Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To examine physician-documented indications for cesarean delivery in order to investigate the specific indications contributing to this increase.
METHODS
We analyzed rates of primary and repeat cesarean delivery, including indications for the procedure, among 32,443 live births at a major academic hospital between 2003–2009. Time trends for each indication were modeled to estimate the absolute and cumulative annualized relative risk of cesarean by indication over time and the relative contribution of each indication to the overall increase in primary cesarean delivery rate.
RESULTS
The cesarean delivery rate increased from 26% to 36.5% between 2003 and 2009; 50.0% of the increase was attributable to an increase in primary cesarean delivery. Among the documented indications, nonreassuring fetal status, arrest of dilation, multiple gestation, pre-eclampsia, suspected macrosomia, and maternal request increased over time, while arrest of descent, malpresentation, maternal-fetal indications, and other obstetric indications (eg, cord prolapse, placenta previa) did not increase. The relative contributions of each indication to the total increase in primary cesarean rate were: Non-reassuring fetal status (32%), labor arrest disorders (18%), multiple gestation (16%), suspected macrosomia (10%), pre-eclampsia (10%), maternal request (8%), maternal-fetal conditions (5%), and other obstetric conditions (1%).
CONCLUSION
Primary cesarean births accounted for 50% of the increasing cesarean rate. Among primary cesareans, more subjective indications (nonreassuring fetal status and arrest of dilation) contributed larger proportions than more objective indications (malpresentation, maternal-fetal, and obstetric conditions).
INTRODUCTION
The cesarean delivery rate in the United States has steadily increased since 1996 when the rate was 21%.1 In 2007, the rate was the highest ever recorded at 32%, representing 1.4 million births and a 53% increase since 1996, 1 This trend encompasses increases in the cesarean rate for women of all ages, races, geographic areas, and gestational ages. Cesarean rates for 2007 by state range from a low of 22.2% in Utah to a high of 38.3% in New Jersey. All states experienced increases in cesarean rates between 1996 and 2007, and six states demonstrated increases of over 70%: Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Nevada, Rhode Island, and Washington.1
Many theories have been proffered to explain this trend including: a decrease in vaginal births after cesarean (VBAC), an increase in cesareans performed for maternal request, increased number of high-risk expectant mothers, the obstetrical medicolegal environment, and changes in provider practice patterns.1, 2 Studies examining differences in medical risk factors for expectant mothers, including obesity, have not concluded that changes in maternal risk profile explain the rising cesarean rate.3–6 Maternal request for elective cesarean also does not appear to account for the magnitude of the increased cesarean rate.7
Population studies largely rely on birth certificate or ICD-9 coding data,3, 7, 8 with neither source yielding accurate information about indication for cesarean delivery.9,10 These studies elucidate trends in repeat and primary cesarean rates, but are unable to differentiate indications for cesarean from conditions simply present during the antenatal or intrapartum period and thus are unable to accurately describe trends in specific indications, such as cesarean for maternal request11, labor arrest disorders, or fetal status. The physician’s rationale and documentation of indication for cesarean birth offers a unique and valuable perspective that may elucidate underlying trends in the use of cesarean that other data sources are unable to address. Studies examining physician-documented indications for cesarean are lacking.
The overall cesarean rate at our institution increased drastically between 2000–2003 (Figure 1), prompting our department to prospectively collect detailed data on indication for every cesarean performed starting in 2003. In this study, we examine physician-documented indications for cesarean birth at a major urban academic medical center in Connecticut, a state with one of the largest rate increases in the nation, to determine which specific indications contributed to the rise in our cesarean delivery rate over a seven year period.
Figure 1.
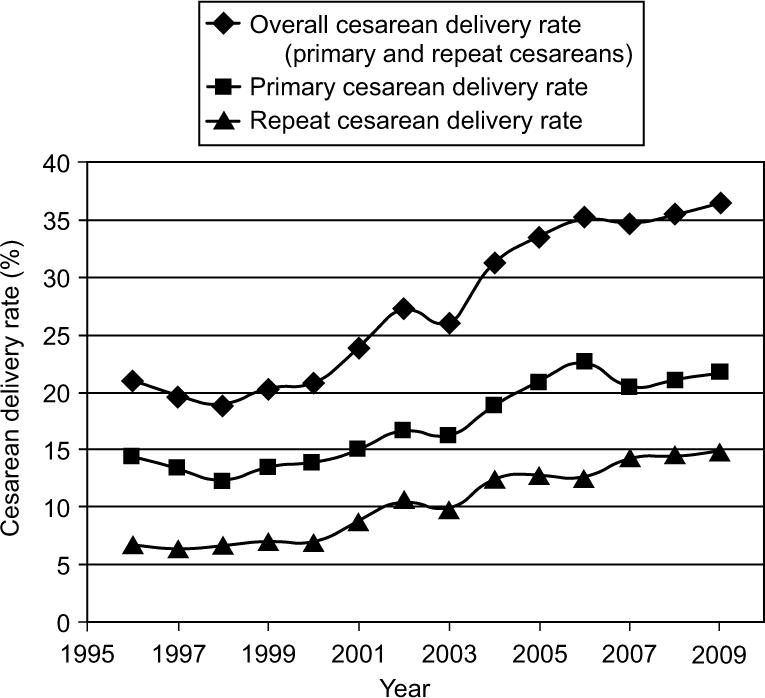
Cesarean delivery rates (%) were calculated for each year from 1996 to 2009. Cesarean rates represent number of cesarean births divided by total live births.
