Abstract
Several studies have identified genes associated with alcohol use disorders, but the variation in each of these genes explains only a small portion of the genetic vulnerability. The goal of the present study was to perform a genome-wide association study (GWAS) in extended families from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) to identify novel genes affecting risk for alcohol dependence. To maximize the power of the extended family design we used a quantitative endophenotype, measured in all individuals: number of alcohol dependence symptoms endorsed (symptom count). Secondary analyses were performed to determine if the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with symptom count were also associated with the dichotomous phenotype, DSM-IV alcohol dependence. This family-based GWAS identified SNPs in C15orf53 that are strongly associated with DSM-IV alcohol (p=4.5×10−8, inflation corrected p=9.4×10−7). Results with DSM-IV alcohol dependence in the regions of interest support our findings with symptom count, though the associations were less significant. Attempted replications of the most promising association results were conducted in two independent samples: non-overlapping subjects from the Study of Addiction: Genes and Environment (SAGE) and the Australian twin-family study of alcohol use disorders (OZALC). Nominal association of C15orf53 with symptom count was observed in SAGE. The variant that showed strongest association with symptom count, rs12912251 and its highly correlated variants (D′=1, r2≥ 0.95), has previously been associated with risk for bipolar disorder.
Keywords: DSM-IV alcohol dependence symptoms, Family-based GWAS, C15orf53, Quantitative traits
Introduction
Alcohol use disorders (AUDs) are among the most common and costly public health problems throughout the world1. Family and twin studies have provided evidence for a genetic predisposition toward AUDs2,3, with genetic factors accounting for approximately 40% to 60% of the total variance in risk for alcohol dependence (AD)3–8.
A variety of study designs have been employed to identify genes influencing the vulnerability to AD. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are a potentially more comprehensive way to study a complex, common disease like AD where we have little knowledge of disease pathophysiology. Several GWAS have sought to identify variants associated with the risk for AD using case-control designs, including treatment seeking subjects with AD9, individuals selected from densely affected families with AD10, a case-control series drawn from treatment and community-based samples from several diseases11, subjects ascertained from large unselected sibships as well as individuals selected for heavier alcohol use12. GWAS using quantitative traits derived from alcohol consumption and AD symptomatology have also been examined in a population-based sample13 and an Australian sample of related individuals12. Results thus far have identified interesting candidate genes for AD, although the overlap of the top genetic signals across studies has been limited.
The Collaborative Study of the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) provides another opportunity to examine genes associated with problematic alcohol use. COGA is a multi-site, longitudinal study established to identify vulnerability genes for AD by recruiting multiplex alcohol dependent families as well as representative families from the community14–18. In the current analysis, we performed a family-based GWAS in large multi-generational families severely affected by AD. These families likely represent a subgroup enriched for AD susceptibility alleles.
The power to identify genes contributing to the risk for disease may be increased through the analysis of quantitative endophenotypes highly correlated with that disorder but measurable in all individuals. Rather than focus on the presence or absence of AD, we used the number of AD symptoms as our primary phenotype. Some research has indicated that AD may be better captured with a symptom count rather than with a dichotomous diagnosis19–21. Evidence from twin studies has shown that two quantitative measures, dependence symptoms and alcohol consumption are highly correlated with alcohol dependence and index closely the risk for alcohol dependence22,23. Symptom counts can be computed for any drinker, including older adolescents who are just beginning to use alcohol but may not fulfill criteria for AD, thus allowing us to use more of our sample in the analysis and increase the power to detect association. Since most other studies on alcoholism have used a dichotomous diagnosis, DSM-IV alcohol dependence, we analyzed the regions of interest identified in the symptom count analysis to evaluate if similar findings emerge.
Material and Methods
COGA Study Subjects
Following approval of institutional review boards at all participating institutions, AD probands were recruited through alcohol treatment programs and administered a validated poly-diagnostic instrument, the Semi-Structured Assessment for the Genetics of Alcoholism (SSAGA), to assess AD14,16,18,19,24. Individuals below the age of 18 were administered an adolescent version of the SSAGA. The same assessment approach, used for all probands and their relatives, was repeated at several-year intervals for a large number of individuals.
The goal of this study was to identify genetic variants associated with alcohol-related phenotypes. All families were reviewed and the genetically most informative subset of COGA families that could be used for analyses of a variety of alcohol-related phenotypes, including DSM-IV symptom count (SC), were selected for a family-based GWAS. Prioritization in selecting subjects for analysis was based on a higher number of AD family members, the number of relatives who supplied DNA, as well as the number of family members with another key COGA phenotype, electrophysiology measures. To reduce the heterogeneity in the sample, only families that were primarily of Caucasian descent were selected for genotyping, yielding a total of 2322 subjects from 118 extended families who were genotyped. The resulting dataset includes multi-generational families affected by AUDs with an average of 20 subjects per family (Figure S1). After genotype quality control and cleaning, correcting pedigree inconsistencies, and processing the phenotypes (see below), 2010 genotyped individuals were included in the subsequent analyses. Full details on the genotype cleaning are included in the supplementary information.
