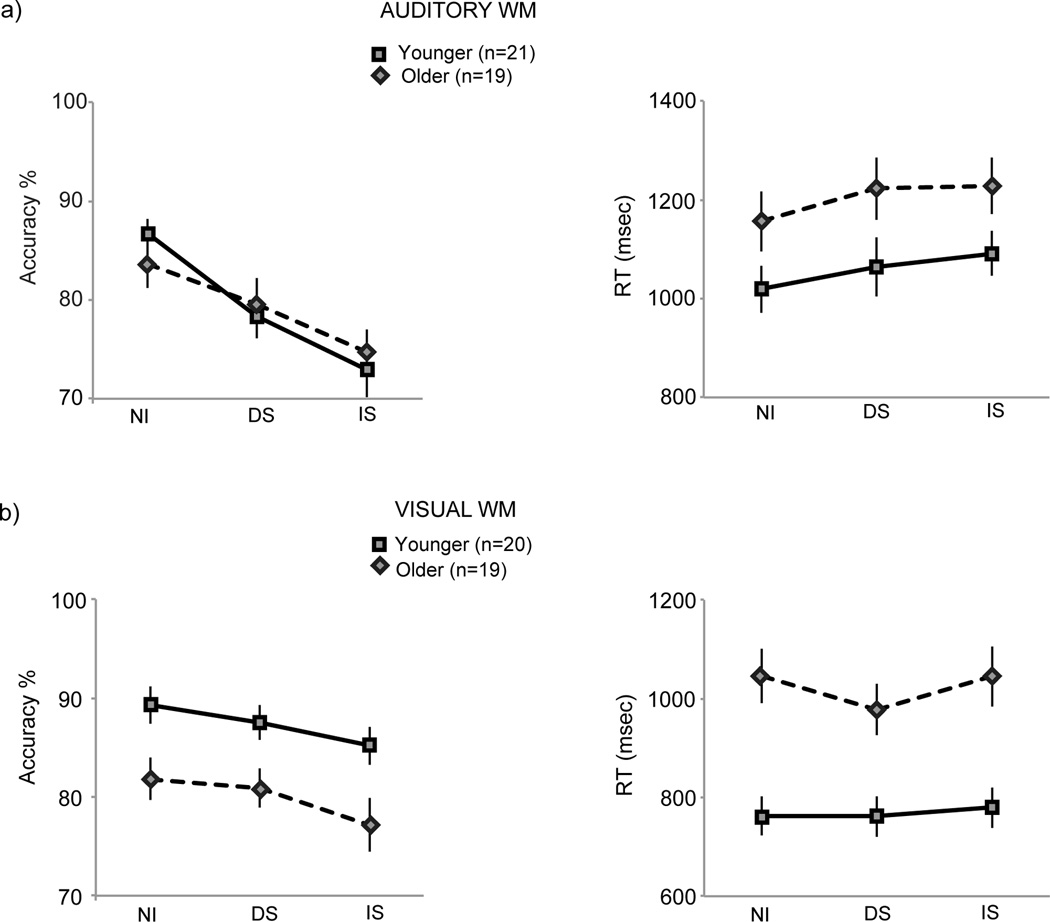
Figure 2.
Behavioral performance in the (a) auditory and (b) visual experiment tasks, accuracy and RT plotted in the left and right columns, respectively. WM accuracy was maximal during NI followed by DS and least during the IS condition in both younger and older adults, in both auditory and visual modalities. Older adults did not suffer relatively greater impacts of interference on WM performance relative to interference impacts observed in younger adults either for accuracy or RT measures.