METHODS
From January 2003 through December 2009, data on all births occurring at Yale-New Haven Hospital were collected, including type of delivery and, if cesarean, indication for the procedure documented by the physician. Yale-New Haven Hospital is a tertiary-level academic center serving a diverse urban and suburban population and is the predominant referral center within a 50-mile radius. Community providers care for approximately two-thirds of all patients; the remainder are the responsibility of the full-time faculty of Yale School of Medicine.
Overall, primary, and repeat cesarean delivery rates and VBAC rates were calculated for each year. Cesarean rates were calculated as number of cesarean births divided by total live births.1 VBAC rate was defined as successful VBAC divided by the number of women who underwent previous cesarean delivery.12 Rates for each indication were calculated annually as the number of cesareans performed for each indication per 1,000 live births and, in the case of primary cesarean, per 1000 women at risk for primary cesarean (with no history of cesarean delivery).
Indications for cesarean delivery are recorded in the medical record, and/or the labor log and subsequently by a departmental nurse administrator exactly as documented by the physician in the medical record. The total number of live births, number of cesarean births (repeat and primary), and number of vaginal births after cesarean (VBACs) have been recorded in this way since 1996, and physician-documented indications for cesarean delivery have been compiled since 2003. In order to validate that recorded indications were accurate and consistent with indications recorded in the medical record, the medical records for all births occurring over three different periods corresponding to changes in personnel were compared with labor log and administrator recorded count data. All three data periods were > 99% consistent with the indication counts generated by medical record review. The Yale University Human Investigation Committee approved this protocol.
In all three data sources, indications are specifically recorded, such as “VP shunt” or “Crohn’s disease”. These indications occur with low frequency and in order to analyze them, we combined indications into larger representative categories. The final categories included: repeat cesarean, arrest of labor dilation or descent (including failed vacuum and failed forceps), non-reassuring fetal heart tracing (NRFHT), multiple gestation, suspected macrosomia, elective per maternal request, preeclampsia/eclampsia/HELLP, malpresentation, maternal/fetal indications, and obstetric indications. Malpresentation represents breech presentation, face presentation, transverse lie and unstable lie. Maternal indications are defined as maternal conditions predating the pregnancy that could complicate delivery (e.g. maternal cardiac disease, pseudotumor cerebri, maternal HIV). Fetal indications encompass antenatal problems preceding the intrapartum period (e.g. fetal anomalies and intra-uterine growth restriction (IUGR)). Obstetric indications are defined as conditions brought about by the presence of the current intrauterine pregnancy (e.g. placental abruption, accreta, and previa, cord prolapse). Preeclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP syndrome are represented in a distinct category due to their higher frequency. Suspected macrosomia was defined by the provider based on either an ultrasound derived estimated fetal weight or a clinical estimated fetal weight. During this time period, the prevailing definition of macrosomia was greater than 5,000 grams for non-diabetics and greater than 4,500 grams for diabetics, and at such thresholds cesarean was encouraged. Cesarean was non-directively offered, though not necessarily encouraged, at thresholds of 4500 grams in non-diabetics and 4000 grams in diabetics, and in some circumstances even lower thresholds were employed.
Cesarean delivery rates among university, high-risk, and private patients were also compared. University patients are defined as those patients who received care from the hospital service in which residents and faculty midwives provide care, supervised by generalist obstetrician/gynecologists in the outpatient setting and by maternal-fetal medicine specialists (acting as hospitalists) during labor and birth. High-risk patients are those patients with high-risk conditions cared for by the same maternal-fetal medicine specialists. Private patients are defined as having providers who practice in the community in a non-hospital-owned practice setting; midwives and physicians in these practices are generalists. Of note, these categories were defined by provider type rather than type of insurance coverage.
Trends in primary cesarean delivery rates were examined as the number of cesareans performed for each indication with respect to the total number of women at risk for primary cesarean delivery annually. Logistic regression modeling was used to estimate risk of primary cesarean delivery over time and for each indication. The numbers of cesareans performed for each indication each year were cumulatively modeled to estimate an odds ratio and percent increase for each indication annually over the 7 year period. The cumulative annualized relative increase from 2003 through 2009 was calculated by compounding the mean annual rate increase over 7 years, thus representing the increased risk of cesarean for pregnant women with no prior cesarean over this time period. Linear regression was performed to estimate the slope of the trend over time within each category and for primary cesareans overall; the relative contribution of each indication to the overall increase in the primary cesarean delivery rate was calculated. This analysis was restricted to the years of complete information on cesarean deliveries and medical indications, during the years 2003–2009. General cesarean delivery rates were calculated back to 1996 to provide more historical data and comparisons. SAS 9.2 software was used for analysis.
RESULTS
From January 2003 to December 2009, a total of 32,443 live births occurred at Yale-New Haven Hospital; 10,757 (33.3%) of those births were delivered by cesarean. Maternal demographic and obstetric/fetal characteristics among all live births during the study period are presented in Table 1. There were slight increases in Hispanic women and unmarried women. Of note, the prevalence of advanced maternal age and birthweight ≥ 4500gm were stable over time.
Table 1.
