Abstract
A dual activation strategy integrating NHC catalysis and a second Lewis base has been developed. NHC-bound homoenolate equivalents derived from α,β-unsaturated aldehydes combine with transient reactive o-quinione methides in an enatioselective formal [4+3] fashion to access 2-benzoxopinones. The overall approach provides a general blueprint for the integration of carbene catalysis with additional Lewis base activations modes.
The advances made by employing chiral catalysts to forge new carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds with high levels of stereoselectivity have provided efficient access to new chiral molecules in high enantiomeric excess with broad potential uses.1 A majority of these strategies rely on a single activation mode, such as Lewis base2 or acid3 catalysis, enamine/iminium ion catalysis,4 hydrogen bond donor/Brønsted acid catalysis,5 σ-bond activation,6 and an immense variety of transition metal chemistry.7 With proper substrate and catalyst design, these diverse sets of reactions access a myriad of distinct compound classes with dizzying arrays of functional groups and ring systems. However, there are inherent limitations of reactivity and selectivity within each activation “sphere”. In many cases, some substrates are simply not reactive enough to engage with a catalyst or the combination of starting materials is ineffective due to poor pairing of electronic parameters (i.e., electrophilicity/nucleophilicity).
N-Heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are versatile Lewis bases capable of promoting a variety of powerful and unconventional bond-forming processes, including acyl anion reactions, homoenolate equivalents, enolate additions and oxidations.8 Inspired by early carbonyl anion catalysis,9 one particularly versatile reaction mode is the NHC-homoenolate described in 2004.10 This process provides a metal free approach to access β-anionic carbonyl systems and we have been exploring this activation mode for the development of multiple new reactions. Carbene catalysis typically entails formal [n+m]-type cycloaddition transformations by virtue of the mechanistic pathway and catalyst turnover (see below). This distinct feature provides a powerful platform for convergent ring formation strategies, so long as the electrophilic partner is reactive enough to engage the NHC-homoenolate in an initial sigma bond-forming event. While it is clear that these homoenolates can undergo additions to reactive electrophilic C=X π systems, such as aldehydes and imines, many classes of less reactive potential partners typically result in no productive interactions. New opportunities in carbene catalysis over the next decade will undoubtedly focus on moving past these standard π systems, but the current challenge remains for identifying what innovative concepts will expedite this evolution.
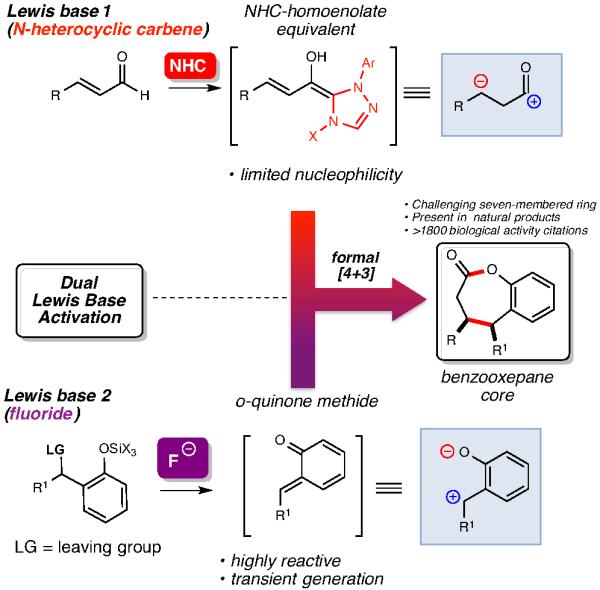
We hypothesized if it were possible to drive NHC-generated homoenolate methodology in new directions by integrating a second mode of activation which could produce more reactive electrophiles beyond stable C=O or C=N π bonds. We successfully integrated Lewis acid activation modes with NHC catalysis11 and utilized this knowledge base to consider additional activation modes such as in situ, Lewis base-promoted electrophile creation (Scheme 1). There have been limited examples of combining carbene catalysis with Lewis acids11,12 as well as Bronsted acids,13 but to date, the idea of a utilizing a second Lewis base activation mode in conjunction with NHCs remains an underexplored strategy.
Scheme 1.
