Abstract
Garcinia is a plant under the family of Clusiaceae that is commonly used as a flavouring agent. Various phytochemicals including flavonoids and organic acid have been identified in this plant. Among all types of organic acids, hydroxycitric acid or more specifically (−)-hydroxycitric acid has been identified as a potential supplement for weight management and as antiobesity agent. Various in vivo studies have contributed to the understanding of the anti-obesity effects of Garcinia/hydroxycitric acid via regulation of serotonin level and glucose uptake. Besides, it also helps to enhance fat oxidation while reducing de novo lipogenesis. However, results from clinical studies showed both negative and positive antiobesity effects of Garcinia/hydroxycitric acid. This review was prepared to summarise the update of chemical constituents, significance of in vivo/clinical anti-obesity effects, and the importance of the current market potential of Garcinia/hydroxycitric acid.
1. Introduction
The world is in health transition. Infection as a major cause of suffering and death is giving way to new epidemics of noncommunicable disorders such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes, which continue to plague the world at an alarming rate [1]. A trend of increasing prevalence of obesity and obesity-related comorbidity and mortality was observed over the last few decades [2]. The International Association of the Study of Obesity (IASO) reported on the country rankings in terms of percentage global prevalence of adult obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) in the year of 2012, where Tonga ranks first with 56.0% obese adults (46.6% of obese male and 70.3% of obese female). In the United States, IASO reported that 35.5% of men and 35.8% women were obese (BMI ≥ 30) [1, 3]. Overweight and obesity are diagnosed based on the body mass index (BMI), which is defined as quotient of body weight (kg) over the square of stature (m2). According to the World Health Organization (WHO) standard, overweight subjects are diagnosed with BMI values in the range of 25–29.99. Obesity itself, defined as BMI ≥ 30, is associated with several chronic and debilitating health problems including hyperlipidemia, hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, cancer, disease of the gall bladder, osteoarthritis, shortage of breath, abnormal dilation of the veins, backache, and even psychological problems [2, 4].
There are a few drugs in the market to ameliorate or prevent obesity, but there are costs, efficacy, and side effects to be considered. For example, the currently available pharmacological agents, Sibutramine, Rimonabant, Orlistat, and Phentermine which are licensed for weight reduction therapy, appear to possess some adverse effects [5–7]. Phentermine, for instance, has been reported to cause dry mouth, insomnia, headache, dizziness, fatigue, and palpitation [6, 7]. In year 2010, FDA had announced the market withdrawal of Meridia (Sibutramine) due to its risk of serious cardiovascular events [6, 7]. Natural products and plant-based dietary supplements have been used by people for centuries. Evidence is starting to emerge to shed light on the consumption of herbs as an effective strategy for disease treatment and health maintenance. Several ethnobotanical studies have reported the bioprospecting surveys on the positive application of herbs in the treatments for obesity [8]. Garcinia has been used for centuries in Asian countries for culinary purposes as a condiment and flavoring agent in place of tamarind or lemon and to make meals more filling [9, 10]. Besides its use as a flavouring agent, the dried rind of G. cambogia combined with salt and other organic acids can help to lower the pH and thus provides a bacteriostatic effect in curing fish. G. cambogia contains large amounts of hydroxycitric acid (HCA). Similar to G. cambogia, G. atroviridis and G. indica also contain significant HCA content and are sometimes used interchangeably with G. cambogia in food preparation. The different features among these three different types of Garcinia are summarised in Table 1 [9, 11–14].
Table 1.
| Species | Common name | Origin | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| G. cambogia | Asam Gelugor | India: found commonly in the evergreen forests of Western Ghats, from Konkan southward to Travancore, and in the Shola forests of Nilgiri. | Small- or medium-sized tree with a rounded crown and horizontal or drooping branches, under the family of Guttiferae. Its fruits are ovoid, about 5 cm in diameter, yellow or red when ripe with six to eight grooves, enclosing six to eight seeds, and are edible. |
|
| |||
| G. atroviridis | Asam Gelugor | Southeast Asia | Small- or medium-sized fruit tree, with drooping branches and ovoid fruits. The fruits are bright orange-yellow when ripe, globose with 12–16 grooves, about 7–10 cm in diameter, and fluted with a firmly textured outer rind and a rather thin and translucent pulp surrounding the seeds. |
|
| |||
| G. indica | Kokum | India: the tropical rain forests of Western Ghats, from Konkan southward to Mysore, Coorg, and Wayanad | Slender evergreen tree with drooping branches. Its fruits are globose or spherical, 2–4 cm in diameter, dark purple when ripe with five to eight large seeds surrounded. |
A myriad of health effects have been attributed to Garcinia (including G. cambogia, G. atroviridis, and G. indica), such as antiobesity effects [15–17], antiulcerogenic [18–20], antioxidative [21–24], antidiabetes [25], antimicrobial [22, 26–28], antifungal [29], anti-inflammatory [30, 31], and anticancer effects [22, 32–34]. In particular, the antiobesity effects of Garcinia or more specifically of its HCA content have been elucidated with unprecedented clarity over the last few decades. Besides its efficacy in the reduction of body weight and food intake, Garcinia/HCA has been proven to be beneficial in ameliorating obesity-related complications such as inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance [21]. The results obtained from several studies supported the positive effects of HCA administration alone or in combination with other ingredients on body weight loss, reduced food intake, increased fat oxidation, or energy expenditure (EE) [16, 17, 35–39] whereas some studies did not [40–42].
In spite of the vastly reported prominent role of HCA in inducing satiety, reduced energy intake and weight gain, and improved blood parameters and substrate oxidation, controversial results regarding its efficacy and safety as an antiobesity dietary supplement had also been reported. Evidence from the in vitro, in vivo, and clinical trials on the safety of Garcinia/HCA as a dietary supplement for treating obesity had been extensively reviewed [43]. However, the efficacy of Garcinia/HCA remains the subject of debate. Despite the previously stated issues, on conclusive evidence for HCA's efficacy in promoting weight loss and suppressing food intake, the marketing of a plethora of over-the-counter slimming aids containing HCA has taken place. The aim of this review is to critically assess the evidence from a very broad range of reports, rigorous clinical trials, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses on the efficacy and potential of Garcinia/HCA as an antiobesity dietary supplement.
2. Uses in Traditional Medical Systems
Botanical dietary supplements usually contain a complex mixture of phytochemicals which have additive or synergistic interactions. Aside from its use as a preservative and as a condiment in cuisine, Garcinia extract has been used in the traditional Ayurvedic medical system [9, 13]. A decoction of G. cambogia is given as purgative in the treatment of intestinal worms and other parasites, for bilious digestive conditions, for dysentery, rheumatism, and in the treatment of tumours. Less commonly, extracts are employed as cardiotonics to treat angina. In veterinary medicine, it is used as a rinse for diseases of the mouth in cattle [12, 77]. The fruit rind is used in rickets and enlargement of spleen and to heal bone fractures [13]. In Southeast Asian folkloric medicine, a decoction of G. atroviridis (leaves and roots) is sometimes used for the treatment of cough, dandruff, earache, stomach pains associated with pregnancy, and throat irritation [49]. The dried fruit of G. atroviridis is used for improving blood circulation, for the treatment of coughs, as a laxative, and as a expectorant. The fruit is used in a lotion with vinegar to rub over the abdomen of women after confinement [9]. Fruit of G. indica is antiscorbutic, cholagogue, cooling, antibilious, emollient, and demulcent. The anthelmintic properties of the fruit of G. indica contributed to its use in haemorrhoids, dysentery, tumor, pains, and heart complaints. Bilious affected sites are treated with syrup from the fruit juice. Kokum butter is astringent and demulcent and is used in diarrhea and dysentery. It is also applied externally for ulcerations, sinuses, fissures of hand, lip, chapped skin, and skin diseases [12, 13, 44, 77].
3. Phytoconstituents
The several compounds which have been isolated from various species of Garcinia are summarised in Table 2. Several types of organic acids such as HCA, citric, tartaric, malic, and succinic acids are isolated from Garcinia. However, HCA is the principal acid of the fruit rinds of G. cambogia, G. indica, and G. atroviridis [12, 27, 45], with its content ascending as listed [46–48]. A substantial amount of (−)-HCA, up to 30% by weight is present in the pericarp of the fruit of G. cambogia. In similar studies conducted by Sullivan et al. [78, 79] and Stallings et al. [80], they observed that of the four isomers of HCA [(–)-HCA, (+)-HCA, (–)-allo-HCA, and (+)-allo-HCA], (−)-HCA, which is also known as (2S, 3S)-HCA, was the only potent inhibitor of ATP citrate lyase. (−)-HCA can be chemically synthesized using citric acid as starting material. Synthetic (−)-HCA offers several advantages including higher purity and lactone stable as compared to natural (−)-HCA [81]. On the other hand, (−)-HCA is a good starting material to synthesize other important chiral synthons and compounds [82].
Table 2.
Phytochemicals of Garcinia.
| Phytochemicals | G. cambogia | G. indica | G. atroviridis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic acids | |||
| (−)-HCA | Fruit rind [45, 46] | Fruit rind [45] | Fruit rind [45] |
| Citric acid | Fruit rind [46] | Leave and fruit rind [47] | Herbal products [48] |
| Tartaric acid | [46]nd | [47]nd | Herbal products [48] |
| Malic acid | Fruit rind [46] | [47]nd | Herbal products [48] |
| Succinic acid | — | [47]nd | — |
| Prenylated benzoquinone | |||
| Atrovirinone | — | — | Root [27] |
| Prenylated depsidone | |||
| Atrovirisidone | — | — | Root [27] |
| Atrovirisidone B | — | — | Root [49] |
| Prenylated hydroquinone | |||
| 4-Methylhydroatrovirinone | — | — | Root [50] |
| 1,4-cis-Docosenoic acid | — | — | Root [50] |
| 14-cis-Docosenoic acid | — | — | Root [50] |
| Flavonoid | |||
| Morelloflavone | — | — | Root [50] |
| Fukugiside | — | — | Root [50] |
| Naringenin | Root [49] | ||
| 3,8′′-Binaringenin | Root [49] | ||
| Xanthone | |||
| Garbogiol | Root [51] | — | — |
| Rheediaxanthone A | Bark [51] | — | — |
| Dioxygenated xanthone | |||
| 1,7-Dihydroxyxanthone | — | Heartwood [52] | — |
| Tetraoxygenated xanthone | |||
| Atroviridin | — | — | Stem bark [53] |
| Tetracyclic xanthone | |||
| Oxyguttiferone K | Fruit [54] | — | — |
| Polyisoprenylated benzophenone | |||
| Garcinol/camboginol (enantiomer of xanthochymol) | Fruit rinds [55, 56] Latex [57] Bark [51] |
[55]nd
Fruit rinds [58] |
— |
| Isogarcinol/cambogin (enantiomer of isoxanthohumol) | Latex [57] Bark [51] |
Fruit rinds [58] | — |
| Isoxanthohumol | Fruit rinds [55] | [55]nd | — |
| Guttiferone I | Fruit [54] | — | |
| Guttiferone J | Fruit [54] | — | |
| Guttiferone K | Fruit [54] | — | |
| Guttiferone M | Fruit [54] | — | |
| Guttiferone N | Fruit [54] | — |
nd: none detected; —: not reported.
