Abstract
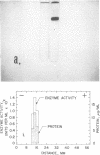
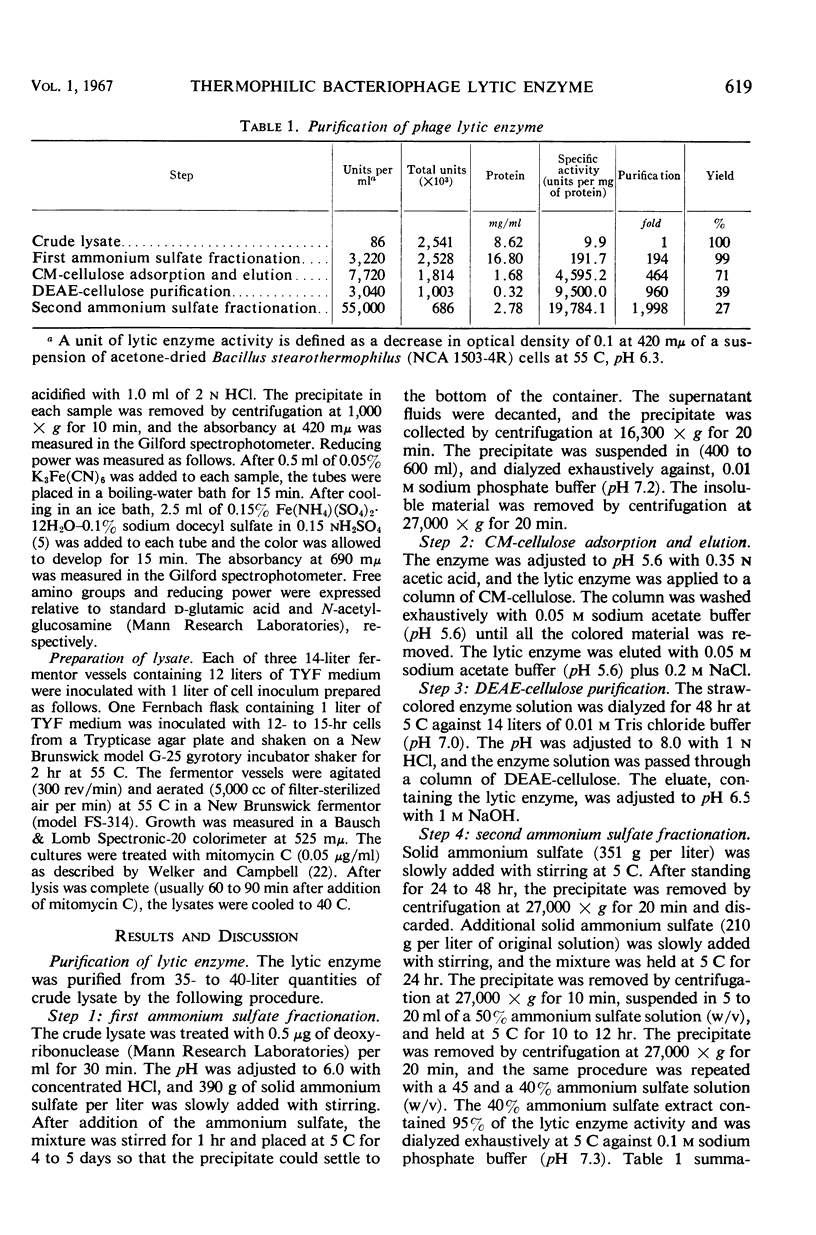
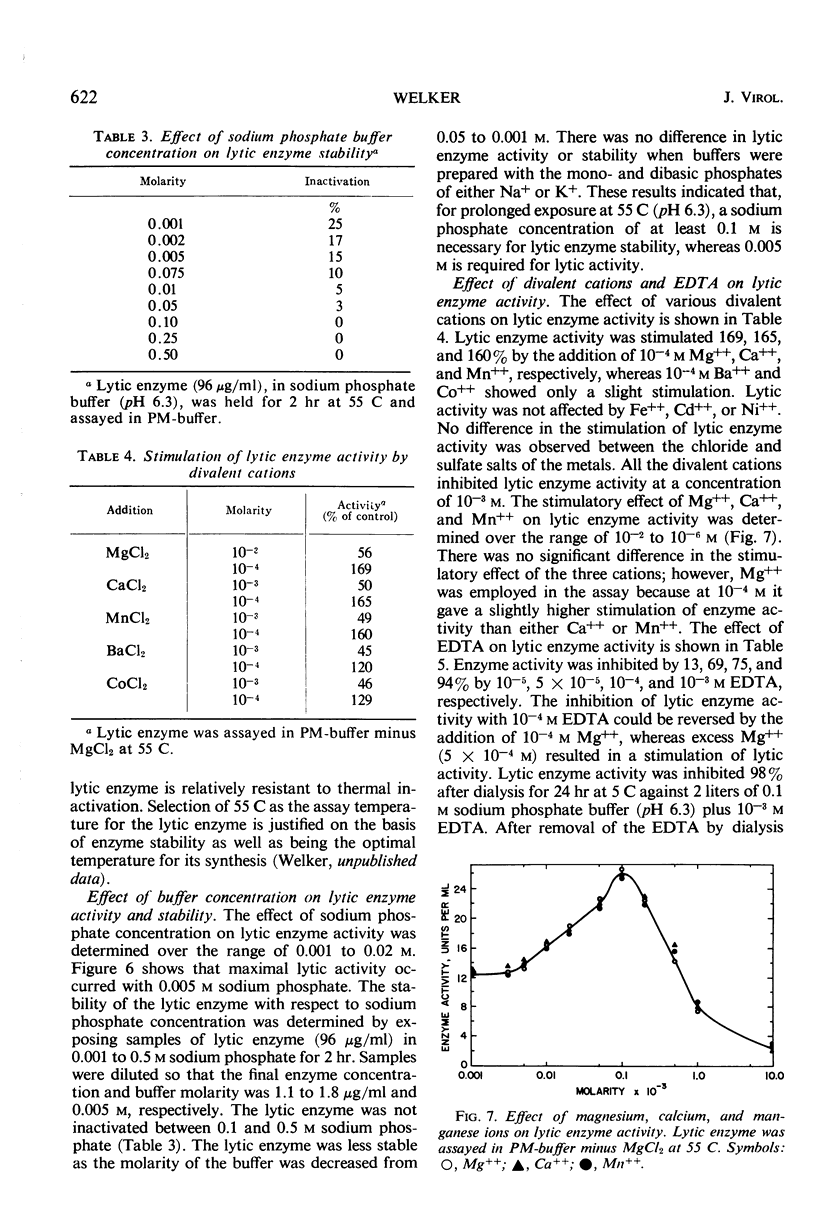
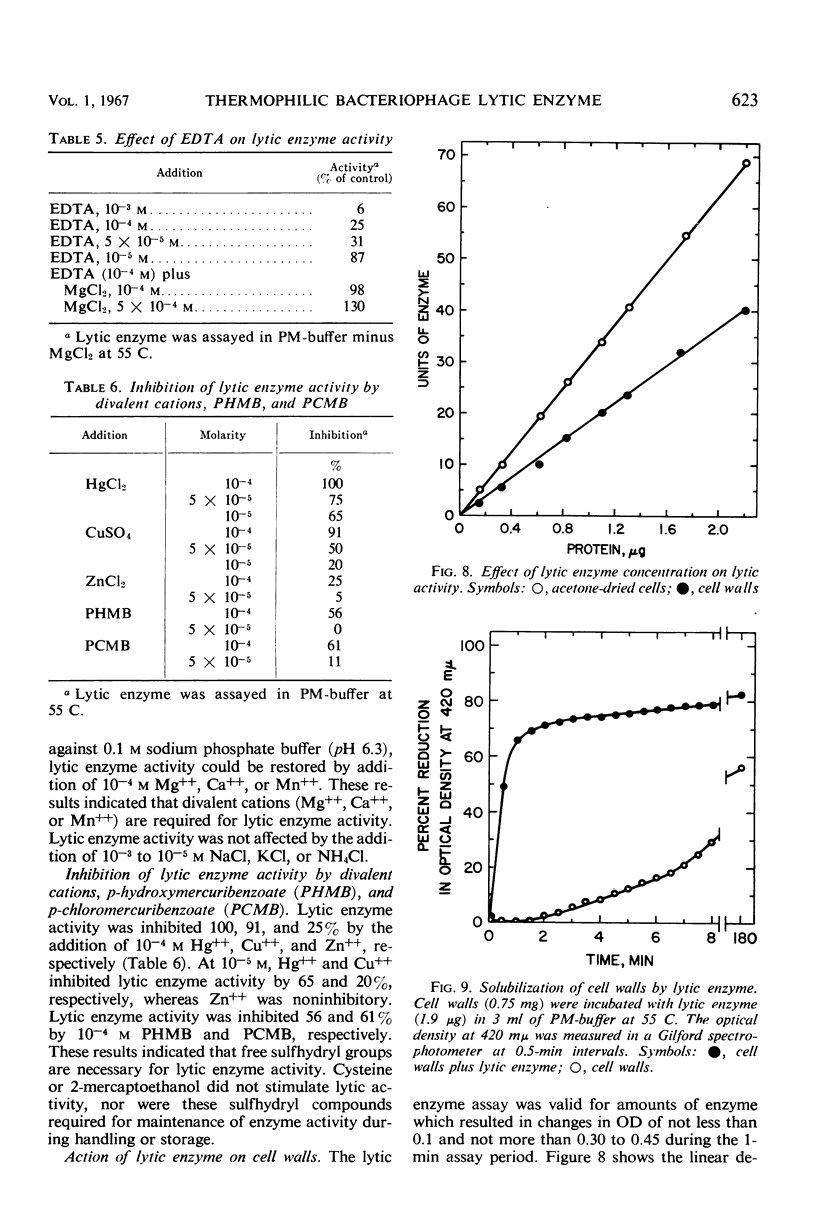
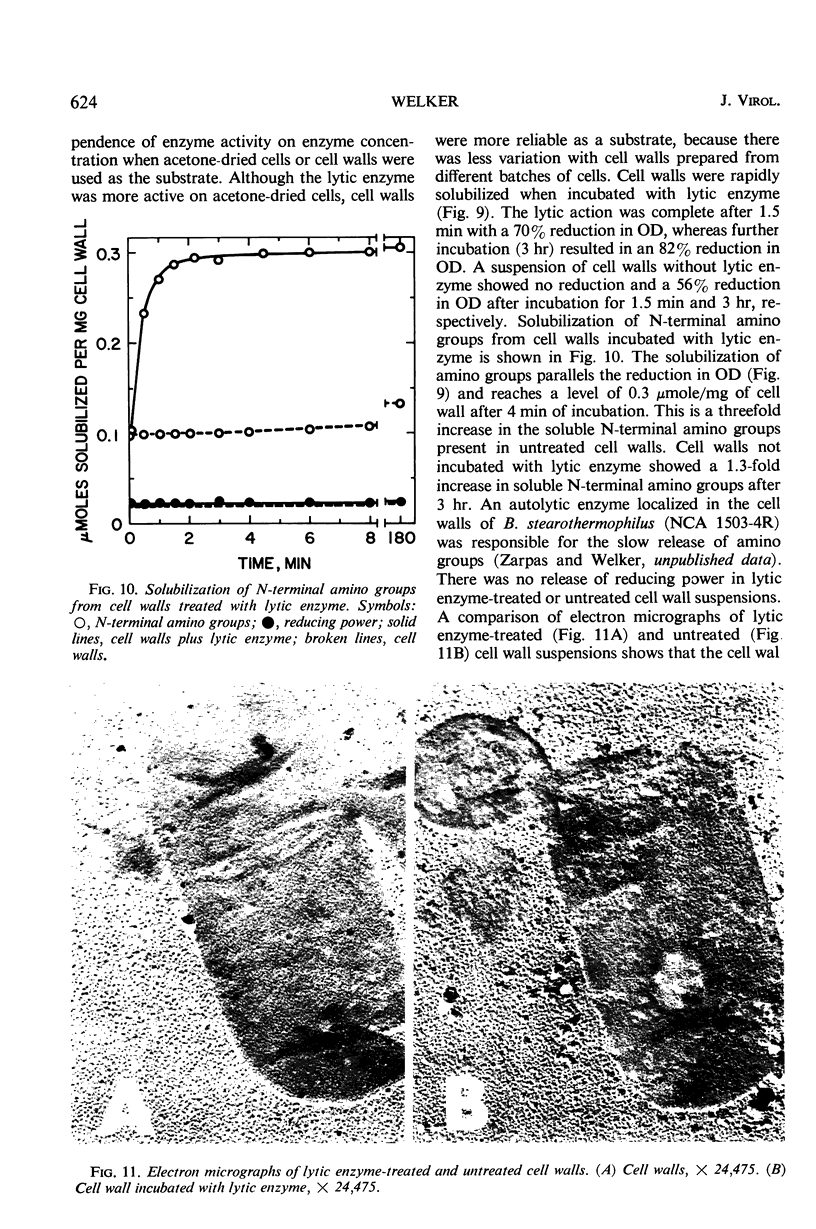
A phage lytic enzyme was isolated from lysates of Bacillus stearothermophilus (NCA 1503-4R). The enzyme was purified 1,998-fold with a 27% recovery of enzyme activity. By use of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and sucrose gradient centrifugation the enzyme was judged free from protein contaminants. The lytic enzyme was active over a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0, with a maximum at 6.3, and it was stable between pH 7.0 and 8.0 and at 5.0 and unstable between pH 5.5 and 6.5. The temperature coefficient (Q10) was 2.27 between 35 and 45 C, 2.01 between 45 and 55 C, and 2.00 between 50 and 60 C. Lytic enzyme in 0.1 m sodium phosphate was not inactivated after a 1-hr exposure to temperatures below 65.5 C, whereas a 1% inactivation was observed at 70.6 C. A 2-hr exposure at 60.1, 65.5, and 70.6 C resulted in an inactivation of 1.2, 9.6, and 12.0%, respectively. A sodium phosphate concentration of at least 0.1 m was necessary for the prolonged exposure of lytic enzyme at 55 C (pH 6.3), whereas 0.005 m was required for maximal lytic activity. Lytic activity was stimulated 169, 165, and 