Abstract
Viruses that infect marine cyanobacteria–cyanophages–often carry genes with orthologs in their cyanobacterial hosts, and the frequency of these genes can vary with habitat. To explore habitat-influenced genomic diversity more deeply, we used the genomes of 28 cultured cyanomyoviruses as references to identify phage genes in three ocean habitats. Only about 6–11% of genes were consistently observed in the wild, revealing high gene-content variability in these populations. Numerous shared phage/host genes differed in relative frequency between environments, including genes related to phosphorous acquisition, photorespiration, photosynthesis and the pentose phosphate pathway, possibly reflecting environmental selection for these genes in cyanomyovirus genomes. The strongest emergent signal was related to phosphorous availability; a higher fraction of genomes from relatively low-phosphorus environments–the Sargasso and Mediterranean Sea–contained host-like phosphorus assimilation genes compared with those from the N. Pacific Gyre. These genes are known to be upregulated when the host is phosphorous starved, a response mediated by pho box motifs in phage genomes that bind a host regulatory protein. Eleven cyanomyoviruses have predicted pho boxes upstream of the phosphate-acquisition genes pstS and phoA; eight of these have a conserved cyanophage-specific gene (PhCOG173) between the pho box and pstS. PhCOG173 is also found upstream of other shared phage/host genes, suggesting a unique regulatory role. Pho boxes are found upstream of high light-inducible (hli) genes in cyanomyoviruses, suggesting that this motif may have a broader role than regulating phosphorous-stress responses in infected hosts or that these hlis are involved in the phosphorous-stress response.
Keywords: cyanophage, cyanobacteria, phosphate, selective pressure
Introduction
Marine viruses affect the life histories and evolution of their hosts and are a central component of the marine food web (Suttle, 2007; Rohwer and Thurber, 2009). Cyanophages, viruses that infect cyanobacteria, are abundant and broadly distributed in the global oceans (Suttle, 2007; Williamson et al., 2008). Cyanophage genomes carry orthologs of host genes involved in a variety of host processes, including phosphate acquisition, carbon metabolism, photosynthesis and response to light stress (Lindell et al., 2004; Mann et al., 2005; Sullivan et al., 2005; Weigele et al., 2007; Sullivan et al., 2010).
The abundance, diversity and phylogenies of shared phage/host genes in numerous sequenced phage genomes suggest cyanophage are involved in remodeling and distributing host genes. For example, phylogenetic grouping suggests that two photosystem genes, psbA and psbD, have been transferred repeatedly from host to phage genomes (Sullivan et al., 2006). Furthermore, cyanophage copies of psbA and a high-light inducible (hli) gene are transcribed and translated during the infection cycle (Lindell et al., 2005; Clokie et al., 2006; Millard et al., 2010).
Host metabolic processes with shared components in host and phage genomes highlight pathways potentially involved in the competition between cell and phage for metabolic resources. Although cyanophage carry genes involved in the light reactions of photosynthesis, thus far, cyanophage genomes lack genes encoding Calvin cycle enzymes, suggesting that phage do not participate in the carbon fixation pathways of their hosts (Sullivan et al., 2010). In fact, there is evidence that phage actively direct carbon flux toward the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), enabling nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis needed for phage replication (Thompson et al., 2011b).
As a corollary, phage genome replication requires phosphorous, which can be extremely scarce in the oligotrophic oceans where Prochlorococcus and its close relative Synechococcus thrive (Wu et al., 2000). Thus it is not surprising that the genomes of all 17 T4-like cyanomyoviruses that infect these cyanobacteria and were available when this study was undertaken (Millard et al., 2009; Sullivan et al., 2010) encode phosphate regulon genes known to be responsive to phosphorus starvation in cyanobacteria (Martiny et al., 2009; Tetu et al., 2009; Sullivan et al., 2010). Some phage genomes encode PstS, a periplasmic high-affinity phosphate-binding protein associated with a phosphate-specific membrane transporter; some encode a homolog of the putative alkaline phosphatase gene phoA. This suggests that there is a selective pressure for phage to retain genes that could facilitate phosphorus acquisition in infected host cells.
Multiple lines of evidence indicate that phosphorus limitation exerts strong selective pressures on Prochlorococcus, providing a context for the patterns in phage. Prochlorococcus primarily utilizes the sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol in lieu of more common phospholipids for membrane construction (Van Mooy et al., 2006). Furthermore, the prevalence of phosphorus-associated genes in cultured strains is associated with phosphate availability in the habitat of origin rather than phylogeny (Martiny et al., 2006, 2009; Coleman and Chisholm, 2010). Similarly, T4-like cyanophage isolated from relatively low-phosphorus environments have more host-like phosphate assimilation genes than those from more phosphorus-replete environments (Sullivan et al., 2010). Finally, in phosphate-starved host cells, transcription of phage versions of both pstS and phoA increases via regulation by the host phoBR two-component system (Zeng and Chisholm, 2012).
The availability of new cyanomyovirus genomes and the observation that the abundance of some shared phage/host genes in phage is correlated with variables such as trophic status, nutrient gradients (for example, phosphate) and salinity (Williamson et al., 2008) in the oceans, led us to further explore genome content and evolution in a closely related set of T4-like cyanomyoviruses. Our analysis does not include the highly divergent non-T4-like cyanomyovirus described recently by Sabehi et al. (2012) as it was not available when we began the work. We compared the frequencies of genes in cyanomyovirus genomes in three marine environments to identify genes that the environments have in common and genes that distinguish them. We also examined features of some of these genes in cultured cyanomyovirus genomes—including 11 reported here for the first time.
Materials and methods
Cyanomyovirus genome collection
Seventeen cyanomyovirus genomes were downloaded from Genbank (Benson et al., 2006); 11 additional genomes sequenced and annotated as described in Henn et al., 2010 are reported here for the first time (Table 1).
Table 1. General features of 28 T4-like cyanomyovirus isolates.
| Strain name | Number of genes | Isolation location | Latitude | Longitude | Host strain used for isolation | Reference | Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-SSM2 | 207 | Sargasso Sea | 34°24′N | 72°03'W | Synechococcus WH8102 | This paper | JF974292 |
| MED4-213 | 216 | HOT ALOHA | 22°45′N | 158°00′W | Prochlorococcus MED4 | This paper | HQ634174 |
| P-RSM1 | 212 | Red Sea | 29°28′N | 34°53′E | Prochlorococcus 9303 | This paper | HQ634175 |
| P-RSM3 | 208 | Red Sea | 29°28′N | 34°53′E | Prochlorococcus NATL2A | This paper | HQ634176 |
| Syn30 | 209 | NE Providence Channel | 25°53′N | 77°34′W | Synechococcus WH7803 | This paper | HQ634189 |
| Syn2 | 201 | Sargasso Sea | 34°06′N | 61°01′W | Synechococcus WH8012 | This paper | HQ634190 |
| Syn10 | 205 | Gulf Stream | 36°58′N | 73°42′W | Synechococcus WH8017 | This paper | HQ634191 |
| P-RSM6 | 221 | Red Sea | 29°28′N | 34°53′E | Prochlorococcus NATL2A | This paper | HQ634193 |
| S-SSM4 | 220 | Sargasso Sea | 34°24′N | 72°03′W | Synechococcus WH8018 | This paper | HQ316583 |
| P-SSM3 | 214 | Sargasso Sea | 31°48′N | 64°16′W | Prochlorococcus NATL2A | This paper | HQ337021 |
| P-SSM5 | 320 | Sargasso Sea | 31°48′N | 64°16′W | Prochlorococcus NATL2A | This paper | HQ632825 |
| P-HM1 | 241 | HOT ALOHA | 22°45'N | 158°00′W | Prochlorococcus MED4 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015280 |
| P-HM2 | 242 | HOT ALOHA | 22°45'N | 158°00′W | Prochlorococcus MED4 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015284 |
| P-RSM4 | 239 | Red Sea | 29°28′N | 34°55′E | Prochlorococcus 9303 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015283 |
| P-SSM2 | 334 | Sargasso Sea | 31°48′N | 64°16′W | Prochlorococcus NATL1A | Sullivan et al. (2005) | NC_006883 |
| P-SSM4 | 221 | Sargasso Sea | 31°48′N | 64°16′W | Prochlorococcus NATL2A | Sullivan et al. (2005) | NC_006884 |
| P-SSM7 | 237 | Sargasso Sea | 31°48′N | 64°16′W | Prochlorococcus NATL1A | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015290 |
| S-PM2 | 244 | English Channel | 50°18′N | 4°12′W | Synechococcus WH7803 | Mann et al. (2005) | AJ630128 |
| S-RSM4 | 237 | Red Sea | 29°28′N | 34°55′E | Synechococcus WH7803 | Millard et al. (2009) | NC_013085 |
| S-SM1 | 234 | Atlantic slope | 38°10′N | 73°09′W | Synechococcus WH6501 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015282 |
| S-SM2 | 267 | Atlantic slope | 38°10′N | 73°09′W | Synechococcus WH8017 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015279 |
| S-SSM5 | 225 | Sargasso Sea | 34°24′N | 72°03′W | Synechococcus WH8102 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015289 |
| S-SSM7 | 319 | Sargasso Sea | 34°24′N | 72°03′W | Synechococcus WH8109 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015287 |
| S-ShM2 | 230 | Atlantic shelf | 39°60′N | 71°48′W | Synechococcus WH8102 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015281 |
| Syn1 | 234 | Woods Hole | 41°31′N | 71°40′W | Synechococcus WH8101 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015288 |
| Syn19 | 215 | Sargasso Sea | 34°06′N | 61°01′W | Synechococcus WH8109 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015286 |
| Syn33 | 227 | Gulf Stream | 25°51′N | 79°26′W | Synechococcus WH7803 | Sullivan et al. (2010) | NC_015285 |
| Syn9 | 228 | Woods Hole | 41°31′N | 71°40′W | Synechococcus WH8012 | Weigele et al. (2007) | NC_008296 |
Abbreviation: HOT, Hawai'i Ocean Time-Series; ALOHA, A Long-term Oligotrophic Habitat Assessment.