(−)-HCA is one of the important supplements for antiobesity and weight management. Its effect on weight management is mainly contributed by giving the feeling of full and satisfaction while the antiobesity effect is by reduction of de novo lipogenesis and acceleration of fat oxidation (Figure 1). In this paper, we aimed to review the mechanism for antiobesity and weight management effects by (−)-HCA (hereafter referred to as HCA)/G. cambogia/G. atroviridis/G. indica extracts and the assessment of these effects in the clinical settings.
Figure 1.
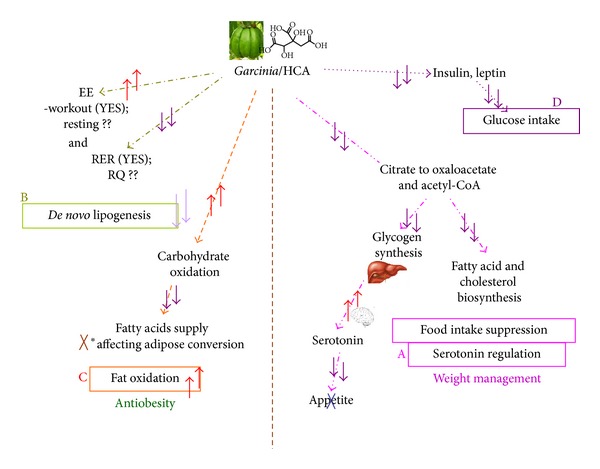
Possible multiple mechanisms that contribute to antiobesity effect of Garcinia/HCA. ↑ indicated increase or stimulation; ↓ indicated reduce or inhibition while ?? indicated that the effect is yet to be confirmed. (A) summary of Serotonin regulation and food intake suppression; (B) summary of reduction of de novo lipogenesis; (C) summary of stimulation on fat oxidation; (D) summary of reduce on glucose intake; (A) and (B) contribute to the weight management effect of Garcinia/HCA while (B) and (C) contribute to antiobesity of Garcinia/HCA.
4. Salts of HCA
On account to the discovery of (−)-HCA as an effective compound in weight management, market demand for the acid has increased tremendously. The commercially available G. cambogia extracts which contain approximately 50% (−)-HCA are prepared from the fruit rind [12, 69]. HCA can exist as a free acid or in the lactone form. The former form is considered to be biologically active. However, the free acid is unstable and is usually converted to its less active lactone form to attain higher stability. To prevent the cyclization of HCA into its less potent lactone, the acid has been combined with various counter ions to form stable salts [83].
Commercial HCA is available in free acid form and as single, double, or triple salts. Preparations with different counter ions contribute to different degree of solubility as well as bioavailability [84]. For example, Na+ salt of HCA had been shown to be more effective than its lactone in inhibiting lipogenesis. However, Na+ salt is highly hygroscopic when bound to (−)-HCA, which would deemed unfavorable for the production of pharmaceuticals for dry delivery [85].
To address the need to achieve higher solubility and stability, recent approaches have been focused more on the preparation of (−)-HCA in the form of a double or triple salt. Similar to its single salts, these double or triple salts also serve as good supply for essential ions [84]. A remarkable example of these would be the Ca2+/K+ salt of (−)-HCA (HCA-SX) or Super CitriMax. In contrast to the single salts, HCA-SX is completely soluble in water and thus confers higher bioavailability [84]. A number of studies on the safety of HCA-SX had been reported [43]. Daily intake of HCA-SX at this dosage was shown to be effective in reducing body weight and BMI of healthy and obese adults after clinical trials of 8 weeks [16, 64]. Gene expression studies also provided additional evidence for the safety of HCA-SX, where genes essential for mitochondrial/nuclear proteins and for fundamental support of adipose tissue were shown to be independent of the regulation by HCA-SX [17, 86].
A typical reduction of food appetite and an increased serotonin availability were observed in all the weight control studies of HCA-SX on both animal and human subjects. These were associated with reduced levels of total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides, and serum leptin as well as increased HDL level and urinary excretion of fat metabolites [15, 16, 64, 84, 87]. In rats, the salt also caused downregulation of genes encoding abdominal fat leptin while expressions of the plasma leptin genes remained unaltered [17]. Nevertheless, it was postulated that a set of obesity regulatory genes [84] and inhibition to the uptake of [3H]-5-HT release in the brain [15] are involved in the appetite suppressing activity of HCA-SX.
In relation to this, gene expression profiling carried out by a research group demonstrated the modulation of a specific set of genes (about 1% of 9960 genes and ESTs) in the adipocytes by dietary HCA-SX supplementation [17]. Further study on cultured mature human adipocytes revealed significant upregulation of 366 and downregulation of 348 the fat- and obesity-related genes [88]. Notably also in the microarray analyses, HCA-SX demonstrated a distinct effect on appetite suppression whereby genes encoding serotonin receptors were shown to be selectively upregulated by the salt [17]. Besides, HCA-SX was also found to be capable of activating hypoxia inducible factor (HIF), a transcription factor involved in energy metabolism [88] and restored the increase in oxidative stress, inflammation, and insulin resistance in obese Zucker rats [21].
5. Antiobesity Effects of Garcinia/HCA
Obesity, particularly caused by accumulation of visceral fat, is a serious risk factor of various life-style diseases such as coronary heart disease, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and cancer [2, 4]. Human obesity is influenced by genetic and environmental factors and particularly by changes in diet and physical activity, which contributes greatly to the development of insulin resistance, a most common underlying abnormality in human obesity [89]. Studies on food sources exerting antiobesity effects have focused on the development of herbal extracts or functional food which can suppress the accumulation of body fat. Several studies were conducted to provide scientific basis on the extensive usage of G. cambogia and G. atroviridis associated with high-fat diet- (HFD-) induced obesity where dyslipidemia, fatty liver, insulin resistance, and hyperleptinemia were acquired along with the overexpression of leptin, TNF-α, resistin, PPARγ2, C/EBPα, and SREBP1c genes in epididymal adipose tissue. The effect of G. cambogia was largely attributed to its HCA content [90, 91]. Subsequent researches proved that the antiobesity effects of G. cambogia/HCA resulted from the combined actions of several mechanisms including suppressing de novo fatty acid biosynthesis and appetite [16, 60] and increasing energy expenditure [39], subsequently reducing body fat accumulation and weight gain in experimental animals [37, 38, 92]. In this review, we arranged the antiobesity effects of Garcinia/HCA based on their distinct mechanisms: (1) serotonin regulation and food intake suppression, (2) decreased de novo lipogenesis, (3) increased fat oxidation, and (4) downregulation of a spectrum of obesity-associated genes.
5.1. Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) Regulation and Food Intake Suppression
HCA, the primary acid in the fruit rinds of G. cambogia, G. atroviridis, and G. indica [45], has been reported as the active ingredient in inhibiting ATP citrate lyase (EC 4.1.3.8) [78, 93]. ATP citrate lyase, which is an extramitochondrial enzyme catalyzing the cleavage of citrate to oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA, was inhibited by HCA. Thus, the availability of two-carbon units required for the initial steps of fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis during carbohydrate feeding was limited [78, 79, 94–97]. As a result, the consumed carbon source was diverted to glycogen synthesis in liver. A signal was then sent to the brain due to this metabolic alteration, resulting in rising of serotonin level concomitant with a reduced appetite. HCA might exhibite its anorectic effect by a second possible mechanism, namely, reducing acetyl CoA, subsequently decreasing malonyl CoA levels and thereby reducing negative feedback on carnitine acyltransferase (CPT-1). The substrate of CPT-1, long-chain acyl CoA(s), may act as a mediator(s) of appetite [98, 99]. More recently, neuropeptide Y (NPY) had also been implicated in the appetite suppression of HCA. Basal concentration of the neurotransmitter was claimed to be significantly reduced in the hypothalamic tissues as a result of supplementation with HCA-SX [84]. However, the role of NPY in this is still vague to date. Several reports supported the serotonin regulation of HCA. Ohia et al. [100] demonstrated that HCA-SX enhanced serotonin availability in isolated rat brain cortex by acting as a mild serotonin receptor reuptake inhibitor (SRRI), without stimulating the central nervous system. Kaur and Kulkarni [36] conducted a study to elucidate the effect of OB-200G, a polyherbal preparation containing aqueous extracts of G. cambogia, Gymnema sylvestre, Zingiber officinale, Piper longum, and resin from Commiphora mukul on the modulation of food intake by serotonin modulators in female mice. The results obtained were compared with fluoxetine, a drug that was reported to enhance 5-HT neurotransmission [101]. Both OB-200G and fluoxetine significantly (P < 0.05) antagonized the hyperphagic effect of p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA), 8-hydroxy-2-(di-N-propylamino)-Tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), cyproheptadine, and 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) which further instigate possible serotonergic involvement in the effects of OB-200G on food intake in female mice. Preuss et al. [16] reported that HCA caused a significant reduction in appetite, weight loss, and plasma leptin level, concomitant with an increase in the serum serotonin level and a favorable lipid profile in human clinical trials. Similar results were also obtained in a study conducted by Asghar et al. [87] They reported on increased brain serotonin level in obese Zucker rats receiving G. cambogia extract, suggesting that the ability of HCA in body weight gain reduction was most probably due to its combined effects on the metabolic and serotonin pathways. In addition, Roy et al. [17] reported that HCA-SX supplementation upregulated prostaglandin D synthase (PDS), aldolase B (AldB), and lipocalin (LCN2) genes in abdominal fat tissue. Further mapping of the candidate genes of known pathways associated with fat metabolism by using functional categorization and pathway construction software showed that supplementation of HCA-SX targeted on the serotonin receptor.