Phenotype
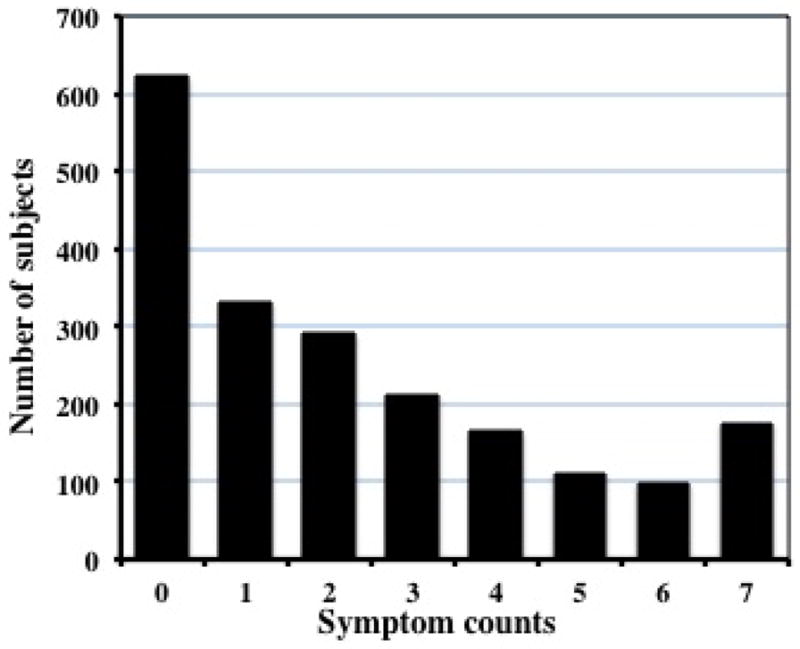
We computed the symptom count (SC) using the seven lifetime diagnostic criteria for DSM-IV alcohol dependence (AD). This measure, with a value ranging from 0 to 7, was available on all individuals with an adolescent or adult SSAGA who had reported ever consuming alcohol. When longitudinal data were available, we used the maximum number of symptoms endorsed at any interview. Individuals who were younger than 15 years at the most recent interview were excluded from the analysis because SC in this population is likely to be non-representative of adult cohorts. Of the 2010 subjects =15yr who drank, 622 did not report any of the 7 symptoms of AD, and 765 had 3 or more such symptoms. The distribution of SC is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Distribution of DSM_IV alcohol dependence symptom count in the genotyped GWAS sample.
DSM-IV AD was used as a secondary phenotype, to enable comparison with other studies in the literature. Given the wide age range of the subjects included in the analysis and the fact that many had not passed through the age of risk for an alcohol use disorder (AUD), the following algorithm was developed to reach the final diagnosis after considering all evaluations. Individuals aged 15 years or older who met DSM-IV criteria at any evaluation were classified as alcohol dependent. Individuals 23 years and older who drank but did not meet criteria for AD on any adult SSAGA were classified as unaffected. Individuals who did not consume alcohol, were under the age of 15 years at all evaluations, or were age 15 through 22 years old and did not meet DSM-IV criteria, were classified as unknown and were removed from subsequent analyses – this avoids ascribing an unaffected status to an adolescent or young adult who may be at high genetic risk but not yet past the peak period of vulnerability. There were 684 subjects in the 118 extended families who met criteria for AD using either an adult or adolescent SSAGA (Table S1). Among 1638 remaining individuals, 964 were classified as unaffected. The average number of individuals in a family diagnosed with AD was 5.9 (Figure S2).
Genotype
Genotyping was performed at the Genome Technology Access Center at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis (http://gtac.wustl.edu/) using the Illumina Human OmniExpress array 12.VI (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). We also included in the analysis genotypes for subjects (n=275) from these 118 families who were genotyped in a previous case-control GWAS using the Illumina 1M array10. For quality control purposes, 51 of the 275 subjects were genotyped again on the Illumina Human OmniExpress array. Imputed data were obtained using the program BEAGLE25. A detailed description of imputation and subsequent data cleaning is included in supplementary information.
Statistical Analysis
A total of 707,557 autosomal SNPs passed quality control. Given their limited power to detect association, SNPs with a minor allele frequency below 5% (n=115,872) were excluded from further analysis. Thus association analysis was performed with the remaining 591,685 SNPs, giving a Bonferronic corrected threshold for genome-wide significance of p=8.45×10−8.
We first tested the effect of covariates on our phenotypes: SC and DSM-IV AD. As expected, gender was a highly significant predictor of SC and DSM-IV AD, and was included as a covariate in all analyses. We identified cohort effects and therefore divided subjects into 4 cohorts based on their year of birth (< 1930, 1930 – 1949, 1950 – 1969, and ≥ 1970). For SC, the age-squared parameter was still significant after cohort effect was included, and the final model therefore included gender, age, age-squared and cohort. For DSM-IV AD, the age-squared parameter was not a significant factor after considering cohort and was omitted. The first principal component from the EIGENSTRAT analysis (pc1), while not statistically significant, was still included in all analyses to reduce the risk of false positive associations due to population stratification.
In this sample, the SC phenotype best fit a negative binomial distribution, which was identified by applying PROC COUNTREG and PROC SGPLOT in SAS (http://support.sas.com/rnd/app/da/glimmix.html). By specifying a negative binomial distribution and a logarithmic link function, we parametrically modeled the observed trait distribution and included relevant covariates described above. Association with SC was analyzed for each SNP using a dose-effect model (number of minor alleles present in each individual) as implemented in PROC GLIMMIX from SAS. To control for relatedness, the test was placed in a general linear mixed model (GLMM) framework26 using an independent working correlation matrix where each family was a separate cluster.