Orthologous gene cluster and shared domain identification
Gene clusters were generated as described previously with slight modifications (Kettler et al., 2007; Kelly et al., 2012). Orthologous genes were assigned using reciprocal best blastp scores (using an e-value cutoff ⩽1E–5) where sequence identity was at least 35% and alignment length was at least 75% of the length of each protein. Clusters of orthologous genes were built by transitively clustering orthologs. This procedure was established to identify complete genes instead of conserved domains that might represent only a small fraction of a gene. To identify conserved domains, genes were run against the Pfam protein families database version 25.0 (Punta et al., 2012) with HMMER 3.0 (Eddy, 1998) using the CAMERA function prediction workflow with default parameters; hits with an e-value ⩽0.001 are reported (Sun et al., 2011).
Cyanomyovirus gene identification in metagenomic data sets
Three data sets from microbial fraction genomic DNA (retained on 0.22 μM filters—phage DNA is ‘by catch' in these samples) were analyzed (Table 2). Two pyrosequence data sets were collected from three depths in the oligotrophic N. Pacific subtropical gyre (Hawai'i Ocean Time-Series (HOT), cruise HOT186) and the Sargasso Sea (Bermuda Atlantic Time Series station (BATS), cruise BATS216) (Frias-Lopez et al., 2008; Coleman and Chisholm, 2010), one was from the deep chlorophyll maximum in the Mediterranean Sea (MedDCM, NCBI Sequence Read Archive Id: SRP002017) (Ghai et al., 2010). The three depths sampled at HOT (25, 75, 110 m) and BATS (20, 50, 100 m) were pooled by site. The MedDCM site was sampled at a single depth, 50 m.
Table 2. Three environmental metagenomic data sets analyzed for cyanomyovirus gene abundance.
| Sample | Depth (m) | Location | Total Reads | Cyanomyophage recruited reads | Publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOT | 25, 75, 110 | North Pacific | 1770399 | 35669 | Coleman and Chisholm (2010) |
| BATS | 20, 50, 100 | Sargasso Sea | 1348140 | 7032 | Coleman and Chisholm (2010) |
| MedDCM | 50 | Mediterranean Sea | 1204382 | 23707 | Ghai et al. (2010) |
Abbreviations: BATS, Bermuda Atlantic Time Series; HOT, Hawai'i Ocean Time-Series; MedDCM, deep chlorophyll maximum in the Mediterranean Sea.
Metagenomic sequences from each sample were recruited to the custom protein database of cyanobacterial and cyanophage orthologous gene clusters described above. This step distinguishes cyanomyovirus genes of interest from (1) cyanobacterial and (2) podo- and siphoviral genes. Sequences and annotations are available in the ProPortal database (Kelly et al., 2012) (http://proportal.mit.edu/) and as a FASTA file (http://proportal.mit.edu/pubdownload/index_V3clusters.html). Reads with best hits to a cyanomyovirus gene (blastx bitscore >50) were required to have their top five hits (if available) to genes in the same cluster. Sequences passing this filter were compared with the NCBI non-redundant (nr) database using blastx with a bitscore comparison to ensure there were no better hits to non-phage protein sequences. The Fisher test (part of the epitools library) and the Bonferroni multiple comparison correction in the R statistical software package (R Development Core Team, 2009) were used to determine the statistical significance of gene cluster abundance when comparing pairs of sites.
Reconstruction of phylogenetic trees
Protein sequences were aligned with MUSCLE v3.6 (Edgar, 2004). Alignments were trimmed such that each column was covered by ⩾90% of the sequences. Trees were reconstructed with PhyML version 2.45 (Guindon et al., 2009) using non-parametric bootstrap analysis with 100 replicates, one category of substitution rate, the JTT model of amino-acid substitution and the proportion of invariable sites fixed. Trees were plotted using iTOL (Letunic and Bork, 2011).
Identification of core gene sets
We defined two broad sets of core genes: one based on cultured, completely sequenced cyanomyoviruses (‘signature core genes') and the other based on the relative abundance of cyanomyovirus genes in the metagenomic data sets (‘metagenome-defined core genes').
Cyanomyovirus signature core genes are, by our definition, those genes that are single copy and have orthologs in all of the complete cyanomyovirus genomes available at the time of this study; 26 genes fit this definition (Table 3). Note that the signature core gene set defined here is a subset of the cyanomyovirus core genes defined in Sullivan et al. (2010), in which sequence profiling techniques and manual curation were used to pull in more distantly related genes and to group together clusters to define core gene groups, respectively. For the purposes of metagenomic recruitment, we wanted our clusters to (1) reflect complete genes instead of partial genes or conserved domains, (2) to be comprised of closely related sequences, and (3) to be automatically produced to facilitate addition of new genomes.
Table 3. Cyanomyovirus signature core genes from 28 cyanomyovirus isolates.
| Gene Cluster | Protein name | Pfam annotation | Pfam description | ProPortal protein cluster description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhCOG71234 | UvsY | UvsY | ||
| PhCOG71329 | Td | PF02511 | Thymidylate synthase complementing protein | Thymidylate synthetase |
| PhCOG71555 | PsbA | PF00124 | Photosynthetic reaction center protein | Photosystem II D1 protein |
| PhCOG71685 | NrdB | PF00268 | Ribonucleotide reductase, small chain | Ribonucleotide reductase |
| PhCOG72002 | Hypothetical protein | |||
| PhCOG72091 | MazG | PF03819 | MazG nucleotide pyrophosphohydrolase domain | Pyrophosphatase |
| PhCOG72096 | gp43 | PF00136/PF03104 | DNA polymerase family B/DNA polymerase family B, exonuclease domain | DNA polymerase |
| PhCOG72133 | gp21 | PF03420 | Prohead core protein protease | Prohead core scaffold and protease |
| PhCOG71393 | RegA | PF01818 | Bacteriophage translational regulator | Endoribonulceases, translational repressor |
| PhCOG72163 | gp6 | Base plate wedge | ||
| PhCOG72320 | gp22 | T4-like prohead core scaffold protein | ||
| PhCOG72416 | gp33 | Late promoter transcription accessory protein | ||
| PhCOG72419 | gp32 | PF08804 | Single-stranded DNA binding | SsDNA-binding protein |
| PhCOG72560 | gp26 | PF12322 | T4 bacteriophage base plate protein | Base plate hub subunit |
| PhCOG72577 | Hypothetical protein | |||
| PhCOG72907 | gp25 | PF04965 | Gene 25-like lysozyme | Base plate wedge subunit |
| PhCOG73251 | gp55 | PF04542 | Sigma-70 region 2 | Sigma factor for late transcription |
| PhCOG199 | gp61 | DNA primase subunit | ||
| PhCOG71136 | PhoH | PF02562 | PhoH | P-starvation-inducible protein |
| PhCOG71424 | gp19 | PF06841 | T4-like virus tail tube protein gp19 | Tail tube monomer |
| PhCOG2 | NrdA | PF03477 | ATP-cone | Ribonucleotide reductase A subunit |
| PhCOG71205 | gp41 | PF03796/PF06745 | DnaB-like helicase C terminal domain/KaiC | DNA primase-helicase |
| PhCOG72128 | Hypothetical protein | |||
| PhCOG72704 | gp15 | Proximal tail sheath stabilization | ||
| PhCOG73063 | gp4 | PF08722 | TnsA endonuclease N terminal | Head completion protein |
| PhCOG73249 | PF11360 | Protein of unknown function (DUF3110) | Hypothetical protein |
Abbreviation: ATP, adenosine phosphate.