Demographic and Obstetric Characteristics
| 2003 (n = 4792) |
2004 (n = 4719) |
2005 (n = 4721) |
2006 (n = 4697) |
2007 (n = 4586) |
2008 (n = 4492) |
2009 (n = 4390) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Race | |||||||
| White | 2948 (61.5) | 2826 (60.0) | 2730 (57.8) | 2631 (56.0) | 2512 (54.8) | 2445 (54.4) | 2386 (54.4) |
| Black | 779 (16.3) | 831 (17.6) | 822 (17.4) | 845 (18.0) | 813 (17.7) | 835 (18.6) | 802 (18.3) |
| Hispanic | 696 (14.5) | 730 (15.5) | 833 (17.6) | 890 (18.9) | 894 (19.5) | 865 (19.3) | 869 (19.8) |
| Asian | 279 (5.8) | 250 (5.3) | 265 (5.6) | 225 (4.8) | 272 (5.9) | 247 (5.5) | 222 (5.1) |
| Other | 90 (1.9) | 82 (1.8) | 71 (1.5) | 106 (2.3) | 95 (2.1) | 100 (2.2) | 111 (2.5) |
| Education | 3141 (66.4) | 3058 (65.4) | 3032 (64.8) | 3041 (64.8) | 2998 (65.4) | 2917 (65.0) | 2911 (66.4) |
| Some college or greater | |||||||
| Married | 3300 (68.9) | 3207 (68.0) | 3094 (65.5) | 3038 (64.7) | 2895 (63.1) | 2859 (63.7) | 2762 (62.9) |
| Medicaid | 1376 (29.1) | 1464 (31.6) | 1509 (32.5) | 1562 (33.8) | 1434 (33.0) | 1429 (33.4) | 1294 (31.9) |
| Multiparous (parity ≥ 1) | 2711 (57.2) | 2729 (58.3) | 2725 (58.2) | 2752 (58.6) | 2681 (58.5) | 2560 (57.0) | 2526 (57.5) |
| Maternal Age > 35yo | 1117 (23.3) | 1104 (23.4) | 1157 (24.5) | 1211 (25.8) | 1129 (24.6) | 1064 (23.7) | 1028 (23.4) |
| Multiple Gestation | 293 (6.1) | 268 (5.7) | 271 (5.7) | 291 (6.2) | 283 (6.2) | 324 (7.2) | 321 (7.3) |
| Congenital Anomalies | 165 (3.5) | 101 (2.2) | 73 (1.6) | 79 (1.7) | 111 (2.4) | 105 (2.3) | 105 (2.4) |
| Preterm (< 37 wks) | 600 (12.7) | 619 (13.2) | 639 (13.7) | 647 (13.8) | 664 (14.5) | 645 (14.4) | 624 (14.2) |
| Birth weight | |||||||
| < 2,500g | 524 (11.0) | 531 (11.3) | 548 (11.6) | 549 (11.7) | 578 (12.6) | 523 (11.7) | 512 (11.7) |
| 2,500g- | 4188 | 4117 | 4117 | 4087 | 3962 | 3922 | 3818 |
| 4,499g | (87.5) | (87.4) | (87.3) | (87.1) | (86.5) | (87.5) | (87.2) |
| ≥ 4,500g | 75 (1.6) | 64 9 (1.4) | 52 (1.1) | 55 (1.2) | 41 (0.9) | 35 (0.8) | 51 (1.2) |
| Induction | 869 (18.1) | 754 (16.0) | 852 (18.1) | 857 (18.3) | 908 (19.8) | 962 (21.4) | 869 (19.8) |
| Operative Vaginal Delivery | 188 (3.9) | 189 (4.0) | 167 (3.5) | 161 (3.4) | 135 (2.9) | 111 (2.5) | 129 (2.9) |
Data are n (%) for all live births. Some columns may not equal 100% due to missing data.
Trends in cesarean delivery were examined in relation to the total number of live births during our study period and the seven years preceding this period (Figure 1). The overall cesarean delivery rate increased both prior to (1996–2002) and during the study time period (2003–2009). The average annual rate was 21.1% in 1996, 26.0% in 2003 and by 2009 was 36.5%, representing a total increase of 73.0%. Both primary and repeat cesarean delivery rates increased throughout the time period. The repeat cesarean rate among all live births was 6.7% in 1996, 9.8% in 2003, and in 2009 was 14.8%, representing an increase of 120.9%. Increasing repeat cesarean rates among parturients reflect the increasing numbers of women presenting with previous cesarean as well as declining trial of labor rates among women with a history of cesarean. After peaking at 43.9% in 1998, the VBAC rate decreased dramatically between 2000 and 2002 and continued to decrease over the study period (Figure 2). In 2003, the VBAC rate had declined to 17.8% and by 2009 was 7.8%.
Figure 2.
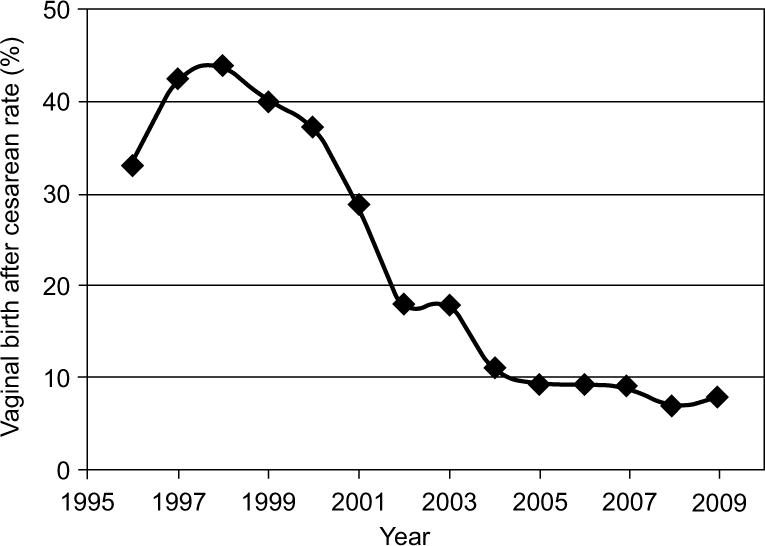
The vaginal birth after cesarean delivery (VBAC) rate was calculated for each year from 1996 to 2009. VBAC rate represents number of successful VBACs divided by the number of women who underwent previous cesarean delivery.
