Background: Annexin A2 is a phospholipid binding protein implicated in endo- and exocytosis.
Results: Annexin A2 induces microdomain formation and inward vesicle budding in giant unilamellar vesicles.
Conclusion: Specific lipid clustering and vesicle budding is triggered by annexin A2.
Significance: Membrane binding by the cytosolic protein annexin A2 can induce the formation of microdomains rich in cholesterol and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.
Keywords: Annexin; Calcium; Lipid Raft; Membrane Structure; Phospholipid Vesicle; Giant Unilamellar Vesicles; Membrane Budding; Membrane Curvature; Microdomain; Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate
Abstract
The formation of dynamic membrane microdomains is an important phenomenon in many signal transduction and membrane trafficking events. It is driven by intrinsic properties of membrane lipids and integral as well as membrane-associated proteins. Here we analyzed the ability of one peripherally associated membrane protein, annexin A2 (AnxA2), to induce the formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2)-rich domains in giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) of complex lipid composition. AnxA2 is a cytosolic protein that can bind PI(4,5)P2 and other acidic phospholipids in a Ca2+-dependent manner and that has been implicated in cellular membrane dynamics in endocytosis and exocytosis. We show that AnxA2 binding to GUVs induces lipid phase separation and the recruitment of PI(4,5)P2, cholesterol and glycosphingolipids into larger clusters. This property is observed for the full-length monomeric protein, a mutant derivative comprising the C-terminal protein core domain and for AnxA2 residing in a heterotetrameric complex with its intracellular binding partner S100A10. All AnxA2 derivatives inducing PI(4,5)P2 clustering are also capable of forming interconnections between PI(4,5)P2-rich microdomains of adjacent GUVs. Furthermore, they can induce membrane indentations rich in PI(4,5)P2 and inward budding of these membrane domains into the lumen of GUVs. This inward vesiculation is specific for AnxA2 and not shared with other PI(4,5)P2-binding proteins such as the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of phospholipase Cδ1. Together our results indicate that annexins such as AnxA2 can efficiently induce membrane deformations after lipid segregation, a mechanism possibly underlying annexin functions in membrane trafficking.
Introduction
Protein-mediated shape changes in membranes are key events in many biological processes ranging from budding and fusion of vesicles to the regulation of cell and organelle morphology. Two principle mechanisms can account for such protein-induced or protein-assisted alterations (1). First, proteins that can interact with integral membrane components and have the capability of self-assembly can induce membrane deformations. Typical examples are coat proteins such as clathrin or coatomer complexes, which assist the budding of vesicles in endocytosis and intracellular membrane trafficking, and proteins containing Bin/amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domains that can sense but also elicit membrane curvature (2–4). Second, amphipathic helices of integral or peripheral membrane-binding proteins can sense lipid packing defects or increased membrane curvature and insert into such sites. Thereby the membrane curvature is further increased, inducing membrane budding and finally fission (5).
Annexins are a family of cytosolic Ca2+-binding proteins that can interact peripherally and in a Ca2+-dependent manner with cellular membranes, preferentially with those containing negatively charged phospholipids. This property has been linked to annexin functions in membrane dynamics, in particular membrane transport and membrane domain formation (6). Ca2+ and lipid binding of annexins is mediated through a specific module, the annexin core domain, which shows a high degree of conservation between different annexin family members. The annexin core forms a slightly curved disc with the Ca2+ and lipid binding sites protruding from the convex side. The concave side of the disc is linked to the variable N-terminal domain that faces the cytosol in membrane-bound proteins and is accessible for interactions with binding partners, in some cases with members of the S100 family of small dimeric, EF-hand type Ca2+-binding proteins (6–8). Several annexins not only bind negatively charged phospholipids in the presence of Ca2+; they can also link two membrane surfaces and aggregate lipid vesicles. Annexin A2 (AnxA2)3 is the best-studied of these membrane aggregating annexins.
In cells AnxA2 can exist as a monomer that is predominantly located in the cytosol and on early endosomes (9) or as a heterotetrameric complex with the S100A10 protein (herein referred to as A2t) that is found in the subplasmalemmal region (10). The S100A10 binding site is restricted to the first 12 N-terminal residues of AnxA2, which form an amphipathic α-helix that is stabilized by posttranslational N-terminal acetylation (11–13). Both monomeric AnxA2 on endosomes and A2t at the plasma membrane are thought to function by organizing membrane domains in conjunction with an underlying actin cytoskeleton (14–17). The ability of AnxA2 to induce and/or stabilize certain membrane microdomains was directly addressed in in vitro approaches employing artificial membranes. Menke et al. (18, 19) showed by atomic force microscopy of planar lipid bilayers composed of phosphatidylcholines/phosphatidylserines that AnxA2 and A2t can induce lipid segregation. Upon Ca2+-dependent lipid binding, the proteins formed micrometer-sized domains that aggregated the protein-bound PS underneath them. Gokhale et al. (20) detected A2t-driven microdomain formation using giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs) and Texas Red-labeled A2t that formed micrometer-sized spots on the GUV membrane. The AnxA2-induced clustering of acidic phospholipids has been linked to a role of the protein in the formation and/or stabilization of so-called rafts (6, 21–23), membrane microdomains rich in glycosphingolipids, cholesterol, and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2). Another characteristic feature of Anx2 is the ability to aggregate lipid vesicles by forming regular junctions or interconnections between two membrane surfaces that were visualized by cryo-electron microscopy (24–25). These junctions most likely also reflect the molecular basis of the well documented chromaffin granule aggregation that is triggered by A2t and proteolytic derivatives representing the A2-core domain (26).
Here we employed GUVs of defined lipid composition and recombinantly expressed AnxA2 derivatives, namely AnxA2, the AnxA2 core domain, and A2t to analyze the molecular details of AnxA2-induced membrane domain formation. We show that all AnxA2 derivatives can induce PI(4,5)P2 segregation and that AnxA2 and PI(4,5)P2 are enriched at interconnection sites of aggregated GUVs. Cholesterol and glycosphingolipids are also recruited to AnxA2-induced microdomains. Furthermore, we show that AnxA2 is able to induce membrane indentations and the formation of PI(4,5)P2-rich vesicles that bud from the limiting membrane into the lumen of GUVs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Lipids
1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-choline(POPC), 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC),1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phosphoinositol-4,5-biphosphate](triammonium salt) (PI(4,5)P2), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-l-serine (sodium salt) (POPS), d-glucosyl-β-1,1′-N-oleoyl-d-erythro-sphingosine (C18:1 β-d-glucosyl-ceramide or glycosphingolipid), 2-(4,4-difluoro-5-methyl-4-bora-3a,4a-diaza-s-indiacene-3-dodecanoyl)-1-hexa-decanoyl-sn-gycero-3-phophocholine (BODIPY-PC), 1-oleoyl-2-[6-[4-(dipyrrometheneboron difluoride)butanoyl]-amino]hexanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (triammonium salt) (TopFluorPI(4,5)P2), and N-[11-(dipyrrometheneboron difluoride) undecanoyl]-d-glucosyl-β1–1′-d-erythro-sphingosine (TopFluor-glucosyl-ceramide or TopFluorCeramide) as well as 23-(dipyrrometheneboron difluoride)-24-norcholesterol (TopFluorChol) were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids Inc. (Alabaster, AL). Cholesterol, fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran (FITC-dextran, Mr 150) were supplied by Sigma, and [1,1′-dioctadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindo-carbocyanineiodide] (DiIC18) by Ana Spec Inc. (Fremont, CA).
Antibodies, Expression Constructs, Proteins, and Synthetic Peptides
Mouse monoclonal anti-AnxA2 antibodies directed against an N-terminal peptide (HH7 (10)) or the C-terminal core domain (BD Purified Mouse Anti-Annexin II, BD Transduction Laboratories) as well as mouse monoclonal anti-S100A10 antibodies (27) were employed to detect the respective proteins in Western blots. Goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated with IRDye 800CW (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE) were used as secondary antibodies. Bacterial expression of AnxA2 employed a construct of the human cDNA sequence cloned into the pSE420 expression vector (pSE420-AnxA2A66E (28). This sequence contained a glutamate-for-alanine substitution at amino acid 66 that was introduced to restore the epitope for a monoclonal antibody (29). The human cDNA sequence encoding S100A10 was cloned into the pKK223-3 vector (30). His-tagged proteins such as the human pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of phospholipase C δ1 were expressed via the pET-23a(+) expression vector. AnxA1 purified from bovine lung was purchased from Meridian Life Sciences Inc. (Memphis, TN) and dialyzed against the appropriate buffer for further experiments.
The N-terminal AnxA2 peptide (Ac-STVHEILCKLSLEG), representing the acetylated variant of residues 2–15 of AnxA2, was synthesized and HPLC-purified as described (31). After labeling with AlexaFluor® 568 C5-maleimide (Invitrogen), it was purified via preparative HPLC on an Agilent VariTide RPC PL1E12-A505 PLRP column. The correct amino acid composition was verified by electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy. The degree of labeling obtained was 1.0.
