Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a major hospital and community pathogen having the aptitude to cause a wide variety of infections in men. The ability of microorganisms to produce biofilm facilitates them to withstand the host immune response and is recognized as one factor contributing to chronic or persistent infections. It was demonstrated that the ica-encoded genes lead to the biosynthesis of polysaccharide intercellular adhesion (PIA) molecules, and may be involved in the accumulation phase of biofilm formation. Different studies have shown the decisive role of the ica gene as virulence factors in staphylococcal infections.
This study was carried out to demonstrate the relationship between ica gene and production of slime layer in S. aureus strains. Sixty S. aureus strains were isolated from patients. The isolates were identified morphologically and biochemically following standard laboratory methods. After identification, the staphylococcal isolates were maintained in trypticase soy broth (TSB), to which 15% glycerol was added, and stored at –20°C. Slime formation and biofilm assay was monitored. A PCR assay was developed to identify the presence of icaD (intercellular adhesion gene) gene in all isolates. Thirty-nine slime producing colonies with CRA plates (65%) formed black colors, the remaining 21 isolates were pink (35%). In the quantitative biofilm assay 35 (58%) produced biofilm while 25 (42%) isolates did not exhibit this property. All isolates were positive for detection of icaD gene by PCR method. The interaction of icaA and icaD in the investigated isolates may be important in slime layer formation and biofilm phenomena.
We propose PCR detection of the ica gene locus as a rapid and effective method to be used for discrimination between potentially virulent and nonvirulent isolates, with implications for therapeutic and preventive measures pertainin to the management of colonized indwelling catheters.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus, biofilm, intercellular adhesion gene, PCR detection
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus ist ein wichtiger nosokomialer und community-assoziierter Krankheitserreger, der verschiedene humane Infektionen verursachen kann. Durch die Fähigkeit von Mikroorganismen zur Biofilmbildung wird ihre Widerstandsfähigkeit gegenüber der Immunabwehr mit der Folge chronischer oder persistierender Infektionen erhöht. Es wurde nachgewiesen, dass durch ica-codierende Gene die Biosynthese des interzellulären Polysaccharid-Adhäsins exprimiert wird, das eine Hauptkomponente für die Akkumulation des Biofilms darstellt. In verschiedenen Studien wurde die kritische Rolle der ica-Gene als Virulenzfaktor für Staphylokokken-Infektionen nachgewiesen.
Die vorliegende Untersuchung wurde durchgeführt, um den Zusammenhang zwischen dem ica- Gen und der Schleimbildung durch S. aureus zu analysieren. Hierzu wurden 60 S. aureus Patientenisolate identifiziert, morphologisch und biochemisch nach Standardmethoden charakterisiert und in Trypticase-Soja-Bouillon (TSB) mit Zusatz von 15% Glycerol bei –20°C aufbewahrt. Die Schleimbildung und Biofilmbildung wurde in einem speziellen Assay detektiert. Mittels eigens entwickelter PCR wurde alle Isolate auf das Vorkommen des icaD (intercellular adhesion gene) untersucht. Von den auf CRA-Platten Schleim produzierenden Kolonien waren 39 (65%) schwarz, die anderen 21 (35%) pinkfarben. Im quantitativen Biofilmassay bildeten 35 der Isolate (58%) einen Biofilm. Bei all diesen Isolaten wurde das icaD-Gen nachgewiesen.
Des lässt den Schluss zu, dass der PCR-Nachweis des ica-Locus als rasche und effektive Methode zur Unterscheidung zwischen potentiell virulenten and avirulenten Isolaten herangezogen werden kann, um die Therapie und Prävention der Biofilmbildung auf Implantaten zu verbessern. Der Synergismus zwischen icaA und icaD in den untersuchten Isolaten scheint bedeutend für die Schleimbildung und Biofilmakkumulation sein.
Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus is an important pathogen causing a wide spectum of infections [1], [2]. A number of studies have been conducted to explain the structures and pathogenic mechanisms by which S. aureus is able to cause serious infections [3], [4]. The ability of S. aureus to produce biofilm enables this organisms to withstand the host immune response and is considered to be the cause of chronic or persistent infections, as biofilm creation protects bacteria from opsonophagocytosis and antimicrobial agents [5]. Another concern related to this pathogen is increasing resistance to oxacillin and other antibiotics, but also distribution of multiresistant isolates within the hospital setting [6]. Staphylococcal pathogenesis is multifactorial, involving a combination of adherence and biofilm formation [7]. Complex aggregations of microorganisms can form irreversible attachments to the surfaces and formation of biofilm [8]. Biofilm producing bacteria are the source for persistent or chronic infections [6]. The significance of biofilm production for the virulence of S. aureus was supported by a number of clinical and animal studies [9]. Cell aggregation and biofilm accumulation are mediated by the products of a gene locus composing of the genes icaADB and C, which encode the essential proteins for the production of polysaccharide intercellular adhesion (PIA) and capsular polysaccharide/adhesion (PS/A) in Staphylococcus spp. [10], [11]. It was demonstrated that the ica-encoded genes are responsible for the biosynthesis of the PIA, which contains N-acetylglucosamine as a main constituent and in the accumulation phase of biofilm formation, playing a crucial role in invasiveness of S. aureus [1]. Different studies have shown the decisive role of the ica gene as virulence factors in staphylococcal infections [4], [11].
In this study, we developed new primers specific for icaD and determined further the possible relationship between icaD gene and producing slime layer in clinical isolates of S. aureus strains.
Materials and methods
1. Bacterial isolates and phenotypic identification
Sixty S. aureus strains were isolated from patients and used in this study. Isolates were identified morphologically and biochemically by standard laboratory methods. The coagulase and DNase tests were performed for discrimination of S. aureus from coagulase negative staphylococci (CoNS). After identification, the staphylococcal isolates were maintained in trypticase soy broth (TSB), to which 15% glycerol was added, and stored at –20°C.
2. Slime forming colony
This test was used to evaluate slime formation in S. aureus strains on CRA plates, as previously described [10]. Pink colonies were recorded as nonbiofilm producers while the black colonies were recognized as biofilm producers.
3. Biofilm assay
S. aureus strains were icubated in (TSB) at 37°C for 24 hours; grown colonies were diluted in 1:200 and incubated in microtiter plates. After 24 hours the wells were washed with PBS buffer two up to three times and left in the room temperature for drying. In the next step 0.4% crystal violet solution was used as stain for 10 min. Finally the absorbance at 490 nm was determined; an OD of 490 nm >0.12 was regarded as a biofilm positive sample.
4. Primer design and PCR amplification
PCR assay was achieved to detect the presence of icaD (intercellular adhesion) gene in all isolates. For preparing DNA, colonies of bacteria were dissolved in 20 µl lysis buffer (0.25% SDS, 0.05N NaOH) and heated at 95°C for 5 min. In the second step, the lysate was centrifuged and diluted using distilled water. A second centrifugation step for 5 min at 16,000 g was performed to remove the cell debris. Supernatants were frozen at –20°C until further use. The primer sequences F: 5' GAA CCG CTT GCC ATG TGT TG 3' (20 bp) & R: 5' GCT TGA CCA TGT TGC GTA ACC 3' (21 bp) for amplifying a 483 bp of icaD gene was designed from the published GenBank sequences (AF086783) with Alleleid 6 Primer Analysis Software. For recognition of icaD gene each 25 µl PCR mixture contained 2.5 µM of MgCI2, 100 µM of each dNTPs, 1U Taq DNA polymerase, and 1 µM of each primer with 200 ng of the DNA sample. PCR amplification was carried out with use of a DNA Thermal cycler (Eppendorf Master cycler personal) with an initial denaturation step (2 min at 95°C) followed by 30 cycles of amplification (denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 57.5°C for 30 s and elongation at 72°C for 40 s). Steps 2–4 were repeated 29 more times. Finally, 7 µl of PCR mixture was analyzed by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. After electrophoresis, gels were seen under UV light. The Gene Ruler TM 100 bp DNA Ladder Plus (Fermentas, Germany) was used as a DNA ladder.