The primary cesarean rate among all live births was 14.4% in 1996, 16.2% in 2003 and by 2009 had increased to 21.7%, an increase of 50.7%. From 2003 through 2009, the primary cesarean delivery rate increased slightly less than the repeat cesarean delivery rate: 6.0% per year (95% CI 4.5, 7.4) compared to 8.0% per year (95% CI 6.2, 9.8), respectively. However, given the relative number of women in each group, 50.0% of the total increase in cesarean deliveries from 2003 through 2009 was attributable to primary cesareans.
Differences in cesarean rates between patients managed by private, university, and high-risk services were examined (Figure 3). The university rate remained consistently lower than the private rate over the entire time period, and both rates remained substantially lower than the high-risk rate. The overall cesarean rate for private patients over the studied time period (2003–2009) was 33.2%, whereas the rate for university patients was 25.6%. The high-risk cesarean rate was 44.6%. The mean annual percent increase for each group over 2003–2009 was as follows: private patients [7.6%/year (95% CI 6.0–9.1)], university patients [6.0% per year (95% CI 3.3–8.9)] and high-risk patients [4.9%/year (95% CI 1.7–8.3)]. Of note, both the university and high-risk service patients were supervised by the same maternal-fetal medicine hospitalists on the labor and birth unit.
Figure 3.
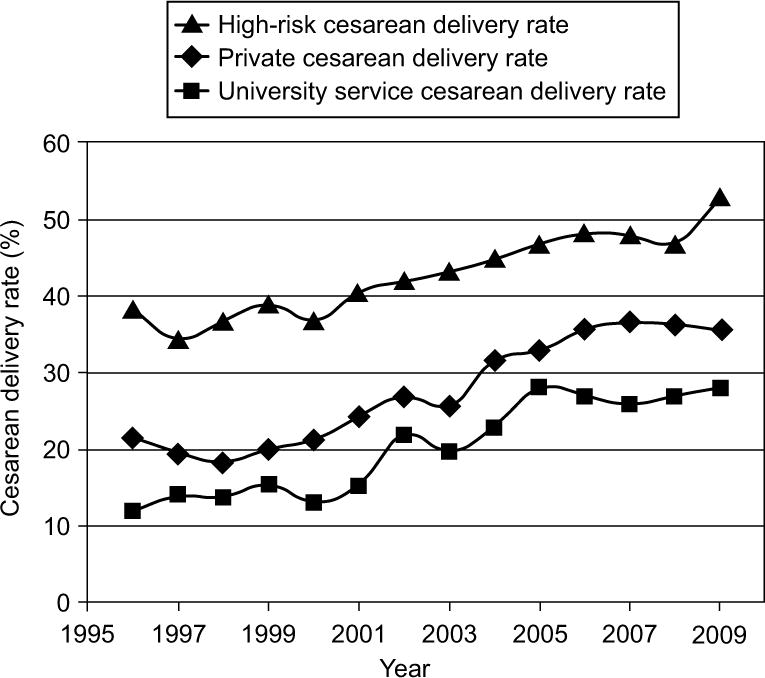
Cesarean delivery rate (%) by provider category. Cesarean delivery rates were calculated for patients cared for by the high risk, private, and university services. Cesarean rates represent number of cesarean deliveries in each category divided by number of live births in each provider category.
Given that primary cesarean deliveries accounted for 50% of the increase in cesarean delivery rate from 2003 through 2009, we examined specific indications that contributed to the rise in primary cesarean rate (Figures 4a and 4b). Over this period, the rate of primary cesarean delivery among women with no history of cesarean birth rose from 18% to 25%. For every 1000 eligible women, an additional 73.6 primary cesareans were performed in 2009 compared to 2003(Table 2). In absolute numbers over this time period, the majority of primary cesareans among at risk parturients (total 232.0 per 1000 eligible women) are attributable to labor arrest disorders (87.9 per 1000), non-reassuring fetal heart rate tracings (55.0 per 1000), and malpresentation (35.4 per 1000). Among the documented indications for cesarean delivery, non-reassuring fetal heart tracing, arrest of dilation, multiple gestation, pre-eclampsia, suspected macrosomia, and maternal request increased significantly (p < 0.05) over time, while arrest of descent, malpresentation, maternal-fetal indications, and other obstetric indications (e.g. cord prolapse, placenta previa) did not increase significantly (Table 2). Absolute differences between 2003 and 2009 illustrate the potential magnitude of change for each indication and demonstrate that labor arrest disorders and non-reassuring fetal heart rate tracings contribute large relative proportions to the total increase despite their smaller annual percent increases over time. A graphical representation shows relative contributions of each indication to the total increase in primary cesarean rate over time (Figure 5). Non-reassuring fetal status contributed the most (32%) followed by arrest of labor disorders (18%), multiple gestation (16%), suspected macrosomia (10%), pre-eclampsia (10%), maternal request (8%), maternal-fetal conditions (5%), and obstetric conditions (1%).
Figure 4.