Leonhardt et al. [102] reported that HCA reduced body weight regain in rats after a period of substantial body weight loss. Besides, HCA temporarily reduced food intake of rats with diets of varying nutrient contents (grounded standard rat chow, high glucose, and high glucose + fat). HCA supplementation caused pronounce suppression of food intake during the entire 10 days of ad libitum feeding period in rats fed with high glucose + fat diet, a diet that had a nutritionally relevant level of dietary fat (24% of energy). These data therefore extended those of the previous studies which reported on the anorectic effects of HCA [96, 97, 103–105]. Moreover, the results obtained were consistent with studies which reported on particularly strong food intake suppression by HCA with high glucose + fat diet and a smaller but still significant suppression with the high glucose diet in other rat models and in different orders [37, 39, 102]. Hence, the feed conversion efficiency [cumulative body weight regain (g)/cumulative food intake (MJ)] in the high glucose and high glucose + fat groups during the 10 ad libitum days was reduced, which indirectly supported that HCA increased energy expenditure in these groups.
Leonhardt and Langhans [39] then extended their study on the long-term effects of HCA on body weight regain and food intake, as well as the effects of HCA on the circadian distribution of food intake and on meal patterns during the dark and light phases. HCA administration significantly reduced the food intake of rats fed with 12% fat diet, but not 1% fat diet, concomitant with significant reduction in weight regain (overall P < 0.01) in both groups. In the study, the rats underwent restrictive feeding for 10 days prior to ad libitum feeding (Experiment 1: normal 1% fat diet and 1% fat diet + 3% HCA; Experiment 2: normal 12% fat diet and 12% fat diet + 3% HCA). The control groups of both experiments had compensated the body weight loss, whereas the HCA-fed rats groups regained only 68 ± 4% (1% fat diet) and 61 ± 8% (12% fat diet) of the body weight regained by their respective control groups after 22 days of such ad libitum feeding. Despite significant reduction in weight regain in rats fed with 1% and 12% fat diet, long-term suppression of HCA on food intake was only detected in combination with 12% fat diet (Experiment 2). This was in line with the results obtained by Leonhardt et al. [106] who suggested that HCA increased energy expenditure. Studies on the effects of HCA on the circadian distribution of food intake and on meal patterns showed that the suppression of food intake occurred predominantly during the dark phase of the first ad libitum days. However later on, HCA suppression of food intake was more effective during the light phase. Further experiments elucidating the effects of HCA in combination with the 12% fat diet on meal size and meal number during the light phase revealed that HCA markedly reduced the meal number, but not the meal size. HCA did not affect any metabolic variables tested (plasma glucose, lactate, triacylglycerol, HDL, free fatty acids, β-hydroxybutyrate, and insulin, hepatic fact, and glycogen concentrations) in both experiments, except decreasing plasma triacylglycerol levels and increasing the liver fat concentration in Experiment 2 (rats fed with 12% fat diet). The fact that HCA did not affect plasma β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) levels did not support the hypothesis that HCA suppressed food intake via increased hepatic fatty acid oxidation.
However, contradicting results were obtained by Kovacs et al. [41, 71] who reported that two-week supplementation with HCA and HCA combined with medium-chain triglycerides did not result in increased satiety. The findings were in line with previous reports where no significant treatment effects were observed on appetite indices (inclusive of mean, peak or nadir hunger ratings, mean ratings of desire to eat, prospective consumption, fullness or sensations of thirst, stomach growling, headache, distraction, irritability, or, as a check on malingering, itchiness) [69]. The lack of efficacy and transient food intake suppression by HCA raised questions about its clinical significance. While negative findings are always open to methodological questions, several questions need to be answered before drawing a definite conclusion. First, the diet administered to the subjects should not promote extreme sensations in the evaluation of the food intake suppression effects of HCA under conditions of energy restriction. However, Mattes and Bormann imposed mild restrictions and thus ruled out this possibility as evidenced by ratings falling in the middle range of the response scales. Second, an energy-restricted diet would prevent the required enzyme alterations (reduction of acetyl-CoA and suppression of formation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I inhibitor malonyl CoA) which altered substrate metabolism and satiety. However, it was unlikely that the moderate energy restricted diet prescribed in the study conducted by Mattes and Bormann [69] hindered the satiety effect of HCA as it still contained at least 30% of energy from fat.
Several factors might contribute to the controversial results of the efficacy of HCA in human studies. One of contributing factors is the highly variable doses used in the human trials which ranged from 5 to 250 mg/kg of HCA per day [42, 70]. Besides, the discrepancy might also be due to the differences in the preparation or extraction of HCA. For instance, the extraction method might increase the formation of HCA in a lactone form, which is less potent in the inhibition of ATP citrate lyase [85, 107]. In order to prevent the cyclization of HCA into the less potent lactone form, preparation using different counte rions (such as potassium, sodium, or calcium) had been applied [84], which contributed to the different degrees of stability, bioavailability, or solubility of HCA [86]. In this respect, Louter-Van De Haar et al. [83] conducted a study on the efficacy of three commercially available HCA products on suppression of food intake in male Wistar rats. Many human studies which reported lack of efficacy used Super CitriMax at considerably lower doses [41, 70, 71]. On the contrary, Preuss et al. [16] reported that high doses of Super CitriMax exerted significant effects in human. Thus, Louter-Van De Haar et al. [83] suggested that the reported lack of efficacy of HCA in suppressing food intake in human subjects might be due to the low doses of a relatively low-effective HCA preparation. Nevertheless, significant suppression of food intake was observed in the studies conducted by Leonhardt and Langhans [39] where Sprague-Dawley rats were supplemented with HCA for 10 days after substantial, fasting-induced weight loss. It seemed that HCA might be more effective in regulating weight gain than promoting weight loss; thus it was more useful for weight maintenance after an initial loss [39, 102]. Hence, differences in the experimental setups such as the difference in rat strains could contribute to such discrepancy.
5.2. Decreased De Novo Lipogenesis
The reduction of the acetyl-CoA by HCA and thus limiting the availability of building blocks required for fatty acid and cholesterol biosynthesis has led to suggestions that HCA inhibited lipogenesis. Several studies conducted by Sullivan and colleagues had confirmed the inhibition of in vivo and in vitro rates of lipogenesis in several tissues reported to convert carbohydrate into fatty acids (such as liver, adipose tissue, and small intestine), in which HCA was predominantly given to rodent models [78, 79, 85, 96, 97, 108]. Lowenstein [108] demonstrated that HCA greatly inhibited in vivo fatty acid synthesis in rat liver. The rats were placed on chow diet for 7–10 days, followed by 45 h of fasting prior to a scheduled diet high in fructose or glucose for 10 to 15 days. The sodium salt of HCA at dose levels of 2 to 20 mM was administered by intraperitoneal injections 45 min before injection of 3H2O. Fatty acid biosynthesis in rat liver (μ moles 3H2O incorporated/g liver/h) was measured 3.5–5 h after starting of the final feeding. Profound decrease in fatty acid synthesis by 25 to 30 days was obtained with an intraperitoneal dose of 0.1 mmole per kg of body weight (equivalent to approximately 2.9 mg of HCA per 150 g rat). In addition, 50% of inhibition was detected at a dose level of 0.28 mmole per kg body weight.
It was reported that G. cambogia/HCA affected respiratory quotient (RQ) and EE in rats and human. Lim et al. [109, 110] showed that short-term administration of HCA decreased the RQ in athletes and in untrained women. Leonhardt et al. [106] further extended their study to determine the effect of HCA on RQ and EE in rats fed ad libitum after a period of substantial weight loss. They reported that HCA markedly decreased RQ and EE during the first two days of ad libitum, reflecting suppression of de novo lipogenesis in rats, which is consistent with the findings of Westerterp-Plantenga and Kovacs [61] in humans.
In this respect, Kovacs and Westerterp-Plantenga [60] further extended their study where the effects of HCA on net fat synthesis as de novo lipogenesis were investigated. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, and crossover design experiment was conducted on 10 sedentary male subjects. The subjects performed glycogen depletion exercise, followed by a 3-day high-fat low-carbohydrate (F/CHO/P, 60/25/15% energy; 100% of EE; depletion period) intake in order to create a similar glycogen storage capacity. Subsequently, a 7-day high-carbohydrate diet (F/CHO/P, <5/>85/10% energy; 130–175% of EE; overfeeding period) supplemented with either 500 mg of regulator HCA (HOB Ireland Ltd.) or placebo was administered. Each intervention ended with a 60 h stay in the respiratory chamber (days 9 and 10). De novo lipogenesis occurred as indicated by RQ > 1.00 in all subjects. Significantly, lower 24 h EE (P < 0.05; on day 9), resting metabolic rate (P < 0.01; on day 10), and RQ at night (P < 0.05; on day 10) were detected with HCA as compared to placebo. Fat balance and thus net fat synthesis as de novo lipogenesis tended to be lower (P < 0.1) with HCA as compared to placebo. Taken all together, Kovacs and Westerterp-Plantenga concluded that the administration of HCA during overfeeding of carbohydrates may reduce de novo lipogenesis.
However, opinions differ widely with respect to this issue. The mechanism underlying the anorectic effect of HCA is still unclear. Furthermore, whether the suppression of body weight regained was solely due to reduced food intake or whether there was involvement of increased EE remained unknown. Contradictory results were reported on the effects of HCA on EE. Previous reports by Leonhardt and colleagues [39, 102] and the results obtained in pair-feeding studies [103] showed reduction of body weight regain and energy conversion ratio by HCA supporting the finding that HCA increased EE. However, reduced energy conversion ratio could be due to decreased nutrient absorption. Vasselli et al. [111] demonstrated an increment in 24 h EE in rats fed with mixed high-carbohydrate diet ad libitum by directly measuring the EE in a whole-body respirometer, albeit no effect on the RQ was detected. Another study conducted by Leray et al. [112] reported that 6 months of HCA administration did not affected EE in adult neutered cats. Besides, most human studies [41, 42, 70] reported that HCA had no effect on EE. Kriketos et al. [42] reported that HCA administration exhibited no effect on lipid oxidation in men during either rest or moderately intense exercise on a cycle ergometer. However, in these studies, the subjects received a much smaller dose, namely, a daily dose of 3.0 g per subject [nearly equal to 1.5 mg/day/mouse]. Furthermore, their experimental period of 3 days was quite short when compared with other studies.
Blunden [113] reported that when Garcinia extract and insulin were added simultaneously, the number of larger droplets markedly decreased while the smaller droplets (10–20 μm2 or <10 μm2) increased in 3T3-L1 cell. The activity of cytosolic glycerophosphate dehydrogenase (GPDH) which converts dihydroxyacetne phosphate to glycerol 3-phosphate (predominant substrate for triglyceride synthesis) increased from undetectable levels to between 100 and 187 U/mg of cytosolic protein after adipose conversion. However, no significant decrease in enzymatic activity was detected after administration of the Garcinia extract. Taken together, the authors therefore suggested that Garcinia extract interferes with lipid synthesis in fat cells via fatty acid supply inhibition without affecting adipose conversion.