Inflation of p values was revealed by preliminary examination of the quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plot (Figure S3). The genomic inflation factor (GIF), calculated by computing the median of the χ2 statistics divided by the median of the central χ2 distribution with df =1, was 1.25. In order to control for this inflation, we used the method of the Genomic Control27 with a λ of 1.25. In particular, we re-computed the level of association with each marker by dividing the observed χ2 with inflation factor λ of 1.25. We verified that these new, inflation corrected p values had a GIF of 1, indicating no further inflation.
The analyses of AD were conducted using the Genome-Wide Association Analyses with Family Data package28. A logistic regression model was employed with gender, age and cohort included as covariates, and a log additive model for each SNP was tested for association. The generalized estimating equation (GEE) framework was used to control for relatedness. No inflation of p values was observed (λ = 1.05).
Replication samples
The Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment (SAGE) sample
The SAGE sample is a case-control series selected from three large, complementary datasets: Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism, Family Study of Cocaine Dependence, and Collaborative Genetics Study of Nicotine Dependence. After removing 129 individuals in SAGE who were also part of the 118 extended families in the primary analysis, data from 2647 subjects of European descent were used to replicate promising associations (p<0.0001) identified in the COGA sample. Detailed characteristics of this sample and the genotyping platform were described in Bierut et al.11. Imputed dosage data were obtained using the same method as described in supplementary information. The distribution of SC was similar to that of the COGA sample. We used PROC GLIMMIX in SAS to test the association of individual SNPs with SC including age, age-squared, gender, nicotine dependence, cocaine dependence, and pc1 as covariates. We used the GEE framework described above to analyze the association with AD.
The Australian Twin-family Study of Alcohol Use Disorder (OZALC) Sample
The twins in this study were initially ascertained through the Australian Twin Registry, followed by cascading recruitment of non-twin siblings, parents, adult offspring and spouses12. Data from 6166 subjects of European descent were used for replication analysis with the SC. Detailed characteristics of this sample and genotyping platform were described in Heath et al.12. Imputed dosage data were obtained using MACH (http://www.sph.umich.edu/csg/abecasis/MACH). The association of individual SNPs with SC was performed using PROC GLIMMIX from SAS. Age and gender were included as covariates for association analysis. The GEE model described above was used for the association analysis with AD.
Results
Association with symptom count
Results for the entire genome are summarized in the Manhattan plot (Figure 2). After correcting for inflated, 72 SNPs of 591,685 genotyped autosomal SNPs tested showed evidence of association with symptom count with inflation corrected p values <10−4 (Table S2). None of these 72 SNPs reached genome-wide significance. Among these top signals, we identified 7 chromosomal loci containing 3 or more SNPs within 50 kb of each other that show association with SC (Table 1).
Figure 2. Manhattan plot of genome-wide association results for DSM-IV alcohol dependence symptom count using negative binomial analysis.
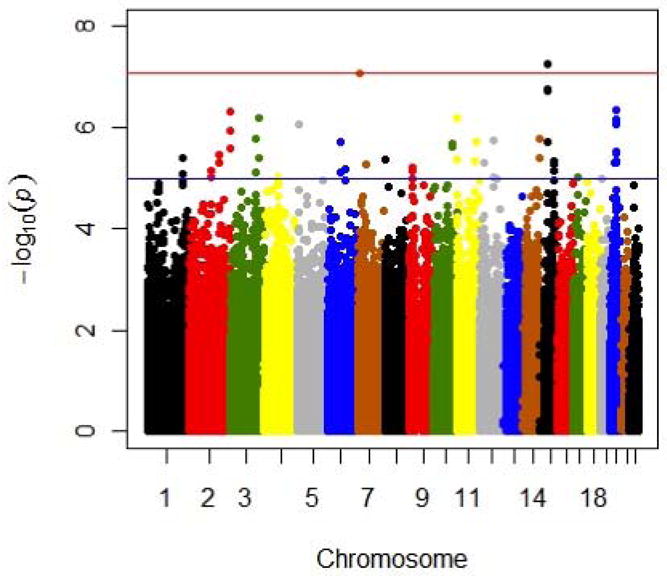
−log10 values shown here were not corrected for inflation factor.
Table 1.
Chromosome regions containing 3 or more SNPs within 50 kb of each other that are associated with symptom count at inflation corrected p<0.0001 and the comparison of association between alcohol dependence symptom count and DSM-IV alcohol dependence in these regions.
