Abstract
We conducted a species diversity study of the hypogeous Ascomycetes of Israel. The hypogeous Ascomycetes in Israel include members of the families Pyronemataceae, Pezizaceae, and Tuberaceae, which are represented by seven species: Hydnocystis piligera, Terfezia arenaria, T. claveryi, T. oligosperma, Tirmania africana, Tuber asa, and T. nitidum; only T. asa is new to Israeli mycobiota. Synonymy, locations, collection data, general distribution, distribution in Israel, descriptions, a key to identification, illustrations, and taxonomic remarks are provided.
Keywords: Ascomycetes, Distribution, Hypogeous, Mediterranean, Mycorrhiza
The hypogeous Ascomycetes represent one of the most interesting and complicated systematic groups of Ascomycetes. The species diversity of this group in Israel is poorly known compared to many other fungal groups, and only a few surveys on this subject have been published. The most notable ones include the elaborations by Rayss [1, 2] and Binyamini [3-5]. However, none of these researchers provided a critical species diversity study or a taxonomic analysis of the hypogeous Ascomycetes in Israel.
Hypogeous fungi colonize a variety of forests and semi-arid ecosystems in the Mediterranean region. Most of these fungi frequently establish mutualistic associations with vascular plants via specialized nutrient-gathering organs called mycorrhizas [6]. Many hypogeous fungi occurring in semi-arid and arid desert ecosystems of the Mediterranean Basin belong to the genera Hydnocystis, Terfezia, Tirmania, and Tuber. Most are endemic not only to Israel but also to the Mediterranean region and establish mycorrhizal symbioses with members of the Cistaceae, mainly with Helianthemum species.
According to classical mycology, most species have been described based on their morphological features such as ascospore and peridium morphology, gleba color, odor and other organoleptic characteristics. However, these fungi are difficult to identify at the species level. The use of morphological features is problematic for the systematics of hypogeous Ascomycetes because of the reduced set of morphological characteristics and homoplasy. Ascocarp features are homoplastic as a result of the parallel evolution of independent lineages of epigeous/hypogeous fruit bodies during the evolutionary history of the Pezizales [7]. This accounts for the early artificial classification of hypogeous fungi in the order Tuberales. Tuberales includes several hypogeous families with similar morphology that originated by parallel or convergent evolution [8]. Realizing that the Tuberales artificially grouped many Pezizales, Trappe [7] transferred some of families from Tuberales to Pezizales and amended some families in Pezizales to include related hypogeous fungi. He also amended the Pezizaceae Fries sensu Korf to accommodate several related hypogeous taxa lacking forcible spore discharge, such as Tirmania. In addition, Trappe [7] included Terfezia in the Terfeziaceae and Picoa in the Balsamiaceae, based on a comparative morphological study.
The increasing amount of molecular phylogenetic data now available has led to a continued revision of the hypogeous Ascomycetes [8-12]. O'Donnell et al. [8] provided support for the occurrence of independent lines of epigeous/hypogeous fruit body evolution in the Pezizales, which has affected classification of the desert truffles. Moreover, an 18S rDNA sequence analysis has revealed a close relationship between Terfezia and the Pezizaceae [13, 14].
Subgeneric relationships within the Pezizales have been subjected to molecular analysis [14-17]. However, other than studies of the genus Tuber [16], no recent work has addressed subgeneric relationships within the hypogeous genera. Many hypogeous Ascomycetes have a rich synonymy, i.e., some species have, at times, been placed in different genera, families, or orders by different authors, and species names have been changed as well. New interpretations based on molecular phylogenetic analyses are leading to the assignment of species to different genera based on generic relationships rather than structural relationships. Therefore, the names accepted in this study have been used currently by many mycologists but are subject to change with new interpretations.
After searching the literature, we found that six species of hypogeous Ascomycetes are known in Israel. During the investigation, one new species from the genus Tuber was added to Israel's mycobiota. At present, the hypogeous Ascomycetes in Israel are represented by seven species.
Materials and Methods
This investigation was based on the 2002 and 2007 growing seasons and on published literature devoted to Ascomycetes of Israel. The collected specimens were preserved at the Institute of Evolution, University of Haifa (HAI, Israel) herbarium. The microscopic characteristics were observed with a Carl Zeiss-amplival microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany), and photomicrographs were taken with a Sony camera (Sony, Tokyo, Japan). Fungal material was mounted on a microscope slide and examined in water using a light/dark field microscope with or without phase contrast at a magnification of up to ×1,000. Micromor-phological characteristics of our specimens were observed using Melzer's reagent. For statistical calculations, 30~40 ascospores, asci, exscipular hyphae, and paraphyses were measured for each preparation.
