |
| Genes with signal peptides | 314 | 16.90 | |
| Genes with transmembrane helices | 484 | 26.05 | |
| CRISPR repeats | 2 |
Figure 3.
Graphical map of the chromosome. From outside to the center: Genes on forward strand (color by COG categories), Genes on reverse strand (color by COG categories), RNA genes (tRNAs green, rRNAs red, other RNAs black), GC content, GC skew (purple/olive).
Table 4. Number of genes associated with the general COG functional categories.
| Code | Value | % age | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| J | 134 | 8.2 | Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis |
| A | ... | ... | RNA processing and modification |
| K | 158 | 9.6 | Transcription |
| L | 75 | 4.6 | Replication, recombination and repair |
| B | 1 | 0.1 | Chromatin structure and dynamics |
| D | 19 | 1.2 | Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning |
| Y | ... | ... | Nuclear structure |
| V | 43 | 2.6 | Defense mechanisms |
| T | 62 | 3.8 | Signal transduction mechanisms |
| M | 98 | 6.0 | Cell wall/membrane biogenesis |
| N | ... | ... | Cell motility |
| Z | ... | ... | Cytoskeleton |
| W | ... | ... | Extracellular structures |
| U | 17 | 1.0 | Intracellular trafficking and secretion, and vesicular transport |
| O | 42 | 2.6 | Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones |
| C | 63 | 3.8 | Energy production and conversion |
| G | 317 | 19.3 | Carbohydrate transport and metabolism |
| E | 105 | 6.4 | Amino acid transport and metabolism |
| F | 52 | 3.2 | Nucleotide transport and metabolism |
| H | 59 | 3.6 | Coenzyme transport and metabolism |
| I | 34 | 2.1 | Lipid transport and metabolism |
| P | 53 | 3.2 | Inorganic ion transport and metabolism |
| Q | 11 | 0.7 | Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism |
| R | 178 | 10.8 | General function prediction only |
| S | 122 | 7.4 | Function unknown |
| - | 358 | 19.3 | Not in COGs |
Acknowledgements
We would like to gratefully acknowledge the help of Gabriele Gehrich-Schröter for growing C. glomerans cultures, and Susanne Schneider for DNA extraction and quality control (both at DSMZ). This work was performed under the auspices of the US Department of Energy Office of Science, Biological and Environmental Research Program, and by the University of California, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC52-07NA27344, and Los Alamos National Laboratory under contract No. DE-AC02-06NA25396, UT-Battelle and Oak Ridge National Laboratory under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725.
References
- 1.Haas F, König H. Coriobacterium glomerans gen. nov., sp. nov. from the intestinal tract of the Red Soldier Bug. Int J Syst Bact 1988; 38:382-384 10.1099/00207713-38-4-382 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rainey FA, Weiss N, Stackebrandt E. Coriobacterium and Atopobium are phylogenetic neighbors within the actinomycetes line of descent. Syst Appl Microbiol 1994; 17:202-205 10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80008-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Collins MD, Wallbanks S. Comparative sequence analysis of the 16S rRNA genes of Lactobacillus minutus, Lactobacillus rimae and Streptococcus parvulus. Proposal for the creation of a new genus Atopobium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 1992; 95:235-240 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05372.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stackebrandt E, Rainey FA, Ward-Rainey NL. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1997; 47:479-491 10.1099/00207713-47-2-479 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Munoz R, Yarza P, Ludwig W, Euzéby J, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Glöckner FO, Rosselló-Móra R. Release LTPs104 of the All-Species Living Tree. Syst Appl Microbiol 2011; 34:169-170 10.1016/j.syapm.2011.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Goodfellow M. Phylum XXVI Actinobacteria phyl. nov. In Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse HJ, Trujillo ME, Suzuki K, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology 2nd ed. 2012a; p.33-34. [Google Scholar]
- 7.König H. Class III. Coriobacteriia class. nov. In: Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse HJ, Trujillo ME, Suzuki K, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology 2nd ed. 2012a; p 1975. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Garrity GM, Lilburn TG, Cole JR, Harrison SH, Euzeby J, Tindall BJ. Taxonomic outline if the bacteria and Archaea, Release 7.7 March 6, 2007. Part 10-The bacteria: Phylum ‘Actinobacteria’: Class Actinobacteria