| Chromosome location | SNP | Position (hg19) | Gene/Transcript | Gene/Transcript position | Alcohol dependence symptom count | DSM-IV alcohol dependence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | p value | Corrected p value | Effect | p value | |||||
| 1q32.3 | rs612414 | 212602176 | NENF | 212606229---212619721 | −0.15 | 1.07E-05 | 7.85E-05 | −0.26 | 2.25E-03 |
| rs583058 | 212610755 | NENF | −0.13 | 1.42E-05 | 9.92E-05 | −0.23 | 9.44E-04 | ||
| rs4804 | 212619339 | NENF | −0.14 | 8.36E-06 | 6.44E-05 | −0.24 | 7.15E-04 | ||
| rs483954 | 212620214 | NENF | −0.15 | 3.90E-06 | 3.47E-05 | −0.27 | 6.30E-04 | ||
|
| |||||||||
| 2q37.3 | rs896543 | 237509207 | CXCR7 | 237478380---237490997 | −0.22 | 4.75E-07 | 6.29E-06 | −0.56 | 4.35E-06 |
| rs6431476 | 237517937 | CXCR7 | −0.20 | 1.14E-06 | 1.28E-05 | −0.51 | 3.92E-06 | ||
| rs7594454 | 237537935 | CXCR7 | −0.18 | 2.60E-06 | 2.49E-05 | −0.44 | 3.05E-05 | ||
|
| |||||||||
| 3q24 | rs7431637 | 143049769 | SLC9A9 | 142984064---143567373 | −0.14 | 7.58E-06 | 5.95E-05 | −0.31 | 3.60E-04 |
| rs10446322 | 143068250 | SLC9A9 | −0.15 | 1.73E-06 | 1.80E-05 | −0.33 | 5.77E-05 | ||
| rs868702 | 143085345 | SLC9A9 | 0.15 | 1.73E-06 | 1.79E-05 | 0.34 | 2.58E-05 | ||
|
| |||||||||
| 4q21.21 | rs12513014 | 81061422 | intergenic | 0.16 | 1.38E-05 | 9.70E-05 | 0.35 | 1.02E-03 | |
| rs13102102 | 81073672 | intergenic | 0.14 | 1.11E-05 | 8.12E-05 | 0.35 | 1.37E-05 | ||
| rs13138779 | 81087073 | intergenic | 0.21 | 9.75E-06 | 7.30E-05 | 0.49 | 7.69E-04 | ||
|
| |||||||||
| 9p22.2 | rs10963462 | 18130036 | intergenic | −0.18 | 6.22E-06 | 5.07E-05 | −0.40 | 1.18E-05 | |
| rs763976 | 18134914 | intergenic | −0.17 | 1.00E-05 | 7.46E-05 | −0.40 | 7.40E-06 | ||
| rs12006002 | 18166899 | intergenic | 0.15 | 7.24E-06 | 5.73E-05 | 0.45 | 4.87E-07 | ||
|
| |||||||||
| 15q14 | rs7168475 | 38960882 | C15orf53 | 38988799---38992239 | −0.18 | 1.98E-06 | 2.00E-05 | −0.39 | 4.66E-04 |
| rs12903120 | 38988097 | C15orf53 | −0.18 | 5.45E-08 | 1.09E-06 | −0.38 | 7.62E-06 | ||
| rs12916379 | 38991520 | C15orf53 | −0.17 | 1.74E-07 | 2.79E-06 | −0.36 | 4.06E-05 | ||
| rs2132157 | 38992547 | C15orf53 | −0.17 | 1.92E-07 | 3.02E-06 | −0.36 | 4.35E-05 | ||
|
| |||||||||
| 15q24.2 | rs2029519 | 75415962 | intergenic | 0.14 | 1.07E-05 | 7.87E-05 | 0.29 | 1.60E-03 | |
| rs4479194 | 75422131 | intergenic | 0.15 | 5.27E-06 | 4.43E-05 | 0.30 | 1.02E-03 | ||
| rs7172677 | 75424593 | intergenic | 0.15 | 7.15E-06 | 5.68E-05 | 0.32 | 5.35E-04 | ||
|
| |||||||||
| 20q11.22 | rs6060124 | 33536897 | GSS | 33516236---33543601 | 0.16 | 4.41E-07 | 5.92E-06 | 0.33 | 2.03E-04 |
| rs6088664 | 33551100 | MYH7B | 33543704---33590240 | −0.15 | 3.23E-06 | 2.98E-05 | −0.27 | 1.91E-03 | |
| rs6579204 | 33553677 | MYH7B | 0.15 | 4.54E-06 | 3.93E-05 | 0.29 | 1.25E-03 | ||
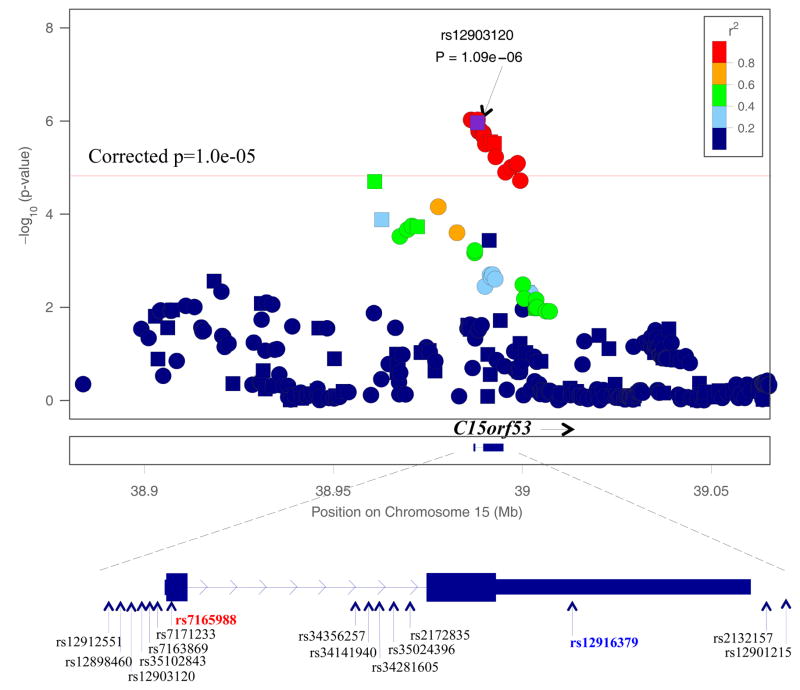
The strongest association was detected with rs12903120 (p=5.45×10−8, inflation corrected p=1.09×10−6) in an uncharacterized gene, C15orf53 on chromosome 15q14. Two other genotyped SNPs, rs12916379 and rs2132157, that are highly correlated with rs12903120 (D′=1, r2=1 in HapMap EUR reference sample) also showed strong association with SC (with inflation corrected p=2.79×10−6 and p=3.02×10−6, respectively) (Table S3). Rs12916379 is located in the 3′ un-translated region of C15orf53 (Figure 3). Using imputed genotypes, 15 additional SNPs in C15orf53 gene region also showed suggestive evidence of association (inflation corrected p≤1.0×10−5) with SC (Table S3). Three of these 15 SNPs have stronger association (inflation corrected 9.4×10−7≤ p ≤9.7×10−7) with SC than the genotyped SNP rs12903120. A non-synonymous coding SNP in C15orf53 that is highly correlated with rs12903120 (rs7165988; r2=0.95, D′=1 in HapMap EUR reference sample) is associated with SC at an inflation corrected p=1.7×10−6.