The habitat and general distribution of hypogeous Ascomycetes species are given according to Saccardo [18], Burdsall [19], Dennis [20], Binyamini [3-5], and Montecchi and Sarasini [21]. All synonyms were adopted from the Index Fungorum online database (http://www.indexfungorum.org/) and were revised by the authors, and the most significant were chosen. The distribution of species is provided, using the natural regions of Israel, according to Feinbrun-Dothan and Danin [22] (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Accepted abbreviations of nature regions of Israel: AP, Akko Plain; AV, Arava Valley; BS, Beit Shean Valley; CC, Carmel Coast; CG, Coast Galilee; CM, Carmel Mount; CN, Central Negev; DS, Dead Sea area; EP, Esdraelon (Yizre'el) Plain; GH, Golan Heights; GM, Gilboa Mount; HE, Hermon Mount; HP, Hula Plain; JD, Judean Desert; JM, Judean Mts.; LG, Lower Galilee; LJ, Lower Jordan Valley; NN, Northern Negev; PP, Philistean Plain; SA, Samaria; SH, Shefela; SN, South Negev; SP, Sharon Plain; UG, Upper Galilee; UJ, Upper Jordan Valley; WN, Western Negev.
Results and Discussion
Pyronemataceae Corda
Genus Hydnocystis Tulasne & C. Tulasne, Parl. Giorn. Bot. Ital. 2(1): 59 (1844).
Type species
Hydnocystis piligera Tul. & Tul., Parl. Giorn. Bot. Ital. I 1(2): 59 (1844).
Hydnocystis piligera Tul. & Tul., Parl. Giorn. Bot. Ital. I 1(2): 59 (1844) (Fig. 2)
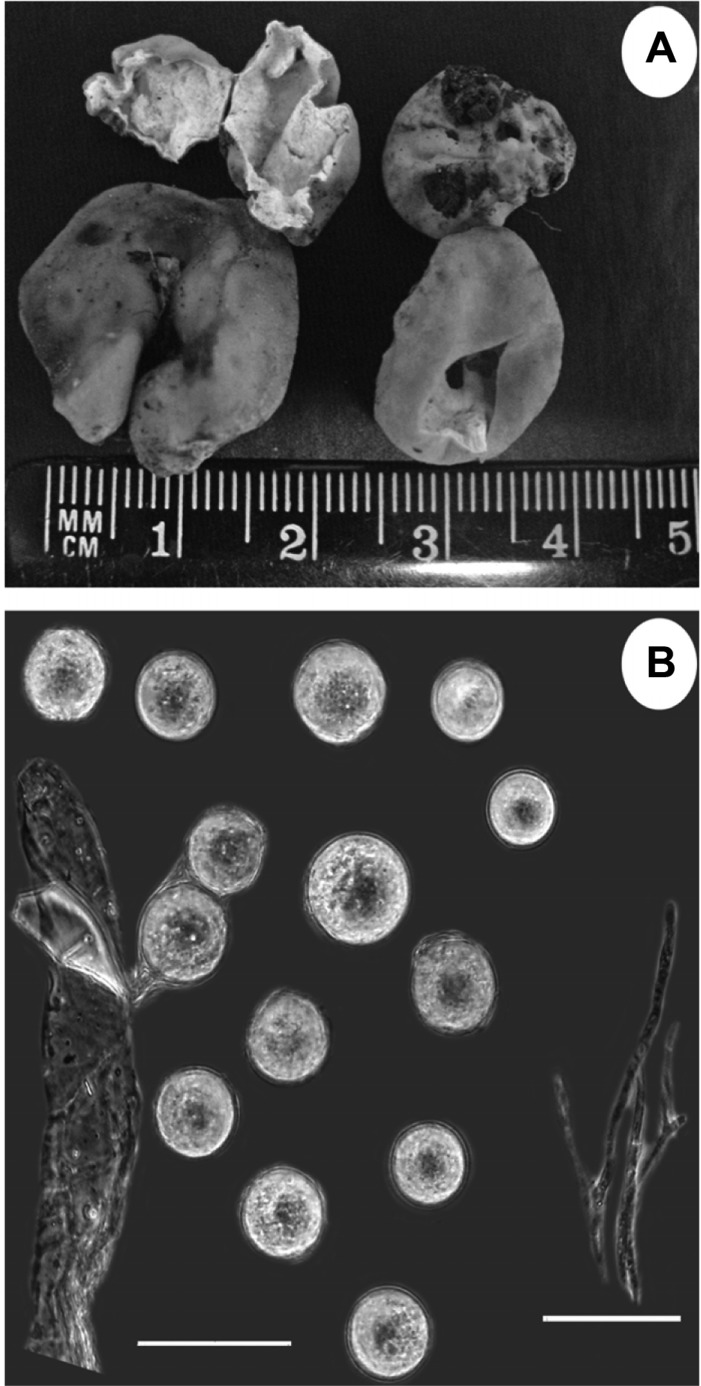
Fig. 2.