Generation of the AnxA2 Core Domain
The AnxA2 core construct was generated by deleting nucleotides 1–96 of the protein-coding region (corresponding to amino acids 1–32) using PCR-mediated mutagenesis. The pSE420-AnxA2A66E construct was used as the template in a KAPA HiFi PCR kit (KAPA Biosystems, Boston, MA) together with the forward primer (5′-CATGGTTTATTCCTCCTTATTTAATCGATAC-3′) and the reverse primer (5′-GATGCTGAGCGGGATGCTTTGAACATTGAAAC-3′) (Biomers, Ulm, Germany). PCR was performed in an Eppendorf Mastercycler DNA Engine Thermal Cycler PCR (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) employing an annealing temperature of 55 °C, 30 s annealing time, and 30 cycles. The PCR product was purified, ligated overnight with T4 DNA ligase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and transformed into bacteria. Plasmid DNA obtained from resistant colonies was sequenced to identify positive clones. Expression of the core construct was carried out as described below for full-length AnxA2 and confirmed by immunoblot analysis using specific antibodies.
Expression and Purification of Recombinant AnxA2
Escherichia coli DH5α cells were transformed with the pSE420-AnxA2A66E expression plasmid and grown in Luria Bertani (LB) medium supplemented with 150 μg/ml ampicillin to an A600 of 0.6 at 37 °C. Expression of recombinant protein was induced by the addition of isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside to a final concentration of 1 mm. After growing for 4 h, bacteria were harvested by centrifugation at 5000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. For purification, a previous protocol (28) was modified. The bacterial cell pellet was resuspended in lysis buffer (50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 300 mm NaCl, 10 mm MgCl2, 2 mm EGTA, 2 mm DTT, and complete protease inhibitor tablet (Roche Applied Science)) at a ratio of 3.0 ml of lysis buffer per gram of wet pellet. Bacteria were lysed by three time passages through a French press, and the lysate was centrifuged at 39.500 × g for 30 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was dialyzed against DE buffer (10 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 10 mm NaCl, 1 mm EGTA, 2 mm DTT) and incubated with DEAE cellulose equilibrated in the same buffer (DE52 Anion Exchange Cellulose, Whatman, Maidstone, UK). The unbound fraction was dialyzed against CM buffer (20 mm sodium acetate, pH 5.6, 10 mm NaCl, 1 mm EGTA, 2 mm DTT) and subjected to cation exchange chromatography on CM52 carboxymethyl cellulose (Whatman). The column containing bound protein was washed with CM buffer and CM buffer plus 100 mm NaCl followed by elution in CM buffer plus 600 mm NaCl. Fractions containing AnxA2 were identified by immunoblotting, concentrated using an Amicon Ultra-4 Centrifugal Filter Unit (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) and dialyzed against suitable buffer for further experiments. Typical yields of pure (>95%) AnxA2 were 4 mg per liter of cell culture. The protein concentration of AnxA2 was determined by absorption spectroscopy using an extinction coefficient of ∈280 = 0.7 cm2 mg−1 (32).
Expression and Purification of Recombinant S100A10
Human S100A10 was cloned into the vector pKK223-3 and expressed in E. coli cells (strain BL21(DE3)pLysS) and purified as described (30). Briefly, transformed bacteria were grown to an A600 of 0.6 at 37 °C in LB medium supplemented with 150 μg/ml ampicillin before protein expression was induced by adding 1 mm isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside. After incubation for 3–4 h at 37 °C, cells were harvested by centrifugation (5000 × g; 10 min) and resuspended in lysis buffer (200 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 200 mm NaCl, 1 mm MgCl2, 1 mm NaN3, 2 mm DTT, Complete EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Mixture (Roche Applied Science)). Cells were lysed by three time passages through a French press, and the remaining cellular debris was removed by centrifugation at 39.500 × g for 30 min. The supernatant was then dialyzed against DE2 buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 20 mm NaCl, 1 mm MgCl2, 1 mm NaN3, 2 mm DTT, Complete EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Mixture) and applied to a DEAE column (DEAE Sephacel, GE Healthcare) equilibrated in DE2 buffer. The flow-through was collected, dialyzed against CM2 buffer (20 mm sodium acetate, pH 5.6, 2 mm DTT, 0.5 mm EDTA, 0.5 mm EGTA, 1 mm NaN3) and applied to a CM2 column equilibrated in CM2 buffer. After washing with CM2 buffer and CM2 buffer plus 100 mm NaCl followed by CM2 buffer plus 300 mm NaCl, the protein was eluted with CM2 buffer containing 500 mm NaCl. The collected fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. S100A10-containing fractions (>90% purity as judged by Coomassie-stained SDS gels) were pooled, concentrated using an Amicon Ultra-4 Centrifugal Filter Unit (Merck Millipore), and dialyzed against the appropriate buffer for further experiments. Protein concentration of S100A10 was determined by absorption spectroscopy using an extinction coefficient of ∈280 = 0.26 cm2 mg−1 (32).
Expression and Purification of His-tagged PH Domain (PLCδ1)
Bacteria (E. coli BL21(DE3)pLysS) transformed with the pET-23a(+) expression vector encoding the His-tagged PH domain of phospholipase C δ1 (PLC-δ1) were grown at 37 °C in LB medium supplemented with 150 μg/ml ampicillin to an A600 of 0.6 before protein expression was induced with 0.5 mm isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside. After 16 h of expression at 26 °C, the PH domain was purified as described (15) with slight modifications. Briefly, cells were lysed by freeze-thaw cycles and sonication in lysis buffer (50 mm NaH2PO4, 10 mm imidazole, pH 7.5, 300 mm NaCl), and the lysates were clarified by centrifugation at 39.500 × g for 30 min at 4 °C. Thereafter, the supernatant was incubated with equilibrated nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid-agarose beads (Qiagen) for 1 h at 4 °C, beads were washed twice with washing buffer (50 mm NaH2PO4, 20 mm imidazole, pH 7.5, 300 mm NaCl), and protein was eluted with washing buffer containing 250 mm imidazole and dialyzed against the appropriate buffer for further experiments.
A2t Reconstitution
Bacterially expressed and purified AnxA2 and S100A10 were dialyzed against gel filtration buffer (phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.4, 2 mm DTT) and concentrated using the Amicon Ultra-15 device. An equimolar mixture containing 2 mg of total protein was incubated for 1 h at 4 °C to reconstitute the complex and then subjected to size exclusion chromatography (Superdex 75 10/300 GL, GE Healthcare). The fractions obtained (0.5 ml) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie staining, and fractions containing the assembled A2t complex, as verified by the presence of both subunits, were pooled and dialyzed against the appropriate buffer for further experiments. Protein concentration of A2t was determined by absorption spectroscopy using an extinction coefficient of ∈280 = 0.65 cm2 mg−1 (32, 33).
Labeling of Proteins
Proteins (except PH domain, see below) and the Ac2–15 peptide were labeled by incubation with a 10× molar excess of AlexaFluor® 568 C5-maleimide (Invitrogen) in PBS, pH 7.4, overnight at 4 °C. Residual dye was quenched by the addition of a 10× excess of β-mercaptoethanol for 20 min at 4 °C. Subsequently, protein was separated from unreacted dye by size exclusion chromatography using NapTM SephadexTM G25 DNA-Grade (GE Healthcare) columns. Protein concentrations were determined by cprotein (mg/ml) = (A280 − (Amax × CFdye))/ϵ280) with CFdye = A280/Amax = 0.417, and Amax = 576 nm. The degree of labeling (mol of dye/mol of protein) was estimated using cprotein (mg/ml) = (Amax × ϵprot)/((A280 − Amax × CFdye) × ϵmax) with ϵmax = 92.000 m−1cm−1, and ϵprot = ϵ280 × Mr prot. Cysteine labeling of the PH domain of PLCδ1 led to a loss of membrane affinity presumably due to conformational alteration or the modification of residues important for lipid binding. Therefore, the DyLightTM 594 microscale antibody labeling kit (DyLight 594 NHS Ester, Thermo Scientific/Pierce) was used instead, and this led to successful labeling with the labeled protein showing GUV binding. Briefly, PH domain (20 μm) in imidazole buffer (250 mm imidazole, 300 mm NaCl, 50 mm NaH2PO4, pH 7.5) was mixed with the reagent according to manufacturer's protocol but without changing the pH and incubated for 3.5 h at room temperature. Separation from unreacted dye was then performed using a purification resin according to manufacturer's protocol. Proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE gels to verify labeling and purity. The following degrees of labeling were obtained: AnxA2, 0.58; AnxA2core, 0.50; A2t, 1.19; S100A10, 0.1; PH domain (PLCδ1), 0.47; AnxA1, 0.55.
GUV Formation
GUVs were prepared using a modified protocol of electroformation (34, 35) or gentle swelling on agarose (36). Briefly, lipid mixtures were prepared from 5 mm stock solutions, spread onto indium tin oxide-covered slides (Präzisions Glas & Optik GmbH, Iserlohn, Germany), and dried under a vacuum for 60 min at 50 °C. After hydration with 304 mm sucrose, 1 mm HEPES, pH 7.4, electroformation using 1V peak to peak rectangular 10 Hz AC voltage (LXI 33220A Frequency Generator, Agilent, Böblingen, Germany) was performed for 1 h at 50 °C. Waveform quality was monitored using a digital Oscilloscope (Textronix TDS 3032B, Beaverton, OR). For agarose swelling, a uniform and thin film of agarose was prepared on a glass slide using a 1% w/v solution of ultra low gelling agarose (Sigma A2576) in double distilled H2O at 50 °C. The lipid mixture was added to the agarose film and allowed to dry for 30 min in a vacuum at 50 °C. Subsequently, the slide was equilibrated in the appropriate buffer for 1 h. GUVs were always prepared freshly at the day of the respective experiment to minimize the risk of lipid degradation. All GUV solutions were diluted 1:4 with PBS, pH 7.4, and contained 250 μm CaCl2 if not otherwise stated. Due to differences in the refractive index, sucrose-containing GUVs that were diluted with PBS exhibit a prominent halo, enabling a distinction between intra-luminal vesicles (ILVs) originating from preparation and ILVs induced by adding protein together with the PBS. Agarose swelling in pure PBS buffer without any sucrose content did not alter the results.