Results
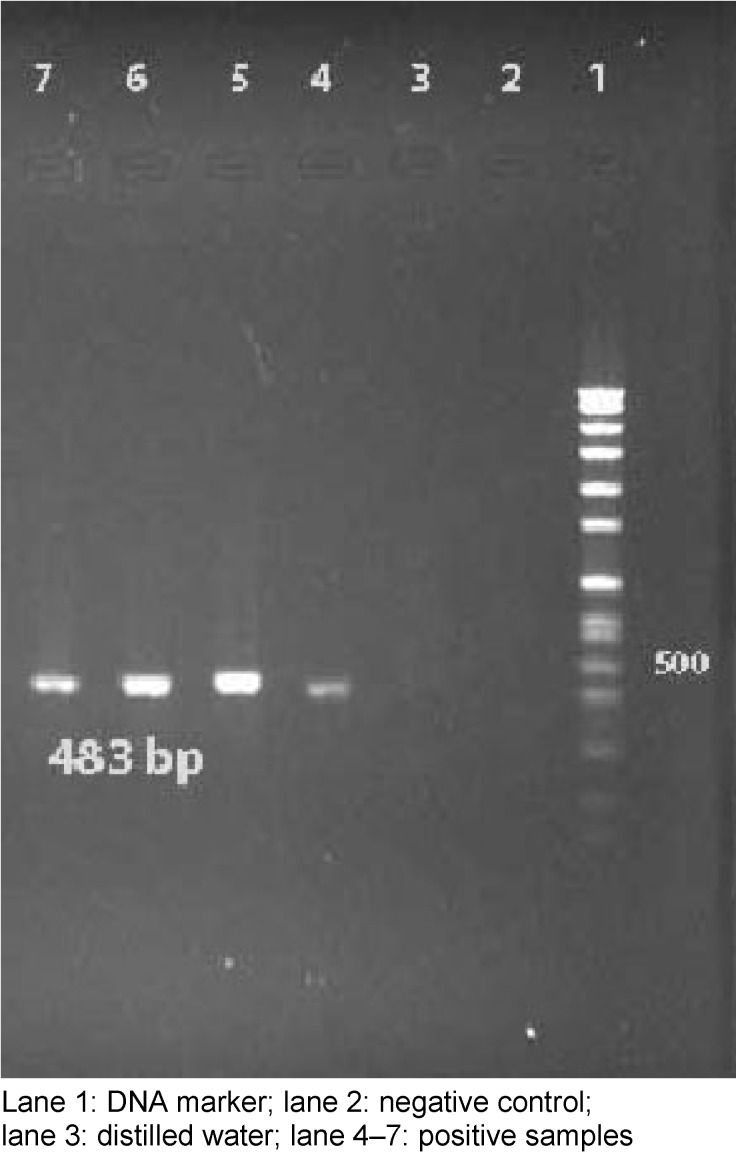
The investigated 60 strains were isolated from samples of blood catheter (40%), urine catheter (27.5%), sputum (8.3%), wounds (10%), and tracheal tube (14.2%), during the period October 2011 to February 2012. Thirthy-nine slime producing colonies with CRA plates (65%) formed black colors and, the remaining 21 were pink (35%). In the quantitative biofilm assay 35 (58%) produced biofilm, while the remaining 25 (42%) isolated did not exhibit this ability. All of these isolates were positive for detection of icaD gene by PCR method (Figure 1 (Fig. 1)).
Figure 1. PCR results of ica gene for S. aureus.
Discussion
S. aureus is responsible for infections in humans. It has been demonstrated that strains having an ability to form biofilm cause additionally “chronic polymer-associated” infection [9], [12], mostly een as implant-associated infections. Biofilm support the adhesion and colonization of S. aureus on surfaces, frequently leading to persistent and difficult to eradicate infections [4], [7]. Indeed, an increasing number of different S. aureus adhesion molecules is found [13]. The ica operon of S. aureus and S. epidermidis contain ica (ADBC) that allow Staphylococcus spp. to form slime layers and biofilm. It was shown that the presence of icaA gene in microorganisms yielded from indwelling catheter samples from patients hospitalized for one week was notably frequent. Cramton et al. [14] demonstrated the presence of icaA gene in S. aureus strains, which was confirmed by Arciola et al. [1] describing 23 S. aureus starins isolated from 14 catheter associated infections with the ability to form slime layer based on te presence of the gene icaA, but also icaD. Indeed, while icaA is required to encode N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase, coexpression of icaD can increase the capsular polysaccharide phenotypes [15], indicating a significant role of the icaD locus as a virulence factor in the pathogenesis of S. aureus isolated from catheters [13], [16].
Infections associated with the use of invasive medical devices, e.g., catheters, are mainly due to S. aureus, particularly those strains which create an extracellular slime and parts of the biofilm, making clinical treatment extremely challenging. The pocess of biofilm formation needs polysaccharide intercellular adhesion, which is synthesized by the enzymes encoded by the intercellular adhesion cluster (ica). In this study, the percentage of slime producing strains was 58%, while 65% of these had black colonies on CRA plate. However, all isolates contain icaD gene. Our study showed that S. aureus isolates had no ability to form biofilm unless they were positive for icaD gene. Subsequently, the PCR product was purified from the gel and sequenced (sequence accession no.: JN226155).