Hydnocystis piligera Tul. & Tul. (HAI-D-035): A, Ascocarps and ascocarp in cross-section; B, Part of ascus, ascospores and paraphyses (scale bars = 50 µm).
Icon
Tulasne & Tulasne, Fung. Hypo. t. 13, fig. II, 1~11, 1851; Burdsall, Mycologia 60(3), 505: fig. 22~25, 1968; Binyamini, Nova Hedvigia XXXII, 18: fig. 1, 19: 7a, b, c, d, 1980; Montecchi & Sarasini, Fungi Ipogei D'Europa, p. 183, 2000.
Ascocarpes: 1.0~2.5 cm in diam, hypogeous, globose to subglobose, flattened, lobed with basal pore, sessile, hollow, brownish to yellow-brown, felted with short fine hairs, sometimes attached to plant debris. Gleba: cream or straw colored, fleshy but firm. Odor: strong and unpleasant. Outer excipulum: composed of Textura angularis about 300 µm thick, cells 10~25 µm broad, pigmented yellowish cream. Excipular hairs in young specimens 50 µm up to 150 µm long, 5~8 µm broad, thick-walled, septate, hyaline or yellowish brown, apex obtuse, bulbose at the base. Inner excipulum: composed of Textura angularis about 200 µm thick, subhymenium with Textura intricata 20~30 µm thick, thin-walled, hymenium about 200~500 µm thick. Asci: cylindrical to subclavate, 180~350 × 20~45 µm, tapering gradually to the base, 8-spored, uniseriate, rarely bi-seriate. Ascospores: globose, 22~28 (~31) µm, hyaline or yellowish, smooth, thin-walled, without oil drops. Paraphyses: 1~3 µm broad, septate, hyaline or slightly yellowish, thin-walled.
Habitat & Distribution in Israel
Fruiting in December, in mixed Pinus and Quercus wood, at or near the soil surface. UG: Hiram Wood, Desember 8, 1976, leg. by students, det. N. Binyamini (Fig. 3) [3].
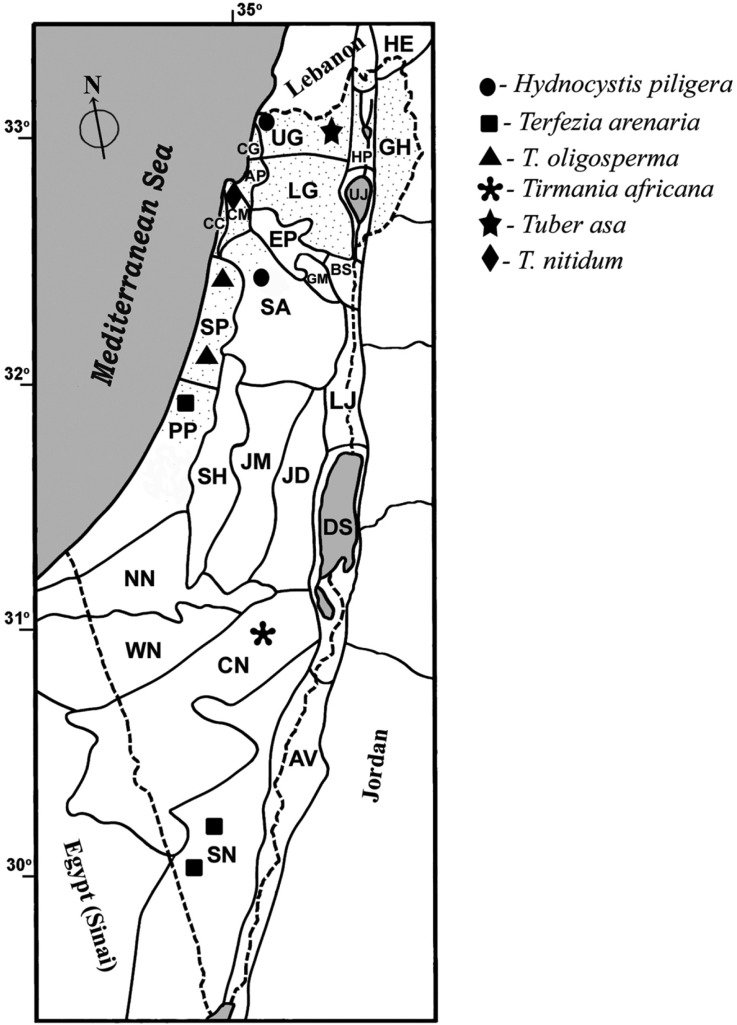
Fig. 3.