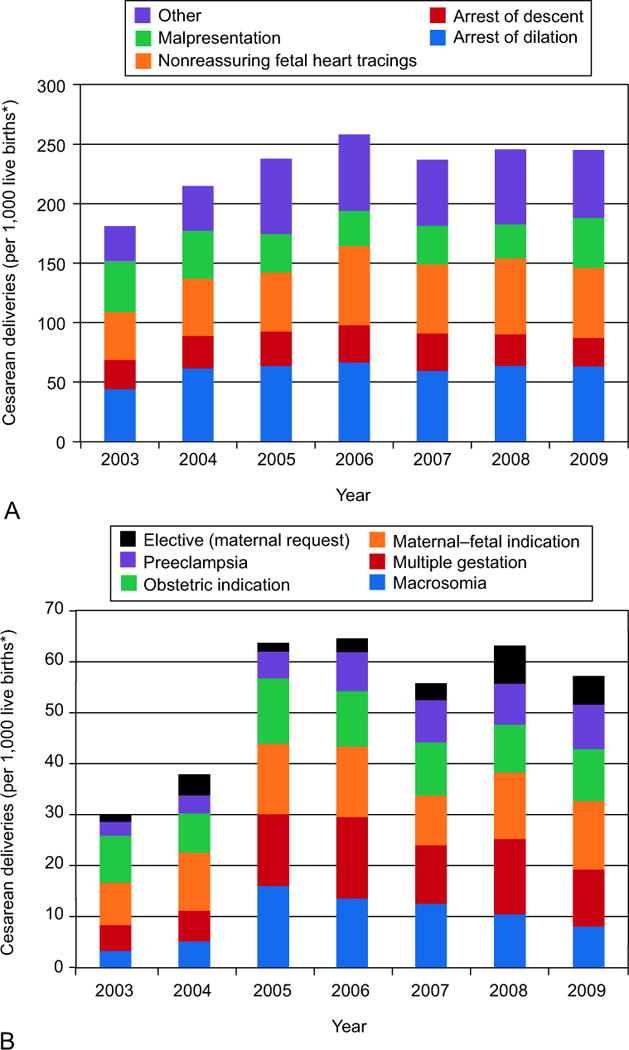
The number of cesarean deliveries performed for each indication per 1,000 women at risk for primary cesarean delivery. A. Primary cesarean deliveries grouped by indication. Each vertical bar represents the total number of primary cesareans performed each year per 1,000 eligible live births, and the divisions within each bar represent the number of cesareans performed for each indication. The purple bar represents an “other” category made up of 6 indications which are delineated further in Figure 4b. B: Primary cesarean deliveries grouped by indication. A smaller scale is provided to allow for a clearer view of how the six indications that make up the “other” category in Figure 4a changed over the 6-year period.
*Eligible live births were births to women with no prior history of cesarean delivery.
Table 2. Cumulative Risk of Primary Cesarean Delivery by Indication from 2003 to 2009.
Primary cesarean rates for each indication per 1000 eligible live births from 2003 to 2009 (adjusted for repeat cesarean rate)*
| 2003 n = 4327 |
2004 n = 4135 |
2005 n = 4128 |
2006 n = 4137 |
2007 n = 3928 |
2008 n = 3845 |
2009 n = 3737 |
Absolute Increase 2003–2009 (crude)† | Mean Annual Increase (95% CI)‡ | Cumulative Annualized Relative Increase (95% CI) § | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Primary Cesareans | 181.2 | 215.0 | 237.9 | 258.2 | 237.0 | 245.8 | 254.7 | 73.6 | 6.0% (4.5, 7.4) | 1.50 (1.36, 1.65) |
| Labor Arrest Disorders | 68.6 | 88.8 | 92.3 | 97.7 | 90.9 | 90.3 | 87.0 | 18.3 | 2.7% (0.6, 4.9) | 1.21 (1.04, 1.40) |
| Arrest of dilation | 43.9 | 61.4 | 63.5 | 66.5 | 59.3 | 63.7 | 63.2 | 19.2 | 3.9% (1.4, 6.5) | 1.31 (1.10, 1.55) |
| Arrest of descent | 24.7 | 27.3 | 28.8 | 31.2 | 31.6 | 26.5 | 23.8 | –0.91 | 0% (–0.04, 3.6) | 1.00 (0.78, 1.28) |
| Macrosomia¶ | 3.2 | 5.1 | 16.0 | 13.5 | 12.5 | 10.4 | 11.2 | 8.0 | 12.3% (5.9, 19.1) | 2.25 (1.49, 3.40) |
| Malpresentation# | 42.5 | 40.4 | 32.2 | 29.5 | 32.3 | 28.6 | 42.0 | –0.5 | –2.8% (–5.9, 0.3) | 0.82 (0.65, 1.02) |
| Maternal-Fetal** | 8.3 | 11.4 | 13.8 | 13.8 | 9.7 | 13.0 | 13.4 | 5.1 | 4.6% (–0.9, 10.4) | 1.37 (0.94, 2.00) |
| Maternal Request|| | 1.4 | 4.1 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 5.6 | 27.0% (14.9, 40.3) | 5.32 (2.64, 10.70) |
| Multiple gestation | 5.1 | 6.0 | 14.1 | 16.0 | 11.5 | 14.8 | 16.3 | 11.2 | 16.5% (10.2, 23.1) | 2.91 (1.97, 4.28) |
| NRFHT | 40.0 | 47.9 | 49.7 | 66.5 | 58.0 | 63.7 | 58.9 | 18.9 | 7.1% (4.4, 9.9) | 1.62 (1.35, 1.94) |
| Other Obstetric Indications†† | 9.2 | 7.7 | 12.8 | 10.9 | 10.4 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 0.9 | 1.4% (–4.3%, 7.5) | 1.10 (0.74, 1.66) |
| Preeclampsia‡‡ | 2.8 | 3.6 | 5.3 | 7.7 | 8.4 | 8.1 | 8.8 | 6.1 | 19.2% (10.5, 28.7) | 3.44 (2.01, 5.85) |
NRFHT, non-reassuring fetal heart tracing
Eligible live births are defined as births at risk for primary cesarean section; all repeat cesarean sections excluded from analysis
Rate in 2009 – rate in 2003 per 1000 eligible live births
Estimated mean annual increase calculated by logistic regression using data from all years, 2003–2009
Cumulative annualized relative increase (2003–2009) calculated by logistic regression, compounding the estimated annual increase over 7 years
Without other documented medical indications
Suspected macrosomia based on ultrasound or clinical estimate
Any non-cephalic presentation
Maternal conditions predating the pregnancy or fetal antenatal problems, such as fetal anomalies, which could preclude vaginal delivery
Conditions brought about by the presence of the current intrauterine pregnancy: placental abruption, accreta, and previa, cord prolapse, cerclage, and chorioamnionitis
Pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, and HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet) syndrome
Figure 5.
