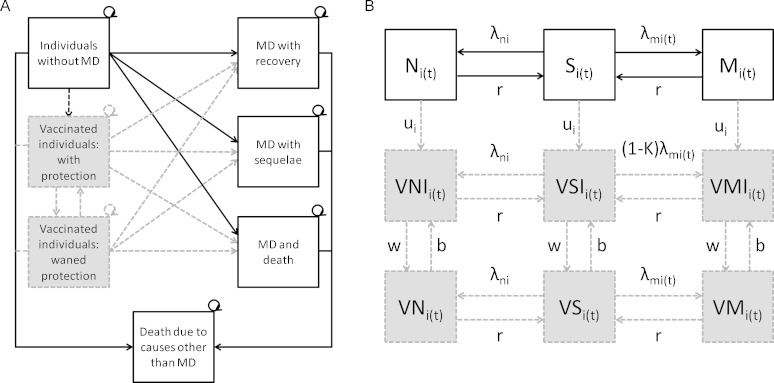
Fig. 1.
Models used to assess the impact of meningococcal vaccination in England. The ‘no vaccination’ model consists of white boxes and solid arrows; the ‘with vaccination’ model includes shaded boxes and dashed arrows in addition. (A) Cohort model structure: MD, meningococcal disease. (B) Dynamic model structure: Once individuals are carriers they have a chance of developing disease, with the same outcomes as shown in (A) S, susceptible non-vaccinated; M, infected carrier of a vaccine preventable meningococcal strain; N, infected carrier of a non-vaccine preventable meningococcal strain; VSI, susceptible vaccinated and immune; VMI, infected carrier of a vaccine preventable meningococcal strain, vaccinated and immune; VNI, infected carrier of a non-vaccine preventable meningococcal strain, vaccinated and immune; VS, susceptible vaccinated not immune; VM, infected carrier of a vaccine preventable meningococcal strain, vaccinated not immune; VN, infected carrier of a non-vaccine preventable meningococcal strain, vaccinated not immune; λm, force of infection for vaccine preventable meningococcal strains; λn, force of infection for non-vaccine preventable meningococcal strains; κ, vaccine efficacy against carriage; u, vaccine uptake; w, waning vaccine protection; b, vaccination booster; i, age; t, time.