5.3. Increased Fat Oxidation
Ishihara et al. [35] conducted a study on acute and chronic effects of HCA on energy metabolism. Acute administration of 10 mg/100 μL of a 0.48 mol/L HCA solution per mice significantly increased (P < 0.05) serum free fatty acid levels and concentration of glycogen in the gastrocnemius muscle, even though the respiratory exchange ratio was not different from that in the control group. On the other hand, chronic administration of 10 mg HCA twice a day significantly lowered (P < 0.01) the RQ during resting and exercising conditions in mice. Lipid oxidation, calculated from RQ, and oxygen consumption were significantly enhanced, and carbohydrate oxidation was significantly less in these mice during the early stages of running (P < 0.01). Taken all together, the authors therefore suggested that chronic administration of HCA augmented the endurance exercise performance in mice via the attenuation of glycogen consumption caused by the promotion of lipid oxidation during running exercise. Furthermore, Ishihara et al. [35] suggested that chronic HCA administration might have increased EE during the 3-week experimental period.
In addition, Lim et al. [109, 110] also showed that short-term administration of HCA increased fat oxidation during exercise in athletes and in untrained women. Lim et al. [110] conducted a randomized, placebo-controlled study where subjects (athletes) consumed HCA (250 mg) or placebo for 5 days, after each time performing cycle ergometer exercise at 60% VO2 max for 60 min followed by 80% VO2 max until exhaustion. The results obtained showed that the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) was significantly lower in the HCA trial than in the control trial (P < 0.05). Fat oxidation was significantly increased by short-term administration of HCA, and carbohydrate oxidation was significantly decreased (P < 0.05) during exercise in athletes. In a continuation of their study, Lim et al. [109] conducted a similar study to evaluate the effects of HCA administration on fat oxidation during exercise in untrained women. The results showed that HCA decreased the RER and carbohydrate oxidation during 1 hour of exercise. In addition, exercise time to exhaustion was significantly enhanced (P < 0.05).
A more recent approach for determining fat metabolism by HCA was conducted by measuring urinary concentration of malondialdehyde (MDA), acetaldehyde (ACT), formaldehyde (FA), and acetone (ACON) of the tested subjects. The urinary excretion of these four metabolites was proposed to be a consequence of enhanced β-oxidation of fats in body tissues [16]. The effect of HCA-SX had been studied extensively by Preuss et al. on obese human subjects [16, 64] as well as on male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. In the randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled clinical studies on obese human, a group of subjects were given 4,667 mg of HCA-SX daily (provided 2,800 mg HCA/day) while the other given a combination of HCA-SX 4,667 mg, 4 mg of niacin-bound chromium (NBC), and 400 mg of gymnema sylvestre extract (GSE) daily. The control group received placebo in 3 equal doses daily at 30 to 60 min before meals. In the trial involving 30 subjects, urinary excretion of fat metabolites was increased by approximately 125–258% whereas in trial involving 60 and 90 obese subjects, the metabolite excretion increased by about 35.6–106.4% [16] and 32–109% [64], respectively. As excretion of fat metabolites was enhanced in groups receiving the combination formula, it was also suggested that HCS-SX, either alone or in combination with NBC and GSE, could effectively promote breakdown of fats [16, 64].
5.4. Downregulation of a Spectrum of Obesity-Associated Genes
Lipogenic transcription factors, including SREBP1c, liver X receptors, PPARγ, and C/EBPα, are highly expressed in the adipose tissue and actively participate in the lipid metabolism of adipocytes by coordinating lipogenic and adipocyte-specific gene expression [114]. PPARγ interacts with several other transcription factors. C/EBPα and PPARγ interact via a positive feedback loop in the differentiated adipocytes, to induce each other's expression [115]. Besides, coexpression of PPARγ with SREBP1c increases the transcriptional activity of PPARγ [116]. aP2 (a marker of terminal adipocyte differentiation), together with several adipocyte-specific genes, including adiponectin, insulin receptor, leptin, glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4), and glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase, are induced during the adipogenic differentiation process [114]. Leptin, a 167-amino acid hormone and a biomarker of the obesity regulatory gene, is produced by fat tissue and is known to regulate energy intake and metabolism. Leptin binds to the medial nucleus of the hypothalamus and induces a sensation of satiety and thus controlling the appetite [98, 117, 118].
Fatty acid synthase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1, and SREBP1c mRNA concentrations were decreased in the adipose tissue of the obese animal models [119]. On the contrary, the mRNA and protein expression of TNFα (which is involved in proinflammation, apoptosis, lipid metabolism, and insulin resistance) were increased in the adipose tissues of the obese rodents and humans [120]. A high level of TNFα suppressed transcription factors such as PPARγ and C/EBPα which, in turn, activated the GLUT4 gene [121, 122].
Hayamizu et al. [123] evaluated the effects of G. cambogia fruit rind extract containing 60% (–)-HCA on serum leptin and insulin in mice. G. cambogia extract reduced serum total cholesterol, triacylglycerol, and nonesterified fatty acids in mice. Nevertheless, the body weight gain and fat pad weight were not affected in the treatment. No significant difference in blood glucose level was detected between groups, but a significant reduction of serum insulin (P < 0.05) was detected, suggesting that the G. cambogia extract efficiently improved glucose metabolism in the treated animals. In addition, the treatment decreased serum leptin levels and the leptin/WAT ratio. Besides, the changed ratio of body weight correlated positively with leptin levels in their study. Furthermore, it had been reported that leptin suppressed the signal transduction of insulin via cytokine interactions [124, 125]. Hayamizu et al. [123] suggested that the observed effect of G. cambogia extract on serum insulin in their study occurred through leptin-like activity.
The antiobesity effects of Garcinia on visceral fat mass, lipid profiles in the serum and liver, serum adipocytokine levels, and regulation of the expression of multiple adipose tissue genes were reviewed. Kim et al. [37] reported the antiobesity effects of a mixture composed of aqueous extract of G. cambogia, soy peptide, and L-carnitine (1.2 : 0.3 : 0.02, w/w/w) on rats rendered obese by high-fat diet (HFD). An HFD (40% fat calories) with identical composition of the high-fat control diet (CD) applied in the study was fed to five-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats for 9 weeks to create an obese conditions in rats that mimic to human obesity. Body weight gain, visceral fat-pad weight, and serum and hepatic biochemistry of rats were measured. The 0.38% mixture-supplemented HFD (D + M) reduced the total body weight and the accumulation of visceral fat mass and lowered the blood and hepatic lipid levels, which led to the improvement of insulin resistance in the HFD-induced obese rats. Moreover, the mixture of G. cambogia, soy peptide, and L-carnitine improved dyslipidemia in rat models with HFD-induced obesity. Downregulation of the expression of leptin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c genes in the epididymal fat tissue of rats fed with CD + M diet was obtained. In contrary, upregulation of the uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) gene in epididymal adipose tissues was induced with CD + M diet. No effect on the food intake of the animals was observed in the study, suggesting that the mixture exerted antiobesity effect via modulation of the metabolic derangement induced by HFD during which interactions between the multiple genes implicated in the process of adipogenesis might be involved, rather than simply suppressing appetite. A similar observation was obtained by Kim et al. [38], where in addition to the reduction of food intake, the food efficiency ratio (FER) was also significantly lower in the G. cambogia diet administrated group than in the HFD mice, implying less efficient transformation of the feed mass into body mass.
6. Human Clinical Trials
The antiobesity effects of G. cambogia in terms of promoting weight loss and lowering cholesterol level were extensively studied. However, evidence for the effectiveness of G. cambogia or its derivative products was largely derived from animal studies [126]. Despite the intriguing evidence of antiobesity effects of G. cambogia from in vitro and animal studies, more equivocal results were obtained from randomized double-blind placebo-controlled experiments dealing with human subjects [127–130]. Hayamizu et al. [59] conducted a crossover design randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to determine the “no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL)” of G. cambogia extract in 44 healthy volunteers (22 males and 22 females) and concluded that G. cambogia is generally safe to be consumed. Several equivocal findings of RCTs were reported on the effectiveness of supplements containing HCA (Table 3). Some studies reported that HCA exerted no significant effects as compared to the placebo group [40, 42, 70] (Table 4). All the above findings were in agreement with the most recent meta-analysis of RCTs which revealed that G. cambogia extract possessed limited or no effects on weight-loss in human subjects [131]. Moreover, this study showed no effect on satiety or calorie intake in overweight individuals consuming their habitual diet, which is in agreement with past studies [41, 60, 75]. However, such comparisons must be made with caution as the variations in the formulations, doses administered, RCTs designs, and study populations might contribute to the discrepancy of the results.
Table 3.
Summary of clinical studies of Garcinia/HCA that have shown significant antiobesity effect.
| Duration | Subject | Treatment | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 days | 44 healthy volunteers | 4 g for the 1st day followed by 3 g until day 10. | Not recorded | [59] |
|
| ||||
| 11 days | Normal, groups: placebo, HCA of total 10 sedentary male under high-fat diet | 1500 mg HCA daily | No significant effects on body weight gain, appetite-related, and plasma parameters but decreased fat deposition **Comments: suggest that (−)-HCA may reduce net fat deposition from de novo lipogenesis during weight gain |
[60] |
|
| ||||
| 2 weeks | BMI 27.5, groups: placebo, HCA of 24 subjects each (12 males, 12 females) | 300 mg HCA | Reduced of energy intake and slight decreased of body weight | [61] |
|
| ||||
| 4 weeks | Obese, hypocaloric diet, groups: placebo, 1 capsule, 2 capsule, (50 subjects each group) | 55 mg G. cambogia + 19 mg chromium + 240 mg chitosan/day | Weight loss associated with lower TC/LDL and higher HDL | [62] |
|
| ||||
| 8 weeks | BMI 25–35, groups: placebo, treatment of 20 each | 1000 mg HCA/day | Reduced of visceral and subcutaneous fat area | [63] |
|
| ||||
| 8 weeks | Moderate obese, groups: placebo, HCA-SX, HCA-SX + NBC + GSE of total 60 | HCA-SX 4667 mg (60% HCA), 4667 mg HCA-SX + 400 μg niacin-bound chromium + 400 mg Gymnema sylvestre extract | Significant (P < 0.05) decrease in BMI, food intake, total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins, triglycerides, and serum leptin levels, increase in high-density lipoprotein levels, and enhanced excretion of urinary fat metabolites (biomarker of fat oxidation, including malondialdehyde, acetaldehyde, formaldehyde, and acetone) in HCA and HCA-NBC-GSE groups | [16] |
|
| ||||
| 8 weeks | BMI 30–50, groups: placebo, 2800 mg HCA; 2800 mg HCA + 400 μg chromium of 30 subjects each | 2800 mg HCA; 2800 mg of HCA-SX + 400 μg chromium + 100 mg gymnemic acid/day | Decreased of body weight, BMI, LDL, and TG and increased fat oxidation | [64] |
|
| ||||
| 8 weeks | Normal, group: 35 healthy subjects on diets 1000, 1200, or 1500 kcal | 1500 mg G. cambogia extract daily | Significant reduction of total cholesterol, triacylglycerol, and body weight associated with reduced appetite | [65] |
|
| ||||
| 8 weeks | Obese, groups: placebo and treatment of total 50 F | 3.45 g G. atroviridis | Significant reduction of body weight, BMI, body fat, lean body mass, and anthropometric parameters (biceps, subscapular, suprailiac crest skinfold thicknesses, and upper arm circumference) but no change of serum lipid profile | [66] |
|
| ||||
| 60 days | Over weight to obese, groups: placebo and treatment of total 58 | 285 mg (−)-HCA in Slim339 G. cambogia extract daily | Significant reduced of body weight (4.7%) | [67] |
|
| ||||
| 12 weeks | BMI 27.5–39, groups: placebo and treatment (18 females/2 males each) of total 40 | 300 mg G. cambogia + 1200 mg Phaseolus vulgaris + 1200 mg inulin/day | Significant body weight lost (3.5 kg versus 1.2 kg) | [68] |
|
| ||||
| 12 weeks | BMI ~28, groups: placebo: 47; treatment: 42 | 2400 mg G. cambogia/day | Significant body weight lost | [69] |
Table 4.