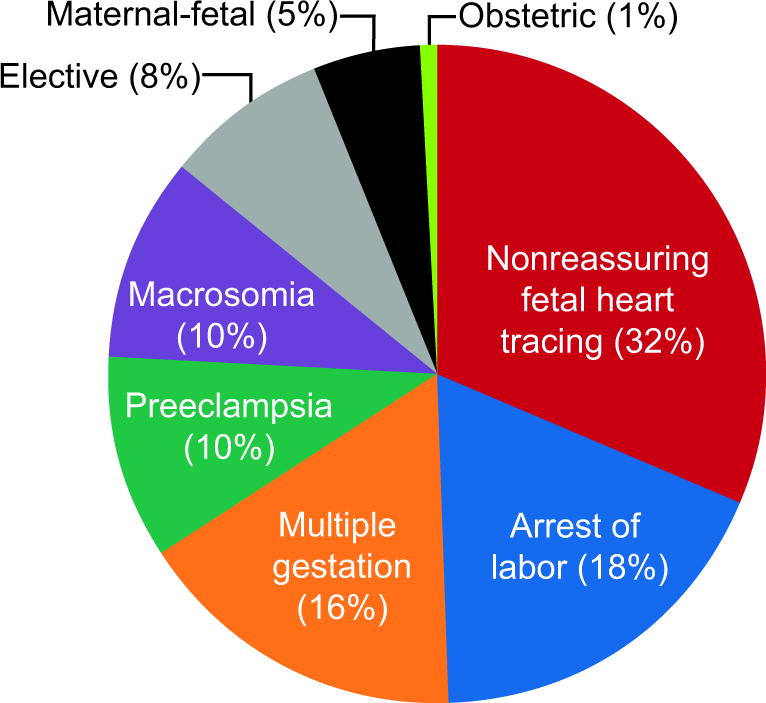
Contribution of each indication to the total increase in primary cesarean deliveries. The proportions each indication contributed to the overall increase in primary cesarean delivery from 2003 to 2009 are graphed in comparison to one another.
The arrest of labor category was divided into arrest of dilation and arrest of descent. The number of cesareans performed for arrest of descent over time remained stable (95% CI, –3.5, 3.6), ), whereas the number performed for arrest of dilation increased 3.9% per year (95% CI, 1.4, 6.5)). Therefore, the increase in overall cesarean delivery rate due to arrest of labor was attributable to arrest of dilation, rather than arrest of descent.
Indications exhibiting large annual percentage increases included maternal request, suspected macrosomia, multiple gestation, and preeclampsia. Women’s cumulative annualized risk for undergoing a primary cesarean delivery for these indications increased significantly over this time period; however, absolute increases were small. The absolute risks of cesarean delivery for the indications of arrest of dilation and non-reassuring fetal heart tracings remained highest among all indications, and both also increased during the study period.
DISCUSSION
Data from a major academic medical center in Connecticut using physician documented indications reveals a rising cesarean delivery rate driven by increases in both repeat and primary cesarean delivery. Among primary cesareans, more subjectively defined indications, such as non-reassuring fetal heart tracings, labor arrest disorders, and suspected macrosomia (clinical or ultrasound estimate), increased, whereas more objectively defined indications, such as malpresentation, maternal/fetal conditions, and obstetric conditions remained stable.
While not necessarily signaling causation, it is instructive to review events from this era, which may have influenced cesarean rates. In 2001, a seminal paper and subsequent editorial describing the risk of uterine rupture in women exposed to vaginal prostaglandins undergoing VBAC 13, 14 suggested that elective repeat cesarean is the safer option when compared with VBAC. Between 1998–2001, new national guidelines recommended that an anesthesiologist should be available immediately in any hospital where VBAC is offered.15–17 A subsequent trend away from VBAC occurred across the country that may have impacted providers at our institution and contributed to the sharp decrease in VBAC from 1998 forward. In 2003 and 2006, respectively, an ACOG bulletin and NIH consensus statement on elective cesarean per maternal request, suggested more patient autonomy regarding cesarean delivery, reflecting a change in national attitudes.18 In 2004 our institution’s cesarean delivery review committee, which reviewed every cesarean for appropriateness of indication, was reframed as a patient safety committee, no longer focusing exclusively on the single process measure of cesarean delivery, but shifting to an outcomes-based approach. This shift was temporally associated with a rise in the cesarean rate. During the same time period, malpractice insurance rates in the state of Connecticut climbed precipitously with insurance companies citing large financial settlements as the cause.