Distribution of hypogeous Ascomycetes representatives in Israel. AP, Akko Plain; AV, Arava Valley; BS, Beit Shean Valley; CC, Carmel Coast; CG, Coast Galilee; CM, Carmel Mount; CN, Central Negev; DS, Dead Sea area; EP, Esdraelon (Yizre'el) Plain; GH, Golan Heights; GM, Gilboa Mount; HE, Hermon Mount; HP, Hula Plain; JD, Judean Desert; JM, Judean Mts.; LG, Lower Galilee; LJ, Lower Jordan Valley; NN, Northern Negev; PP, Philistean Plain; SA, Samaria; SH, Shefela; SN, South Negev; SP, Sharon Plain; UG, Upper Galilee; UJ, Upper Jordan Valley; WN, Western Negev.
Material examined
SA: Reihan forest, on the ground, under Pinus sp., February 19, 2007, leg. Y.Ur, det. G. Barseghyan (HAI-D-035) (Fig. 3).
Habitat & General distribution
Mycorrhizal species. In the Mediterranean shrub environments, in sandy forest soil, associated with Cupressus, Pinus, Cistus, and Pistacia. Asia: China, Israel. Europe: Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Russia, Spain, and Switzerland.
Note
H. piligera is a rare species for Israeli and Asian mycobiota. This species is strongly characterized by its epithecium structural elements and spherical ascospores [21].
Pezizaceae Dumort
Genus Terfezia (Tul. & C. Tul.) Tul. & C. Tul. Fungi Hypog.: 172 (1851).
Type species
Terfezia arenaria (Moris) Trappe, Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 57(1): 90 (1971).
KEY TO THE SPECIES KNOWN IN ISRAEL
1A. Ascospores globose...2
1B. Ascospores subglobose to ovoid...Terfezia oligosperma Tul. & C. Tul.
2A. Brownish color, coarsely warted at maturity, without any mark of reticulum...Terfezia arenaria (Moris) Trappe
2B. Ascospores white-yellowish to yellow, completely reticulate at maturity, with low thickness meshes...Terfezia claveryi Chatin
Terfezia arenaria (Moris) Trappe, Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 57(1): 90 (1971) (Fig. 4)
Fig. 4.
Terfezia arenaria (Moris) Trappe (HAI-D-091): A, Ascocarps and ascocarp in cross-section; B, Warted ascospores (scale bar = 50 µm).
= Tuber arenaria Moris, Brit. Sp. Ang. Lich. 3: 222 (1829).
= Terfezia leonis (Tul. & C. Tul.) Tul., Expl. Sci. Alg., Bot., Atlas 1: 432 (1895).
Icon
Binyamini, Nova Hedvigia XXXII, 18: fig. 2, 20: 9a,b, 1980 (as Terfezia leonis); Montecchi & Sarasini, Fungi Ipogei D'Europa, p. 183, 2000.
Ascocarps: subglobose, 4~10 cm in diam, tuberiform, with short basal mycelial tuft, whitish at first, then ochraceous, becoming brown with age. Peridium: often cracked, surface glabrous and smooth, consisting primaily of large isodiametric cells of (8~) 15~25 × 15~40 (~45) µm, slightly brownish, walls of cells thin and delicate. Gleba: fleshy, compact and elastic, initially white or flesh-colored, then greenish or reddish becoming brown, with evident sterile veins, 1~2 mm broad, irregularly delimiting fertile areas. Odor weak, fruity, taste mild. Asci: subglobose, sometimes ovoid, randomly arranged in a hyphal tissue, 72~81 × 82~97 µm, usually with 4~6 spores at maturity, hyaline, thin-walled, sessile or substipitate, ascospores loosely arranged within ascus. Ascospores: globose, coarsely warted at maturity, (16~) 20~25 × 22~22.5 (~25) µm broad (including warts), Q = 0.9~1.1, hyaline when young and slightly brownish at maturity, walls 1~1.5 µm broad, warts truncate-tipped, 1.5~2 µm broad.
Habitat & Distribution in Israel
SN: in Negev sand dunes, fruiting from March to May, in depths of 5~20 cm, very close to Helianthemum sessilliflorum roots, February 28, 1973, leg. K. Avshalom, det. N. Binyamini; March 19, 1974, leg. Zeelim, det. N. Binyamini (Fig. 3) [3].
Material examined
PP: Ashdod, in sand, very close to H. sessilliflorum roots, January 15, 2002, leg. & det. SP. Wasser (HAI-D-091) (Fig. 3).