As expected (Coleman and Chisholm, 2010), for the signature core genes there is a linear relationship between the number of reads detected in metagenomic databases and gene length; we use this relationship to define a range of values that encompasses the length-normalized abundance of most signature core genes (Figure 1). The kernel density estimator function ‘density' in the stats library of the R statistical software package was used to identify the first and the third quartile range for the length-normalized abundance of signature core genes in each environment using default bandwidth selection (R Development Core Team, 2009).
Figure 1.
Relationship between gene length and reads detected for cyanomyovirus genes observed in metagenomic databases from three different environments: Sargasso Sea (BATS), N. Pacific (HOT) and Mediterranean Sea (MedDCM). Red circles indicate single copy signature core genes identified in 28 cultured cyanomyovirus genomes. The linear relationship (adjusted r2 values are 0.89, 0.95 and 0.94 for BATS, HOT and MedDCM respectively) between gene length and the number of times a gene is found supports the assertion that these genes are core in the wild populations of cyanomyoviruses as well.
This procedure allowed us to identify genes belonging to a ‘metagenome-defined core', which is the set of phage genes in each metagenomic data set that, when normalized to gene length, occur at the same frequency as the signature core genes—that is, they are likely present in every cyanomyovirus. In some cases, genes fall in this group in all three environments, which we refer to as the ‘metagenome-shared core'.
Identification of pho box motifs in cultured cyanomyovirus genomes
Previous work used consensus sequences to identify putative pho boxes upstream of the PhCOG173 gene in P-SSM7 and upstream of the pstS gene in P-SSM4 (Sullivan et al., 2010). Here, we used 129 pho box motifs computationally predicted upstream of genes in four Prochlorococcus and two marine Synechococcus genomes (Su et al., 2007) to generate a position weight matrix of the pho box motif with the Bio.Motif module from the Biopython software package (Cock et al., 2009). The position weight matrix was used to search upstream intergenic regions in the cyanomyovirus genomes for putative binding sites for the response regulator phoB. A log-odds threshold was used to identify putative motifs, the threshold was set at: threshold_balanced(1000). Motifs were required to be on the same strand and within 100 base pairs upstream of a gene.
Results and discussion
Gene frequency in different environments
To explore emergent patterns relating habitat to gene content in cyanomyovirus populations, we used predicted protein sequences from 28 cultured cyanomyovirus genomes to first define genes as either conserved or flexible and then to recruit homologous genes from metagenomic databases from the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (HOT), the Sargasso Sea (BATS) and the Mediterranean Sea (MedDCM) (Table 2).
Cyanomyovirus signature core gene set
Given the constraints imposed when building orthologous gene clusters (see Methods), the 11 new cyanomyovirus genomes increase the total cyanomyovirus ‘pan genome' from approximately 1500 (Sullivan et al., 2010) to approximately 2000 genes (Supplementary Figure S1). There is a well-defined set of 26 clusters of orthologous genes shared by all 28 cyanomyovirus genomes (Table 3)—defined here as ‘signature core genes'—that we used to assess the relative abundance of all other cyanomyovirus genes in each environmental sample. This set includes genes with host homologs—that is, shared phage/host genes—such as the pyrophosphatase mazG and the phosphate-starvation-inducible gene phoH. If these genes are also single copy core genes in wild phage genomes, their abundance should be directly proportional to gene length in each environment (Coleman and Chisholm, 2010), and indeed it is (Figure 1).
Shared metagenome-defined core gene set
Twenty-one genes were present within a range of values defined by the length-normalized abundance of signature core genes at all three sites. This set, plus applicable signature core genes, constitutes the ‘metagenome-shared core' (Table 4). These genes encode phage structural proteins, hypothetical genes and shared phage/host genes such as the UvsW helicase and an endonuclease, indicating that some shared phage/host genes have become part of the core cyanomyovirus gene complement in multiple habitats. In most cases, a gene identified as core in the metagenomes was absent from only one or two of the 28 genomes of cultured strains, making its presence in the metagenome-shared core unsurprising. However, the hypothetical gene PhCOG71299, observed in only 16 of the 28 genomes, nonetheless appears at core frequencies in all three environments. This gene may be more prevalent in wild genomes than our cultured set would predict, or alternatively it may be multi-copy in some wild phage (Table 4). Notably, only between 6% and 11% of cyanomyovirus gene clusters are abundant at or above the boundaries set by the signature core genes per site, highlighting extremely high diversity at the level of individual genes in wild cyanomyovirus genomes (red circles, Supplementary Figure S2).
Table 4. Metagenome-shared core genes.
| Gene cluster | Gene | Pro/Syn domain homolog? | Cyanomyovirus genes in cluster | Pfam annotation | Pfam domain description | ProPortal gene cluster description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhCOG131 | gp3 | 27 | Head-proximal tip of tail tube tail completion+sheath stabilizer protein | |||
| PhCOG71175 | 27 | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| PhCOG71207 | Y | 27 | PF00154 | RecA | UvsX RecA-like | |
| PhCOG71233 | UvsW | Y | 27 | PF04851 | Type III restriction enzyme, res subunit | RNA-DNA+DNA-DNA helicase |
| PhCOG71299 | PurM | 16 | Hypothetical protein | |||
| PhCOG71328 | 30 | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| PhCOG71617 | CobS | Y | 27 | PF07728 | AAA domain (dynein-related subfamily) | Porphyrin biosynthetic protein |
| PhCOG71620 | gp46 | Y | 27 | PF02463 | RecF/RecN/SMC N terminal domain | Recombination endonuclease subunit |
| PhCOG71713 | Hsp20 | Y | 27 | PF00011 | Hsp20/alpha crystallin family | Heat-shock protein |
| PhCOG71874 | 26 | Exonuclease | ||||
| PhCOG72064 | gp17 | Y | 26 | PF03237 | Terminase-like family | Terminase DNA packaging enzyme large subunit |
| PhCOG72066 | Y | 27 | PF00565 | Staphylococcal nuclease homologue | Endonuclease | |
| PhCOG72135 | gp20 | 27 | Portal vertex protein of head | |||
| PhCOG72256 | NrdC | Y | 37 | PF00462 | Glutaredoxin | Glutaredoxin |
| PhCOG72398 | Hli03 | Y | 46 | High light inducible proteins | ||
| PhCOG72740 | gp44 | 27 | PF00004 | ATPase family associated with various cellular activities (AAA) | Clamp loader subunit | |
| PhCOG72737 | gp45 | 27 | Sliding clamp DNA polymerase accessory protein | |||
| PhCOG72834 | gp51 | 20 | Base plate hub assembly catalyst | |||
| PhCOG72960 | 27 | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| PhCOG173 | 40 | Hypothetical protein | ||||
| PhCOG73250 | gp47 | Y | 26 | PF00149 | Calcineurin-like phosphoesterase | Recombination endonuclease subunit |
Abbreviation: SMC, structural maintenance of chromosomes.
Genes present at signature core gene frequencies in one or two environments
Thirty genes were found at signature core gene frequencies in one or two of the three environments, most of which were annotated as ‘hypothetical' (Supplementary Table S1). Some annotated proteins, such as the phosphate-binding protein PstS, an iron-dependent oxygenase and the hli gene cluster hli04 (all core at BATS) have homologs in host genomes, while others, such as the bacterial DNA methylase Dam (core at HOT) do not. The shared Calvin cycle regulatory gene CP12 is core at HOT and MedDCM but not at BATS.
Pairwise site by site comparisons
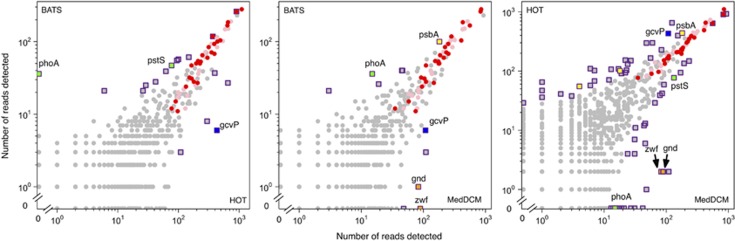
We used pairwise comparisons of gene frequencies in different environments to identify further signals of environment-specific selective pressures on phage populations (Figure 2). Seventy-one unique genes were statistically overrepresented at one or more of the sites (Tables 5, 6, 7). We found some phage structural genes overrepresented at particular sites. Phage structural genes can be sequence diverse (Sullivan et al., 2010), and we hypothesize that the dominant sequence type for some structural genes might vary site to site, and this may be the source of our observation of structural genes that are specific to particular sites.
Figure 2.