Dual Lewis base activation strategy
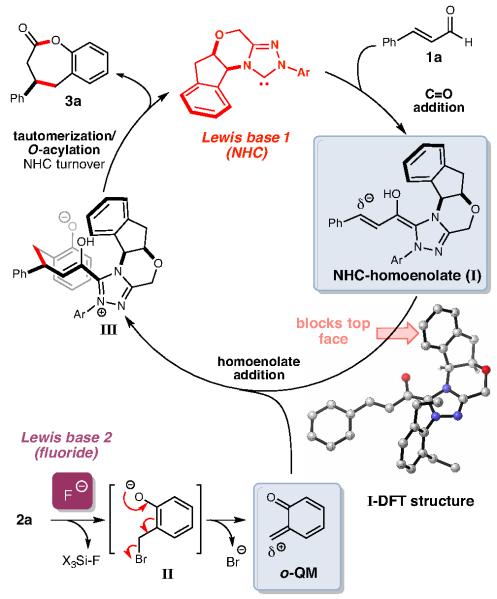
To pursue this new strategy, we proposed that the production of highly reactive o-quinone methides (o-QMs) generated under fluoride conditions through a desilylation/elimination cascade could be combined with an NHC-homoenolate catalytic cycle.14 o-QMs are considerably more reactive than regular αβ-unsaturated ketones and esters since nucleophilic attack on the external carbon produces an aromatic alcohol (phenol/phenoxide) and this aromatization process of the ring is a highly thermodynamically favorable. Although stable o-QMs are known, the more reactive variants are useful intermediates in synthesis and can be produced in situ through the addition of light, oxidants, or fluoride.15 In the context of this new NHC reaction, we desired access to as many different possible o-QM structures through an in situ approach (e.g., fluoride), thereby ensuring the broadest potential substrate scope at the onset of these studies should our concept prove successful. However, the fleeting nature of many of these species combined with their propensity to undergo dimerization via a [4+2] pathway or react with even weak nucleophiles were possible obstacles.15c If successful, the productive realization of this new dual Lewis base activation strategy would produce seven-membered lactones (2-benzoxopinones) which are found in natural products and are the core constituents for numerous small molecules with broad biological activity.16
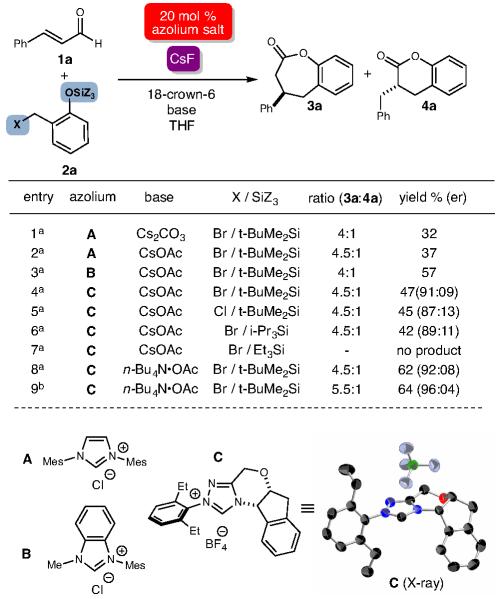
We initially considered four challenges of this potential reaction: 1) the compatibility of the second Lewis base with the in situ generated NHC, 2) the compatibility of the highly reactive o-QM with a nucleophilic NHC catalyst, 3) the potentially unproductive behavior of transient o-QMs under the reaction conditions (e.g., dimerization), and 4) the requirement of equilibrium populations of both NHC-bound homoenolate and o-QM to lead to a productive bond-forming process. With these issues in mind, major questions remained at the onset about the suitable fluoride source to promote the optimal rate of o-QM production in situ. Guided by these issues of compatibility and competing rates, extensive tuning of the major reaction parameters (catalyst structure, base composition, fluoride source) was required to address the complex and interconnected issues above. To our delight, the proper rate of o-QM production was successfully achieved through the use of a crown ether/fluoride combination with a t-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS) phenol substrate (Table 1). For the initial set of investigations, the bromide leaving group in the presence of Cs2CO3 provided the encouraging levels of conversion to the desired product, albeit in low yield, with achiral imidiazolium- and benzimidazolium-derived carbenes (prepared in situ from A and B, respectively, entries 1-3).17
Table 1.