The usual GUV lipid mixture (GLM) consisted of POPC/DOPC/POPS/cholesterol/PI(4,5)P2 (38.4%:19.2%:20%:19.2%:3%) doped with 0.2 mol % of TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 or 0.2 mol % of TopFluorChol if not otherwise stated. Experiments directed at analyzing the behavior of glycosphingolipids employed a lipid mixture of POPC/DOPC/POPS/cholesterol/PI(4,5)P2/C18:1 β-d-glucosyl-ceramide (33.8%:20%:20%: 20%:3%:3%) doped with 0.2 mol % of TopFluor-glucosyl-ceramide (GLM II). All GUV measurements were carried out under the same conditions at 20 °C, typically 15 min after preparation on the coverslip. Exchanging Hepes-buffered saline for PBS had no effect on the measurement.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
CLSM employed a Leica DMRE with a TCS SL scanning unit equipped with a PH HCX PL APO CS 63.0 × 1.32 OIL PH3UV objective (Leica Microsystems Heidelberg GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). For excitation, a 488-nm argon laser and a 543-nm helium-neon laser were used with a conservative separation of band pass filters to minimize risk of cross-talk. Band pass (bp) filters were set to 495–535 nm for the green channel (TopFluorPI(4,5)P2, TopFluorChol, and BODIPY-PC) and 620–750 nm for the red channel (AlexaFluor® and DyLightTM dye). Flow chamber experiments were performed using a POC-R2 flow chamber (Pecon, Erbach, Germany) on a Zeiss LSM 780 microscope equipped with an Pln Apo 63×/1.4 oil DICII M27 objective as well as an argon laser (LASOS RMC 7812 Z2) and a DPSS 561-10 laser (Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Jena, Germany). Specimen excitation was performed using the 488-nm argon laser and the 561-nm DPSS laser line with band pass filters adjusted to 495–555 nm (FITC-dextran) and 620–750 nm (AlexaFluor®).
Superresolution Structured Illumination Microscopy (SR-SIM)
SR-SIM was performed on a Zeiss AxioObserver Z.1-Elyra S.1 system equipped with a pln Apo 63×/1.4 oil DIC M27 objective. For excitation. a 488- and 561-nm diode laser was used (Carl Zeiss Microscopy). Images were recorded using a 28-μm grid and bp 495–550 for the 488-nm laser and a 34-μm grid, bp 570–620 for the 561-nm laser. Structured illumination was performed with three rotations and five phases (positions) of the grids. Images were then calculated using Zeiss ZEN 2010 D v.7.0 software (Carl Zeiss Microimaging GmbH 1997–2011, Jena, Germany).
Fluorescence Intensity Evaluation
The mean fluorescence intensity of a circular area within the center of ILVs was calculated using ImageJ v. 1.44p (Wayne Rasband, National Institutes of Health).
RESULTS
Purification and Labeling of Recombinant AnxA2 Derivatives
To analyze lipid binding and aggregation properties of AnxA2 and derivatives thereof, we used fluorescently labeled GUVs (see below) and recombinantly expressed and fluorophor-labeled annexin and S100 proteins. Bacterial expression of AnxA2 and its mutants was achieved by using a system that faithfully executed the posttranslational N-terminal modifications seen in mammalian cells, i.e. removal of the starting methionine and acetylation of the new N-terminal serine residue (13). Correct N-terminal processing of full-length AnxA2 enabled efficient S100A10 binding and thus correct reconstitution of the heterotetrameric AnxA2-S100A10 complex (herein referred to as A2t). To visualize the different protein derivatives in comparison to TopFluor-labeled PI(4,5)P2 present in the GUVs, all annexin proteins examined (monomeric AnxA2, the AnxA2 core mutant, A2t, AnxA1, and the N-terminal AnxA2 peptide) were treated with the cysteine-selective dye AlexaFluor® 568 C5-maleimide, resulting in efficient labeling (not shown). AnxA2 contains four cysteine residues; two of those are exposed on the surface of the protein core, one is buried within the core domain and thus most likely inaccessible for the reagent, and one is located in the N-terminal S100A10 binding domain (PDB ID 1XJL) (37). The ligand S100A10 contains two cysteine residues, Cys-61 located at the beginning of the second EF-hand loop and Cys-82, found in a helix of the AnxA2 binding domain (12). Although AnxA2 and S100A10 could be labeled efficiently by AlexaFluor® C5-maleimide, gel filtration analysis revealed that none of the labeled species could be reconstituted with native AnxA2 or S100A10, respectively, to form a functional A2t complex (not shown). Thus, chemical modification of at least one of the exposed cysteines in AnxA2 (Cys-9, Cys-133, Cys-262) or S100A10 (Cys-61, Cys-82) interferes with complex formation. Therefore, to label A2t, the complex was first reconstituted from the purified individual subunits using established procedures (13) and then reacted with AlexaFluor® 568 C5-maleimide. This yielded a fluorescently labeled complex in which both subunits were modified (Fig. 1A). In the case of S100A10, this indicates that Cys-61 must have received the label, as the only other cysteine, Cys-82, had been shown before to be inaccessible for chemical derivatization in A2t (38).
FIGURE 1.
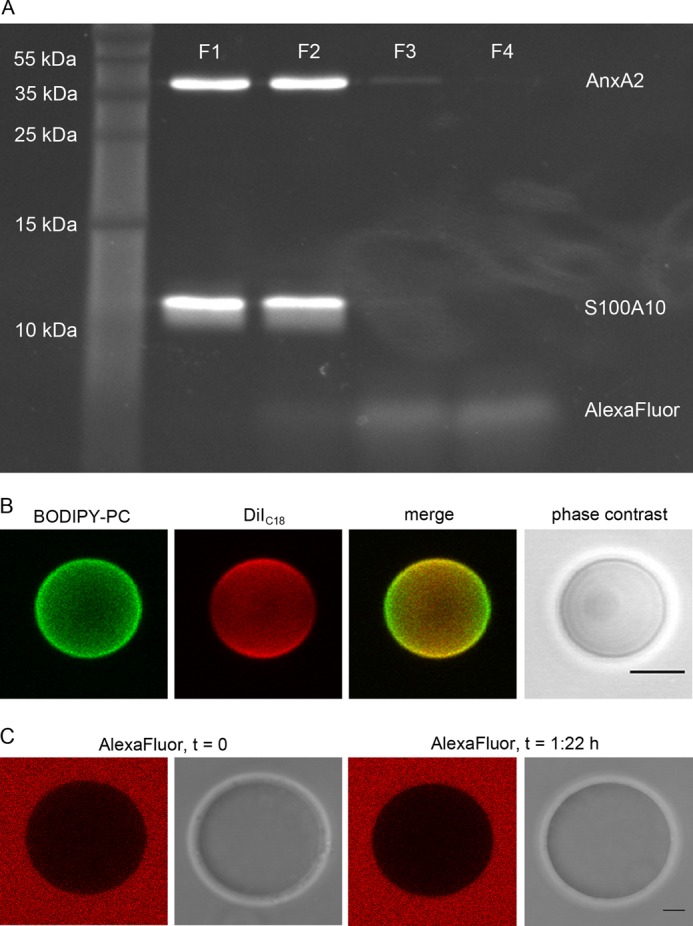
AlexaFluor® C5-maleimide labels both subunits in A2t, and the GUV lipid mixture employed shows no intrinsic phase separation. A, A2t was labeled by incubation with a 10-fold excess of AlexaFluor® C5-maleimide at 4 °C overnight, unbound dye was quenched with β-mercaptoethanol, and the mixture was then fractionized by size exclusion chromatography. The first four fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE and labeled proteins visualized by UV-light. B, GUVs composed of POPC/DOPC/POPS/cholesterol/PI(4,5)P2 (38.4%:19.2%:20%:19.2%:3%) (GLM) were labeled with 0.1% BODIPY-PC and 0.1% DiIC18 in the presence of 500 μm CaCl2 (two-dimensional projection of three-dimensional image). C, GUVs were incubated with an excess of 50 μm AlexaFluor® 568 dye (equatorial slice). Red images. AlexaFluor® 568; grayscale, associated phase contrast images. Note the equal distribution of the lipid dyes over the GUV membrane and the absence of AlexaFluor® 568 uptake into GUVs. Bars are 5 μm.
