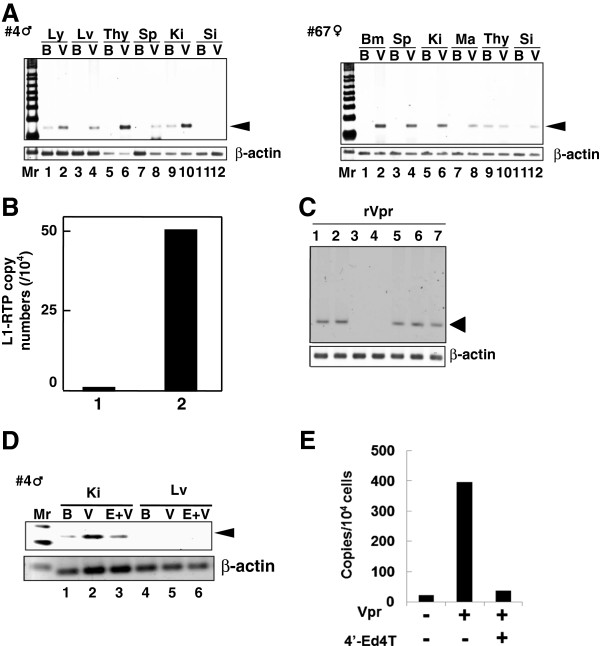
Figure 3.
L1-RTP induction by rVpr in vivo. A. Induction of L1-RTP after intraperitoneal injection of rVpr. rVpr (200 ng; three injections every 2 days) was administered intraperitoneally into two strains of hL1-Tg mice (#4 and 67). On day 2 after the last injection, DNA was extracted from each organ and subjected to the PCR-based assay. Ly, lymph node; Lv, liver; Thy, thymus; Sp, spleen; Ki, kidney; Si, small intestine; Bm, bone marrow; Ma, mammary gland; B, buffer; V, rVpr. Arrowhead indicates L1-RTP. Mr, molecular weight marker. B. Effects low dose of rVpr. hL1-Tg mice (#4) were injected six-times with buffer (lane 1) or 10 ng rVpr (lane 2), and DNA extracted from kidney was subjected to the qPCR analysis. C. RTIs blocked rVpr-induced L1-RTP. Effects of RTIs (25 μM each) on rVpr-induced L1-RTP was examined. Lane 1, 10 ng/mL rVpr + lamivudine; lane 2, rVpr + AZT; lane 3, rVpr + d4T; lane 4, rVpr + tenofovir; lane 5, rVpr + nevirapine; lane 6, rVpr + efavirenz, lane 7, rVpr + saquinavir. D. RTIs inhibited rVpr-induced L1-RTP in vivo. Two hours before intravenous administration of 250 ng rVpr, 50 μmoles of 4′-Ed4T was injected intraperitoneally. Lanes 1 and 4, buffer (B); lanes 2 and 5, rVpr (V); lanes 3 and 6, rVpr + 4′-Ed4T (E); Ki, kidney; Lv, liver. E. Results of qPCR assay. Similar experiments with Figure 2D were done, and L1-RTP was measured by the qPCR.