Since the presence of adhesion molecules is required for the establishement of an infection, the presence of ica adhesion genes may explain the role of the various adhesion mechanisms in the pathogenesis infection associated with in-dwelling medical devices [17], [18]. It can be concluded that infections caused by ica locus carriing S. aureus strains can lead to clinically difficult to treat conditions. The detection of the ica locus in clinical S. aureus isolates may improve the clinical decision for treatment and prevention options, and could support development of strategies to interact the bacterial capacity to colonize and invade in-dwelling medical devices. PCR detection of the ica operon may be an effective method to differentiate between virulent and non virulent strains. Finally, the synergistic effect of icaA and icaD genes in the clinical S. aureus starines investigated here may be important to further understand slime layer formation and biofilm phenomena.
Notes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Arciola CR, Baldassarri L, Montanaro L. Presence of icaA and icaD genes and slime production in a collection of staphylococcal strains from catheter-associated infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Jun;39(6):2151–2156. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.6.2151-2156.2001. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.39.6.2151-2156.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gordon RJ, Lowy FD. Pathogenesis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2008 Jun 1;46(Suppl 5):S350–S359. doi: 10.1086/533591. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/533591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.O'Neill E, Pozzi C, Houston P, Smyth D, Humphreys H, Robinson DA, O'Gara JP. Association between methicillin susceptibility and biofilm regulation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from device-related infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2007 May;45(5):1379–1388. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02280-06. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02280-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rohde H, Frankenberger S, Zähringer U, Mack D. Structure, function and contribution of polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA) to Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation and pathogenesis of biomaterial-associated infections. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Jan;89(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2009.10.005. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2009.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Foster TJ. Immune evasion by staphylococci. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005 Dec;3(12):948–958. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1289. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Martín-López JV, Pérez-Roth E, Claverie-Martín F, Díez Gil O, Batista N, Morales M, Méndez-Alvarez S. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates Harboring the ica Gene Cluster Needed for Biofilm Establishment. J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Apr;40(4):1569–1570. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1569-1570.2002. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.40.4.1569-1570.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Klug D, Wallet F, Kacet S, Courcol RJ. Involvement of adherence and adhesion Staphylococcus epidermidis genes in pacemaker lead-associated infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Jul;41(7):3348–3350. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.7.3348-3350.2003. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JCM.41.7.3348-3350.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stobie N, Duffy B, McCormack DE, Colreavy J, Hidalgo M, McHale P, Hinder SJ. Prevention of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation using a low-temperature processed silver-doped phenyltriethoxysilane sol-gel coating. Biomaterials. 2008 Mar;29(8):963–969. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.10.057. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.10.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Götz F. Staphylococcus and biofilms. Mol Microbiol. 2002 Mar;43(6):1367–1378. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02827.x. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frank KL, Patel R. Poly-N-acetylglucosamine is not a major component of the extracellular matrix in biofilms formed by icaADBC-positive Staphylococcus lugdunensis isolates. Infect Immun. 2007 Oct;75(10):4728–4742. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00640-07. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00640-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004 Feb;2(2):95–108. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro821. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Götz F. Staphylococci in colonization and disease: prospective targets for drugs and vaccines. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004 Oct;7(5):477–487. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.08.014. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2004.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rooijakkers SH, van Kessel KP, van Strijp JA. Staphylococcal innate immune evasion. Trends Microbiol. 2005 Dec;13(12):596–601. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2005.10.002. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2005.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cramton SE, Gerke C, Schnell NF, Nichols WW, Götz F. The intercellular adhesion (ica) locus is present in Staphylococcus aureus and is required for biofilm formation. Infect Immun. 1999 Oct;67(10):5427–5433. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.10.5427-5433.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Satorres SE, Alcaráz LE. Prevalence of icaA and icaD genes in Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strains isolated from patients and hospital staff. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2007 Jun;15(2):87–90. doi: 10.21101/cejph.a3396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.O'Gara JP. ica and beyond: biofilm mechanisms and regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 May;270(2):179–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00688.x. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Merlino J, Watson J, Rose B, Beard-Pegler M, Gottlieb T, Bradbury R, Harbour C. Detection and expression of methicillin/oxacillin resistance in multidrug-resistant and non-multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Central Sydney, Australia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002 May;49(5):793–801. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkf021. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkf021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Otto M. Staphylococcal biofilms. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;322:207–228. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75418-3_10. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75418-3_10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]