AnxA2 Induced Formation of Lipid Domains and Vesicle Interconnections
To record the formation of protein-induced membrane domains, we first established a homogeneous lipid bilayer system showing no intrinsic phase separation at 20 °C. We used GLMs that resembled to some extent the composition of the mammalian plasma membrane (21, 39), albeit not containing sphingomyelin, which is typically found in the extracellular leaflet and thus not in contact with cytosolic AnxA2. Furthermore, we wanted to generate a lipid mixture with a low probability of intrinsic phase separation and, therefore, employed a GUV lipid membrane consisting of POPC/DOPC/POPS/cholesterol/PI(4,5)P2 (38.4%:19.2%:20%:19.2%:3%), doped with 0.2 mol % TopFluorPI(4,5)P2. This system was first probed for intrinsic phase separation by adding phase selective dyes. For many lipid mixtures, BODIPY-PC is known to show a preference for the liquid disordered (ld) phase, whereas DiIC18 prefers to integrate into the liquid ordered (lo) over the ld phase when lipids with unsaturated fatty acids are present (40–42). Fig. 1B shows that the GLM chosen produces vesicles that exhibit a homogeneous distribution of these markers, indicating the absence of phase separation or vesicle pinching. Note the orientation-dependent fluorescence intensity of DiIC18 that is a result of the excitation probability using linear polarized laser light (photoselection), indicating directed incorporation into the bilayer. In contrast, the fluorophore of BODIPY-PC has a higher degree of rotational freedom leading to a homogeneous appearance around the vesicle. We also verified that the AlexaFluor® 568 dye used to label the proteins is not incorporated into the membrane even at prolonged incubation times (Fig. 1C). The presence of Ca2+ ions up to 500 μm did not induce phase separation or any longer (>2 μm) vesicle interconnections (sites of vesicle aggregation) in the absence of protein (Fig. 1B). However, increasing the PI(4,5)P2 levels to more than 10 mol % revealed a tendency to induce Ca2+-dependent PI(4,5)P2-containing phases in the absence of protein (not shown). Therefore, the above GLM with a PI(4,5)P2 content of 3% was chosen for further experiments.
Next we employed GUVs and AlexaFluor® 568-labeled AnxA2 derivatives (monomeric AnxA2, A2t, or the AnxA2core construct) to determine via fluorescence microscopic analysis parameters affecting protein binding to the membrane. Specifically, we varied the protein and Ca2+ concentration in the solution and the ratio of negatively charged lipids in the membrane system. As expected, these experiments revealed that higher amounts of the negatively charged anchor lipid POPS (5–20%) and high concentrations of CaCl2 (50–500 μm) resulted in higher GUV-bound AlexaFluor® 568 fluorescence, indicative of increased protein binding. Best signal-to-noise ratios were obtained with a system containing 3 mol % of PI(4,5)P2 and 20 mol % of POPS as lipid anchors in the model membrane, 250 μm Ca2+ in the buffer solution, and 80–100 nm AnxA2 or A2t. For the AnxA2 core and the PH domain, the concentration was adjusted to obtain similar vesicle affinity. Therefore, these parameters were kept constant in subsequent experiments.
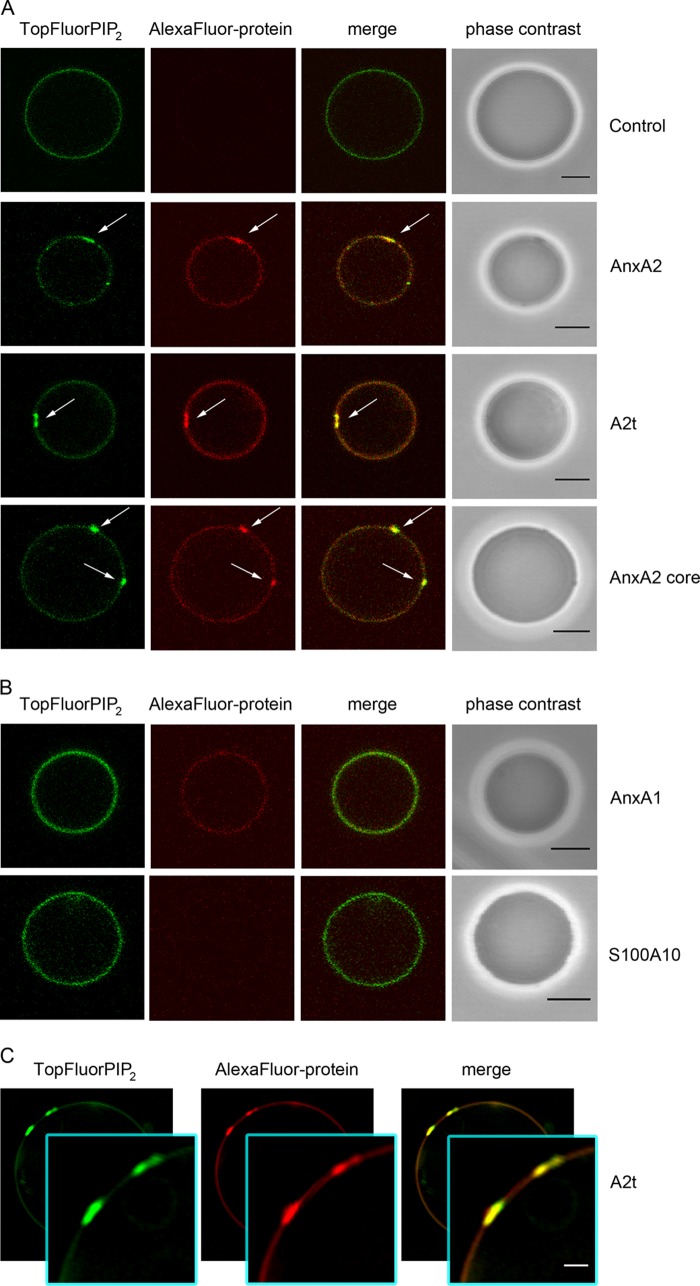
Using these conditions, all AnxA2 derivatives (AnxA2, A2t, AnxA2 core) induced the formation of 0.5–2 ± 0.2 μm large TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 domains that co-localized with the labeled proteins (Fig. 2A). The protein-induced PIP2 segregation is particularly evident in high resolution analysis employing SR-SIM (Fig. 2C). 25, 29, and 21% of the GUVs analyzed show such microdomain formation in the presence of AnxA2, A2t, and the AnxA2 core, respectively (Table 1). To verify that these effects were specific for AnxA2 and its derivatives, we carried out control experiments employing purified AnxA1, the closest homologue to AnxA2 in the annexin family. AlexaFluor® 568-labeled AnxA1, when added at the same concentrations (80–100 nm), also bound to the GUV membrane. However, in contrast to what was observed with AnxA2, AnxA1 did not induce domain formation in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+ (Fig. 2B). AlexaFluor® 568-labeled S100A10, the smaller subunit of the A2t complex, was used as an additional control. This protein did not show any GUV binding and thus did not induce domains, further revealing the specific role of AnxA2 in PI(4,5)P2 binding and domain formation (Fig. 2B). The N-terminal domain of AnxA2 harbors an amphipathic helix (residues Ser-2 to Gly-14), and it has been speculated that such amphipathic helices in annexins or other membrane proteins can insert into membranes (4, 43). Therefore, we also analyzed whether a synthetic peptide comprising residues 2–15 of AnxA2 could interact with GUVs and possibly induce lipid segregation. However, no binding of AlexaFluor® 568-labeled peptide was observed even at high peptide concentrations (supplemental Fig. S1). This result was supported by liposome-pelleting experiments that revealed no interaction of the unmodified peptide with POPC/DOPC/POPS/cholesterol (40:20:20:20) liposomes. Together these experiments show that the core domain of AnxA2 is responsible for triggering the formation of PI(4,5)P2-rich domains in lipid bilayer systems showing no intrinsic phase separation.
FIGURE 2.
AnxA2 derivatives induce protein/PI(4,5)P2-rich domains on GUVs. GLM GUVs doped with 0.2 mol % TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 were incubated with AlexaFluor® 568-labeled proteins in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+. The distribution of TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 and AlexaFluor® 568-labeled protein over the GUV membrane was analyzed by CLSM and SR-SIM. A, shown are is microdomains induced by AnxA2 (90 nm), A2t (81.6 nm), and the AnxA2 core Δ32 (895 nm). B, membrane-bound AnxA1 (87.5 nm) does not induce microdomain formation, and S100A10 (216.6 nm) shows no membrane affinity. Note the formation of domains rich in PI(4,5)P2 and protein induced by AnxA2, AnxA2 core, and A2t (white arrows) but not by AnxA1 or S100A10. Control: GUVs without protein. Bars correspond to 5 μm. C, SR-SIM images of A2t induced microdomains rich in PI(4,5)P2. The insets show higher magnifications of two microdomains, 1.1 ± 0.1 and 1.3 ± 0.1 μm in size. Bar, 1 μm. The full image covers 17.5 × 17.5 μm.
TABLE 1.
Frequency of protein-induced microdomains, interconnection sites, and ILVs on GUVs
n is the number of vesicles analyzed in at least three independent experiments, and TF-chol corresponds to a GLM model where TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 is exchanged for TopFluor-cholesterol. In the GLM II model, C18:1 ß-d-glucosyl-ceramide is added, and TopFluorCeramide is used as label.
| Protein derivative | GUVs containing protein-induced microdomains | GUVs containing protein-induced interconnection sites | GUVs containing ILVs (with uptake of outside medium) |
|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | % | |
| AnxA2 (n = 152, GLM) | 25 | 9 | 9 |
| AnxA2 (n = 44, TF-chol) | 20 | 5 | 7 |
| A2t (n = 142, GLM) | 29 | 8 | 12 |
| A2t (n = 171, GLM II) | 15 | 9 | 5 |
| A2t (n = 43, TF-chol) | 19 | 9 | 5 |
| AnxA2 core (n = 134, GLM) | 21 | 4 | 5 |
| GUVs w/o protein (n = 215, GLM, TF-chol) | 0 | 0 | <1 |
| GUVs w/o protein (n = 134, GLM II) | 0 | 0 | <1 |
PI(4,5)P2 is a lipid shown to directly bind AnxA2 (15, 44), and any AnxA2 clustering is thus expected to also cluster PI(4,5)P2. To determine whether other lipids that do not directly bind AnxA2 but are found in raft microdomains are also clustered after the AnxA2-PI(4,5)P2 interaction, we replaced TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 by TopFluor-cholesterol and recorded the cholesterol distribution in relation to that of AlexaFluor® 568-A2t. Whereas the GUV membrane showed a uniform cholesterol distribution in the absence of protein, A2t induced an accumulation of cholesterol underneath the protein clusters, indicating the presence of raft-like lipid domains that are formed upon A2t-PI(4,5)P2 interaction and clustering (Fig. 3A, Table 1).