NHC/Fluoride-promoted reaction of 1a and 2aa
|
1a (1 equiv), 2a (2 equiv), CsF (2 equiv), 18-crown ether-6 (2 equiv), base (30 mol %), THF (0.15 M in 1a), 23 °C, 3 h.
reactions performed at −18 °C for 12 h. Er was determined by chiral stationary-phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Mes, 2,4,6-Me-C6H2.
A competing reaction pathway was the generation of 4a, which forms from the protonation of the NHC-homoenolate followed by a formal [4+2] pathway (see below for reaction pathway discussions). With CsOAc as base and chiral triazolium NHC C, good levels of enantioselectivity were observed (91:9 er) with only moderate yield (47%, entry 4). A further examination of the o-QM precursor indicated that triisopropyl (TIPS) can also facilitate the reaction in the presence of fluoride without major differences in the results (entry 4 vs. 6), but still only <50% yields. In contrast, the more labile triethylsilylphenol (TES protecting group) did not afford product (entry 7).
The leaving group to expedite elimination and produce o-QM in situ can be either bromide or chloride without noticeable differences in overall reactivity. The optimal combination of CsF/18-crown-6 for o-QM generation and n-Bu4N•OAc as a mild base provided the formal [4+3] lactone product was obtained in moderate yield and excellent enantioselectivity (entry 8, 62%, 92:8 er). The lowering of the reaction temperature to −18 °C from 0 °C increased the time necessary for consumption of 1a, but also provided better stereoselectivity (dr = 5.5:1, er = 96:4, entry 9).18
With conditions to generate each reactive intermediate independently at productive concentrations, we explored the scope of this transformation (Table 2).
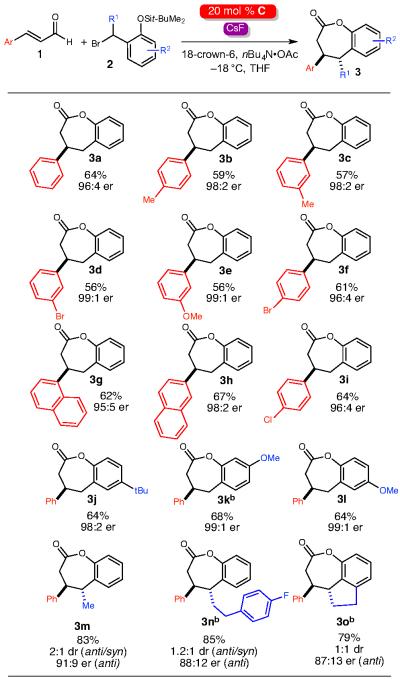
Table 2.
Scope of dual activation formal [4+3] annulationa
|
Reactions were performed at 0.4 mmol with 1 equiv of 1, 2 equiv of 2, 0.3 equiv base, 2 equiv CsF and 2 equiv crown ether in THF (0.15 M in 1). Isolated yields of 3 are reported. Er was determined by chiral stationary-phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Benzylic chloride was used for 2 instead of benzylic bromide.
Cinnamaldehyde derivatives bearing electron donating and electron withdrawing groups were well tolerated. (3a-3i). Aryl modifications on the aldehyde substrate did not impact yields or chemoselectivity substantially. The ability to employ either bromide or chloride leaving groups on 1 (Table 1) allowed for the use of benzylic chloride o-QM precursors when the corresponding benzylic bromides were too unstable (e.g., 3k, 3n and 3o). For these cases, the corresponding benzyl chlorides can be successfully employed in the reaction and thus effectively expand the scope of the overall process.