Comparisons of cyanomyovirus gene reads detected in three different ocean environments. Circles indicate equally represented phage genes and purple outlined squares represent genes that are statistically differentially represented in one of the two environments being compared. Signature core genes are red, genes with abundances similar to signature core genes in all three environments (‘metagenome-shared core') are pink. Six phage/host shared genes of particular interest are labeled: phoA and pstS (green) are phosphate-associated, psbA (yellow) is a photosystem gene, additional HOT-overrepresented genes in the neighborhood of psbA, a heme oxygenase and a gene of unknown function, are also colored yellow, gnd and zwf (orange) are PPP genes and gcvP is the glycine cleavage system P-protein. Tables 5, 6, 7 include detailed information for each overrepresented gene.
Table 5. Statistically overrepresented cyanomyovirus genes in a comparison of the North Pacific Gyre (HOT) and the Sargasso Sea (BATS).
| PhCOG | Bonferroni adjusted Fisher score | BATS | HOT | ProPortal description | Overrepresented at | Sig. core? | In host? | Pfam domain | Pfam description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhCOG72627 | 5.30E-26 | 36 | 0 | PhoA | BATS | ||||
| PhCOG2105 | 8.08E-23 | 6 | 431 | Glycine dehydrogenase | HOT | Y | PF02347/PF01212 | Glycine cleavage system P-protein/Beta-eliminating lyase | |
| PhCOG72964 | 2.54E-21 | 27 | 653 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG73281 | 1.23E-11 | 8 | 297 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_1324 | 3.64E-09 | 21 | 6 | Hypothetical | BATS | ||||
| PhCOG71200 | 1.65E-06 | 57 | 100 | Hypothetical | BATS | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_1323 | 1.35E-06 | 55 | 94 | Hypothetical | BATS | ||||
| PhCOG73152 | 7.66E-06 | 47 | 77 | PstS | BATS | Y | PF01547 | Bacterial extracellular solute-binding protein | |
| PhCOG72544 | 9.22E-05 | 39 | 62 | 2OG-Fe(II) oxygenase | BATS | Y | PF03171 | 2OG-Fe(II) oxygenase superfamily | |
| PhCOG1447 | 2.28E-03 | 28 | 42 | RNaseH | BATS | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_657 | 2.94E-04 | 25 | 29 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | BATS | ||||
| PhCOG564 | 2.55E-03 | 37 | 397 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG72672 | 3.66E-03 | 61 | 148 | Tail sheath monomer | BATS | PF04984 | Phage tail sheath protein | ||
| PhCOG72704 | 8.90E-03 | 118 | 368 | Proximal tail sheath stabilization | BATS | Y | |||
| PhCOG2 | 1.18E-04 | 260 | 905 | Ribonucleotide reductase A subunit | BATS | Y | PF02867/PF00317/PF03477 | Ribonucleotide reductase, barrel domain/Ribonucleotide reductase, all-alpha domain/ATP cone domain | |
| PhCOG73058 | 8.99E-03 | 3 | 109 | T4-like base plate hub and tail lysozyme | HOT | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_1479 | 5.32E-03 | 21 | 26 | Transketolase central region-containing protein | BATS |
Abbreviation: ATP, adenosine triphosphate.
Table 6. Statistically overrepresented cyanomyovirus genes in a comparison of the Mediterranean Sea (MedDCM) and the Sargasso Sea (BATS).
| PhCOG | Bonferroni adjusted Fisher score | BATS | MedDCM | ProPortal description | Overrepresented at | Sig. core? | In host? | Pfam domain | Pfam domain description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhCOG72627 | 2.92E-10 | 36 | 15 | PhoA | BATS | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_1479 | 2.16E-08 | 21 | 3 | Transketolase central region-containing protein | BATS | ||||
| PhCOG969 | 2.68E-07 | 0 | 89 | G6PDH | MedDCM | Y | PF02781/PF00479 | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, C-terminal domain/Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, NAD-binding domain | |
| PhCOG258 | 4.76E-06 | 3 | 110 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG964 | 2.30E-05 | 1 | 83 | 6PGDH | MedDCM | PF03446/PF00393/PF03807 | NAD-binding domain of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase/6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, C-terminal domain/NADP oxidoreductase coenzyme F420-dependent | ||
| PhCOGOrphan_620 | 3.03E-04 | 26 | 19 | Hypothetical | BATS | ||||
| PhCOG71555 | 3.93E-04 | 100 | 181 | Photosystem II D1 protein | BATS | Y | Y | PF00124 | Photosynthetic reaction center protein |
| PhCOG3728 | 5.96E-04 | 40 | 45 | Putative nucleotidyltransferase | BATS | ||||
| PhCOG4334 | 7.68E-04 | 40 | 46 | Nucleotide sugar epimerase | BATS | Y | |||
| PhCOG2105 | 1.32E-03 | 6 | 108 | Glycine dehydrogenase | MedDCM | Y | PF02347/PF01212 | Glycine cleavage system P-protein/Beta-eliminating lyase | |
| PhCOG71205 | 8.62E-03 | 185 | 431 | DNA primase-helicase | BATS | Y |
Abbreviations: NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADP, NAD phosphate.
Table 7. Statistically overrepresented cyanomyovirus genes in a comparison of the North Pacific Gyre (HOT) and the Mediterranean Sea (MedDCM).
| PhCOG | Bonferroni adjusted Fisher score | HOT | MedDCM | ProPortal description | Overrepresented at | Sig. core? | In host? | Pfam domain | Pfam domain annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PhCOG72964 | 1.22E-45 | 653 | 124 | Baseplate wedge initiator protein | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG258 | 5.58E-38 | 2 | 110 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG969 | 8.40E-30 | 2 | 89 | G6PDH | MedDCM | Y | PF02781/PF00479 | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, C-terminal domain/glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, NAD-binding domain | |
| PhCOG964 | 1.79E-27 | 2 | 83 | 6PGDH | MedDCM | PF03446/PF00393/PF03807 | NAD-binding domain of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase/6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, C-terminal domain/NADP oxidoreductase coenzyme F420-dependent | ||
| PhCOG73281 | 2.22E-23 | 297 | 48 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG2105 | 3.16E-20 | 431 | 108 | Glycine dehydrogenase | HOT | Y | PF02347/PF01212 | Glycine cleavage system P-protein/beta-eliminating lyase | |
| PhCOG71491 | 1.64E-18 | 299 | 60 | DNA adenine methylase | HOT | PF01555 | DNA methylase | ||
| PhCOG97 | 1.24E-15 | 924 | 928 | VrlC | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG72264 | 3.36E-15 | 1 | 48 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG2051 | 7.01E-15 | 110 | 6 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG72516 | 2.73E-14 | 0 | 42 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG72672 | 1.38E-13 | 148 | 233 | Tail sheath monomer | MedDCM | PF04984 | Phage tail sheath protein | ||
| PhCOG71457 | 2.03E-12 | 153 | 22 | Hypothetical | HOT | Y | |||
| PhCOGOrphan_1323 | 2.27E-12 | 94 | 170 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_12 | 2.42E-12 | 102 | 7 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG71083 | 2.25E-10 | 65 | 1 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_404 | 6.41E-10 | 0 | 31 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_1324 | 7.25E-10 | 6 | 46 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG71124 | 1.09E-09 | 150 | 27 | Phycoerythrobilin | HOT | PF05996 | Ferredoxin-dependent bilin reductase | ||
| PhCOG73276 | 2.23E-09 | 107 | 13 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG96 | 6.69E-09 | 135 | 194 | Base plate wedge | MedDCM | PF09215 | Bacteriophage T4, Gp8 | ||
| PhCOG73152 | 1.88E-08 | 77 | 133 | PstS | MedDCM | Y | PF01547 | Bacterial extracellular solute-binding protein | |
| PhCOG1139 | 2.49E-08 | 0 | 27 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG2 | 3.34E-08 | 905 | 832 | Ribonucleotide reductase A subunit | MedDCM | Y | PF02867/PF00317/PF03477 | Ribonucleotide reductase, barrel domain/ribonucleotide reductase, all-alpha domain/ATP cone domain | |
| PhCOG72825 | 4.52E-08 | 131 | 24 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG73058 | 1.34E-07 | 109 | 17 | T4-like base plate hub and tail lysozyme | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG73171 | 1.05E-06 | 47 | 1 | NifU-like protein | HOT | Y | |||
| PhCOG1447 | 1.28E-06 | 42 | 86 | RNaseH | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG564 | 4.06E-06 | 397 | 154 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | HOT | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_1292 | 4.72E-06 | 4 | 31 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG1681 | 5.31E-06 | 68 | 7 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG71433 | 5.49E-06 | 13 | 46 | Plastocyanin | MedDCM | Y | PF00127 | Copper-binding proteins, plastocyanin/azurin family | |
| PhCOG72321 | 5.80E-06 | 39 | 79 | Precursor of major head subunit | MedDCM | PF07068 | Major capsid protein Gp23 | ||