FIGURE 3.
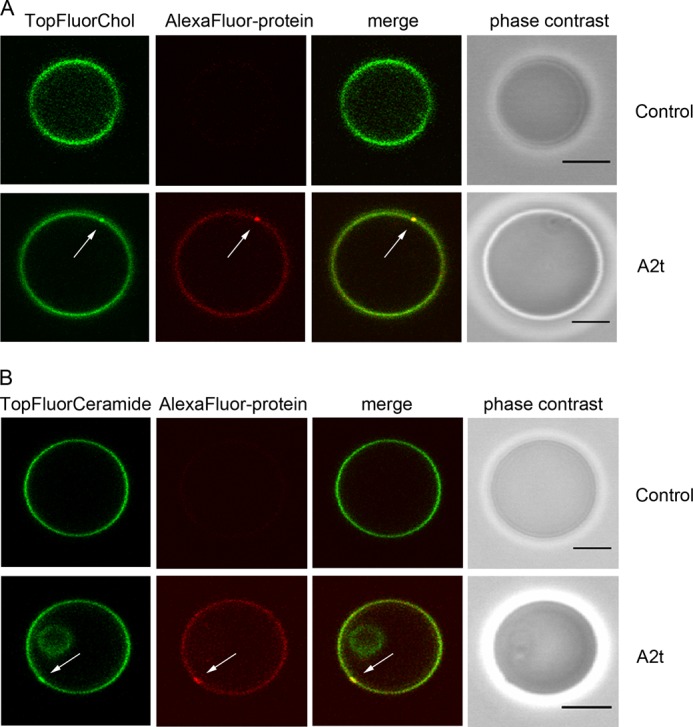
A2t induces protein/cholesterol/glycosphingolipid-rich domains on GUVs. A, GLM GUVs doped with 0.2 mol % of TopFluorChol and prepared on agarose were incubated with AlexaFluor® 568-labeled A2t (64.2 nm) in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+. B, GUVs composed of POPC/DOPC/POPS/cholesterol/PI(4,5)P2/C18:1 β-d-glucosyl-ceramide (33.8%:20%:20%:20%:3%:3%) doped with 0.2 mol % of TopFluor-glucosyl-ceramide (TopFluorCeramide) (GLM II) and prepared on agarose were incubated with 64.2 nm AlexaFluor® 568-labeled A2t in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+. Microdomains rich in cholesterol or glycosphingolipid are highlighted by white arrows. Bars are 5 μm.
Another class of lipids known to be enriched in raft-like membrane domains are glycosphingolipids (23). Therefore, we also analyzed whether glycosphingolipids are co-recruited to the AnxA2/PIP2 clusters by employing GUVs consisting of POPC/DOPC/POPS/cholesterol/PI(4,5)P2/C18:1 β-d-glucosyl-ceramide (33.8%: 20%:20%:20%:3%:3%) (GLM II) doped with 0.2 mol % of TopFluor-glucosyl-ceramide. Again, the homogeneous distribution of labeled lipid seen in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+ and absence of protein was altered by the addition of AlexaFluor® 568-labeled A2t with glycosphingolipid- and A2t-rich microdomains being easily discernible (Fig. 3B, Table 1). The intensity of TopFluorChol and TopFluor-glucosyl-ceramide label in the microdomains appears somewhat less as compared with that of TopFluorPI(4,5)P2. This most likely reflects the fact that the latter directly interacts with the domain-inducing annexin, whereas cholesterol and glycosphingolipids are indirectly sequestered in the course of raft domain formation (45).
In addition to triggering the formation of PI(4,5)P2-, cholesterol- and glycosphingolipid-rich domains, the A2t complex, monomeric AnxA2, and the AnxA2 core construct were also able to induce vesicle-vesicle interactions and the formation of extended membrane interconnections enriched in both TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 and AlexaFluor® 568-AnxA2 (Fig. 4). 9, 8, and 4% of the GUVs analyzed are engaged in such interconnections in the presence of AnxA2, A2t, and the AnxA2 core, respectively (Table 1). In contrast, no evidence for membrane interconnections was found when AnxA1 was added to the GUV preparations under the same conditions. Interestingly, the membranes at sites of vesicle contact (interconnections) appeared relatively flat in comparison to the curved GUV, in particular when the connected vesicles were of similar size, suggesting a regular protein array forming at the site of membrane linkage. This is consistent with the arrangement of A2t and AnxA2 at intermembrane junctions that were visualized by high resolution cryo-electron microscopy (24).
FIGURE 4.
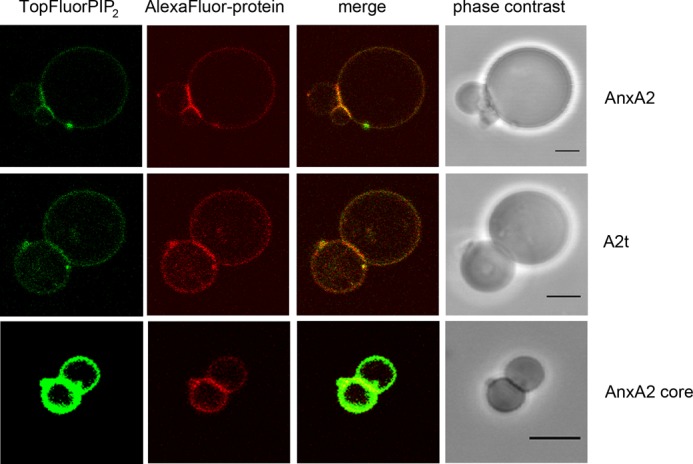
Interconnections between GUVs induced by AnxA2 derivatives. GUVs containing 0.2 mol % TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 were incubated with AlexaFluor® 568-labeled AnxA2 (90 nm), A2t (81.6 nm), or the AnxA2 core domain Δ32 (914 nm) in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+ and then inspected by fluorescence microscopy. Note the formation of interconnections/junctions induced by the different AnxA2 derivatives. These junctions are rich in protein and PI(4,5)P2. Bars, 5 μm.
AnxA2 Induces Membrane Indentation and Inward Vesicle Budding
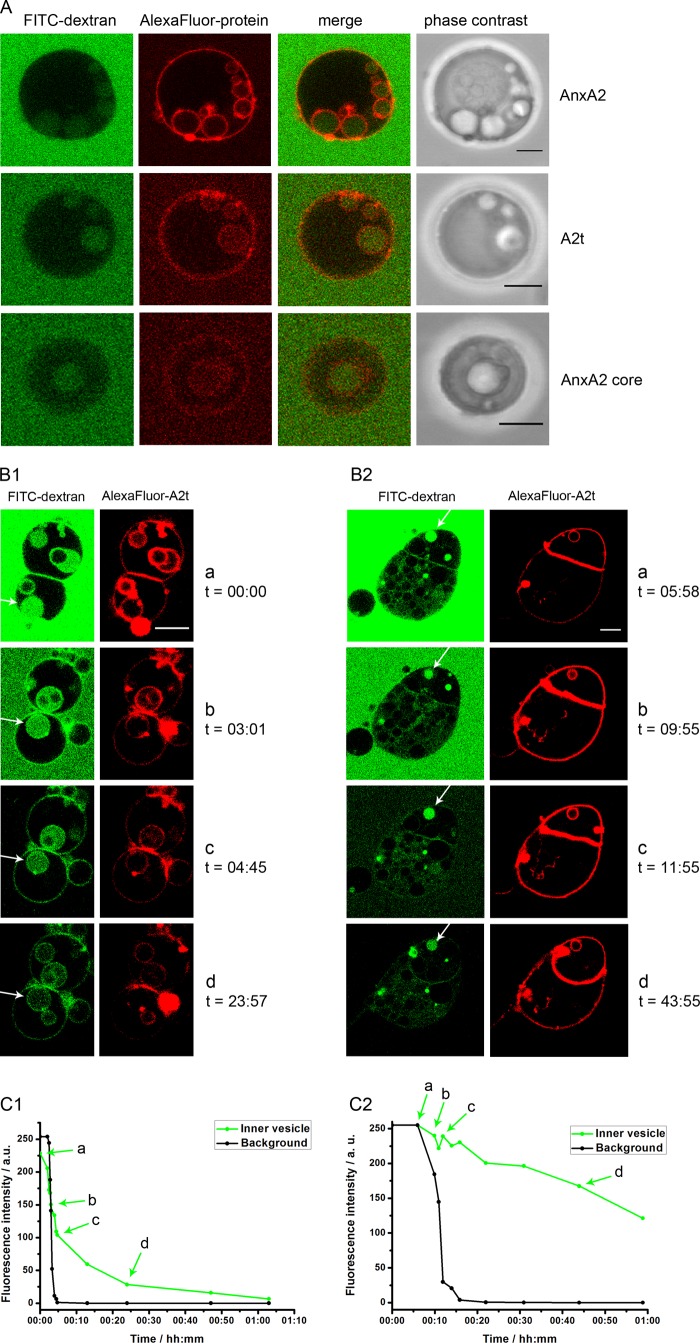
Upon closer inspection of GUVs treated with different AnxA2 derivatives we noted the appearance of intra-luminal vesicles of different sizes that were also discernible in phase contrast images (Fig. 5A). Protein-induced ILVs were observed in ∼9, 12, and 5% of GUVs treated with AnxA2, A2t, and AnxA2core, respectively (Table 1). Interestingly, the ILVs showed enriched TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 and AlexaFluor® 568-AnxA2 fluorescence indicative of PI(4,5)P2 and AnxA2 or its derivatives being present on the inner surface of the ILV membrane (Fig. 5). The view that the AnxA2 proteins cover the inner membrane layer of ILVs was supported by the absence of AnxA2-covered interconnection sites between ILVs and the inner face of the limiting GUV membrane (Figs. 5A and 6A).