We also explored the scope of the o-QM precursor. A brief survey on the aromatic ring showed that yields were increased with electron donating groups (3j-3l). A current limitation that is not surprising is that electron withdrawing groups on the o-QM did not furnish any product (not shown). These groups presumably stabilize the resulting anionic phenoxide intermediate to the point where ejection of the bromide or chloride leaving group is not favored. The incorporation of additional substitution in the benzylic position of the o-bromo benzylphenol TBS ethers is possible (3m-3o) and extends the scope of the formal [4+3] process to include the generation of vicinal substituted products. The diastereoselectivity for these reactions is moderate, but this particular process is more challenging since β-substitution of αβ-unsaturated electrophiles (in this case, the o-QM) greatly slows down typical Michael/conjugate additions. With a highly reactive aldehyde like acrolein (5), the unexpected dihydrocoumarin 6 is obtained exclusively with excellent yield and enantioselectivity. The high yield of this particular reaction is surprising giving the penchant for acrolein to oligomerize under typical nucleophilic conditions.19
Our current understanding of the pathway is shown in Scheme 3. The initial addition of the NHC (Lewis base 1) to the αβ-unsaturated aldehyde furnishes extended Breslow intermediate I after formal 1,2-hydrogen migration. The second Lewis base, fluoride ion, promotes generation of the o-QM electrophile from silylated phenol 2 via a desilylation/elimination cascade (2→II→o-QM). The pairing of the t-butyldimethyl silyl group and bromide leaving group produces the appropriate concentration of the sensitive o-QM for the desired transformation. Based on DFT calculations (B3LYP/6-31G*, gas phase), the NHC-homoenolate (I) exhibits a strong preference for reaction away from the more hindered face generated by the amino-indanol phenyl framework (I-DFT, as drawn). This nucleophile captures the transient o-QM through a carbon-carbon bond forming conjugate addition with what seems an open transition state. For o-QMs with β-substitution (leading to products 3m, 3n, and 3o), this leads to low levels of diasteromeric control. At this point in the cycle, intermediate III undergoes taumerization and intramolecular O-acylation of the phenoxide anion,20 thereby releasing the carbene catalyst (C) and benzoxopinone product (3). The absolute strereochemistry of the product was confirmed by X-ray and then further assigned by analogy (see Supporting information). We attribute this difference in reactivity of acrolein (formal [4+2]) vs. the β-aryl substrates (formal [4+3]) to a fast protonation of this specific NHC-homoenolate intermediate. This protonated intermediate is an NHC-enolate equivalent that undergoes a subsequent Michael addition/O-acylation process similar to the catalytic cycle above, this time forming the observed six-membered ring.21 The addition of a proton (H+) to the β-position is competitive if there is no aryl substitution in this location (e.g., acrolein, crotonaldehyde). However, this pathway is slower than C–C bond formation with the o-QM when a β-aryl substituent is present (e.g., cinnamaldehyde). Essentially, the fluoride ion, promotes generation of the o-QM electrophile from stability of the extended Breslow intermediate determines the fate of the nucleophilic NHC intermediate.
Scheme 3.
Reaction pathway
This process is a convergent, catalytic enantioselective route to these seven-membered ring lactones and enables rapid access to biologically relevant structures, including related benzoxepanes and benzoazepinones (Scheme 4). Prior routes to these compounds are scarce and the dearth of convergent strategies to access them has presumably hampered investigation of their full potential. For example, benzoxopinone 3 was smoothly transformed into benzoxepane 7, which contains the core found in many compounds in the heliannuol family of natural products and could be utilized to access structural analogs.22 In addition, the related benzoxepanes are known central nervous system depressants.23 The overall replacement of the oxygen atom in 3a with a nitrogen substituent can be easily accomplished in four steps. This series of transformations accesses benzoazepinones which are related in structure to benzodiazepines drugs (e.g., Xanax, Valium)24 by virtue of the seven-membered azepine structure fused to an aryl ring.25 Benzoazepinones with the same N,N-dimethylethyl side chain are related to the FDA-approved drug diltiazem,26 a potent calcium channel blocker (Cardizem) and SQ 31,486, a candidate to reduce myocardial ischemia for cardioprotective treatments.27
Scheme 4.