| PhCOGOrphan_394 | 6.01E-06 | 0 | 21 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG71750 | 6.38E-06 | 101 | 18 | gp7 | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG71460 | 1.04E-05 | 12 | 44 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_657 | 1.37E-05 | 29 | 66 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG71159 | 1.42E-05 | 55 | 4 | Heme oxygenase | HOT | Y | |||
| PhCOG71555 | 2.40E-05 | 438 | 181 | Photosystem II D1 protein | HOT | Y | Y | PF00124 | Photosynthetic reaction center protein |
| PhCOG71986 | 3.74E-05 | 0 | 19 | Antioxidant protein | MedDCM | Y | |||
| PhCOG72368 | 3.74E-05 | 0 | 19 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG72879 | 1.25E-04 | 57 | 6 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG73056 | 1.98E-04 | 41 | 2 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG72250 | 2.33E-04 | 0 | 17 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG71068 | 2.74E-04 | 36 | 1 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG73044 | 2.80E-04 | 103 | 23 | Phage tail fiber-like protein | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG73097 | 3.61E-04 | 59 | 92 | Carbamoyltransferase | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOGOrphan_658 | 3.82E-04 | 7 | 31 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG2016 | 5.10E-04 | 29 | 0 | Hypothetical | HOT | Y | |||
| PhCOGOrphan_620 | 5.35E-04 | 91 | 19 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG1098 | 5.81E-04 | 0 | 16 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG73282 | 6.19E-04 | 71 | 12 | Base plate wedge | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG456 | 1.45E-03 | 0 | 15 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | Y | |||
| PhCOG72627 | 1.45E-03 | 0 | 15 | PhoA | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG739 | 1.45E-03 | 0 | 15 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG71169 | 1.74E-03 | 228 | 84 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG72664 | 1.90E-03 | 4 | 24 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG224 | 1.94E-03 | 94 | 22 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG1544 | 3.62E-03 | 0 | 14 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | ||||
| PhCOG963 | 4.59E-03 | 38 | 3 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG4516 | 4.85E-03 | 166 | 56 | Hypothetical | HOT | ||||
| PhCOG72163 | 5.12E-03 | 641 | 560 | Base plate wedge | MedDCM | Y | |||
| PhCOG72041 | 8.20E-03 | 11 | 32 | Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole-succinocarboxamide synthase | MedDCM | Y | PF01259 | SAICAR synthetase | |
| PhCOG529 | 9.02E-03 | 0 | 13 | Hypothetical | MedDCM | Y |
Abbreviations: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADP, NAD phosphate; SAICAR, phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide.
Fifteen overrepresented genes have host homologs—that is, are shared phage/host genes with the potential to interface with host metabolic pathways and processes (Millard et al., 2009; Sullivan et al., 2010; Sharon et al., 2011; Thompson et al., 2011b; Zeng and Chisholm, 2012). Of particular interest are those related to phosphorous acquisition, because this element can be a defining variable in the structure and function of marine microbial systems and has a key role in shaping the genome content of cyanobacterial hosts (Martiny et al., 2009; Coleman and Chisholm, 2010).
Features of phosphate-acquisition genes in cultured and wild phage
Frequency at BATS and MedDCM relative to HOT
The frequency of phoA and pstS—cyanomyovirus genes with host homologs involved in the phosphate stress response (Martiny et al., 2006; Hsieh and Wanner, 2010; Zeng and Chisholm, 2012)—was elevated at BATS and MedDCM relative to HOT (Tables 5, 6, 7, Figure 2, green squares). Notably, phosphate concentrations in North Atlantic surface waters are in the nanomolar range—as are those in the Mediterranean Sea—and at least an order of magnitude lower than surface levels in the North Pacific (Wu et al., 2000; Moutin and Raimbault, 2002). In fact, at BATS, phage pstS occurs at signature core gene frequencies (that is, it is likely present in all cyanomyoviruses), and it is nearly so at MedDCM, indicating that it has been incorporated into the genomes of essentially all cyanomyoviruses in these environments. Prochlorococcus' phoA gene is also overrepresented at BATS vs HOT, while pstS, a core gene in Prochlorococcus genomes, is not (Coleman and Chisholm, 2010), indicating that phage pstS is selected for independently of its abundance in host genomes. The higher frequency of these phosphate-acquisition-related phage genes at BATS and MedDCM relative to HOT suggests that cyanomyovirus populations retain genes that facilitate host functions under the selective pressure of phosphate limitation.
There are also interfaces between host phosphate acquisition and viral genomes in eukaryotic systems—for example, the PHO4 phosphate transporter superfamily (Pfam ID: PF01384) has been found in eukaryotic viruses (Monier et al., 2012). Although this gene is not yet found in Prochlorococcus and is only in one Synechococcus (Synechococcus WH5701, protein ID: WH5701_07531), a single metagenomic read containing both pho4 and a cyanomyovirus gene was observed, suggesting that cyanophage could also carry this gene (Monier et al., 2012).
Explorations of the phylogeny of shared phage/host genes have suggested that cyanophage acquired pstS from host cells (Martiny et al., 2009; Ignacio-Espinoza and Sullivan, 2012); however, not all shared phage host genes have a phylogeny consistent with host origins (Ignacio-Espinoza and Sullivan, 2012). As more and longer environmentally isolated sequences for these shared genes become available, we will be better able to define the flow of genes between phage, host and possibly other microbes in marine environments.
The metagenomic patterns observed here reflect the link between phosphate-acquisition genes in phage and the regulation of phosphate-acquisition genes in the host by phosphate availability (Zeng and Chisholm, 2012; and see below). Phosphate availability controls expression of host pstS and alkaline phosphatase genes in both marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus (Scanlan et al., 1993; Martiny et al., 2006; Tetu et al., 2009) through the PhoB/PhoR (PhoBR) two-component regulatory system (Hsieh and Wanner, 2010) that is widespread in bacteria, including Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus (Kettler et al., 2007; Scanlan et al., 2009; Tetu et al., 2009). Genes regulated by PhoBR have conserved sites (pho boxes) immediately upstream of their promoters to which the transcriptional activator PhoB binds (Lamarche et al., 2008). The presence of pho boxes in cyanomyovirus genomes (Sullivan et al., 2010) and recent evidence that they are involved in sensing and responding to host phosphate-starvation status during infection in one phage/host pair (Zeng and Chisholm 2012) led us to explore this motif more deeply.
Pho box motifs in cultured cyanomyovirus genomes
To improve on analyses in our previous work (Sullivan et al., 2010)—while recognizing that computational predictions ultimately require experimental confirmation—we used a position weight matrix based on predicted Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus pho box motifs (Su et al., 2007), tailoring our search to capture host-like pho boxes. In the 28 genomes we found 186 genes from 112 orthologous gene clusters with intergenic upstream pho boxes within 100 bp of the gene's start site (Supplementary Table S2).
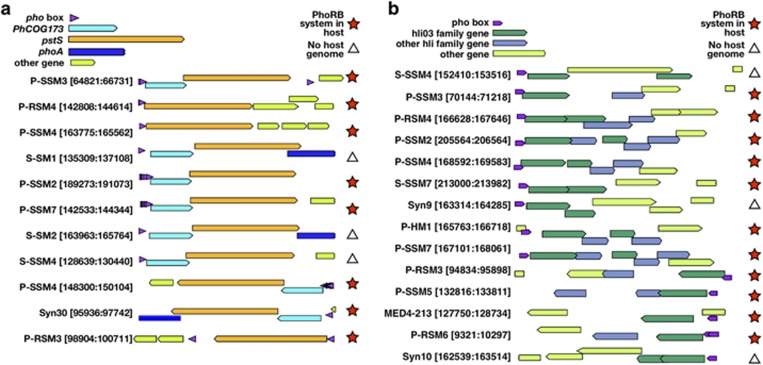
Pho boxes upstream of phage pstS/PhCOG173. As reported in Sullivan et al. (2010), and Zeng and Chisholm (2012), pho boxes near pstS are often accompanied by a gene between the pho box and pstS, referred to as DUF680 in the former and PhCOG173 in the latter. Phage lacking PhCOG173 upstream of pstS have pho boxes directly upstream of pstS. In 11 out of 16 phages containing pstS/PhCOG173, pho boxes were found <100 bp upstream of these genes (Figure 3a) and slightly further (121 bp) in a twelfth phage (S-SSM7) (Supplementary Table S3). In the three phages (P-SSM3, P-SSM2 and P-SSM7), there were multiple tandem pho boxes upstream of these genes. The phage PhCOG173 gene family is conserved (see below), and its expression is upregulated in cyanomyoviruses infecting host cells that are P-stressed (Zeng and Chisholm, 2012). Notably, PhCOG173 has no detectable orthologs in host genomes and pho boxes are found directly upstream of it in eight cyanomyovirus genomes. Therefore, we postulate that the positioning of pho boxes in front of numerous copies of PhCOG173 is a result of selection rather than chance and that this gene may have a role in either phosphate acquisition or in a more general phosphate-stress response.