Given that the repeat cesarean rate is over 90% for women with a prior cesarean, many have speculated that much of the increase in cesareans has been driven by decreasing VBAC rates. However, our data concurs with other studies that reveal a steadily rising primary cesarean delivery rate.19 At our institution, the largest contributor to the increasing primary cesarean delivery rate was non-reassuring fetal heart tracing. The variability of fetal heart tracing interpretation has been documented20, 21 and a lack of available fetal scalp blood sampling kits in the United States has further complicated the objectivity of fetal heart rate interpretation. Providers may be more apt to proceed with cesarean delivery for questionable tracings in the recent medicolegal climate,22 and patients may desire cesarean if they perceive any risk to their fetus based on abnormalities in the tracing even if it remains overall reassuring. It is also possible that our effort to standardize fetal heart rate interpretation, as part of our comprehensive patient safety effort, had effects on this observation.23 Standardization theoretically attempts to improve the objectivity of this test, however this study is unable to assess exactly what effect standardization had on the rise in this indication for cesarean.
The nationally decreasing rates of operative vaginal deliveries are likely associated with more cesareans performed for labor arrest disorders;24 however, our data do not show an increase in the use of cesarean for arrest of descent during this time period. Rather most of the increase in cesarean for labor arrest disorders manifested in arrest of dilation. The diagnosis of arrest of dilation is relatively subjective with large variability among clinicians in frequency of cervical exams, determination of adequate uterine contractions, and choice of temporal endpoint. Patients may also play a role in the decision to intervene during slowly progressing labors, especially when other clinical issues, such as maternal fever, arise. The increase in cesarean delivery for arrest of dilation may be associated with increasing use of induction of labor for medical and non-medical reasons;25 however, our institution has not experienced large increases in induction over this time period (Table 1).
Both multiple gestation and pre-eclampsia increased as indications for cesarean delivery at a much faster rate than the incidences of multiple gestation26 and preeclampsia27, 28 in the population are increasing. Our estimates yield rates of cesarean for these indications 200% and 87% higher than would be expected based on increases in incidence of multiple gestation and preeclampsia, respectively. This may be due to increased use of cesarean delivery for vertex presenting twins and the use of cesarean rather than induction of labor for preeclampsia, despite practice guidelines supporting vaginal delivery in these circumstances.29–31 Similarly, cesareans for suspected macrosomia increased at 12.3%/year over this time period, despite stable rates of actual macrosomia at our hospital (Table 1) demonstrating that cesarean is being utilized more frequently in these circumstances, rather than actual increases in the incidence of macrosomia.
The contribution of maternal request cesareans to the overall cesarean rate has recently received much attention. Our data indicates that this category did not make up a large percentage (8%) of the increase in the overall cesarean delivery rate; however, it was the most rapidly increasing category (27%/year). Studying maternal request cesarean delivery in the United States population has been challenging, because maternal request cesarean is not an indication readily identifiable by ICD-9 coding systems or birth certificate data. Our study uses physician-recorded information from the labor unit, allowing documentation of patient preference and revealing that small (7/1000 eligible women in 2009) but increasing numbers of women in our region are requesting cesareans without medical indication.
There are several limitations to this study. First, this data represents one institution, a large urban academic medical center in Connecticut, and thus may not be generalizable to populations with different demographic and regional characteristics. Second, because our data represents one institution, the number of births in the cohort is lower than many other studies using birth certificate data or ICD-9 codes to study cesarean delivery trends. These studies have the benefit of large numbers to examine general trends; however, they lack specific information about indications, rely on often misclassified coding data, often have large “other” categories, and contain a large amount of missing data.32,33 Our study benefits from the specificity of physician-documented indications over seven years and demonstrates the importance of evaluating each indication independently over time.
Why providers are more apt to perform cesareans for subjective and elective indications over recent years is a complex issue. Medicolegal reasons, scheduling issues, economic pressures, provider- and patient-driven medicalization of birth, increased labor induction rates, and a broader perception of cesareans as safe have all been raised as possibilities. The role of medicolegal concerns has been documented with increasing cesarean rates as malpractice premiums and the number of litigated cases increase.34–36 Patient preference also cannot be discounted in these trends. Decision to pursue a cesarean is not one made by the provider alone but one of shared decision making between provider and patient. Patient preferences and perception of risk do contribute, for instance, to decisions to attempt VBAC or vaginal delivery of multiple gestation. This does point out, however, that subjective phenomena may have influence even in seemingly objective criteria. Unfortunately, this analysis cannot account for the contribution of the patient’s decision-making to changes in indications for cesarean.
While cesarean delivery rates that are too low are associated with increased adverse events, cesarean delivery rates above the risk-adjusted expected rate for an institution have not been shown to improve maternal or neonatal outcomes, but do add cost and unnecessary intervention.37 Efforts to address the rising cesarean rate may benefit from attempts to convert subjective indications into objective ones though clearer evidence-based guidelines regarding fetal status, labor arrest, and assessment of macrosomia, as well as increased provider accountability for the decision to perform cesarean at the practice, departmental, hospital, or state level. In addition, increased patient education and involvement in decisions during pregnancy, changes in methods of reimbursement, and medical-legal reform may all be areas where potential improvements can be identified.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Cheryl Raab for her assistance with data collection.
Presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine in San Francisco, CA, February 11th, 2011.