Habitat & General distribution
Mycorrhizal fungi. Linked mainly to the coastal and sandy soil of Mediterranean areas, but also to the semi-desert inland areas. Africa: Morocco. Asia: Israel, China, Turkey, United Arab Emirates. Europe: Italy, Spain, Sweden. North: America: USA.
Note
This is a rare species for Israeli mycobiota. This species was found for the first time and described in Israel by Rayss [2]. After Binyamini [3], a detailed discussion and a comparison with species described by Tulasne and Tulasne [23] and Bataille [24] as T. leonis was conducted. The name T. leonis, under which this species is commonly known, has to be rejected as an illegitimate name, according to Trappe and all other modern authors.
Terfezia claveryi Chatin, La Truffe: 74 (1892)
Icon
Montecchi & Sarasini, Fungi Ipogei D'Europa, p. 222~223, 2000.
Ascocarps: 10 cm in diam, subglobose-compressed or pyriform, lobate, with short, sterile base, surface gibbous, ochraceous to reddish brown, stained blackish brown with maturity. Peridium: rather thick, 0.8~1.2 mm, whitish, becoming brown when cut, constituted of filamentous hyphae, 8~12 µm in diam, parallel to the surface. Gleba: fleshy, compact, at first whitish or flesh colored, then yellowish-reddish, subdivided by paler veins. Odor: reminiscent of pepper. Asci: globose, 8-spored, randomly arranged in the hyphal tissue, 50~90 × 50~75 µm. Ascopores: globose, confusedly disposed in the ascus, whitish-yellowish to yellow, then immature nearly smooth-asperulate, when completely mature reticulate, with low thickness meshes, about 2 µm high, irregular, 16~23 µm in diam, including ornamentations.
Habitat & General distribution
Mycorrhizal species. Linked mainly to the desert lands of the South Mediterranean basin and the Middle East, in sandy soils covered with Helianthemum species, especially H. aegyptiacum. Asia: Iraq, Israel, Kuwait, Syria. Europe: Spain. North America: USA.
Note
This is a very rare species for Israeli mycobiota. Terfezia claveryi was found in Israel for the first time by Rayss [1]; the location of the sample collection or the herbarium as well as other important information was not mentioned. This species has since been properly characterized by its ascosporal ornamentation and habitat.
Terfezia oligosperma Tul. & C. Tul., Fungi Hypog.: 176 (1851)
= Delastreopsis oligosperma (Tul. & C.Tul.) Mattir., Bolm. Soc. Broterisna, Coimbra (1905).
= Tuber oligospermum (Tul. & C. Tul.) Trappe, Mycotaxon 9(1): 336 (1979).
Icon
Binyamini, Nova Hedvigia XXXII, 18: fig. 3, 19: 8, 1980; Montecchi & Sarasini, Fungi Ipogei D'Europa, p. 300, 2000 (as Tuber oligospermum).
Ascocarps: 3~4 cm in diam, irregularly globose, slightly folded, light clay color, peridium about 0.5 mm thick. Peridium: consisting of interwoven hyphae 3~8 µm broad, hyaline. Gleba: dirty white, then brown to dark brown, fleshy, solid, marbled with white irregular veins. Glebal fertile pocket separated by sterile undifferentiated veins, the hyphal hyaline, thin-walled 4~7 µm broad. Asci: subglobose or ovoid, 60~120 × 50~75 µm broad, shortly stalked, thin-walled, hyaline, spores loosely arranged within, 1~4 spored, mostly 1~2 spored at maturity. Ascospores: globose ornamented with spines and alveolate polygonal cells, 30~47 µm broad (including spines), hyaline or yellowish when young, brown at maturity, walls 1~1.5 µm thick, spines 2.5~3.5 µm long.
Habitat & Distribution in Israel
Fruiting from January to April, in wood of Pinus halepensis at a depth of 3~5 cm or at the surface of soil at maturity, in groups of 3~8. The outward sign of the presence of these fungi is the appearance of cracks in a slight elevation of the soil. SP: Tel Aviv, Ramat Gan Park, March 22, 1977, January 24, 1979, leg. B. Shemen, det. N. Binyamini (Fig. 3) [3].
Habitat & General distribution
Mycorrhizal species. Not a very common species, generally growing in deciduous woods, preferably with a Mediterranean climate, typical on sandy coast-lines, where it grows in autumn and also in spring in warmer locations. Asia: Israel. Europe: France.
Note
This fungi was described for the first time in Israel by Reichert [25] under the name Delastripsis oligosperma. Mycorrhizal fungi, mostly endemic to arid and semi-arid areas of the Mediterranean Region, are associated with Helianthemum species [26].
Genus Tirmania Chatin, Truffe, Edn 2: 80 (1892)
Type species
Tirmania africana Chatin, Truffe, Edn 2: 80 (1892).