Figure 3. Plot of chromosome 15q14 association with DSM_IV alcohol dependence symptom count.
Squares represent genotyped SNPs; Circles represent imputed SNPs. SNP rs7165988 (in red) is a non-synonymous coding variant. SNP rs12916379 (in blue) is in 3′un-translated region of C15orf53.
Association with DSM-IV alcohol dependence in the regions of interest
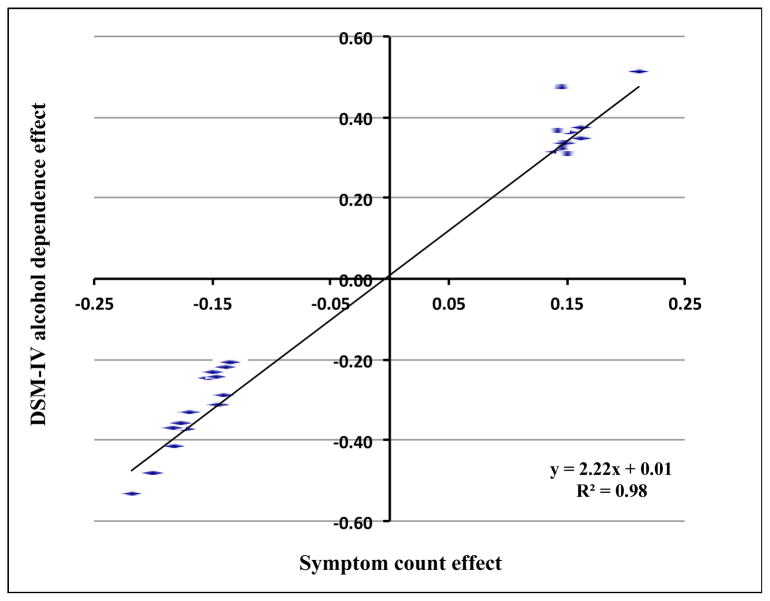
We tested whether SNPs in the 7 chromosome regions associated with SC were also associated with DSM-IV AD. Our association analysis using a GEE model found none of the genotyped SNPs in these regions attained genome-wide significance with DSM-IV AD. By comparing the associations for SC with DSM-IV AD, we observed a less significant association with the dichotomous diagnostic trait than the association with SC (Table 1). However, the effect sizes between the two phenotypes were highly correlated (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Correlation between symptom count effect and DSM-IV alcohol dependence effect in COGA sample.
Replication of association in SAGE and OZALC studies
Seventy-two SNPs that associated with SC (with corrected p<10−4) in the COGA families were tested in SAGE. Based on a prior hypothesis (our initial results from GWAS) for each SNP regarding the direction of effect, we found 5/72 SNPs showing nominal association with the same direction of effect for SC (0.007≤p≤0.05). However, none of these SNPs is significant after correcting for multiple testing. We then tested the replication of the 18 SNPs in C15orf53 that showed suggestive evidence of association with SC in COGA sample (inflation corrected p=1.0×10−5). Using imputed data, 8 of these 18 SNPs showed nominal association with SC in SAGE sample (p≤0.03) (Table S3). These 18 SNPs all lie within a single LD bin (r2=0.8, D′≥0.9), so the data shown in Table S3 reflects a single statistical test.
Sixty-nine of the 72 SNPs associated with SC (with inflation corrected p<10−4) in the COGA families were tested in OZALC. None of these SNPs showed association with SC in this sample (Table S2). Association of SNPs in the C15orf53 gene region (rs2132157, rs12916379 and rs12903120, with p=0.03, p=0.03, and p=0.05, respectively) was observed with DSM-IV AD but not with SC (data not shown).
DISCUSSION
We conducted a family-based GWAS and identified genome-wide significant association (p=5.4×10−8) between SC and SNPs in chromosome 15q14. However, the Q-Q plot for the COGA family-based sample suggests genomic inflation factor of 1.25. One possible explanation is the presence of polygenic inheritance29. The SC trait is likely due to many loci of small effect. Because of this and the high LD in the dense map, it is possible that there are relatively few genomic regions free of loci with small effect moderately inflating GIF. A second possibility is that the inflation may be due to the presence of very large families in our sample. Since our association test controls for relatedness by treating each family as a separate cluster, this may be insufficient in families where distantly related individuals should not be clustered into the same class. After correcting for the genomic inflation factor of 1.25 using the genomic controls method, none of the SNPs associated with SC reached genome-wide significance.
Most GWAS studies do not employ family-based data; thus, there are inherent challenges in estimating the power of the sample to detect particular effect sizes. However, the implementation of a correlation matrix subdivided by family clusters to control for relatedness among the families pares symptom count analysis to an association test similar to a case-control study, as do the generalized estimating equations (GEE) used to analyze alcohol dependence. Both methods provide similar power estimates based on simulation studies30,31. For this sample, we estimated power using Quanto32. These extended pedigrees have 70% power to detect an effect size of 1.1 for symptom count when the minor allele frequency is between 0.10 and 0.30.