Figure 3.
Predicted pho boxes immediately upstream of (a) PhCOG173 and/or pstS and (b) the hli03 gene cluster in cyanomyovirus genomes. Phage genome names and the genomic indices of the displayed region are indicated. Putative pho box motifs are shown as purple arrows. The genomic region in (a) is larger than the region in (b) and the pho box motif and genes are scaled in size accordingly. Red stars indicate that the host strain on which the phage was isolated contained the PhoBR two-component phosphate sensing system; white triangles indicate that the host genome is not currently available. The PhCOG173 (cyan), pstS (orange), phoA (blue), hli03 (dark green) and other hli genes (light blue) are highlighted with specific colors; all other genes are shown in light green.
Although not all Prochlorococcus contain the PhoBR system (Kettler et al., 2007), those hosts with sequenced genomes on which cyanomyoviruses containing pho boxes were isolated do contain PhoBR (Figure 3a, Supplementary Materials and Methods). Notably, phage Syn19, Syn2, S-SSM5 and P-RSM1, isolated on PhoBR-containing Synechococcus hosts WH8102, WH8012 and WH8109 and Prochlorococcus host MIT9303, respectively, do not have identifiable pho boxes directly upstream of PhCOG173. They do, however, have pho boxes elsewhere in this genomic region: Syn19 has a pho box upstream of the hypothetical protein Syn19_155, three genes upstream of PhCOG173/pstS, and its ortholog in Syn2, CPTG_00065, also has an upstream pho box. S-SSM5 and P-RSM1 contain pho boxes 142 and 135 bp upstream of the heat-shock protein Hsp20, respectively, which lies immediately upstream of PhCOG173 (Supplementary Table S3). It is therefore possible that additional genes in this region are responsive to regulatory signals from the host PhoBR system.
Pho boxes upstream of phage hli genes There are 46 hli03 genes in the cyanomyovirus genomes—18 genomes have multiple copies and 10 have a single copy. The hli03 genes are closely spaced in genomes with multiple copies and frequently found with other hli gene family members. In 13 out of 14 cases, there is a pho box upstream of the first hli03 copy in the genome (Figure 3b), raising the intriguing possibility that the host PhoBR system might also regulate the expression of phage hli03. PhoB can regulate non-phosphate-related genes in bacteria, such as virulence genes in Vibrio cholerae (Pratt et al., 2010), antibiotic-regulating genes in Streptomyces (Santos-Beneit et al., 2011) and acid-stress genes in Escherichia coli (Suziedeliene et al., 1999). Although there is no direct evidence that PhoBR regulates other genes in cyanophage hosts, some predicted that pho boxes in marine Synechococcus (Su et al., 2007) are upstream of hli genes. There is no such evidence for Prochlorococcus thus far.
Hli genes are similar in sequence to chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins that are often upregulated under changes in light intensity in cyanobacteria (Dolganov et al., 1995; Funk and Vermaas, 1999; Bhaya et al., 2002; Steglich et al., 2006). There are numerous hlis in Prochlorococcus genomes (Coleman and Chisholm, 2007). Although their location and binding partners in the cell remains unclear (Storm et al., 2008; Muramatsu and Hihara, 2012), hlis display different expression patterns over the diel cycle (Zinser et al., 2009) and generally fall into two categories (Bhaya et al., 2002): (1) Single copy core hlis and (2) multi-copy non-core hlis. Multi-copy hlis have orthologs, such as hli03, in phage (Lindell et al., 2004). Genes in this category are often found in hyper-variable regions in host genomes and are upregulated in response to changes in light (Steglich et al., 2006), iron (Thompson et al., 2011a) and nitrogen (Tolonen et al., 2006) in host cells, as well as stress imposed by phage infection (Lindell et al., 2004, 2007). In the case of nitrogen, binding sites for the global nitrogen regulator NtcA were found upstream of hlis with differential transcription under changing nitrogen conditions (Tolonen et al., 2006). Interestingly, hlis do not appear to be upregulated in response to phosphate stress in Prochlorococcus (Martiny et al., 2006), although in Synechococcus sp. WH8102 a possible hli (SYNW2180) was upregulated in a PtrA protein transcriptional response gene mutant during phosphate stress relative to the wild-type strain (Ostrowski et al., 2010). This hli has no homologs in phage.
PhCOG173, a conserved, cyanophage-specific gene neighboring multiple shared phage-host genes
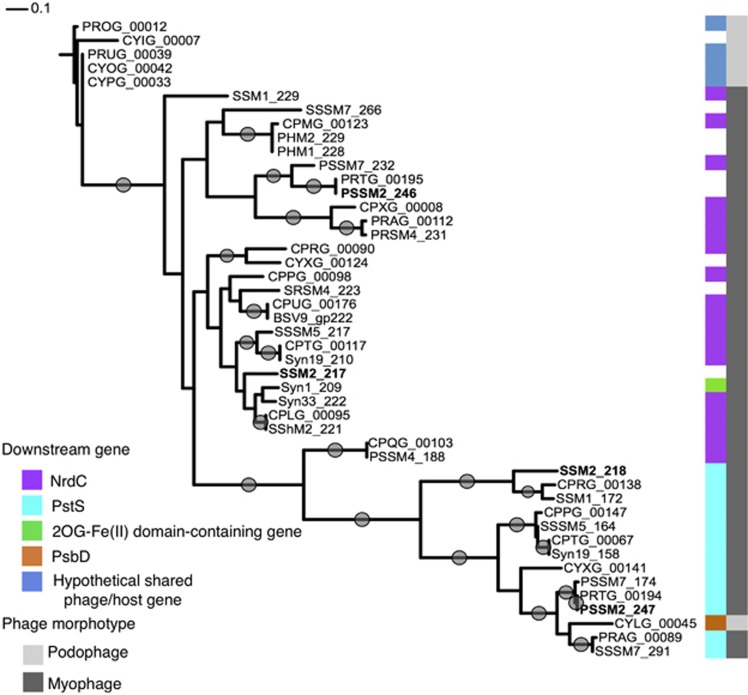
PhCOG173 is found in all 28 cyanomyoviruses (Figure 4, genes with dark gray bars) and is multi-copy in 12 genomes. Eight of these have one copy of the gene upstream of pstS and another upstream of glutaredoxin (called nrdC in phage genomes and grxC in host genomes), a single copy core gene in Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Glutaredoxin is found in all 28 cyanomyovirus genomes and is multi-copy in 10 genomes. Glutaredoxins help regulate cellular redox state (Lillig et al., 2008), suggesting that PhCOG173 is not only involved in influencing phosphate acquisition in host cells but may also alter cellular redox state. Phage may use an altered redox state to direct host metabolism toward nucleotide production (Thompson et al., 2011b). Alternatively, phage glutaredoxin could manipulate stress responses in host cells brought on by changes in redox state.
Figure 4.
Phylogeny of PhCOG173, a conserved phage gene cluster adjacent to shared phage/host genes. The PhCOG173 cluster, present in both cyanopodovirus and cyanomyovirus genomes (light gray and dark gray bars, respectively) but not host genomes, is found upstream of numerous shared phage/host genes, and phylogenetic groups are associated with different downstream host genes (colored bars). White bars indicate that the downstream gene is not shared with any sequenced host genome. Genes in bold indicate genomes where two copies of PhCOG173 are located next to each other, that is, in the P-SSM2 genome, PhCOG173 gene PSSM2_246 is immediately upstream of the PhCOG173 gene PSSM2_247. The tree is rooted with cyanopodovirus gene PROG_00012. Gray circles indicate >0.8 branch support. The scale bar represents 0.1 substitutions per site.
Among sequenced podovirus isolates, six also contain the PhCOG173 gene. The association between PhCOG173 and shared phage/host genes extends to five cyanopodoviruses (Figure 4, genes with light gray bars; Labrie et al., 2013). In four out of these five instances, the gene was found upstream of a shared phage/host gene of unknown function (PhCOG73321), and in one instance, it was upstream of the photosystem gene psbD.
PhCOG173 proteins form phylogenetic groups that are linked to their downstream gene—for example, glutaredoxin and pstS—when that gene is host-like, suggesting differing functional roles related to that gene (Figure 4). In genomes where two copies of PhCOG173 are located next to each other, the genes cluster separately phylogenetically (see PSSM2_246 and PSSM2_247 and SSM2_217 and SSM2_218, set in bold in Figure 4), suggesting that they were not a recent gene duplication and supporting the possibility of differing functional roles.