FIGURE 5.
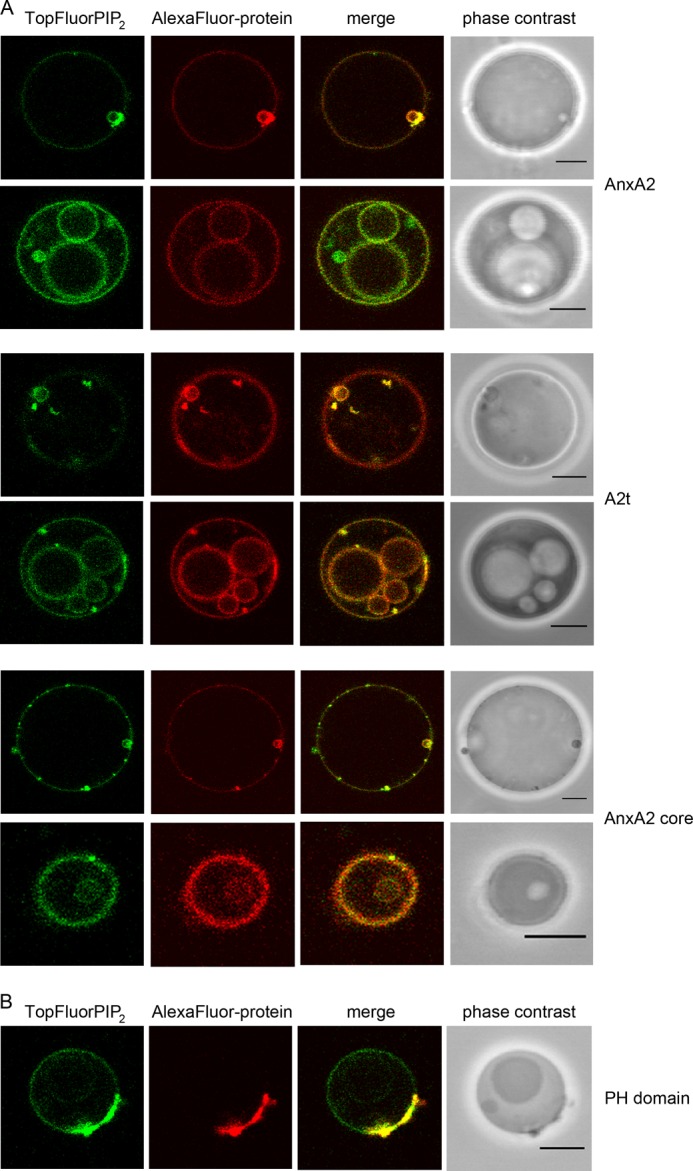
AnxA2-induced membrane budding. A, GUVs containing 0.2 mol % TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 were incubated with AlexaFluor® 568-labeled AnxA2 (91.3 nm), A2t (81.6 nm), or the AnxA2 core domain Δ32 (895 nm) in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+ and then analyzed by CLSM. Note the formation of ILVs positive for PI(4,5)P2 and AnxA2 derivatives. B, GUVs containing 0.2 mol % of TopFluorPI(4,5)P2 were incubated with DyLight™ 594-labeled PH domain (504 nm) in PBS and analyzed by CLSM. Note the presence of PI(4,5)P2/PH domain aggregates on the GUV membrane but the absence of protein-positive ILVs. Bars, 5 μm.
FIGURE 6.
Characterization of ILVs induced by AnxA2 and derivatives. A, unlabeled GUVs were kept in 1 mg/ml FITC-dextran (Mr 150) and incubated in the presence of 250 μm Ca2+ together with AlexaFluor® 568-labeled AnxA2 (91.3 nm), A2t (102 nm), or the AnxA2 core domain Δ32 (1371 nm). Note that the formation of ILVs is accompanied by the uptake of FITC-dextran. B, unlabeled GUVs were placed into a flow chamber and incubated with AlexaFluor® 568-labeled A2t (100 nm) in PBS containing 1 mg/ml FITC-dextran (Mr 150) and 250 μm Ca2+ for 30 min at 25 °C. Subsequently, the mixture was washed with PBS containing 250 μm Ca2+ without FITC-dextran, and decline of FITC fluorescence was recorded by on-line microscopy. C, fluorescence intensity profiles of ILVs is depicted by a white arrow in B with C1 corresponding to B1 and C2 corresponding to B2. Time point 0 denotes the start of the washing. The ILV fluorescence was measured in the center of each vesicle, and the background intensity was measured outside of the vesicles. Bars, 5 μm. a.u., absorbance units.
To determine whether the induction of ILVs is specific for AnxA2 and its derivatives (A2t, AnxA2 core), we analyzed whether another PI(4,5)P2-binding protein, the PH domain of PLCδ1, can also trigger the appearance of ILVs in PI(4,5)P2-containing GUVs. In contrast to AnxA2 or A2t, the incubation of GUVs with high concentrations of AlexaFluor® 568-labeled PH domain (504 nm) did not trigger the formation of ILVs (Fig. 5B). Rather, larger protein aggregations are found on the GUV membrane, and these sites are also positive for PI(4,5)P2 (Fig. 5B).
Our above approaches reveal that AnxA2, A2t, and AnxA2core can induce the appearance of ILVs in GUVs containing PI(4,5)P2 and that this activity of AnxA2 is not a property shared by other PI(4,5)P2-binding proteins. However, although some ILVs appear to have pinched off from the limiting GUV membrane, the microscopic analysis does not allow a clear distinction between deeply invaginated GUV membranes appearing as internal vesicles and vesicles that have actually sealed off from the limiting membrane. To distinguish between these possibilities we incubated the GUVs with the different protein derivatives in a solution containing FITC-dextran that was unable to penetrate the GUV membrane (supplemental Fig. S2). Protein-induced ILV formation was accompanied by an uptake of FITC-dextran into ILVs (Fig. 6A, control; supplemental Fig. S2) in line with the formation of ILVs through inward indentation of the limiting GUV membrane, i.e. away from the surrounding, FITC-dextran containing medium. Next, the FITC-dextran medium was replaced with label-free solution, and the decline of FITC fluorescence in the ILVs was recorded over time by online microscopy of the GUVs. Fig. 6, B and C, reveal that two types of FITC-dextran-labeled ILV populations are discernible; one, in which the internal (FITC-dextran) fluorescence was lost with a relatively fast kinetic in the range of minutes, and a second, in which the fluorescence signal remained trapped in the ILVs for an extended period of time. In fact, when fluorescence bleaching is taken into account, the FITC fluorescence in the second type of ILVs remained basically unchanged for 1 h. This indicates that at least the latter ILVs, which formed in response to A2t treatment, have no connection to the external milieu and thus are indeed bona fide vesicles that had pinched off the limiting GUV membrane.
DISCUSSION
The Ca2+-dependent binding of AnxA2 to membranes containing negatively charged phospholipids has been documented in many systems. These include chromaffin granule membranes and liposomes of different lipid composition (26, 46) but also solid-supported membranes and GUVs (18–20). In cells the protein has been linked to the formation and/or stabilization of membrane microdomains that are rich in PI(4,5)P2 and cholesterol. Such domains are found in the plasma membrane and in endosomal membranes and are often enriched at sites of membrane association with an underlying actin cytoskeleton (14–15, 47). Thus, AnxA2 is not only considered to be a membrane microdomain (raft) marker but also a protein capable of inducing larger raft clusters (6, 21–22). Although it has been speculated that such clustering is driven by intrinsic protein properties, the actual formation of AnxA2/lipid clusters on membranes has so far only been shown by employing atomic force microscopy on solid-supported membranes (19) and microscopic analysis of GUVs containing fluorescent lipids (20). To map the protein domain responsible for mediating lipid segregation, we now extended these analyses by using different AnxA2 derivatives and GUVs of defined lipid composition resembling to some extent the plasma membrane of animal cells. We show that AnxA2 induces the formation of larger PI(4,5)P2-, cholesterol-, and glycosphingolipid-containing domains and that the protein is enriched at sites of membrane-membrane contact (interconnection sites). Such contacts indicate that AnxA2 can induce GUV aggregation by linking two membrane surfaces similar to what has been observed before by cryo-electron microscopy (24, 25). PI(4,5)P2 clustering and GUV aggregation was observed even more efficiently for the A2t complex, indicating that S100A10 binding to the N-terminal domain of AnxA2 enhances the lipid segregation properties of AnxA2, possibly by physically linking two membrane binding AnxA2 moieties.