Tirmania africana Chatin, Truffe, Edn 2: 80 (1892)
Icon
Binyamini, Nova Hedvigia XXXII, 18: fig. 4, 20: fig. 10 a, b, c, 1980.
Ascocarps: subglobose often flattened, potato-shaped, sessile or sometimes shortly stalked, reaching 6~12 cm in diam, and whitish to white cream, smooth. Peridium: 1.5~2 mm thick. Gleba: white fleshy, solid, faintly marbled with a few wide veins 2~5 mm broad. Odor: slightly spermatic when young and weak at maturity. Asci: ovoid or broadly clavate 50~80 × 40~50 µm, usually with 6~8 spores at maturity, thin-walled, shortly stalked hyaline, ascospores loosely arranged within. Ascospores: oval, 15~19 × 12~13.5 µm broad, Q = 1.2~1.4 smooth, hyaline, thin-walled, 0.5~1 µm thick, sometimes with oil drop. Peridium consisting of prosenchymatic hyphae 5~7 µm broad, walls of cells thin. Glebal fertile pockets by sterile undifferentiated veins consisting of hyphae 7~11 µm broad, thin-walled, but sometimes inflated up to 18 µm.
Habitat & Distribution in Israel
CN: fruiting from March to May in Negev sand dunes at a depth of 10~20 cm close to H. sessiliflorum roots. Two additional plants close to the ascocarpsare Artemisia monosperma and Plantago albicans, February 28, 1973, leg. K. Avshalom, det. N. Binyamini (Fig. 3) [3].
Habitat & General distribution
Mycorrhizal fungi. In deserts with the development of various Helianthemum species. Africa: Algeria, Morocco. Asia: Israel.
Note
This is a rare species for Israeli mycobiota. This species was found for the first time and briefly described in Israel by Rayss [2]. According to Montecchi and Sarasini [21], Tirmania africana is in synonymy with T. nivea and its current name is T. africana, according to the Index Fungorum online database. This species can be confused morphologicaly with T. pinoi but the smooth surface and ellipsoid spores of T. africana make it easy to distinguish from T. pinoi.
Tuberaceae Dumort
Genus Tuber P. Micheli ex F.H. Wigg., Prim. Fl. Holsat. (Kiliae) (1780).
Type species
Tuber aestivum Vittad., Monogr. Tuberac. (Milano): 38 (1831).
Key to the species known in Israel
1A. Ascospores globose, subglobose to ellipsoid, with brown ornamentation and alveolate reticulum...Tuber asa Tulasne & C. Tulasne
1B. Ascospores ellipsoid to fusiform, light brown, covered with numerous slender spines...Tuber nitidum Vittad.
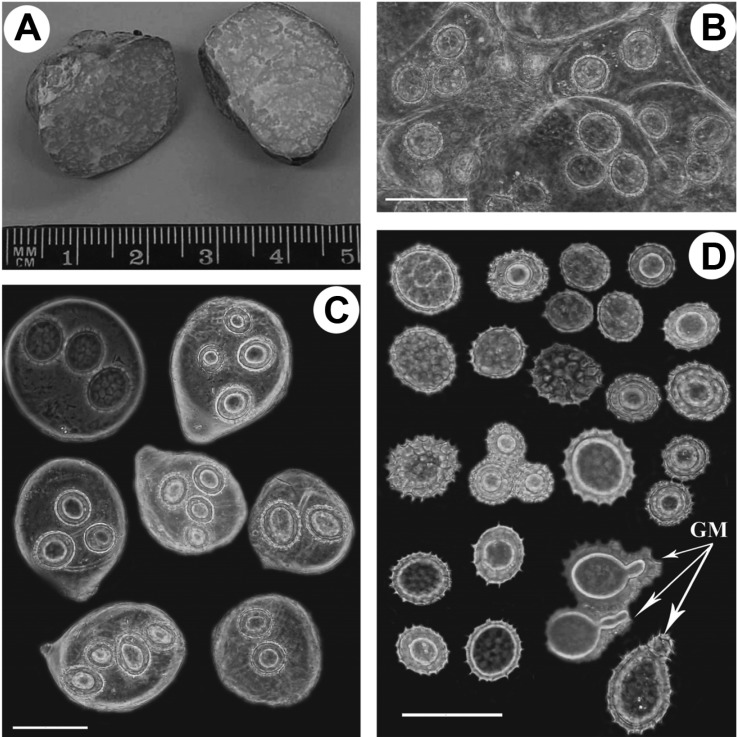
Tuber asa Tulasne & C. Tulasne, Fungi hypogaei. Hist. et Monog. Des Champ. Hypogés: 222. (1851) (Fig. 5)
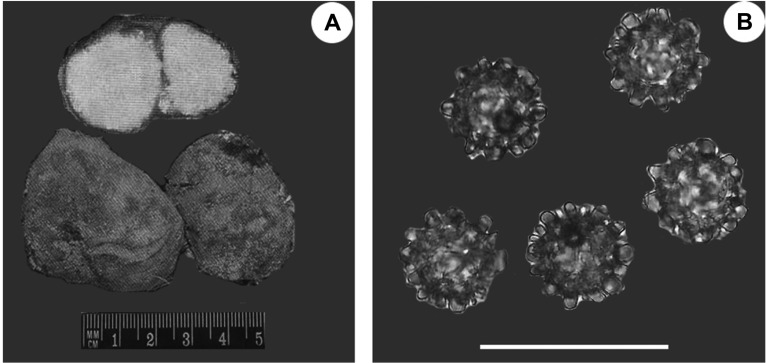
Fig. 5.