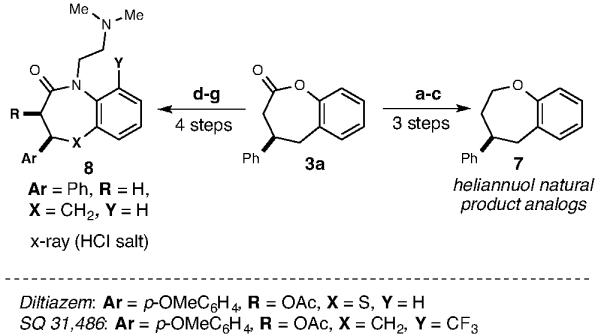
Synthesis of benzooxepanes and benzoazepinonesa
aReaction conditions: (a) Me2S-BH3, THF; 85%. (b) TsCl, Et3N, CH2Cl2. (c) NaH, THF; 53% both steps. (d) H2SO4, MeOH; 74%. (e) Tf2O, DCM; 99%. (f) Pd(OAc)2, rac-BINAP, Cs2CO3, H2N(CH2)2N(CH3)2, THF; 91%. (g) aq. LiOH, THF; then HBTU, i-Pr2EtN, DMF, 65% (as the HCl salt)
This report highlights the new integration of two distinct Lewis base activation modes to discover an enantioselective organocatalytic formal [4+3] heterocycloaddition. The successful realization of this challenging “dual activation” concept has been achieved through concomitant in situ generation of two reactive, transient species: a nucleophilic NHC-homonenolate and a highly electrophilic ortho-quinone methide. In a broader strategic sense, the employment of a second Lewis base compatible with N-heterocyclic carbenes that accesses reactive electrophiles greatly expands the potential for new reaction discovery with these powerful organocatalysts.
Supplementary Material
Scheme 2.
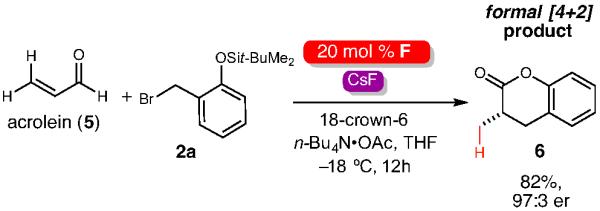
Formal [4+2] reaction with acrolein
Acknowledgements
Procedures and analyses of reactions are provided in the Supplementary Material section. We thank Prof. P. H.-Y. Cheong and R. Johnston (Oregon State University) for performing DFT calculations and Dr. P. Sui (Northwestern) for X-ray crystallographic assistance. Financial support was provided by the National Institute of General Medical Science, NIH (R01 GM073072). A. O. acknowledges the Basque Government for a predoctoral grant and the UPV/EHU (UFI QOSYC 11/22) for financial support.
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available: Experimental procedures and spectral data for new compounds (PDF). This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Jacobsen EN, Pfaltz A, Yamamoto H. Comprehensive Asymmetric Catalysis, I-III. 1-3 ed. Springer; Berlin, Germany: 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 2.(a) Denmark SE, Beutner GL. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008;47:1560–1638. doi: 10.1002/anie.200604943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Denmark SE, Stavenger RA. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000;33:432–440. doi: 10.1021/ar960027g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yamamoto H. Lewis acids in organic synthesis. Wiley-VCH: Weinheim; New York: 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) MacMillan DWC. Nature. 2008;455:304–308. doi: 10.1038/nature07367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Mukherjee S, Yang JW, Hoffmann S, List B. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5471–5569. doi: 10.1021/cr0684016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Doyle AG, Jacobsen EN. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5713–5743. doi: 10.1021/cr068373r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Pihko PM. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004;43:2062–2064. doi: 10.1002/anie.200301732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Taylor MS, Jacobsen EN. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006;45:1520–1543. doi: 10.1002/anie.200503132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Jain P, Antilla JC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:11884–11886. doi: 10.1021/ja104956s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Liang T, Zhang ZJ, Antilla JC. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010;49:9734–9736. doi: 10.1002/anie.201004778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Rueping M, Nachtsheim BJ, Ieawsuwan W, Atodiresei I. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011;50:6706–6720. doi: 10.1002/anie.201100169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Akiyama T. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5744–5758. doi: 10.1021/cr068374j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Shen B, Makley DM, Johnston JN. Nature. 2010;465:1027–U1082. doi: 10.1038/nature09125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (i) Terada M. Synthesis. 2010:1929–1982. [Google Scholar]
- 6.For leading reviews, see: Lyons TW, Sanford MS. Chem. Rev. 2010;110:1147–1169. doi: 10.1021/cr900184e. Engle KM, Mei T-S, Wasa M, Yu J-Q. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011;45:788–802. doi: 10.1021/ar200185g.