Interestingly, mutational analysis and the use of synthetic peptides show that the core domain of AnxA2 is not only necessary but also sufficient to trigger PI(4,5)P2 domain formation and GUV aggregation. Thus, the N-terminal amphipathic α-helix in AnxA2 that had been discussed to be required for AnxA2-mediated membrane aggregation by providing a second membrane binding site is dispensable for this property. Because AnxA2 cores most likely contain only one membrane binding site, core-induced GUV aggregation could be mediated by a zipper-like mechanism in which AnxA2 cores line up in an anti-parallel pattern with the membrane binding surface of one AnxA2 core bound to PI(4,5)P2 head groups of one GUV and the next AnxA2 core facing PI(4,5)P2 head groups of the opposing GUV with its membrane binding site (Fig. 7A1). Such an arrangement would predict that sites of protein-protein interaction exist in membrane-bound AnxA2 cores and that these interactions stabilize interconnection sites and thereby the bridging of adjacent GUVs. Indeed, high resolution structural analysis has revealed that two AnxA2 cores can associate in an upside down (or anti-parallel) fashion stabilized by interchain contacts (37). In contrast to AnxA2, AnxA1 is not capable of inducing PI(4,5)P2 domain formation and GUV aggregation. Although the N-terminal regions of AnxA1 and A2 are completely different, the two core domains show a considerable degree of similarity. However, significant structural and presumably also functional differences must exist as we show here that PI(4,5)P2 clustering can be triggered by the AnxA2 core but not by AnxA1 at 250 μm Ca2+. Possible structural differences that could account for this finding lie in the PI(4,5)P2 binding site that had been mapped in AnxA2 to encompass residues Lys-279 and Lys-281 (20). Lysine 279 is not conserved in AnxA1, and AnxA1 appears not to be capable of high affinity PI(4,5)P2 binding (15). Thus, the direct and high affinity interaction with a raft lipid might be the prerequisite for an annexin to induce microdomain formation. Future experiments have to reveal whether other raft lipid-binding annexins can also induce such microdomains.
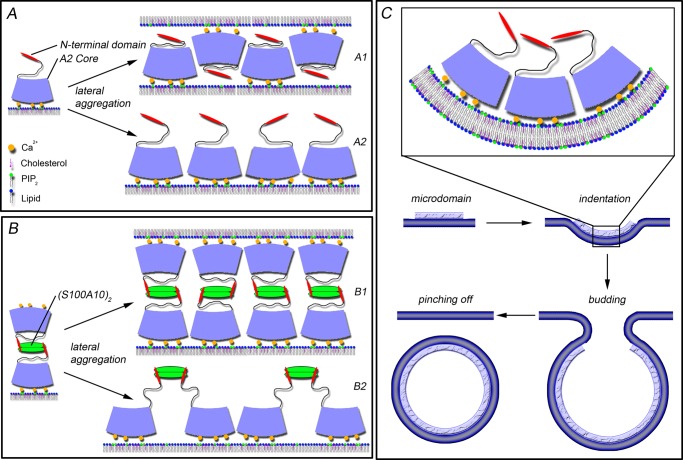
FIGURE 7.
Model of AnxA2- and A2t-driven microdomain formation and membrane budding. A, shown are lateral aggregates of AnxA2 formed in an anti-parallel (A1) or a parallel (A2) orientation on a membrane surface containing PI(4,5)P2 and cholesterol (25, 37). The anti-parallel configuration could induce membrane interconnections (A1), whereas both configurations cluster PI(4,5)P2 and cholesterol. B, shown are lateral aggregates of A2t. B1 depicts an orientation with one core subunit facing one and the other a second membrane thereby inducing membrane interconnections. B2 shows parallel aligned core subunits facing one membrane and inducing microdomain formation (25, 58). C, AnxA2 induced vesicle budding. Four steps are proposed: microdomain formation, indentation of the membrane, membrane budding, and eventually vesicle pinching off. Due to intrinsic curvature of the core domain, the parallel orientation of aggregated AnxA2 cores is expected to induce micro scale membrane bending.
Another unexpected observation was the presence of ILVs within GUVs that were induced by AnxA2, A2t, and AnxA2 cores. Similar structures were, for example, induced by the influenza virus M2 protein due to the activity of an amphipathic α-helix in M2 that inserted into the GUV membrane (48). The N-terminal amphipathic α-helix of AnxA2 could in principle also be capable of inserting into membranes, thereby causing membrane deformations leading eventually to membrane indentations. However, in contrast to what was observed for M2, the N-terminal helix in AnxA2 is unlikely to be involved in ILV formation for two major reasons. First, ILVs are formed most efficiently in response to treatment with the A2t complex, and in this complex the N-terminal α-helix of AnxA2 is engaged in a tight interaction with the S100A10 subunit and thus most likely not available for membrane insertion (12). Second, although less efficiently, the AnxA2 core domain lacking the N-terminal helix can also trigger membrane indentation and ILV formation, showing that the N-terminal domain is dispensable for this activity. Given the geometry of the AnxA2 core, which forms a slightly curved disc with the Ca2+/lipid binding sites located at the convex side, it seems plausible that parallel (side-by-side) association of membrane-bound AnxA2 cores can induce membrane bending, eventually leading to indentation and budding (Fig. 7, A2 and C). Thus, it appears that membrane-bound AnxA2 cores present in monomeric AnxA2 and the AnxA2 core constructs can assume two orientations, parallel or anti-parallel; the former would support membrane indentation, and the latter would form a rigid scaffold that can also provide binding sites for a second membrane surface (Fig. 7). In the case of A2t complexes, interconnection sites are most likely formed by two cores of one complex facing opposite GUV membranes (Fig. 7B1), whereas raft clustering and eventually also membrane indentation would require two cores of one complex binding to the same membrane (Fig. 7B2).
Both properties of AnxA2 are observed in our lipid binding studies, i.e. induction of membrane scaffolds and membrane indentations that can develop into vesicles, and are likely to be of relevance for intracellular AnxA2 activities. As AnxA2 is a cytosolic protein, any AnxA2-triggered membrane indentations must occur in a manner topologically leading to vesicle budding away from the cytosol. Such budding is relevant at endosomes leading to the formation of multivesicular endosomes and at the plasma membrane during microvesicle formation or when certain viruses bud from infected cells. Indeed, AnxA2 has been implicated in endosomal dynamics (17, 49–52), but a direct involvement in the formation of intra-luminal vesicles that bud off from the limiting endosomal membrane to sequester membrane proteins to the degradative pathway could not be demonstrated (53). However, several reports have linked AnxA2 to the budding of viruses and the formation of plasma membrane vesicles that are shed from cells. For example, AnxA2 was shown to interact with the Gag protein of HIV-1 at sites of PI(4,5)P2 containing lipid rafts and to increase virus production (54), and it is also found in microvesicles released from cancer cells (55). A scaffolding function of AnxA2 that can cluster PI(4,5)P2 and other interacting lipids into larger domains is likely to be of relevance in several membrane related signaling and transport events. These include the formation of actin assembly sites at the plasma membrane (14, 47), the organization of lipid domains (rafts) in sarcolemmal differentiation and during osteoblastic mineralization (56, 57), and the formation of rafts required for efficient exocytosis of dense core granules in neuroendocrine cells (16). Thus, the novel properties reported here for AnxA2 and its derivatives using artificial membrane systems could represent the molecular basis of AnxA2 activities observed in cells. Future studies analyzing the lipid aggregation/indentation induced by AnxA2 in cells have to substantiate this and have to address the question of how AnxA2 can switch from a scaffolding to a membrane budding activity.
Acknowledgments
We thank Rakesh Kumar Harishchandra for the initial introduction into different preparative methods, Julian Matern and Henning Mootz (University of Muenster) for help with HPLC, Thomas Zobel (University of Muenster) for introduction into SR-SIM, and David Grill for assistance with protein purification.
This work was supported by German Research Council Grant DFG SFB 858, Project B4.

This article contains supplemental Figs. S1 and S2.
- AnxA2
- annexin A2
- A2t
- annexin A2-S100A10 heterotetramer
- CF
- correction factor
- PI(4,5)P2
- phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
- GUV
- giant unilamellar vesicle
- PH
- pleckstrin homology
- POPC
- 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- DOPC
- 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
- PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2)
- 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phosphoinositol-4,5-biphosphate](triammonium salt)
- POPS
- 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-l-serine (sodium salt)
- CLSM
- confocal laser scanning microscopy
- SR-SIM
- superresolution structured illumination microscopy
- GLM
- GUV lipid mixture
- ILV
- intra-luminal vesicle.