Summary of clinical studies of Garcinia/HCA that have shown none significant antiobesity effect.
| Duration | Subject | Treatment | Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 day | Normal, groups: placebo, HCA of total 10 cyclists | 4300 g HCA | No significant changes in total fat and carbohydrate oxidation rates | [70] |
|
| ||||
| 2 weeks | Normal-moderately obese, group: placebo, HCA, and HCA + MCT of total 7 males and 14 females | 500 mg HCA; 500 mg HCA + 3 g medium chain triacylglycerols (MCT) | No significant differences in satiety, daily energy intake and body weight loss within all groups **Comment: subjects were under negative energy balance conditions (eliminating the possibility of de novo lipogenesis and reservation of glycogen reserves had occurred; thus, the only possible remaining mechanism increased hepatic fatty acid oxidation) |
[71] |
|
| ||||
| 2 weeks | Normal-moderately obese, groups: placebo, HCA, and HCA + MCT of total 11 male | 500 mg HCA; 500 mg HCA + 3 g medium chain triacylglycerols (MCT) | No significant differences in body weight reduction, EE, appetite ratings, and substrates oxidation (protein, fat, and carbohydrate oxidation) within all groups **Comment: 2-week intervention is too short |
[41] |
|
| ||||
| 2 weeks | Normal-moderately obese, groups: placebo, HCA of total 10 sedentary males, with or without moderately intense exercise | 3 g (−)-HCA daily | No significant difference in RQ, EE, and blood parameters during rest nor during exercise | [42] |
|
| ||||
| 8 weeks | 39 subjects | 1500 mg G. cambogia + 300 μg chromium picolinate/day | No significant difference in control and placebo | [72] |
|
| ||||
| 10 weeks | Overweight, groups: treatment: 29; placebo: 29 | 2 g G. cambogia extract daily | No clinically significant differences in body composition, plasma lipid profiles, antioxidant enzyme activity, and plasma adipocytokines | [73] |
|
| ||||
| 12 week | Obese, treatment: 5 M, 61 F; placebo: 14 M, 55 F |
G. cambogia extract: 3000 mg of (50% of HCA); Diet: 5020 kJ/day (1200 kcal/day) |
No significant difference in body weight and fat mass loss | [40] |
|
| ||||
| 12 weeks | Obese, groups: treatment: 36 F, 11 M; placebo: 41 F, 10 M | Botanical extract (1000 mg HCA daily) | No difference between placebo and treatment group but significant change of the body composition improvement index, body free fat mass, weight, BMI, and some other anthropometric measurements in both treatment and placebo groups | [74] |
|
| ||||
| 12 weeks | Obese, groups: treatment: 25 F, 7 M; placebo: 21 F, 5 M. | 2.4 g G. cambogia (52.4% HCA) + 1.5 g A. konjac (94.9% glucomannan) | No significantvariation in body weight/other anthropometric and calorimetric parameters but significant hypercholesterolemic | [75] |
|
| ||||
| 12 weeks | BMI 28, groups: placebo: 23; treatment: 21 | 1,667.3 mg of G. cambogia extract/day (1,000 mg HCA/day) | No significant effect | [76] |
Preclinical studies using rodent models have confirmed the body weight reduction, appetite suppression, and subsequently food intake reduction effects of HCA in rats. Clinically, however, HCA failed to perform well. Several factors that might contribute to this scenario are the ATP citrate lyase which might be important only at very high carbohydrate diets, a type of diet that most studies did not prescribe. Besides, a high-fiber diet can bind to HCA and block it, thus reducing its efficacy. HCA and G. cambogia exerted potential effects in weight management, but clinical studies have yet to prove optimum conditions for HCA to be effective. For instance, Sullivan et al. [85] reported that hepatic lipid synthesis was reduced only if HCA was administered before the beginning of feeding, reaching optimum 30–60 minutes prior to feeding. The reason for this remains unknown.
7. Patents and Commercialization
The claims on enhanced human health associated with Garcinia/HCA had been reviewed in Section 4. In particular, the antiobesity effects of Garcinia/HCA were extensively reported. This has resulted in the availability of numerous commercialized weight-management products derived from Garcinia/HCA (Table 5). Several products of G. cambogia or its derivatives had been patented and commercialized. As of August 2012, a total of 66 patents that apply to G. cambogia or HCA derived from Garcinia were filed with the US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) since 1976 (search of US Patents and Trademark Office in year 2012 using Google patent search). These patents are on various aspects, including HCA enrichment from Garcinia rind, HCA and food products/dietary supplements prepared therefrom, methods of production, and their use. The majority of the patents are related to G. cambogia/atroviridis and/or HCA derived from Garcinia on obesity and weight loss. The patent numbers are as follows: 8,197,867, 8,097,286, 8,017,147, 8,003,138, 7,943,186, 7,943,183, 7,927,636, 7,858,128, 7,846,970, 7,772,428, 7,741,370, 7,687,082, 7,550,161, 7,507,421, 7,431,951, 7,335,651, 7,311,929, 7,230,131, 7,214,823, 7,208,615, 7,189,416, 7,179,488, 7,063,861, 6,982,098, 6,899,891, 6,875,891, 6,855,358, 6,770,782, 6,706,899, 6,676,977, 6,610,277, 6,565,847, 6,541,026, 6,489,492, 6,485,710, 6,476,071, 6,447,807, 6,428,806, 6,426,077, 6,413,545, 6,399,089, 6,395,296, 6,277,396, 6,221,901, 6,217,898, 6,160,172, 6,147,228, 6,113,949, 6,054,128, 5,972,357, 5,911,992, 5,783,603, 5,656,314, 5,612,039, 5,536,516, 4,007,208, 4,006,166, 4,005,086, 7,119,110, 3,994,927, 3,993,668, 7,153,877, 3,993,667, 4,028,397, 7,153,528, 7,015,250, 6,638,542, 6,579,866, 6,482,858, 6,441,041, 6,383,482, 6,207,714, 5,817,329, 5,626,849, and 3,965,121.
Table 5.
Commercialized dietary supplements that contain G. cambogia extract/HCA.