FUNDING: Dr. Jessica Illuzzi received support from the NICHD as a Women’s Reproductive Health Research Scholar (NIH K12 HD047918).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Financial Disclosure: The authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Menacker F, Hamilton BE. Recent trends in cesarean delivery in the United States. NCHS Data Brief. 2010:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.ACOG Practice bulletin no. 115: Vaginal birth after previous cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;116:450–63. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181eeb251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Declercq E, Menacker F, Macdorman M. Maternal risk profiles and the primary cesarean rate in the United States, 1991–2002. Am J Public Health. 2006;96:867–72. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2004.052381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Declercq E, Menacker F, MacDorman M. Rise in “no indicated risk” primary caesareans in the United States, 1991–2001: cross sectional analysis. BMJ. 2005;330:71–2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38279.705336.0B. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rhodes JC, Schoendorf KC, Parker JD. Contribution of excess weight gain during pregnancy and macrosomia to the cesarean delivery rate, 1990–2000. Pediatrics. 2003;111:1181–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Reddy UM, Ko CW, Willinger M. Maternal age and the risk of stillbirth throughout pregnancy in the United States. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;195:764–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2006.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.MacDorman MF, Menacker F, Declercq E. Cesarean birth in the United States: epidemiology, trends, and outcomes. Clin Perinatol. 2008;35:293–307. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2008.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Menacker F, Declercq E, Macdorman MF. Cesarean delivery: background, trends, and epidemiology. Semin Perinatol. 2006;30:235–41. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2006.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Denk CE, Kruse LK, Jain NJ. Surveillance of cesarean section deliveries, New Jersey, 1999–2004. Birth. 2006;33:203–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-536X.2006.00105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Osterman MJ, Martin JA, Menacker F. Expanded health data from the new birth certificate, 2006. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2009;58:1–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gossman GL, Joesch JM, Tanfer K. Trends in maternal request cesarean delivery from 1991 to 2004. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;108:1506–16. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000242564.79349.b7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vaginal birth after cesarean birth--California, 1996–2000. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51:996–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Greene MF. Vaginal delivery after cesarean section--is the risk acceptable? N Engl J Med. 2001;345:54–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200107053450108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lydon-Rochelle M, Holt VL, Easterling TR, Martin DP. Risk of uterine rupture during labor among women with a prior cesarean delivery. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:3–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200107053450101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Committee opinion. Induction of labor for vaginal birth after cesarean delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:679–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Approach VBAC deliveries cautiously, experts say. Hosp Peer Rev. 1998;23:189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.ACOG practice bulletin. Vaginal birth after previous cesarean delivery. Number 5, July 1999 (replaces practice bulletin number 2, October 1998). Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 1999;66:197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.ACOG Committee Opinion. Surgery and patient choice: the ethics of decision making. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102:1101–6. doi: 10.1016/j.obstetgynecol.2003.09.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Getahun D, Strickland D, Lawrence JM, Fassett MJ, Koebnick C, Jacobsen SJ. Racial and ethnic disparities in the trends in primary cesarean delivery based on indications. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:422e1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.07.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Beaulieu MD, Fabia J, Leduc B, et al. The reproducibility of intrapartum cardiotocogram assessments. Can Med Assoc J. 1982;127:214–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nielsen PV, Stigsby B, Nickelsen C, Nim J. Intra- and inter-observer variability in the assessment of intrapartum cardiotocograms. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1987;66:421–4. doi: 10.3109/00016348709022046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zain HA, Wright JW, Parrish GE, Diehl SJ. Interpreting the fetal heart rate tracing. Effect of knowledge of neonatal outcome. J Reprod Med. 1998;43:367–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pettker CMTSNE, Buhimschi CS, Raab CA, Copel JA, Kuczynski E, Lockwood CJ, Funai EF. Impact of a comprehensive patient safety strategy on obstetric adverse events. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;200 doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Menacker F, Martin JA. Expanded health data from the new birth certificate, 2005. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2008;56:1–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang J, Troendle J, Reddy UM, et al. Contemporary cesarean delivery practice in the United States. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;203:326e1–e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.06.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Martin JAHB, Sutton PD, Ventura SJ, Mathews Osterman MJK. Births: Final data for 2008. National vital statistics reports. Vol. 59. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuklina EV, Ayala C, Callaghan WM. Hypertensive disorders and severe obstetric morbidity in the United States. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:1299–306. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a45b25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kuklina EV, Meikle SF, Jamieson DJ, et al. Severe obstetric morbidity in the United States: 1998–2005. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:293–9. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181954e5b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Number 33, January 2002. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2002;77:67–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Guidelines for perinatal care: American Academy of Pediatrics [and] the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 2007. Intrapartum and Postpartum Care of the Mother, Chapter 5; p. 161. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guidelines for perinatal care: American Academy of Pediatrics [and] the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. 2007. Obstetric and Medical Complications, Chapter 6; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kahn EB, Berg CJ, Callaghan WM. Cesarean delivery among women with low-risk pregnancies: a comparison of birth certificates and hospital discharge data. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;113:33–40. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e318190bb33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Headley AJ, Fulcomer MC, Bastardi MM, Im W, Sass MM, Chung K. The use of missing birth record data as a marker for adverse reproductive outcomes: a geocoded analysis of birth record data. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98:1078–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Murthy K, Grobman WA, Lee TA, Holl JL. Association between rising professional liability insurance premiums and primary cesarean delivery rates. Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110:1264–9. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000287294.89148.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ryan K, Schnatz P, Greene J, Curry S. Change in cesarean section rate as a reflection of the present malpractice crisis. Conn Med. 2005;69:139–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zwecker P, Azoulay L, Abenhaim HA. Effect of Fear of Litigation on Obstetric Care: A Nationwide Analysis on Obstetric Practice. Am J Perinatol. 2011 doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1271213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Srinivas E, Fager C, Lorch SA. Evaluating the risk-adjusted cesarean elivery rate as a measure of obstetric quality. Obstet Gynecol. 2010;115:1007–13. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181d9f4b6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