REFERENCES
- 1. Zimmerberg J., Kozlov M. M. (2006) How proteins produce cellular membrane curvature. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 9–19 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Mim C., Unger V. M. (2012) Membrane curvature and its generation by BAR proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 37, 526–533 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Faini M., Beck R., Wieland F. T., Briggs J. A. (2013) Vesicle coats. Structure, function, and general principles of assembly. Trends Cell Biol. 23, 279–288 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Antonny B. (2011) Mechanisms of membrane curvature sensing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 80, 101–123 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Cornell R. B., Taneva S. G. (2006) Amphipathic helices as mediators of the membrane interaction of amphitropic proteins and as modulators of bilayer physical properties. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 7, 539–552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Gerke V., Creutz C. E., Moss S. E. (2005) Annexins: linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 449–461 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gerke V., Moss S. E. (2002) Annexins. From structure to function. Physiol. Rev. 82, 331–371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Raynal P., Pollard H. B. (1994) Annexins. The problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1197, 63–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Morel E., Gruenberg J. (2007) The p11/S100A10 light chain of annexin A2 is dispensable for annexin A2 association to endosomes and functions in endosomal transport. PLoS ONE 2, e1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Thiel C., Osborn M., Gerke V. (1992) The tight association of the tyrosine kinase substrate annexin II with the submembranous cytoskeleton depends on intact p11- and Ca2+-binding sites. J. Cell Sci. 103, 733–742 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Johnsson N., Marriott G., Weber K. (1988) p36, the major cytoplasmic substrate of src tyrosine protein kinase, binds to its p11 regulatory subunit via a short amino-terminal amphipathic helix. EMBO J. 7, 2435–2442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Réty S., Sopkova J., Renouard M., Osterloh D., Gerke V., Tabaries S., Russo-Marie F., Lewit-Bentley A. (1999) The crystal structure of a complex of p11 with the annexin II N-terminal peptide. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 6, 89–95 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Nazmi A. R., Ozorowski G., Pejic M., Whitelegge J. P., Gerke V., Luecke H. (2012) N-terminal acetylation of annexin A2 is required for S100A10 binding. Biol. Chem. 393, 1141–1150 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Oliferenko S., Paiha K., Harder T., Gerke V., Schwärzler C., Schwarz H., Beug H., Günthert U., Huber L. A. (1999) Analysis of Cd44-containing lipid rafts. Recruitment of annexin II and stabilization by the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 146, 843–854 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Rescher U., Ruhe D., Ludwig C., Zobiack N., Gerke V. (2004) Annexin 2 is a phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate binding protein recruited to actin assembly sites at cellular membranes. J. Cell Sci. 117, 3473–3480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Chasserot-Golaz S., Vitale N., Umbrecht-Jenck E., Knight D., Gerke V., Bader M.-F. (2005) Annexin 2 promotes the formation of lipid microdomains required for calcium-regulated exocytosis of dense-core vesicles. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 1108–1119 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Morel E., Parton R. G., Gruenberg J. (2009) Annexin A2-dependent polymerization of actin mediates endosome biogenesis. Dev. Cell 16, 445–457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Menke M., Ross M., Gerke V., Steinem C. (2004) The molecular arrangement of membrane-bound annexin A2-S100A10 tetramer as revealed by scanning force microscopy. Chembiochem 5, 1003–1006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Menke M., Gerke V., Steinem C. (2005) Phosphatidylserine membrane domain clustering induced by annexin A2/S100A10 heterotetramer. Biochemistry 44, 15296–15303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Gokhale N. A., Abraham A., Digman M. A., Gratton E., Cho W. (2005) Phosphoinositide specificity of and mechanism of lipid domain formation by annexin A2-p11 heterotetramer. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 42831–42840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kiessling V., Wan C., Tamm L. K. (2009) Domain coupling in asymmetric lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1788, 64–71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Kiessling V., Crane J. M., Tamm L. K. (2006) Transbilayer effects of raft-like lipid domains in asymmetric planar bilayers measured by single molecule tracking. Biophys. J. 91, 3313–3326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lingwood D., Simons K. (2010) Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327, 46–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Lambert O., Gerke V., Bader M.-F., Porte F., Brisson A. (1997) Structural analysis of junctions formed between lipid membranes and several annexins by cryo-electron microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 272, 42–55 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Lambert O., Cavusoglu N., Gallay J., Vincent M., Rigaud J. L., Henry J.-P., Ayala-Sanmartin J. (2004) Novel organization and properties of annexin 2-membrane complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 10872–10882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. (1988) Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature 331, 88–91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Osborn M., Johnsson N., Wehland J., Weber K. (1988) The submembranous location of p11 and its interaction with the p36 substrate of pp60 src kinase in situ. Exp. Cell Res. 175, 81–96 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Tran J. T., Rosengarth A., Luecke H. (2002) Cloning, purification, and crystallization of full-length human annexin 2. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 58, 1854–1857 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Thiel C., Weber K., Gerke V. (1991) Characterization of a Ca2+-binding site in human annexin II by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 14732–14739 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Kube E., Becker T., Weber K., Gerke V. (1992) Protein-protein interaction studied by site-directed mutagenesis. Characterization of the annexin II-binding site on p11, a member of the S100 protein family. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14175–14182 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. König J., Prenen J., Nilius B., Gerke V. (1998) The annexin II-p11 complex is involved in regulated exocytosis in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 19679–19684 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gerke V., Weber K. (1985) Calcium-dependent conformational changes in the 36-kDa subunit of intestinal protein I related to the cellular 36-kDa target of Rous sarcoma virus tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 1688–1695 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Ross M., Gerke V., Steinem C. (2003) Membrane composition affects the reversibility of annexin A2t binding to solid supported membranes. A QCM study. Biochemistry 42, 3131–3141 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Angelova M. I., Dimitrov D. S. (1986) Liposome electroformation. Faraday Discuss. Chem. Soc. 81, 303–311 [Google Scholar]
- 35. Kauscher U., Stuart M. C., Drücker P., Galla H.-J., Ravoo B. J. (2013) Incorporation of amphiphilic cyclodextrins into liposomes as artificial receptor units. Langmuir 29, 7377–7383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Horger K. S., Estes D. J., Capone R., Mayer M. (2009) Films of agarose enable rapid formation of giant liposomes in solutions of physiologic ionic strength. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 1810–1819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Rosengarth A., Luecke H. (2004) Annexin A2. Does it induce membrane aggregation by a new multimeric state of the protein? Annexins 1, 129–136 [Google Scholar]
- 38. Johnsson N., Weber K. (1990) Alkylation of cysteine 82 of p11 abolishes the complex formation with the tyrosine-protein kinase substrate p36 (annexin 2, calpactin 1, lipocortin 2). J. Biol. Chem. 265, 14464–14468 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. van Meer G., Voelker D. R., Feigenson G. W. (2008) Membrane lipids. Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 112–124 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Morales-Penningston N. F., Wu J., Farkas E. R., Goh S. L., Konyakhina T. M., Zheng J. Y., Webb W. W., Feigenson G. W. (2010) GUV preparation and imaging. Minimizing artifacts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1798, 1324–1332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Juhasz J., Davis J. H., Sharom F. J. (2012) Fluorescent probe partitioning in GUVs of binary phospholipid mixtures. Implications for interpreting phase behavior. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1818, 19–26 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Baumgart T., Hunt G., Farkas E. R., Webb W. W., Feigenson G. W. (2007) Fluorescence probe partitioning between Lo/Ld phases in lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768, 2182–2194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Rosengarth A., Gerke V., Luecke H. (2001) X-ray structure of full-length annexin 1 and implications for membrane aggregation. J. Mol. Biol. 306, 489–498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Hayes M. J., Merrifield C. J., Shao D., Ayala-Sanmartin J., Schorey C. D., Levine T. P., Proust J., Curran J., Bailly M., Moss S. E. (2004) Annexin 2 binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate on endocytic vesicles is regulated by the stress response pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 14157–14164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Levental I., Grzybek M., Simons K. (2011) Raft domains of variable properties and compositions in plasma membrane vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 11411–11416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Powell M. A., Glenney J. R. (1987) Regulation of calpactin I phospholipid binding by calpactin I light-chain binding and phosphorylation by p60v-src. Biochem. J. 247, 321–328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Zobiack N., Rescher U., Laarmann S., Michgehl S., Schmidt M. A., Gerke V. (2002) Cell-surface attachment of pedestal-forming enteropathogenic E. coli induces a clustering of raft components and a recruitment of annexin 2. J. Cell Sci. 115, 91–98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Rossman J. S., Jing X., Leser G. P., Lamb R. A. (2010) Influenza virus M2 protein mediates ESCRT-independent membrane scission. Cell 142, 902–913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Gruenberg J., Emans N. (1993) Annexins in membrane traffic. Trends Cell Biol. 3, 224–227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Harder T., Gerke V. (1993) The subcellular distribution of early endosomes is affected by the annexin II2p11(2) complex. J. Cell Biol. 123, 1119–1132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Zobiack N., Rescher U., Ludwig C., Zeuschner D., Gerke V. (2003) The annexin 2/S100A10 complex controls the distribution of transferrin receptor-containing recycling endosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 4896–4908 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Mayran N., Parton R. G., Gruenberg J. (2003) Annexin II regulates multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the degradation pathway of animal cells. EMBO J. 22, 3242–3253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. White I. J., Bailey L. M., Aghakhani M. R., Moss S. E., Futter C. E. (2006) EGF stimulates annexin 1-dependent inward vesiculation in a multivesicular endosome subpopulation. EMBO J. 25, 1–12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Harrist A. V., Ryzhova E. V., Harvey T., González-Scarano F. (2009) Anx2 interacts with HIV-1 Gag at phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate-containing lipid rafts and increases viral production in 293T cells. PLoS ONE 4, e5020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Sandvig K., Llorente A. (2012) Proteomic analysis of microvesicles released by the human prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11, 10.1074/mcp.M111.012914 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Draeger A., Monastyrskaya K., Burkhard F. C., Wobus A. M., Moss S. E., Babiychuk E. B. (2003) Membrane segregation and downregulation of raft markers during sarcolemmal differentiation in skeletal muscle cells. Dev. Biol. 262, 324–334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Gillette J. M., Nielsen-Preiss S. M. (2004) The role of annexin 2 in osteoblastic mineralization. J. Cell Sci. 117, 441–449 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Rescher U., Gerke V. (2008) S100A10/p11. Family, friends, and functions. Pflugers Arch. 455, 575–582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]