| Product name | Company | Concentration of HCA | Doses recommended (daily) | Formulation of supplement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Super CitriMax HCA-600-SXS | Inter health N.I. | 60% (−)-HCA in its free form, 1.0% (−)-HCA in its lactone form | 3 capsules, 3 times daily, 30–60 min before meal | 3 capsules per serving: G. cambogia extract 1500 mg (providing 900 mg of HCA), calcium 150 mg, potassium 225 mg, 0.5% sodium, 0.1% magnesium, 0.03% iron, 0.05% total phytosterols, 0.3% total protein, 4.5% moisture, and 8.5% soluble dietary fiber |
|
| ||||
| GarCitrin | Sabinsa Corporation | 50% (−)-HCA | 500 mg, 3 times daily | 500 mg of GarCitrin (providing 250 mg of HCA) and 5% Garcinol |
|
| ||||
| Sci-Fit Pro Cut | 50% (−)-HCA | 4 capsules, 2-3 times daily, 30–60 min before meal | 4 capsules per serving: G. cambogia 1000 mg (providing 500 mg of HCA), green tea extract 500 mg (98% polyphenols) (45% epigallocatechin/EGCG), guarana extract 910 mg (22% caffeine), caffeine 100 mg, L-carnitine 100 mg, white willow bark extract 100 mg (standardized for 15% salicin), dandelion 100 mg, juniper berry extract 100 mg, buchu extract 100 mg, and chromium 200 mg | |
|
| ||||
| G. cambogia and Kola Nut 450 mg | TerraVita | — | 1 capsule, 3 times daily, with meals | 225 mg G. cambogia fruit, 225 mg kola nut |
|
| ||||
| G. cambogia | ProThera, Inc. | 50% (−)-HCA | 1–6 capsules daily, before meals. | 500 mg G. cambogia (providing min. 250 mg of HCA), vegetarian capsule (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, water), cellulose, magnesium stearate, and silicon dioxide |
|
| ||||
| G. cambogia Plus | Atrium Inc | 50% (−)-HCA | 2 capsules, 3 times daily | Chromium 166 μg (as Cr picolinate 500 mg and Cr arginate 160 mg), G. cambogia 340 mg (providing 170 mg of HCA), atractylodes 80 mg, citrus aurantii 80 mg, gelatin, rice powder, and magnesium staerate |
|
| ||||
| G. cambogia Plus | BioCare Ltd. | 50% (−)-HCA | 3 capsules daily, 20 min before food | G. cambogia 500 mg, vitamin B5 (calcium pantothenate) 6 mg, vitamin C (ascorbic acid) 5 mg, manganese gluconate(providing 270 μg elemental manganese) 2.5 mg, and chromium polynicotinate 0.9 mg (providing 100 μg elemental chromium) |
|
| ||||
| Garcinia 1000 | Source Naturals | 50% (−)-HCA | 1 tablet, twice daily, 1 hour before meal | Chromium (as chromiumpolynicotinate [ChromeMate] and chromium picolinate) 150 μg, sodium 25 mg, G. cambogia fruit extract (providing 500 mg of HCA) 1 g |
|
| ||||
| Garcinia 1000 hydroxycitric acid | Nature's life | 50% (−)-HCA | — | G. cambogia rind concentrate (providing 500 mg of HCA) 1 g, cellulose, silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate and “Micro-Cellulose” coating |
|
| ||||
| Citrin | Natural Nirvana | — | 1 capsule, 2 times daily | G. cambogia 495 mg, BioPerine 5 mg |
|
| ||||
| HCA 450 mg tablet | Higher nature | 450 mg HCA per tablet | 1-2 tablets, 3 times daily, 30 min before meal | Tamarind fruit extract, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate (vegetarian source), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose coating, silicon dioxide, and acacia powder |
|
| ||||
| HCA Hydroxy citric acid | Viridian Nutrition Ltd. | 50% (−)-HCA | 1 capsule, 3 times daily, before meal | G. cambogia (providing 250 mg HCA) 500 mg, viridian bilberry extract, alfalfa, spirulina blend 150 mg, and vegetarian cellulose capsule 120 mg |
|
| ||||
| HCA hydroxycitric acid | Life Extension Foundation | 50% (−)-HCA | 1 capsule, 3 times daily, 45 min before meals with 1 capsule of CitriChrome | G. cambogia (fruit) (providing 250 mg of HCA) 500 mg |
|
| ||||
| Hydroxycitrate | Solgar | 50% (−)-HCA | 1 capsule, 30–60 min before meal | G. cambogia fruit powdered extract (providing 250 mg [50%] HCA) 500 mg, hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose, vegetable magnesium stearate, and silicon dioxide |
|
| ||||
| Hydroxycitrate Plus | Metagenics | — | 1 tablet, 3 times daily, 30–60 min before meal | Garcinia fruit extract (G. cambogia) 500 mg, L-carnitine 100 mg, niacin (as niacinamide) 50 mg, pantothenic acid (as D-calcium pantothenate) 25 mg, riboflavin 10 mg, manganese (as manganese arginine) 750 μg, and chromium (as chromium nicotinate glycinate) 75 μg |
8. Conclusions
The nutraceutical industry is flourishing, and interest in establishing scientific credibility has attained importance for many companies and scientists. In the recent years, more clinical trials had been conducted to elucidate the functional effects of Garcinia/HCA supplementation on promoting human health. A multitude of metabolic functions had been reported for HCA or HCA-containing Garcinia extract, such as reducing blood lipids, inducing weight loss, suppressing appetite, and reducing food intake based on results obtained in both animal trials and human clinical trials (Figure 1). These discoveries make the development of evidence-based adjuvant modalities to curb the trend of the increasing prevalence of obesity and obesity-related comorbidity and mortality possible. We have previously reviewed and concluded that Garcinia extract and HCA were generally safe to be consumed. Collective results from 17 clinical studies which involved 873 subjects demonstrated the safety of HCA and HCA-SX for human consumption [43]. These studies provided scientific evidence that intake of HCA and HCA-SX alone did not produce adverse effects and a dietary dosage of up to 2800 mg/day was regarded as the “no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL)” of HCA-SX in human [84]. Based on these animal and human safety data, HCA-SX also received self-affirmed GRAS status in the USA by the Burdock Group in year 2003 [132]. However, definitive conclusions that Garcinia/HCA supplements are efficient tools against various health problems especially obesity remain to be proven in larger-scale and longer-term clinical trials, despite substantial public interest in such supplements. Many diet supplements containing Garcinia/HCA marketed as weight management products are the combination of active ingredients rather than containing a single agent. Thus it is difficult to evaluate the effectiveness of single agents when the combination products are tested. In addition, awareness of the safety and efficacy of the weight management supplements available in the market should be raised among health care providers in order to assist their patients in analyzing the risks and benefits of the dietary supplements. Thus, scientific investigations on the potential health promoting effects of herbal preparations as diet supplement are prerequisites for new discoveries of alternative therapies.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Professor S. G. Tan for the proofreading of this paper.
References
- 1.WHO. Global database on body mass index. http://apps.who.int/bmi/index.jsp, 2012.
- 2.expert consultation WHO. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. The Lancet. 2004;363:157–163. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.International Association for the Study of Obesity (IASO) % Global prevalence of adult obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2): country rankings 2012. http://www.iaso.org/site_media/uploads/Global_prevalence_of_adult_obesity_Ranking_by_country_2012.pdf, 2012.
- 4.WHO. WHO Technical Report Series. 894. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2000. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic, report of a WHO consultation. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bray GA, Greenway FL. Pharmacological treatment of the overweight patient. Pharmacological Reviews. 2007;59(2):151–184. doi: 10.1124/pr.59.2.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.United States Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Endocrinologic and metabolic drugs advisory committee. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/EndocrinologicandMetabolicDrugsAdvisoryCommittee/UCM224180.pdf, 2012.
- 7.United States Food and Drug Administration. Meridia (sibutramine): market withdrawal due to risk of serious cardiovascular events. http://www.fda.gov/safety/medwatch/safetyinformation/safetyalertsforhumanmedicalproducts/ucm228830.htm, 2010.
- 8.Heber D. Herbal preparations for obesity: are they useful? Primary Care. 2003;30(2):441–463. doi: 10.1016/s0095-4543(03)00015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lim TK. Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants. Vol. 2. Heidelberg, Germany: Springer; 2012. (Fruits). [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sergio W. A natural food, the Malabar Tamnarind, may be effective in the treatment of obesity. Medical Hypotheses. 1988;27(1):39–40. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(88)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Drury H. The Useful Plants of India: With Notices of Their Chief Value in Commerce, Medicine, and the Arts. 2nd edition. London, UK: William H. Allen & Co.; 1873. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jena BS, Jayaprakasha GK, Singh RP, Sakariah KK. Chemistry and biochemistry of (−)-hydroxycitric acid from Garcinia. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2002;50(1):10–22. doi: 10.1021/jf010753k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Khare CP. Indian Medicinal Plants: An Illustrated Dictionary. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sreenivasan A, Venkataraman R. Chromatographic detection of the organic constituents of Gorikapuli (Garcinia cambogia Desr.) used in pickling fish. Current Science. 1959;28:151–152. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ohia SE, Opere CA, LeDay AM, Bagchi M, Bagchi D, Stohs SJ. Safety and mechanism of appetite suppression by a novel hydroxycitric acid extract (HCA-SX) Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2002;238(1-2):89–103. doi: 10.1023/a:1019911205672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Preuss HG, Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Rao CVS, Dey DK, Satyanarayana S. Effects of a natural extract of (−)-hydroxycitric acid (HCA-SX) and a combination of HCA-SX plus niacin-bound chromium and Gymnema sylvestre extract on weight loss. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 2004;6(3):171–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-8902.2004.00328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Roy S, Rink C, Khanna S, et al. Body weight and abdominal fat gene expression profile in response to a novel hydroxycitric acid-based dietary supplement. Gene Expression. 2003;11(5-6):251–262. doi: 10.3727/000000003783992289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Deore AB, Sapakal VD, Dashputre NL, Naikwade NS. Antiulcer activity of Garcinia indica linn fruit rinds. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science. 2011;1:151–154. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mahendran P, Vanisree AJ, Shyamala Devi CS. The antiulcer activity of Garcinia cambogia extract against indomethacin induced gastric ulcer in rats. Phytotherapy Research. 2002;16(1):80–83. doi: 10.1002/ptr.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yamaguchi F, Saito M, Ariga T, Yoshimura Y, Nakazawa H. Free radical scavenging activity and antiulcer activity of garcinol from Garcinia indica fruit rind. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2000;48(6):2320–2325. doi: 10.1021/jf990908c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Asghar M, Monjok E, Kouamou G, Ohia SE, Bagchi D, Lokhandwala MF. Super CitriMax (HCA-SX) attenuates increases in oxidative stress, inflammation, insulin resistance, and body weight in developing obese Zucker rats. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2007;304(1-2):93–99. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9489-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mackeen MM, Ali AM, Lajis NH, et al. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, antitumour-promoting and cytotoxic activities of different plant part extracts of Garcinia atroviridis Griff. ex T. Anders. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2000;72(3):395–402. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(00)00245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yamaguchi F, Ariga T, Yoshimura Y, Nakazawa H. Antioxidative and anti-glycation activity of garcinol from Garcinia indica fruit rind. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2000;48(2):180–185. doi: 10.1021/jf990845y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yonei Y, Takahashi Y, Hibino S, Watanabe M, Yoshioka T. Effects on the human body of a dietary supplement containing L-carnitine and Garcinia cambogia extract: a study using double-blind tests. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition. 2008;42(2):89–103. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.2008014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wielinga PY, Wachters-Hagedoorn RE, Bouter B, et al. Hydroxycitric acid delays intestinal glucose absorption in rats. American Journal of Physiology. 2005;288(6):G1144–G1149. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00428.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Negi PS, Jayaprakasha GK. Control of foodborne pathogenic and spoilage bacteria by garcinol and Garcinia indica extracts, and their antioxidant activity. Journal of Food Science. 2004;69(3):FMS61–FMS65. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Permana D, Lajis NH, Mackeen MM, et al. Isolation and bioactivities of constitutents of the roots of Garcinia atroviridis . Journal of Natural Products. 2001;64(7):976–979. doi: 10.1021/np000563o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Varalakshmi KN, Sangeetha CG, Shabeena AN, Sunitha SR, Vapika J. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of Garcinia indica fruit rind extract. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences. 2010;7:652–656. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mackeen MM, Ali AM, Lajis NH, Kawazu K, Kikuzaki H, Nakatani N. Antifungal garcinia acid esters from the fruits of Garcinia atroviridis . Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C. 2002;57(3-4):291–295. doi: 10.1515/znc-2002-3-416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Reis SBD, De Oliveira CC, Acedo SC, et al. Attenuation of colitis injury in rats using Garcinia cambogia extract. Phytotherapy Research. 2009;23(3):324–329. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Syahida A, Israf DA, Permana D, et al. Atrovirinone inhibits pro-inflammatory mediator release from murine macrophages and human whole blood. Immunology and Cell Biology. 2006;84(3):250–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1711.2006.01426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mazzio EA, Soliman KFA. In vitro screening for the tumoricidal properties of international medicinal herbs. Phytotherapy Research. 2009;23(3):385–398. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Parasramka MA, Gupta SV. Garcinol inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Nutrition and Cancer. 2011;63(3):456–465. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2011.535962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Prasad S, Ravindran J, Sung B, Pandey MK, Aggarwal BB. Garcinol potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis through modulation of death receptors and antiapoptotic proteins. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 2010;9(4):856–868. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 35.Ishihara K, Oyaizu S, Onuki K, Lim K, Fushiki T. Chronic (−)-hydroxycitrate administration spares carbohydrate utilization and promotes lipid oxidation during exercise in mice. Journal of Nutrition. 2000;130(12):2990–2995. doi: 10.1093/jn/130.12.2990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kaur G, Kulkarni SK. Investigations on possible serotonergic involvement in effects of OB-200G (polyherbal preparation) on food intake in female mice. European Journal of Nutrition. 2001;40(3):127–133. doi: 10.1007/s003940170013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kim YJ, Kim K, Kim MS, Lee JH, Lee KP, Park T. A mixture of the aqueous extract of Garcinia cambogia, soy peptide and L-carnitine reduces the accumulation of visceral fat mass in rats rendered obese by a high fat diet. Genes and Nutrition. 2008;2(4):353–358. doi: 10.1007/s12263-007-0070-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kim K, Lee HN, Kim YJ, Park T. Garcinia cambogia extract ameliorates visceral adiposity in C57BL/6J mice fed on a high-fat diet. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry. 2008;72(7):1772–1780. doi: 10.1271/bbb.80072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Leonhardt M, Langhans W. Hydroxycitrate has long-term effects on feeding behavior, body weight regain and metabolism after body weight loss in male rats. Journal of Nutrition. 2002;132(7):1977–1982. doi: 10.1093/jn/132.7.1977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Heymsfield SB, Allison DB, Vasselli JR, Pietrobelli A, Greenfield D, Nunez C. Garcinia cambogia (hydroxycitric acid) as a potential antiobesity agent: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1998;280(18):1596–1600. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.18.1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kovacs EMR, Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Saris WHM. The effects of 2-week ingestion of (−)-hydroxycitrate and (−)-hydroxycitrate combined with medium-chain triglycerides on satiety, fat oxidation, energy expenditure and body weight. International Journal of Obesity. 2001;25(7):1087–1094. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kriketos AD, Thompson HR, Greene H, Hill JO. (−)-Hydroxycitric acid does not affect energy expenditure and substrate oxidation in adult males in a post-absorptive state. International Journal of Obesity. 1999;23(8):867–873. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0800965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chuah LO, Yeap SK, Ho WY, Beh BK, Banu Alitheen N. In vitro and in vivo toxicity of Garcinia or hydroxycitric acid: a review. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2012;2012:12 pages. doi: 10.1155/2012/197920.e197920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sharma PC, Yelne MB, Dennis TJ. Database on Medicinal Plants Used in Ayurveda. Vol. 2. New Delhi, India: Central Council for Research in Ayurveda & Siddha; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lewis YS, Neelakantan S. (−)-Hydroxycitric acid-the principal acid in the fruits of Garcinia cambogia desr. Phytochemistry. 1965;4(4):619–625. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jayaprakasha GK, Sakariah KK. Determination of organic acids in Garcinia cambogia (Desr.) by high- performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A. 1998;806(2):337–339. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jayaprakasha GK, Sakariah KK. Determination of organic acids in leaves and rinds of Garcinia indica (Desr.) by LC. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2002;28(2):379–384. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(01)00623-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Muensritharam L, Tolieng V, Chaichantipyuth C, Petsom A, Nhujak T. Capillary zone electrophoresis for separation and analysis of hydroxycitric acid and hydroxycitric acid lactone: application to herbal products of Garcinia atroviridis Griff. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2008;46(3):577–582. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2007.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Permana D, Abas F, Maulidiani M, et al. Atrovirisidone B, a new prenylated depsidone with cytotoxic property from the roots of Garcinia atroviridis . Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C. 2005;60(7-8):523–526. doi: 10.1515/znc-2005-7-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Permana D, Lajis NH, Shaari K, et al. A new prenylated hydroquinone from the roots of Garcinia atroviridis Griff ex T. Anders (Guttiferae) Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung B. 2003;58(4):332–335. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Iinuma M, Ito T, Miyake R, Tosa H, Tanaka T, Chelladurai V. A xanthone from Garcinia cambogia . Phytochemistry. 1998;47(6):1169–1170. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cotterill PJ, Scheinmann F, Puranik GS. Phenolic compounds from the heartwood of Garcinia indica . Phytochemistry. 1977;16(1):148–149. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kosin J, Ruangrungsi N, Ito C, Furukawa H. A xanthone from Garcinia atroviridis . Phytochemistry. 1998;47(6):1167–1168. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Masullo M, Bassarello C, Suzuki H, Pizza C, Piacente S. Polyisoprenylated benzophenones and an unusual polyisoprenylated tetracyclic xanthone from the fruits of Garcinia cambogia . Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2008;56(13):5205–5210. doi: 10.1021/jf800416j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kumar S, Sharma S, Chattopadhyay SK. High-performance liquid chromatography and LC-ESI-MS method for identification and quantification of two isomeric polyisoprenylated benzophenones isoxanthochymol and camboginol in different extracts of Garcinia species. Biomedical Chromatography. 2009;23(8):888–907. doi: 10.1002/bmc.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Chattopadhyay SK, Kumar S. A rapid liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for quantification of a biologically active molecule camboginol in the extract of Garcinia cambogia . Biomedical Chromatography. 2007;21(1):55–66. doi: 10.1002/bmc.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rama Rao AV, Venkatswamy G, Pendse AD. Camboginol and cambogin. Tetrahedron Letters. 1980;21(20):1975–1978. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Krishnamurthy N, Lewis YS, Ravindranath B. On the structures of garcinol, isogarcinol and camboginol. Tetrahedron Letters. 1981;22(8):793–796. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hayamizu K, Ishii Y, Kaneko I, Shen M, Okuhara Y, Sakaguchi H, et al. No-Observed-Adverse-Effect Level (NOAEL) and sequential-high- dose administration study on Garcinia cambogia extract in humans. Journal of Oleo Science. 2002;51:365–369. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kovacs EMR, Westerterp-Plantenga MS. Effects of (−)-hydroxycitrate on net fat synthesis as de novo lipogenesis. Physiology and Behavior. 2006;88(4-5):371–381. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Kovacs EMR. The effect of (−)-hydroxycitrate on energy intake and satiety in overweight humans. International Journal of Obesity. 2002;26(6):870–872. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Girola M, Bernardi MDe, Contos S. Dose effect in lipid lowering activity of a new dietary integrator (Chitosan, Garcinia cambogia extract, and Chrome) Acta Toxicologica Et Therapeutica. 1996;17:25–40. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hayamizu K, Ishii Y, Kaneko I, et al. Effects of Garcinia cambogia (Hydroxycitric Acid) on visceral fat accumulation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Current Therapeutic Research. 2003;64(8):551–567. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2003.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Preuss HG, Garis RI, Bramble JD, et al. Efficacy of a novel calcium/potassium salt of (−)-hydroxycitric acid in weight control. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Research. 2005;25(3):133–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Roman Ramos R, Flores Saenz J, Alarcon Aguilar en MCF. Control of obesity with Garcinia cambogia extract. Investigacion Medica Internacional. 1996;22(3):97–100. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Roongpisuthipong C, Kantawan R, Roongpisuthipong W. Reduction of adipose tissue and body weight: Effect of water soluble calcium hydroxycitrate in Garcinia atroviridis on the short term treatment of obese women in Thailand. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2007;16(1):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Toromanyan E, Aslanyan G, Amroyan E, Gabrielyan E, Panossian A. Efficacy of Slim339 in reducing body weight of overweight and obese human subjects. Phytotherapy Research. 2007;21(12):1177–1181. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Thom E. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a new weight-reducing agent of natural origin. Journal of International Medical Research. 2000;28(5):229–233. doi: 10.1177/147323000002800505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mattes RD, Bormann L. Effects of (−)-hydroxycitric acid on appetitive variables. Physiology and Behavior. 2000;71(1-2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(00)00321-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Van Loon LJC, Van Rooijen JJM, Niesen B, Verhagen H, Saris WHM, Wagenmakers AJM. Effects of acute (−)-hydroxycitrate supplementation on substrate metabolism at rest and during exercise in humans. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2000;72(6):1445–1450. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/72.6.1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kovacs EMR, Westerterp-Plantenga MS, De Vries M, Brouns F, Saris WHM. Effects of 2-week ingestion of (−)-hydroxycitrate and (−)-hydroxycitrate combined with medium-chain triglycerides on satiety and food intake. Physiology and Behavior. 2001;74(4-5):543–549. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(01)00594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Conte AA. A non-prescription alternative in weight reduction therapy. American Journal of Bariatric Medicine. summer1993:17–19. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kim J, Jeon S, Park K, et al. Does Glycine max leaves or Garcinia cambogia promote weight-loss or lower plasma cholesterol in overweight individuals: a randomized control trial. Nutrition Journal. 2011;10(1, article 94) doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-10-94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Opala T, Rzymski P, Pischel I, Wilczak M, Woźniak J. Efficacy of 12 weeks supplementation of a botanical extract-based weight loss formula on body weight, body composition and blood chemistry in healthy, overweight subjects—a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. European Journal of Medical Research. 2006;11(8):343–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Vasques CAR, Rossetto S, Halmenschlager G, et al. Evaluation of the pharmacotherapeutic efficacy of Garcinia cambogia plus amorphophallus konjac for the treatment of obesity. Phytotherapy Research. 2008;22(9):1135–1140. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Hayamizu K, Tomi H, Kaneko I, Shen M, Soni MG, Yoshino G. Effects of Garcinia cambogia extract on serum sex hormones in overweight subjects. Fitoterapia. 2008;79(4):255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2007.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.The Wealth of India: Raw Materials IV. New Delhi, India: CSIR; 1956. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Sullivan AC, Triscari J, Spiegel HE. Metabolic regulation as a control for lipid disorders. I. Influence of, (−)-hydroxycitrate on experimentally induced obesity in the rodent. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 1977;30:767–776. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sullivan AC, Triscari J, Spiegel HE. Metabolic regulation as a control for lipid disorders. II. Influence of (−)-hydroxycitrate on genetically and experimentally induced hypertriglyceridemia in the rat. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 1977;30(5):777–784. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.5.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stallings WC, Blount JF, Srere PA, Glusker JP. Structural studies of hydroxycitrates and their relevance to certain enzymatic mechanisms. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 1979;193(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kjeldstadli J, Thom E. Synthetically prepared composition for treatment and/or prophylaxis of overweight, and use thereof. US patent, EP, 1007027 A2, 2000.