Thus, the cyanophage-specific PhCOG173 gene is associated with multiple shared phage/host genes with very different functions related to cellular stressors and metabolism, such as phosphate acquisition, light harvesting and cellular redox state. Its conservation across multiple phage morphotypes highlights the importance of this functionally uncharacterized gene and strongly suggests that phage utilize genes not observed in host genomes to affect host metabolic processes.
Differential abundance in metagenomic databases of shared phage/host genes related to photorespiration, photosynthesis and the PPP
Although the phosphate-acquisition-related genes and their associated regulatory features were a strong emergent signal from this data set, there are other phage/host-shared genes differentially retained by phage in environmental comparisons (Figure 2; Tables 5, 6, 7) presumably reflecting selection by as yet unidentified environmental factors. We mention a few intriguing genes here.
The phage gene encoding the glycine cleavage system P-protein (gcvP, PhCOG2105), a large gene (>900aa) that is core in Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus genomes (CyCOG4223), was overrepresented in phage at HOT relative to both BATS and MedDCM and was overrepresented at MedDCM in comparison to BATS, where it is almost completely absent (Tables 5, 6, 7; Figure 2, blue squares). This gene is part of a photorespiratory pathway in cyanobacteria and involved in the reversible interconversion of serine and glycine (Hasse et al., 2007; Eisenhut et al., 2008; Muramatsu and Hihara, 2012).
In some cases, we observed habitat-specific overabundance of neighborhoods containing multiple gene sets. For example, the photosystem-associated phage gene psbA (PhCOG71555) is overrepresented at HOT in comparison to MedDCM. Two neighboring genes, a small, hypothetical cyanophage gene (PhCOG71750) and a shared phage/host heme oxygenase (Ho1, PhCOG71159), were also overrepresented at HOT in comparison to MedDCM (Figure 2, yellow squares). Heme oxygenase is transcribed during infection of Prochlorococcus strain NATL1A (Dammeyer et al., 2008), and its expression is upregulated under iron starvation in some cyanobacteria (Cornejo et al., 1998) but not in Prochlorococcus (Thompson et al., 2011a). Heme oxygenase overabundance at HOT could be related to relatively low iron availability in the Pacific, known to limit Prochlorococcus growth (Mann and Chisholm, 2000).
In a second example, phage glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (zwf, PhCOG969) and phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (gnd, PhCOG964), core PPP genes in host genomes, were overrepresented at MedDCM in comparison to both HOT and BATS (Figure 2, orange squares); an additional shared phage/host Calvin cycle regulatory gene, CP12 (PhCOG71523), was found at signature core gene frequencies at MedDCM and HOT. The gnd/zwf region is variable in cyanophage genomes (Millard et al., 2009), and our previous work indicates that some phage are designed to redirect host metabolism away from carbon fixation and towards nucleotide synthesis via the PPP (Thompson et al., 2011b). Why this would be more necessary in one environment than another remains unknown.
Other genes from this region are also overrepresented in the MedDCM sample, including the shared phage/host plastocyanin gene petE, part of the electron transport chain, and two small, functionally unannotated phage-specific genes, PhCOG71460, and PhCOG1139. The unannotated phage genes may have roles in the PPP, alternatively they may be phage genes selected to flank host-like genes for an unknown purpose.
Conclusions
We demonstrate that environment-specific selection pressures can dictate the frequency of occurrence of some shared phage/host genes in wild cyanophage, highlighting gene flow between cyanobacterial and cyanophage genomes in the marine environment. Notably, the core status of a gene in host genomes (such as the PPP genes discussed above and pstS) does not necessarily reflect its abundance in phage. Furthermore, regulatory motifs for shared phage/host genes are not always acquired with the host gene but appear to be selected for independently in phage genomes as demonstrated by the presence of motifs associated with host phosphate sensing found upstream of the phage-specific gene PhCOG173.
The ecological origins of the considerably greater numbers of differentially abundant genes in the comparison between the HOT and MedDCM sites are not clear. We speculate that as additional metagenomic data sets and associated metadata for environmental samples become available, we will be able to tease apart in more detail the environmental drivers of differences in phage populations between environments.
The ability to identify core-like genes in environmental samples, independent of the prevalence of those genes in sequenced genomes, provides a means to derive an environmentally relevant core genome for these genetically diverse organisms. Finally, our work illustrates the power of metagenomics-based approaches for revealing some of the interplay between phage and host genomes in marine environments, and we anticipate the analyses described here will also be relevant to elucidating the genetic and metabolic ties between phage and host in other systems.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mark Breidenbach (Berkeley), Quincey Justman (Harvard), John Chodera (Berkeley), Jessie Thompson, Paul Berube, Steve Biller, and Qinglu Zeng (MIT) and Maureen Coleman (U Chicago) for useful discussions, Matt Sullivan (U Arizona) for collection and isolation of phage and Sara Roggensack and Brianne Holmbeck (MIT) for phage DNA sample preparation. This work was supported by grants to SWC from The National Science Foundation (NSF) Biological Oceanography Section, the NSF Center for Microbial Oceanography Research and Education, the US Department of Energy-GTL and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on The ISME Journal website (http://www.nature.com/ismej)
Supplementary Material
References
- Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Wheeler DL. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D16–D20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaya D, Dufresne A, Vaulot D, Grossman A. Analysis of the hli gene family in marine and freshwater cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002;215:209–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clokie MR, Shan J, Bailey S, Jia Y, Krisch HM, West S, et al. Transcription of a ‘photosynthetic' T4-type phage during infection of a marine cyanobacterium. Environ Microbiol. 2006;8:827–835. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cock PJ, Antao T, Chang JT, Chapman BA, Cox CJ, Dalke A, et al. Biopython: freely available Python tools for computational molecular biology and bioinformatics. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1422–1423. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman ML, Chisholm SW. Code and context: Prochlorococcus as a model for cross-scale biology. Trends Microbiol. 2007;15:398–407. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2007.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman ML, Chisholm SW. Ecosystem-specific selection pressures revealed through comparative population genomics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:18634–18639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009480107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo J, Willows RD, Beale SI. Phytobilin biosynthesis: cloning and expression of a gene encoding soluble ferredoxin-dependent heme oxygenase from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant J. 1998;15:99–107. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammeyer T, Bagby SC, Sullivan MB, Chisholm SW, Frankenberg-Dinkel N. Efficient phage-mediated pigment biosynthesis in oceanic cyanobacteria. Curr Biol. 2008;18:442–448. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.02.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolganov NA, Bhaya D, Grossman AR. Cyanobacterial protein with similarity to the chlorophyll a/b binding proteins of higher plants: evolution and regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:636–640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy SR. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:755–763. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/14.9.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:1792–1797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhut M, Ruth W, Haimovich M, Bauwe H, Kaplan A, Hagemann M. The photorespiratory glycolate metabolism is essential for cyanobacteria and might have been conveyed endosymbiontically to plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:17199–17204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807043105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frias-Lopez J, Shi Y, Tyson GW, Coleman ML, Schuster SC, Chisholm SW, et al. Microbial community gene expression in ocean surface waters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:3805–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708897105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk C, Vermaas W. A cyanobacterial gene family coding for single-helix proteins resembling part of the light-harvesting proteins from higher plants. Biochemistry. 1999;38:9397–9404. doi: 10.1021/bi990545+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghai R, Martin-Cuadrado AB, Molto AG, Heredia IG, Cabrera R, Martin J, et al. Metagenome of the Mediterranean deep chlorophyll maximum studied by direct and fosmid library 454 pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2010;4:1154–1166. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guindon S, Delsuc F, Dufayard JF, Gascuel O. Estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies with PhyML. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;537:113–137. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-251-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasse D, Mikkat S, Thrun HA, Hagemann M, Bauwe H. Properties of recombinant glycine decarboxylase P- and H-protein subunits from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:1297–1301. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.02.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn MR, Sullivan MB, Stange-Thomann N, Osburne MS, Berlin AM, Kelly L, et al. Analysis of high-throughput sequencing and annotation strategies for phage genomes. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh YJ, Wanner BL. Global regulation by the seven-component Pi signaling system. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010;13:198–203. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignacio-Espinoza JC, Sullivan MB. Phylogenomics of T4 cyanophages: lateral gene transfer in the ‘core' and origins of host genes. Environ Microbiol. 2012;14:2113–2126. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly L, Huang KH, Ding HM, Chisholm SW. ProPortal: a resource for integrated systems biology of Prochlorococcus and its phage. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D632–D640. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettler GC, Martiny AC, Huang K, Zucker J, Coleman ML, Rodrigue S, et al. Patterns and implications of gene gain and loss in the evolution of Prochlorococcus. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:e231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrie SJ, Frois-Moniz K, Osburne MS, Kelly L, Roggensack SE, Sullivan MB, et al. Genomes of marine cyanopodoviruses reveal multiple origins of diversity. Environ Microbiol. 