The strongest association (inflation corrected 9.4×10−7≤p≤ 9.8×10−6) was detected with a group of 18 highly correlated variants (r2≥=0.95) within and flanking C15orf53. Interestingly, recent GWAS data has reported consistent evidence showing that variation in a region close to C15orf53 influences susceptibility for bipolar disorder 33–36. SNPs that influenced bipolar disorder susceptibility (rs12912251, rs2172835, and rs12899449) also show strong association with SC (inflation corrected p=9.4×10−7, p=3.1×10−6, and p=1.26×10−5, respectively) in COGA families severely affected by AD. The alleles that are associated with reduced risk for BD are also associated with lower dependence symptom counts. We did not detect association between symptom counts and other variants reported by the Psychiatric GWAS Consortium Bipolar Disorder Working Group (2011) to be strongly associated with bipolar disorder. This suggests a specific effect of this gene on risk for bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence rather than a more general shared underlying liability to both disorders. Studies of psychiatric disorders have shown that bipolar disorder and alcoholism commonly co-occur37–39, and that individuals with bipolar disorder have a greater likelihood of AUDs than the general population40. Approximately 46% of subjects with bipolar disorder type I have AUDs, while 39% of subjects with a less severe form of mania, bipolar disorder II, have an AUDs37–39. The association of C15orf53 with SC detected in this study suggests the possibility of a specific genetic link between bipolar disorder and alcoholism.
Two of the imputed SNPs showing strong association with SC are located within the exons of C15orf53 (Figure 3). C15orf53 encodes an uncharacterized protein of 179 amino acids with homology to uncharacterized proteins in other species including chimpanzee, gibbon and orangutan. Rs7165988 in exon 1 results in a non-synonymous coding change of valine to leucine at codon 3. This substitution is predicted to be possibly damaging by POLYPHEN41. Rs12916379 is located within the 3′ UTR of C15orf53 and could influence transcript stability. Our preliminary data showed that C15orf53 mRNA expression is detectable in 9 brain regions tested though the expression level is low. The method of this assay is included in the supplementary information.
There are 5 additional candidate genes located in chromosomal regions showing association with SC (Table 1). Among these, SLC9A9 encodes a sodium and hydrogen exchanger in chromosome 3q24, and is of particular interest as it has been linked to tobacco smoking initiation, a behavior highly comorbid with alcohol use42. Studies have repeatedly shown evidence of association between SLC9A9 and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)43–45. Because inattention is a predictor of smoking initiation46 and ADHD and smoking are co-transmitted through families more often than expected by chance47, it is possible SLC9A9 influences both smoking and inattention. The association of SLC9A9 with SC identified in this study suggests a genetic connection between ADHD, smoking and alcoholism. Our preliminary data showed that SLC9A9 mRNA expression is detectable in human frontal cortex. Total mRNA expression in brain tissues derived from alcoholics is 1.09 fold higher than in the brain tissues derived from non-alcoholic subjects. Another gene of interest, CXCR7 in chromosome 2q37.3, encodes C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7, a member of the G-protein coupled receptor family. Our preliminary assay with human frontal cortices showed CXCR7 total mRNA expression is 1.33 fold higher in alcoholics, compared to the expression level in non-alcoholic subjects. The method of these assays is included in the supplementary information.
To date, four previous case-control GWAS analyses of AUDs have not provided evidence of association that reached genome-wide significance with AD or quantitative traits 9–12. In this study our approach to identifying genetic risk factors for alcohol problems focused primarily on a quantitative measure of alcohol symptom count, rather than an AUD diagnosis. Our SC measure was based on 7 DSM-IV AD criteria and deliberately excluded the 4 criteria associated with DSM-IV alcohol abuse. We crafted this measure to allow the most straightforward comparisons between findings for SC and findings for diagnosis of dependence. Dimensional dependence measures such as SC are more powerful than dichotomized phenotypic measures (i.e. DSM-IV AD) for detecting risk factors, especially in samples containing adolescent subjects. In the present study, we compared chromosomal regions that showed strong associations with both SC and DSM-IV AD and consistently observed a stronger relationship for genetic variants with SC than with DSM-IV AD (Table 1, Figure 4); the effect sizes and directions for both phenotypes were relatively consistent.
Although we are encouraged by our findings, we recognize that there are limitations to our study. Among our top candidate genes, we only detected nominal association for C15orf53 and SC in SAGE. Several reasons could possibly explain this limited replication. First, the power to replicate findings of small effect across studies in samples of the size used in this study is low. Second, in contrast to the COGA sample, neither the SAGE nor the OZALC samples were ascertained from large families severely affected by AUDs. It is possible that severely affected families have a concentration of genetic variants that influence risk for alcoholism and that may have less effect on alcoholism in the general population. A coordinated evaluation including many more families severely affected by alcoholism is necessary to confirm our findings.