Tuber asa Tulasne & C. Tulasne (HAI-D-033): A, Cross-section of ascocarp; B, Hymenium (asci, spores); C, Asci with 2~4 ascospores; D, Ascospores with ornamentation (GM, germination of ascospores) (scale bars = 50 µm).
Icon
Montecchi & Sarasini, Fungi Ipogei D'Europa, p. 257, 2000.
Ascocarps: 15~25 cm in diam, irregularly tuberous, gibbose, glabrous, dirty yellowish to dark olive, with smooth surface. Peridium: whitish to crime, thick with interwoven hyphae. Odor: intense and pleasant. Gleba: light gray-brown to beige, marbled with narrow off-white anastomozed veins. Asci: ovoid-ellipsoid to subglobose, 70~78 × 50~65 µm, thin-walled, hyaline, sessile or with a short stem, reaction with Meltzer's reagent negative, asci non-amyloid, 2~4 spored. Ascospores: globose, ellipsoid-subglobose, 21~44 × 18~35 µm (not including ornamentation), Q = 1.1~1.2, with brown ornamentation an alveolate reticulum, ascospore walls 1.8~3.2 µm thick. Paraphyses: absent.
Material examined
Israel, UG: Goren Park, in sandy soil close to Cistus incanus roots, at a depth of 10~15 cm, April 7, 2007, leg. Z. Shafranov & R. Kuznetsov, det. G. Barseghyan (HAI-D-033) (Fig. 3).
Habitat & General distribution
Mycorrhizal species. Not a very common species, generally found in dry and sandy soils of coast-lines with a Mediterranean climate, in desert areas, with the sole presence of various species of Cistus, Tuberaria, Helianthemum, and Ephedra. Asia: Israel. Europe: Italy, Spain.
Note
This is a new species for Israeli mycobiota that can be confused with similar species, such as T. oligospermum, but this species does not have a pleasant odor, and all ascospores are spherical. T. puberulum have very similar odor, but ascospores are smaller and usually have ovoid or spheric forms.
Tuber nitidum Vittad., Monograph: 48 (1831)
= Tuber rufum f. nitidum (Vittad.) Montecchi & Lazzari, Atlante Fotografico di Funghi Ipogei (Trento):197 (1993).
Icon
Montecchi & Sarasini, Fungi Ipogei D'Europa, p. 317, 2000 (as Tuber rufum f. nitidum).
Ascocarps: 1~2 cm in diam, globose to subglobose, slightly compressed, hard. Peridium: smooth or slightly papillate, yellowish-brown to grayish-orange, shining. Gleba: white, becoming grayish with reddish tinge, veins few, remain white. Odor: light, unpleasant and acid when mature. Asci: ellipsoid, pyriform, stalked, 40~70 × 14~18 µm, 1~5-spored, but mostly 3~4-spored. Ascospores: ellipsoid to fusiform, 20~27 × 14~18 µm, Q = 1.4~1.5, light brown, covered with numerous slender spines.
Habitat & Distribution in Israel
CM: rare, in open places on the northern side of Mt. Carmel, March 26, 1987, leg and det. N. Binyamini (Fig. 3) [5].
Habitat & General distribution
Mycorrhizal species. This species is associated with both coniferous and deciduous trees, widely spread in all environments. Asia: Israel. Europe: Austria, Italy, Poland, Spain, Switzerland.
Note
This is a very rare species for Israeli mycobiota. According to Hawker [27], this species is very close to Tuber rufum but differs in color. The hymenium does not have a red tinge, and the spore spines are more slender and more densely crowded [5]. According to Montecchi and Sarasini [21], the differential characteristics of this "form" are limited to the fairly regular fruit bodies' form and light colors on a smooth and bright surface, even during late maturity. Due to these characteristics, this entity could be mistaken for a species in the so-called T. puberulum group, but the aculeate and none reticulate-alveolate spores, or in the case of immature ascospores, the peridium structure of the interwoven hyphae eliminate any doubt.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Zohar Shafranov (Israel) and Mr. Roman Kuznetsov (Israel) for their help in collecting materials.