2013;15:1356–1376. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarche MG, Wanner BL, Crepin S, Harel J. The phosphate regulon and bacterial virulence: a regulatory network connecting phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008;32:461–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive Tree Of Life v2: online annotation and display of phylogenetic trees made easy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:W475–W478. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillig CH, Berndt C, Holmgren A. Glutaredoxin systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1780:1304–1317. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell D, Jaffe JD, Coleman ML, Futschik ME, Axmann IM. Rector T et al. Genome-wide expression dynamics of a marine virus and host reveal features of co-evolution. Nature. 2007;449:83–86. doi: 10.1038/nature06130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell D, Jaffe JD, Johnson ZI, Church GM, Chisholm SW. Photosynthesis genes in marine viruses yield proteins during host infection. Nature. 2005;438:86–89. doi: 10.1038/nature04111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell D, Sullivan MB, Johnson ZI, Tolonen AC, Rohwer F, Chisholm SW. Transfer of photosynthesis genes to and from Prochlorococcus viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:11013–11018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401526101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann EL, Chisholm SW. Iron limits the cell division rate of Prochlorococcus in the eastern equatorial Pacific. Limnol Oceanogr. 2000;45:1067–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Mann NH, Clokie MR, Millard A, Cook A, Wilson WH, Wheatley PJ, et al. The genome of S-PM2, a ‘photosynthetic' T4-type bacteriophage that infects marine Synechococcus strains. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:3188–3200. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.9.3188-3200.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny AC, Coleman ML, Chisholm SW. Phosphate acquisition genes in Prochlorococcus ecotypes: evidence for genome-wide adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:12552–12557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601301103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny AC, Huang Y, Li W. Occurrence of phosphate acquisition genes in Prochlorococcus cells from different ocean regions. Environ Microbiol. 2009;11:1340–1347. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard AD, Gierga G, Clokie MRJ, Evans DJ, Hess WR, Scanlan DJ. An antisense RNA in a lytic cyanophage links psbA to a gene encoding a homing endonuclease. ISME J. 2010;4:1121–1135. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard AD, Zwirglmaier K, Downey MJ, Mann NH, Scanlan DJ. Comparative genomics of marine cyanomyoviruses reveals the widespread occurrence of Synechococcus host genes localized to a hyperplastic region: implications for mechanisms of cyanophage evolution. Environ Microbiol. 2009;11:2370–2387. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier A, Welsh RM, Gentemann C, Weinstock G, Sodergren E, Armbrust EV, et al. Phosphate transporters in marine phytoplankton and their viruses: cross-domain commonalities in viral-host gene exchanges. Environ Microbiol. 2012;14:162–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutin T, Raimbault P. Primary production, carbon export and nutrients availability in western and eastern Mediterranean Sea in early summer 1996 (MINOS cruise) J Mar Syst. 2002;33:273–288. [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M, Hihara Y. Acclimation to high-light conditions in cyanobacteria: from gene expression to physiological responses. J Plant Res. 2012;125:11–39. doi: 10.1007/s10265-011-0454-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski M, Mazard S, Tetu SG, Phillippy K, Johnson A, Palenik B, et al. PtrA is required for coordinate regulation of gene expression during phosphate stress in a marine Synechococcus. ISME J. 2010;4:908–921. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt JT, Ismail AM, Camilli A. PhoB regulates both environmental and virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 2010;77:1595–1605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry J, Tate J, Boursnell C, et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D290–D301. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team 2009R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria; ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org . [Google Scholar]
- Rohwer F, Thurber RV. Viruses manipulate the marine environment. Nature. 2009;459:207–212. doi: 10.1038/nature08060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabehi G, Shaulov L, Silver DH, Yanai I, Harel A, Lindell D. A novel lineage of myoviruses infecting cyanobacteria is widespread in the oceans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:2037–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115467109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Beneit F, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Martin JF. Complex transcriptional control of the antibiotic regulator afsS in Streptomyces: PhoP and AfsR are overlapping, competitive activators. J Bacteriol. 2011;193:2242–2251. doi: 10.1128/JB.01462-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlan DJ, Mann NH, Carr NG. The response of the picoplanktonic marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus species WH7803 to phosphate starvation involves a protein homologous to the periplasmic phosphate-binding protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993;10:181–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlan DJ, Ostrowski M, Mazard S, Dufresne A, Garczarek L, Hess WR, et al. Ecological genomics of marine picocyanobacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2009;73:249–299. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00035-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon I, Battchikova N, Aro EM, Giglione C, Meinnel T, Glaser F, et al. Comparative metagenomics of microbial traits within oceanic viral communities. ISME J. 2011;5:1178–1190. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steglich C, Futschik M, Rector T, Steen R, Chisholm SW. Genome-wide analysis of light sensing in Prochlorococcus. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:7796–7806. doi: 10.1128/JB.01097-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm P, Hernandez-Prieto MA, Eggink LL, Hoober JK, Funk C. The small CAB-like proteins of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 bind chlorophyll. In vitro pigment reconstitution studies on one-helix light-harvesting-like proteins. Photosynth Res. 2008;98:479–488. doi: 10.1007/s11120-008-9368-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su Z, Olman V, Xu Y. Computational prediction of Pho regulons in cyanobacteria. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:156. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan MB, Coleman ML, Weigele P, Rohwer F, Chisholm SW. Three Prochlorococcus cyanophage genomes: signature features and ecological interpretations. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan MB, Huang KH, Ignacio-Espinoza JC, Berlin AM, Kelly L, Weigele PR, et al. Genomic analysis of oceanic cyanobacterial myoviruses compared with T4-like myoviruses from diverse hosts and environments. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12:3035–3056. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02280.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan MB, Lindell D, Lee JA, Thompson LR, Bielawski JP, Chisholm SW. Prevalence and evolution of core photosystem II genes in marine cyanobacterial viruses and their hosts. PLoS Biol. 2006;4:e234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun SL, Chen J, Li WZ, Altintas I, Lin A, Peltier S, et al. Community cyberinfrastructure for Advanced Microbial Ecology Research and Analysis: the CAMERA resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:D546–D551. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttle CA. Marine viruses—major players in the global ecosystem. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:801–812. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suziedeliene E, Suziedelis K, Garbenciute V, Normark S. The acid-inducible asr gene in Escherichia coli: transcriptional control by the phoBR operon. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:2084–2093. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.7.2084-2093.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetu SG, Brahamsha B, Johnson DA, Tai V, Phillippy K, Palenik B, et al. Microarray analysis of phosphate regulation in the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH8102. ISME J. 2009;3:835–849. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson AW, Huang K, Saito MA, Chisholm SW. Transcriptome response of high- and low-light-adapted Prochlorococcus strains to changing iron availability. ISME J. 2011a;5:1580–1594. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson LR, Zeng Q, Kelly L, Huang KH, Singer AU, Stubbe J, et al. Phage auxiliary metabolic genes and the redirection of cyanobacterial host carbon metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011b;108:E757–E764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102164108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolonen AC, Aach J, Lindell D, Johnson ZI, Rector T, Steen R, et al. Global gene expression of Prochlorococcus ecotypes in response to changes in nitrogen availability. Mol Syst Biol. 2006;2:53. doi: 10.1038/msb4100087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Mooy BA, Rocap G, Fredricks HF, Evans CT, Devol AH. Sulfolipids dramatically decrease phosphorus demand by picocyanobacteria in oligotrophic marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:8607–8612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600540103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigele PR, Pope WH, Pedulla ML, Houtz JM, Smith AL, Conway JF, et al. Genomic and structural analysis of Syn9, a cyanophage infecting marine Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Environ Microbiol. 2007;9:1675–1695. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson SJ, Rusch DB, Yooseph S, Halpern AL, Heidelberg KB, Glass JI, et al. The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Expedition: metagenomic characterization of viruses within aquatic microbial samples. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e1456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J, Sunda W, Boyle EA, Karl DM. Phosphate depletion in the western North Atlantic Ocean. Science. 2000;289:759–762. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5480.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng Q, Chisholm SW. Marine viruses exploit their host's two-component regulatory system in response to resource limitation. Curr Biol. 2012;22:124–128. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.11.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinser ER, Lindell D, Johnson ZI, Futschik ME, Steglich C, Coleman ML, et al. Choreography of the transcriptome, photophysiology, and cell cycle of a minimal photoautotroph, Prochlorococcus. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e5135. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.