- 9.Kageyama A, Benno Y, Nakase T. Phylogenetic and phenotypic evidence for the transfer of Eubacterium aerofaciens to the genus Collinsella as Collinsella aerofaciens gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1999; 49:557-565 10.1099/00207713-49-2-557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kaltenpoth M, Winter SA, Kleinhammer A. Localization and transmission route of Coriobacterium glomerans, the endosymbiont of pyrrhocorid bugs. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2009; 69:373-383 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00722.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.König H. Genus I. Coriobacterium. In: Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse H-J, Trujillo ME, Suzuki K, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology 2nd ed. 2012b; pp. 1977-1978. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990; 215:403-410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Korf I, Yandell M, Bedell J. BLAST, O'Reilly, Sebastopol, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 14.DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 2006; 72:5069-5072 10.1128/AEM.03006-05 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Porter MF. An algorithm for suffix stripping. Program: electronic library and information systems 1980; 14:130-137.
- 16.Lee C, Grasso C, Sharlow MF. Multiple sequence alignment using partial order graphs. Bioinformatics 2002; 18:452-464 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.452 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 2000; 17:540-552 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web-servers. Syst Biol 2008; 57:758-771 10.1080/10635150802429642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hess PN, De Moraes Russo CA. An empirical test of the midpoint rooting method. Biol J Linn Soc Lond 2007; 92:669-674 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00864.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pattengale ND, Alipour M, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Moret BME, Stamatakis A. How many bootstrap replicates are necessary? Lect Notes Comput Sci 2009; 5541:184-200 10.1007/978-3-642-02008-7_13 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Swofford DL. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and Other Methods), Version 4.0 b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pagani I, Liolios K, Jansson J, Chen IM, Smirnova T, Nosrat B, Markowitz VM, Kyrpides NC. The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.4: status of genomic and metagenomic projects and their associated metadata. Nucleic Acids Res 2012; 40:D571-D579 10.1093/nar/gkr1100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Saunders E, Pukall R, Abt B, Lapidus A, Glavina Del Rio T, Copeland A, Tice H, Cheng JF, Lucas S, Chen F, et al. Complete genome sequence of Eggerthella lenta type strain (VPI 0255T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:174-182 10.4056/sigs.33592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pukall R, Lapidus A, Nolan M, Copeland A, Glavina Del Rio T, Lucas S, Chen F, Tice H, Cheng JF, Chertkov O, et al. Complete genome sequence of Slackia heliotrinireducens type strain (RHS 1T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:234-241 10.4056/sigs.37633 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mavrommatis K, Pukall R, Rohde C, Chen F, Sims D, Brettin T, Kuske C, Detter JC, Han C, Lapidus A, et al. Complete genome sequence of Cryptobacterium curtum type strain (12-3T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:93-100 10.4056/sigs.12260 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Copeland A, Sikorski J, Lapidus A, Nolan M, Glavina Del Rio T, Lucas S, Chen F, Tice H, Pitluck S, Cheng JF, et al. Complete genome sequence of Atopobium parvulum type strain (IPP 1246T). Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:166-173 10.4056/sigs.29547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Göker M, Held B, Lucas S, Nolan M, Yasawong M, Glavina Del Rio T, Tice H, Cheng JF, Bruce D, Detter JC, et al. Complete genome sequence of Olsenella uli type strain (AVPI D76D-27CT). Stand Genomic Sci 2010; 3:76-84 10.4056/sigs.1082860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Field D, Garrity G, Gray T, Morrison N, Selengut J, Sterk P, Tatusova T, Thomson N, Allen MJ, Angiuoli SV, et al. The minimum information about a genome sequence (MIGS) specification. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26:541-547 10.1038/nbt1360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87:4576-4579 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Garrity GM, Holt JG. The Road Map to the Manual. In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 1, Springer, New York, 2001, p. 119-169. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhi XY, Li WJ, Stackebrandt E. An update of the structure and 16S rRNA gene sequence-based definition of higher ranks of the class Actinobacteria, with the proposal of two new suborders and four new families and emended descriptions of the existing higher taxa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009; 59:589-608 10.1099/ijs.0.65780-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garrity GM, Holt JG. Taxonomic Outline of the Archaea and Bacteria In: Garrity GM, Boone DR, Castenholz RW (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 1, Springer, New York, 2001, p. 155-166. [Google Scholar]
- 33.BAuA. 2010, Classification of bacteria and archaea in risk groups. http://www.baua.de TRBA 466, p. 63.