- 7.Hartwig JF. Organotransition Metal Chemistry. University Science Books; Mill Valley, CA: 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 8.For reviews and recent examples on NHC catalysis covering these different reaction manifolds, see: Enders D, Niemeier O, Henseler A. Chem. Rev. 2007;107:5606–5655. doi: 10.1021/cr068372z. Marion N, Diez-Gonzalez S, Nolan IP. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:2988–3000. doi: 10.1002/anie.200603380. Phillips EM, Chan A, Scheidt KA. Aldrichimica Acta. 2009;43:55–66. Ryan SJ, Candish L, Lupton DW. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013;42:4906–4917. doi: 10.1039/c3cs35522e. Hao L, Du Y, Lv H, Chen XK, Jiang HS, Shao YL, Chi YR. Org. Lett. 2012;14:2154–2157. doi: 10.1021/ol300676w. Jian TY, Sun LH, Ye S. Chem. Commun. 2012;48 doi: 10.1039/c2cc35273g. Jian TY, Chen XY, Sun LH, Ye S. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013;11 doi: 10.1039/c2ob26804c. Nair V, Menon RS, Biju AT, Sinu CR, Paul RR, Jose A, Sreekumar V. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:5336–5346. doi: 10.1039/c1cs15139h. Vora HU, Wheeler P, Rovis T. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2012;354:1617–1639. doi: 10.1002/adsc.201200031. Douglas J, Churchill G, Smith AD. Synthesis. 2012:2295–2309. Izquierdo J, Hutson GE, Cohen DT, Scheidt KA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012;51:11686–11698. doi: 10.1002/anie.201203704. De Sarkar S, Biswas A, Samanta RC, Studer A. Chem. Eur. J. 2013;19:4664–4678. doi: 10.1002/chem.201203707.
- 9.(a) Sheehan JC, Hunneman DH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966;88:3666–3667. [Google Scholar]; (b) Enders D, Breuer K, Runsink J, Teles JH. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1996;79:1899–1902. [Google Scholar]; (c) Breslow R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958;80:3719–3726. [Google Scholar]; (d) Enders D, Breuer K, Teles JH. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1996;79:1217–1221. [Google Scholar]; (e) Stetter H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1976;15:639–712. [Google Scholar]; (f) Stetter H, Hilboll G, Kuhlmann H. Chem. Ber. 1979;112:84–94. [Google Scholar]
- 10.(a) Burstein C, Glorius F. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004;43:6205–6208. doi: 10.1002/anie.200461572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Sohn SS, Rosen EL, Bode JW. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:14370–14371. doi: 10.1021/ja044714b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Chan A, Scheidt KA. Org. Lett. 2005;7:905–908. doi: 10.1021/ol050100f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.(a) Cohen DT, Cardinal-David B, Scheidt KA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011;50:1678–1682. doi: 10.1002/anie.201005908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Cohen DT, Scheidt KA. Chem. Sci. 2012;3:53–57. doi: 10.1039/C1SC00621E. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Dugal-Tessier J, O’Bryan EA, Schroeder TBH, Cohen DT, Scheidt KA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012;51:4963–4967. doi: 10.1002/anie.201201643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Cardinal-David B, Raup DEA, Scheidt KA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:5345–5346. doi: 10.1021/ja910666n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Raup DEA, Cardinal-David B, Holte D, Scheidt KA. Nat. Chem. 2010;2:766–771. doi: 10.1038/nchem.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) Mo JM, Chen XK, Chi YR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:8810–8813. doi: 10.1021/ja303618z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Rong ZQ, Jia MQ, You SL. Org. Lett. 2011;13:4080–4083. doi: 10.1021/ol201595f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Qi J, Xie XG, Han RF, Ma DH, Yang J, She XG. Chem. Eur. J. 2013;19:4146–4150. doi: 10.1002/chem.201204386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhao XD, DiRocco DA, Rovis T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:12466–12469. doi: 10.1021/ja205714g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.(a) Mattson AE, Scheidt KA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:4508–4509. doi: 10.1021/ja068189n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Li TH, Rokita SE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991;113:7771–7773. [Google Scholar]; (c) Pande P, Shearer J, Yang JH, Greenberg WA, Rokita SE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:6773–6779. [Google Scholar]; (d) Veldhuyzen WF, Pande P, Rokita SE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:14005–14013. doi: 10.1021/ja036943o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Weinert EE, Dondi R, Colloredo-Melz S, Frankenfield KN, Mitchell CH, Freccero M, Rokita SE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:11940–11947. doi: 10.1021/ja062948k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(a) Wan P, Barker B, Diao L, Fischer M, Shi YJ, Yang C. Can. J. Chem. 1996;74:465–475. [Google Scholar]; (b) Chiang Y, Kresge AJ, Zhu Y. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000;72:2299–2308. [Google Scholar]; (c) Van de Water RW, Pettus TRR. Tetrahedron. 2002;58:5367–5405. [Google Scholar]; (d) Luan Y, Schaus SE. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:19965–19968. doi: 10.1021/ja309076g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Willis NJ, Bray CD. Chem. Eur. J. 2012;18:9160–9173. doi: 10.1002/chem.201200619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Pathak TP, Gligorich KM, Welm BE, Sigman MS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:7870–7871. doi: 10.1021/ja103472a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.During review of this work, a related reaction involing the NHC-catalyzed addition of homoenolate equivalents to stable o-QMs was reported by Ye and coworkers: DOI: 10.1002/anie.201303903.