In summary, our family-based GWAS identified SNPs in the gene C15orf53 that showed suggestive evidence of association with DSM-IV alcohol dependence symptom count. Interestingly, SNPs in this gene have previously been associated with risk for bipolar disorder in other GWAS and suggest there may be some common genetic factors contributing to both disorders.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA)
COGA, Principal Investigators B. Porjesz, V. Hesselbrock, H. Edenberg, L. Bierut, includes ten different centers: University of Connecticut (V. Hesselbrock); Indiana University (H.J. Edenberg, J. Nurnberger Jr., T. Foroud); University of Iowa (S. Kuperman, J. Kramer); SUNY Downstate (B. Porjesz); Washington University in St. Louis (L. Bierut, A. Goate, J. Rice, K. Bucholz); University of California at San Diego (M. Schuckit); Rutgers University (J. Tischfield); Southwest Foundation (L. Almasy), Howard University (R. Taylor) and Virginia Commonwealth University (D. Dick). A. Parsian and M. Reilly are the NIAAA Staff Collaborators. We continue to be inspired by our memories of Henri Begleiter and Theodore Reich, founding PI and Co-PI of COGA, and also owe a debt of gratitude to other past organizers of COGA, including Ting-Kai Li, currently a consultant with COGA, P. Michael Conneally, Raymond Crowe, and Wendy Reich, for their critical contributions. This national collaborative study is supported by NIH Grant U10AA008401 from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
The Study of Addiction: Genetics and Environment (SAGE)
Funding support for SAGE was provided through the NIH Genes, Environment and Health Initiative (GEI) (U01 HG004422). SAGE is one of the genome-wide association studies funded as part of the Gene Environment Association Studies (GENEVA) under GEI. Assistance with phenotype harmonization and genotype cleaning, as well as with general study coordination, was provided by the GENEVA Coordinating Center (U01 HG004446). Assistance with data cleaning was provided by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Support for collection of datasets and samples was provided by COGA (U10 AA008401), the Collaborative Genetic Study of Nicotine Dependence (COGEND; P01 CA089392), and the Family Study of Cocaine Dependence (FSCD; R01 DA013423, R01 DA019963). Genotyping at the Johns Hopkins University Center for Inherited Disease Research was supported by the NIH GEI (U01HG004438) grant, NIAAA, NIDA, and the NIH contract “High throughput genotyping for studying the genetic contributions to human disease”
The Australian Twin-family Study of Alcohol Use Disorder (OZALC) Sample
The OZALC study was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants AA07535, AA07728, AA13320, AA13321, AA14041, AA11998, AA17688, DA012854, and DA019951; by Grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (241944, 339462, 389927, 389875, 389891, 389892, 389938, 442915, 442981, 496739, 552485, and 552498); by Grants from the Australian Research Council (A7960034, A79906588, A79801419, DP0770096, DP0212016, and DP0343921); and by the 5th Framework Programme (FP-5) GenomEUtwin Project (QLG2-CT-2002-01254). Genotyping at Center for Inherited Disease Research was supported by a Grant to the late Richard Todd, M.D., Ph.D., former Principal Investigator of Grant AA13320. We acknowledge the contribution of Anjali Henders and Yi-Ling for their technical assistance.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest
Drs. LJ Bierut, AM Goate, AJ Hinrichs, J Rice and JC Wang are listed as inventors on the patent “Markers for Addiction” (US 20070258898) covering the use of certain SNPs in determining the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of addiction.
Supplementary information is available at Molecular Psychiatry’s website
References
- 1.Organization, W.H. Global strategy to reduce the harmful use of alcohol. World Health Organization; 2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goodwin DW, et al. Drinking problems in adopted and nonadopted sons of alcoholics. Archives of general psychiatry. 1974;31:164–9. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1974.01760140022003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Heath AC, et al. Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol dependence risk in a national twin sample: consistency of findings in women and men. Psychological medicine. 1997;27:1381–96. doi: 10.1017/s0033291797005643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dick DM, et al. Role of GABRA2 in trajectories of externalizing behavior across development and evidence of moderation by parental monitoring. Archives of general psychiatry. 2009;66:649–57. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kendler KS, Neale MC, Heath AC, Kessler RC, Eaves LJ. A twin-family study of alcoholism in women. The American journal of psychiatry. 1994;151:707–15. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.5.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Prescott CA, Kendler KS. Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol abuse and dependence in a population-based sample of male twins. The American journal of psychiatry. 1999;156:34–40. doi: 10.1176/ajp.156.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Prescott CA, et al. Genomewide linkage study in the Irish affected sib pair study of alcohol dependence: evidence for a susceptibility region for symptoms of alcohol dependence on chromosome 4. Molecular psychiatry. 2006;11:603–11. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schuckit MA, et al. A genome-wide search for genes that relate to a low level of response to alcohol. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2001;25:323–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Treutlein J, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence. Archives of general psychiatry. 2009;66:773–84. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Edenberg HJ, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence implicates a region on chromosome 11. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2010;34:840–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bierut LJ, et al. A genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:5082–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911109107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Heath AC, et al. A quantitative-trait genome-wide association study of alcoholism risk in the community: findings and implications. Biological psychiatry. 2011;70:513–8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.02.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kendler KS, et al. Genomewide association analysis of symptoms of alcohol dependence in the molecular genetics of schizophrenia (MGS2) control sample. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2011;35:963–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Begleiter H, Porjesz B, Wang W. Event-related brain potentials differentiate priming and recognition to familiar and unfamiliar faces. Electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology. 1995;94:41–9. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(94)00240-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Edenberg HJ. The collaborative study on the genetics of alcoholism: an update. Alcohol research & health: the journal of the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. 2002;26:214–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Foroud T, et al. Alcoholism susceptibility loci: confirmation studies in a replicate sample and further mapping. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2000;24:933–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nurnberger JIWR, Jr, Bucholz K, O’Connor S, Meyer ET, Reich T, Rice J, Schuckit M, King L, Petti T, Bierut L, Hinrichs AL, Kuperman S, Hesselbrock V, Porjesz B. A family study of alcohol dependence: coaggregation of multiple disorders in relatives of alcohol-dependent probands. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:1246–1256. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.61.12.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Reich T, et al. Genome-wide search for genes affecting the risk for alcohol dependence. American journal of medical genetics. 1998;81:207–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bucholz KK, et al. Can we subtype alcoholism? A latent class analysis of data from relatives of alcoholics in a multicenter family study of alcoholism. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 1996;20:1462–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb01150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hasin DS, Liu X, Alderson D, Grant BF. DSM-IV alcohol dependence: a categorical or dimensional phenotype? Psychological medicine. 2006;36:1695–705. doi: 10.1017/S0033291706009068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Heath AC, Martin NG. Genetic influences on alcohol consumption patterns and problem drinking: results from the Australian NH&MRC twin panel follow-up survey. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1994;708:72–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb24699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Grant JD, et al. Alcohol consumption indices of genetic risk for alcohol dependence. Biological psychiatry. 2009;66:795–800. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.05.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kendler KS, Myers J, Dick D, Prescott CA. The relationship between genetic influences on alcohol dependence and on patterns of alcohol consumption. Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research. 2010;34:1058–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hesselbrock MEC, Bucholz KK, Schuckit M, Hesselbrock V. A validity study of the SSAGA--a comparison with the SCAN. Addiction. 1999;94:1361–1370. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.1999.94913618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Browning BL, Browning SR. A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype-phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals. American journal of human genetics. 2009;84:210–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hadfield JD, Nakagawa S. General quantitative genetic methods for comparative biology: phylogenies, taxonomies and multi-trait models for continuous and categorical characters. Journal of evolutionary biology. 2010;23:494–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2009.01915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Devlin BRK. Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics. 1999;55:997–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.1999.00997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chen MH, Yang Q. GWAF: an R package for genome-wide association analyses with family data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:580–1. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yang JWM, Purcell S, Lettre G, Estrada K, Willer CJ, Smith AV, Ingelsson E, O’Connell JR, Mangino M, Mägi R, Madden PA, Heath AC, Nyholt DR, Martin NG, Montgomery GW, Frayling TM, Hirschhorn JN, McCarthy MI, Goddard ME, Visscher PM GIANT Consortium. Genomic inflation factors under polygenic inheritance. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011;19:807–812. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Litaker M, Ferris D. Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference of the SouthEast SAS Users Group. 2004. A simulation study to evaluate ANOVA and GEE for Comparing Correlated Proportions with Missing Values. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xue X, et al. Marginal and mixed-effects models in the analysis of human papillomavirus natural history data. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:159–69. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gauderman W. M.J. QUANTO 1.2. A computer program for power and sample size calculations for genetic-epidemiology studies. 2006 [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ferreira MA, et al. Collaborative genome-wide association analysis supports a role for ANK3 and CACNA1C in bipolar disorder. Nature genetics. 2008;40:1056–8. doi: 10.1038/ng.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Liu Y, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data of bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. Molecular psychiatry. 2011;16:2–4. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sklar P, et al. Large-scale genome-wide association analysis of bipolar disorder identifies a new susceptibility locus near ODZ4. Nature genetics. 2011;43:977–83. doi: 10.1038/ng.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Smith EN, et al. Genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder in European American and African American individuals. Molecular psychiatry. 2009;14:755–63. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kessler RC, et al. Comorbidity of DSM-III-R major depressive disorder in the general population: results from the US National Comorbidity Survey. The British journal of psychiatry. Supplement. 1996:17–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Regier DA, et al. Comorbidity of mental disorders with alcohol and other drug abuse. Results from the Epidemiologic Catchment Area (ECA) Study. JAMA: the journal of the American Medical Association. 1990;264:2511–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sonne JE, Zeifer B, Linstrom C. Manifestations of otosyphilis as visualized with computed tomography. Otology & neurotology: official publication of the American Otological Society, American Neurotology Society [and] European Academy of Otology and Neurotology. 2002;23:806–7. doi: 10.1097/00129492-200209000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Helzer JEP, TR The Co-Occurrence of Alcoholism with other Psychiatric Disorders in the General Population Its Impact on Treatment. J Stud Alcohol. 1988;49:219–224. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1988.49.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Vasily Ramensky PB, Sunyaev Shamil. Human non-synonymous SNPs: server survey. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:3894–3900. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vink JM, et al. Genome-wide association study of smoking initiation and current smoking. American journal of human genetics. 2009;84:367–79. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Franke B, et al. Multicenter analysis of the SLC6A3/DAT1 VNTR haplotype in persistent ADHD suggests differential involvement of the gene in childhood and persistent ADHD. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:656–64. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Markunas CA, et al. Genetic variants in SLC9A9 are associated with measures of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in families. Psychiatric genetics. 2010;20:73–81. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e3283351209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mick E, et al. Family-based genome-wide association scan of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2010;49:898–905. e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2010.02.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Barman SK, Pulkkinen L, Kaprio J, Rose RJ. Inattentiveness, parental smoking and adolescent smoking initiation. Addiction. 2004;99:1049–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2004.00789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Monuteaux MC, et al. The familial association between cigarette smoking and ADHD: a study of clinically referred girls with and without ADHD, and their families. Nicotine & tobacco research: official journal of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco. 2008;10:1549–58. doi: 10.1080/14622200802326137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.