References
- 1.Rayss T. Nouvelle contribution á l'étude de la mycoflore de Palestine (Deuxieme partie) Palest J Bot. 1940;1:313–355. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rayss T. On the hypogeous fungi of Israel. Mada. 1956;6:9–13. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Binyamini N. Addenda to the Hypogeous Mycoflora of Israel. Nova Hedwigia. 1980;32:9–20. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Binyamini N. Larger fungi of Israel: Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina (Aphyllophorales, Auriculariales, Tremellales and Gasteromycetes) Tel Aviv: Ramot Publishing Co.; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Binyamini N. Rare and interesting records of the higher fungal flora of Israel. IV. Opera Bot. 1989;100:23–27. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Trappe JM. Use of truffles and false-truffles around the world. In: Bencivenga M, Granetti B, editors. Acti del II Congresso Internationale sul Tartufo. Spoleto: Comunità Montana dei Monti Martani e del Serrano; 1992. pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Trappe JM. The orders, families, and genera of hypogeous Ascomycotina (truffles and their relatives) Mycotaxon. 1979;9:297–340. [Google Scholar]
- 8.O'Donnell K, Cigelnik E, Weber NS, Trappe JM. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetous truffles and the true and false morels inferred from 18S and 28S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. Mycologia. 1997;89:48–65. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gargas A, Taylor JW. Phylogeny of Discomycetes and early radiations of the apothecial Ascomycotina inferred from SSU rDNA sequence data. Exp Mycol. 1995;19:7–15. doi: 10.1006/emyc.1995.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Spatafora JW. Ascomal evolution among filamentous ascomycetes: evidence from molecular data. Can J Bot. 1995;73:S811–S815. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Landvik S, Egger KN, Schumacher T. Towards a subordinal classification of the Pezizales (Ascomycota): phylogenetic analyses of SSU rDNA sequences. Nord J Bot. 1997;17:403–418. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Harrington FA, Pfister DH, Potter D, Donoghue MJ. Phylogenetic studies within the Pezizales. I. 18S rRNA sequence data and classification. Mycologia. 1999;91:41–50. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Percudani R, Trevisi A, Zambonelli A, Ottonello S. Molecular phylogeny of truffles (Pezizales: Terfeziaceae, Tuberaceae) derived from nuclear rDNA sequence analysis. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1999;13:169–180. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1999.0638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Norman JE, Egger KN. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Peziza and related genera. Mycologia. 1999;91:820–829. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Harrington FA, Potter D. Phylogenetic relationships within Sarcoscypha based upon nucleotide sequences of the internal transcribed spacer of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Mycologia. 1997;89:258–267. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Roux C, Séjalon-Delmas N, Martins M, Parguey-Leduc A, Dargent R, Bécard G. Phylogenetic relationships between European and Chinese truffles based on parsimony and distance analysis of ITS sequences. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;180:147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb08789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Norman JE, Egger KN. Phylogeny of the genus Plicaria and its relationship to Peziza inferred from ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. Mycologia. 1996;88:986–995. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Saccardo PA. Sylloge fungorum omnium hucusque cognitorum. Ann Arbor: Edwards Brothers, Inc.; 1882-1931. T. 1-25; 1902: 16; 1906: 18; 1913: 22; 1931: 25. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Burdsall HH., Jr A revision of the genus Hydnocystis (Tuberales) and of the hypogeous species of Geopora (Pezizales) Mycologia. 1968;60:496–525. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dennis RW. British ascomycetes. 2nd ed. Vaduz: Gantner AR & Verlag KG; 1981. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Montecchi A, Sarasini M. Funghi ipogei d'Europa. Trento: AMB Fondazione Centro Studi Micologici; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Feinbrun-Dothan N, Danin A. Analytical flora of Eretz-Israel. 2nd ed. Jerusalem: CANA Publishing House; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tulasne LR, Tulasne C. Fungi hypogaei. Histoire et monographie des champignons hypogés. Paris: Friedrich Klincksieck; 1851. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bataille MF. Flore analytique et descriptive des tubéroîdées de l'Europe et de l'Afrique du Nord. Bull Soc Mycol Fr. 1921;37:155–207. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Reichert I. Studies on mushrooms and other fungi of the forests of Palestine. Palest J Bot. 1944;4:193–204. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Díez J, Manjón JL, Hawker LE. British hypogeous fungi. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B. 1954;237:429–546. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hawker LE. British hypogeous fungi. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B. 1954;237:429–546. [Google Scholar]