- 17.Additional fluoride sources were examined, including Me4N•F and TBAT, but these only provided trace amounts of desired product. See Supporting information for details.
- 18.The avoidance of standard nucleophilic amine bases used for NHC production from the corresponding azolium salt (e.g., triazabicyclodecene, 8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene, Et3N) was key for a successful process and understandable given the highly reactive nature of the o-QM in solution during the reaction. Lastly, omitting the CsF in the reaction based on entry 9, Table 1 provides no observable product.
- 19.Cronotonaldehyde as a substrate gave prodominantly the formal [4+2] product in a 57:43 ratio of formal [4+3] to [4+2] products (overall yield of 48%). The er for the [4+3] adduct was 95:5 and the er for the [4+2] compound was 99:1. Investigations to change this ratio by modulation of the reaction conditions (e.g., base, solvent) have resulted in no improvement to date.
- 20.(a) Kawanaka Y, Phillips EM, Scheidt KA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:18028–18029. doi: 10.1021/ja9094044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Phillips EM, Wadamoto M, Roth HS, Ott AW, Scheidt KA. Org. Lett. 2009;11:105–108. doi: 10.1021/ol802448c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lv H, You L, Song Y. For the NHC-catalyzed addition of ketene-derived enolates to stable o-quinone methides. Adv. Syn. Catal. 2009;351:2882–2826. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Macias FA, Varela RM, Torres A, Molinillo JMG. J. Nat. Prod. 1999;62:1636–1639. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Porter JH, Prus AJ. Psychopharmacol. 2009;203:189–191. doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1478-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.(a) Costantino L, Barlocco D. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006;13:65–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Schuetz H. Benzodiazepines II. A Handbook. Springer Verlag; Berlin: 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 25.(a) Das J, Floyd DM, Kimball SD, Duff KJ, Lago MW, Krapcho J, White RE, Ridgewell RE, Obermeier MT, Moreland S, et al. J. Med. Chem. 1992;35:2610–2617. doi: 10.1021/jm00092a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Das J, Floyd DM, Kimball SD, Duff KJ, Vu TC, Lago MW, Moquin RV, Lee VG, Gougoutas JZ, Malley MF, et al. J. Med. Chem. 1992;35:773–780. doi: 10.1021/jm00082a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Floyd DM, Kimball SD, Krapcho J, Das J, Turk CF, Moquin RV, Lago MW, Duff KJ, Lee VG, White RE, et al. J. Med. Chem. 1992;35:756–772. doi: 10.1021/jm00082a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Floyd DM, Moquin RV, Atwal KS, Ahmed SZ, Spergel SH, Gougoutas JZ, Malley MF. J. Org. Chem. 1990;55:5572–5579. [Google Scholar]
- 26.O’Connor SE, Grosset A, Janiak P. Fund. & Clin. Pharmacol. 1999;13:145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1999.tb00333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Grover GJ, Sleph PG, Parham CS, Brittain RJ, Krapcho J, Moreland S. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1990;16:219–227. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199008000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.