- 34.Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 2000; 25:25-29 10.1038/75556 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Haas F, König H. Characterization of an anaerobic symbiont and the associated aerobic bacterial flora of Pyrrhocoris upterus (Heteroptera: Pyrrhocoridae). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 1987; 45:99-106 [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schleifer KH, Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev 1972; 36:407-477 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schumann P. Peptidoglycan Structure. In Taxonomy of Prokaryotes. In: Rainey F, Oren A (eds) Methods in Microbiology, vol. 38, London: Academic Press. 2011; pp. 101-129. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Klenk HP, Göker M. En route to a genome-based classification of Archaea and Bacteria? Syst Appl Microbiol 2010; 33:175-182 10.1016/j.syapm.2010.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wu D, Hugenholtz P, Mavromatis K, Pukall R, Dalin E, Ivanova NN, Kunin V, Goodwin L, Wu M, Tindall BJ, et al. A phylogeny-driven genomic encyclopaedia of Bacteria and Archaea. Nature 2009; 462:1056-1060 10.1038/nature08656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mavromatis K, Land ML, Brettin TS, Quest DJ, Copeland A, Clum A, Goodwin L, Woyke T, Lapidus A, Klenk HP, et al. The fast changing landscape of sequencing technologies and their impact on microbial genome assemblies and annotation. PLoS ONE 2012; 7:e48837 10.1371/journal.pone.0048837 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gemeinholzer B, Dröge G, Zetzsche H, Haszprunar G, Klenk HP, Güntsch A, Berendsohn WG, Wägele JW. The DNA Bank Network: the start from a German initiative. Biopreserv Biobank 2011; 9:51-55 10.1089/bio.2010.0029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.JGI website. http://www.jgi.doe.gov/
- 43.The Phred/Phrap/Consed software package. http://www.phrap.com
- 44.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 2008; 18:821-829 10.1101/gr.074492.107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Han C, Chain P. Finishing repeat regions automatically with Dupfinisher. In: Proceeding of the 2006 international conference on bioinformatics & computational biology. Arabnia HR, Valafar H (eds), CSREA Press. June 26-29, 2006: 141-146. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lapidus A, LaButti K, Foster B, Lowry S, Trong S, Goltsman E. POLISHER: An effective tool for using ultra short reads in microbial genome assembly and finishing. AGBT, Marco Island, FL, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hyatt D, Chen GL, LoCascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ. Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics 2010; 11:119 10.1186/1471-2105-11-119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mavromatis K, Ivanova NN, Chen IM, Szeto E, Markowitz VM, Kyrpides NC. The DOE-JGI Standard operating procedure for the annotations of microbial genomes. Stand Genomic Sci 2009; 1:63-67 10.4056/sigs.632 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Pati A, Ivanova NN, Mikhailova N, Ovchinnikova G, Hooper SD, Lykidis A, Kyrpides NC. GenePRIMP: a gene prediction improvement pipeline for prokaryotic genomes. Nat Methods 2010; 7:455-457 10.1038/nmeth.1457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Markowitz VM, Ivanova NN, Chen IMA, Chu K, Kyrpides NC. IMG ER: a system for microbial genome annotation expert review and curation. Bioinformatics 2009; 25:2271-2278 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]