- 82.Haleema S, Sasi PV, Ibnusaud I, Polavarapu PL, Kagan HB. Enantiomerically pure compounds related to chiral hydroxy acids derived from renewable resources. RSC Advances. 2012;2:9257–9285. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Louter-Van De Haar J, Wielinga PY, Scheurink AJW, Nieuwenhuizen AG. Comparison of the effects of three different (−)-hydroxycitric acid preparations on food intake in rats. Nutrition and Metabolism. 2005;2, article 23 doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-2-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Downs BW, Bagchi M, Subbaraju GV, Shara MA, Preuss HG, Bagchi D. Bioefficacy of a novel calcium-potassium salt of (−)-hydroxycitric acid. Mutation Research. 2005;579(1-2):149–162. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Sullivan AC, Hamilton JG, Miller ON, Wheatley VR. Inhibition of lipogenesis in rat liver by (−)-hydroxycitrate. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 1972;150(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Bagchi D, Trimurtulu G, Raju AVK, Sengupta K, Murthy PBS, Rao TVN. Comparative bioavailability of (−)-hydroxycitric acid from oral administration of HCA calcium salt and calcium-potassium double salt in Albino Wistar rats. Journal of the Federation of American Societies For Experimental Biology. 2010;24:p. 505. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Asghar M, Zeyssig R, Monjok E, et al. Hydroxycitric acid (HCA-SX) decreases oxidative stress and insulin resistance and increases brain serotonin levels in obese Zucker rats. Experimental Biology Meeting. 2006;20A655.4 [Google Scholar]
- 88.Roy S, Shah H, Rink C, et al. Transcriptome of primary adipocytes from obese women in response to a novel hydroxycitric acid-based dietary supplement. DNA and Cell Biology. 2007;26(9):627–639. doi: 10.1089/dna.2007.0617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Uauy R, Díaz E. Consequences of food energy excess and positive energy balance. Public Health Nutrition. 2005;8(7 A):1077–1099. doi: 10.1079/phn2005797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Shara M, Ohia SE, Yasmin T, et al. Dose- and time-dependent effects of a novel (−)-hydroxycitric acid extract on body weight, hepatic and testicular lipid peroxidation, DNA fragmentation and histopathological data over a period of 90 days. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2003;254(1-2):339–346. doi: 10.1023/a:1027358106407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Shara M, Ohia SE, Schmidt RE, et al. Physico-chemical properties of a novel (−)-hydroxycitric acid extract and its effect on body weight, selected organ weights, hepatic lipid peroxidation and DNA fragmentation, hematology and clinical chemistry, and histopathological changes over a period of 90 days. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 2004;260(1):171–186. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000026069.53960.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Amin KA, Kamel HH, Abd Eltawab MA. Protective effect of Garcinia against renal oxidative stress and biomarkers induced by high fat and sucrose diet. Lipids in Health and Disease. 2011;10, article 6 doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Watson JA, Fang M, Lowenstein JM. Tricarballylate and hydroxycitrate: substrate and inhibitor of ATP: citrate oxaloacetate lyase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 1969;135(C):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90532-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Berkhout TA, Havekes LM, Pearce NJ, Groot PHE. The effect of (−)-hydroxycitrate on the activity of the low-density-lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase levels in the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. Biochemical Journal. 1990;272(1):181–186. doi: 10.1042/bj2720181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Chee H, Romsos DR, Leveille GA. Influence of (−) hydroxycitrate on lipogenesis in chickens and rats. Journal of Nutrition. 1977;107(1):112–119. doi: 10.1093/jn/107.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Sullivan AC, Triscari J, Hamilton JG, Miller ON. Effect of (−)-hydroxycitrate upon the accumulation of lipid in the rat: II. Appetite. Lipids. 1974;9(2):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF02532137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Sullivan AC, Triscari J, Hamilton JG. Effect of (−)-hydroxycitrate upon the accumulation of lipid in the rat: I. Lipogenesis. Lipids. 1974;9(2):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02532136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lopaschuk GD, Ussher JR, Jaswal JS. Targeting intermediary metabolism in the hypothalamus as a mechanism to regulate appetite. Pharmacological Reviews. 2010;62(2):237–264. doi: 10.1124/pr.109.002428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Rederman NB, Saha AK, Vavvas D, Witters LA. Malonyl-CoA, fuel sensing, and insulin resistance. American Journal of Physiology. 1999;276:E1–E18. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1999.276.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Ohia SE, Awe SO, LeDay AM, Opere CA, Bagchi D. Effect of hydroxycitric acid on serotonin release from isolated rat brain cortex. Research Communications in Molecular Pathology and Pharmacology. 2001;109(3-4):210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.McGuirk J, Muscat R, Willner P. Effects of chronically administerd fluoxetine and fenfluramine on food intake, body weight and the behavioural satiety sequence. Psychopharmacology. 1992;106(3):401–407. doi: 10.1007/BF02245426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Leonhardt M, Hrupka B, Langhans W. Effect of hydroxycitrate on food intake and body weight regain after a period of restrictive feeding in male rats. Physiology and Behavior. 2001;74(1-2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(01)00547-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Greenwood MR, Cleary MP, Gruen R, et al. Effect of (−)-hydroxycitrate on development of obesity in the Zucker obese rat. The American journal of physiology. 1981;240(1):E72–E78. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.1.E72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Sullivan AC, Triscari J. Metabolic regulation as a control for lipid disorders. I. Influence of (−)-hydroxycitrate on experimentally induced obesity in the rodent. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 1977;30(5):767–776. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/30.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Triscari J, Sullivan AC. Comparative effects of (−)-hydroxycitrate and (+)-allo hydroxycitrate on acetyl CoA carboxylase and fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis in vivo. Lipids. 1977;12(4):357–363. doi: 10.1007/BF02533638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Leonhardt M, Balkan B, Langhans W. Effect of hydroxycitrate on respiratory quotient, energy expenditure, and glucose tolerance in male rats after a period of restrictive feeding. Nutrition. 2004;20(10):911–915. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2004.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Cheema Dhadli S, Halperin ML, Leznoff CC. Inhibition of enzymes which interact with citrate by (−)-hydroxycitrate and 1,2,3 tricarboxybenzene. European Journal of Biochemistry. 1973;38(1):98–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Lowenstein JM. Effect of (−)-hydroxycitrate on fatty acid synthesis by rat liver in vivo. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1971;246(3):629–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Lim K, Ryu S, Nho H, et al. (−)-Hydroxycitric acid ingestion increases fat utilization during exercise in untrained women. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology. 2003;49(3):163–167. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.49.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lim K, Ryu S, Ohishi Y, et al. Short-term (−)-hydroxycitrate ingestion increases fat oxidation during exercise in athletes. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology. 2002;48(2):128–133. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.48.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Vasselli JR, Shane E, Boozer CN, Heymsfield SB. Garcinia cambogia extract inhibits body weight gain via increased Energy Expenditure (EE) in rats. The FASEB Journal. 1998;12(4):p. A505. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Leray V, Dumon H, Martin L, et al. No effect of conjugated linoleic acid or Garcinia cambogia on fat-free mass, and energy expenditure in normal cats. Journal of Nutrition. 2006;136(7) doi: 10.1093/jn/136.7.1982s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Blunden G. Garcinia extract inhibits lipid droplet accumulation without affecting adipose conversion in 3T3-L1 cells. Phytotherapy Research. 2001;15(2):172–173. doi: 10.1002/ptr.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Rosen ED, Walkey CJ, Puigserver P, Spiegelman BM. Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes and Development. 2000;14(11):1293–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Rosen ED, Hsu C, Wang X, et al. C/EBPα induces adipogenesis through PPARγ: a unified pathway. Genes and Development. 2002;16(1):22–26. doi: 10.1101/gad.948702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Kim JB, Wright HM, Wright M, Spiegelman BM. ADD1/SREBP1 activates PPARγ through the production of endogenous ligand. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(8):4333–4337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Dagogo-Jack S. Human leptin regulation and promise in pharmacotherapy. Current Drug Targets. 2001;2(2):181–195. doi: 10.2174/1389450013348623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Staiger H, Tschritter O, Machann J, et al. Relationship of serum adiponectin and leptin concentrations with body fat distribution in humans. Obesity Research. 2003;11(3):368–372. doi: 10.1038/oby.2003.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Nadler ST, Stoehr JP, Schueler KL, Tanimoto G, Yandell BS, Attie AD. The expression of adipogenic genes is decreased in obesity and diabetes mellitus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2000;97(21):11371–11376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.21.11371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993;259(5091):87–91. doi: 10.1126/science.7678183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Stephens JM, Pekala PH. Transcriptional repression of the C/EBP-α and GLUT4 genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by tumor necrosis factor-α. Regulation is coordinate and independent of protein synthesis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1992;267(19):13580–13584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Xing H, Northrop JP, Russell Grove J, Kilpatrick KE, Jui-Lan SU, Ringold GM. TNFα-mediated inhibition and reversal of adipocyte differentiation is accompanied by suppressed expression of PPARγ without effects on Pref-1 expression. Endocrinology. 1997;138(7):2776–2783. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.7.5242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Hayamizu K, Hirakawa H, Oikawa D, et al. Effect of Garcinia cambogia extract on serum leptin and insulin in mice. Fitoterapia. 2003;74(3):267–273. doi: 10.1016/s0367-326x(03)00036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Laubner K, Kieffer TJ, Lam NT, Niu X, Jakob F, Seufert J. Inhibition of preproinsulin gene expression by leptin induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes. 2005;54(12):3410–3417. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Lustig RH. Childhood obesity: behavioral aberration or biochemical drive? Reinterpreting the first law of thermodynamics. Nature Clinical Practice Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2006;2(8):447–458. doi: 10.1038/ncpendmet0220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Pittler MH, Ernst E. Dietary supplements for body-weight reduction: a systematic review. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2004;79(4):529–536. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/79.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Badmaev V, Majeed M, Conte AA, et al. Garcinia cambogia for weight loss [letter] Journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;282(3):233–235. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Badmaev V, Majeed M, Conte AA, et al. Garcinia cambogia for weight loss [letter] Journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;282(3):233–235. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Badmaev V, Majeed M, Conte AA, et al. Garcinia cambogia for weight loss [letter] Journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;282(3):233–235. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Schaller JL. Garcinia cambogia for weight loss [letter] The journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;282(3):234–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Onakpoya I, Hung SK, Perry R, Wider B, Ernst E. The use of Garcinia extract (Hydroxycitric Acid) as a weight loss supplement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Journal of Obesity. 2011;2011:9 pages. doi: 10.1155/2011/509038.509038 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Deshmukh NS, Bagchi M, Yasmin T, Bagchi D. Safety of a novel calcium/potassium salt of hydroxycitric acid (HCA-SX): I. Two-generation reproduction toxicity study. Toxicology Mechanisms and Methods. 2008;18(5):433–442. doi: 10.1080/15376510802084030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