160% by 10−4m Mg++, Ca++, and Mn++, respectively. Lytic activity was inhibited 75% by 10−4m ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The EDTA inhibition could be reversed by the addition of excess Mg++, Ca++, or Mn++. Lytic activity was not affected by NaCl, KCl, or NH4Cl. Lytic activity was inhibited 100, 91, 25, 61, and 56% by 10−4m Hg++, Cu++, Zn++, p-chloromercuribenzoate, and p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, respectively. Cysteine or 2-mercaptoethanol did not stimulate lytic activity, nor were these sulfhydryl compounds required for maintenance of enzyme activity during handling or storage. Cell walls were rapidly solubilized when incubated with lytic enzyme. Lytic action was complete after 1.5 min, with a 70% reduction in optical density (OD). Cell walls without lytic enzyme showed no reduction in OD during this period. The solubilization of N-terminal amino groups paralleled the reduction in OD and reached a level of 0.3 μmole/mg of cell wall after 4 min of incubation. Cell walls with and without lytic enzyme treatment showed a 3- and a 1.3-fold increase, respectively, in N-terminal amino groups after 3 hr of incubation. There was no release of reducing power in either the untreated cell wall suspensions or those treated with lytic enzyme. Electron micrographs of treated and untreated cell walls showed that the enzyme partially degrades the cell wall with the release of small wall fragments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKULIS S. S., SMITH C., BOLTRALIK J. J., HEYMANN H. STRUCTURE OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. IV. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF STREPTOCOCCAL PHAGE MURALYSIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4027–4033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGHTY C. C., HAYASHI J. A. Enzymatic properties of a phage-induced lysin affecting group A streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:1058–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.1058-1068.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N., WITTNER M. K. OBSERVATIONS ON THE GROUP C STREPTOCOCCAL BACTERIOPHAGE AND LYTIC ENZYME SYSTEM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:496–502. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.496-502.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B., SUZUKI G. Relation of endolysin to lysis by lambda bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:596–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.596-597.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., FUERST C. R. The mechanism of lysis by phage studied with defective lysogenic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):518–526. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M. Studies on bacteriophages of hemolytic streptococci. I. Factors influencing the interaction of phage and susceptible host cell. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):365–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAASS D., WEIDEL W. FINAL PROOF FOR THE IDENTITY OF ENZYMIC SPECIFICITIES OF EGG-WHITE LYSOZYME AND PHAGE T2 ENZYME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 29;78:369–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91648-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERIGAN T. C., DREYER W. J. Studies on the antigenic combining sites in bacteriophage lysozyme. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 May 8;103:765–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb53733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY J. S. A phage-associated enzyme of Bacillus megaterium which destroys the bacterial cell wall. Virology. 1957 Dec;4(3):563–581. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY J. S. An agent derived from B. megaterium phage G which dissolves the bacterial cell wall. Virology. 1960 Jun;11:510–513. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., JOHNSON M. J. A submicrodetermination of glucose. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Virolysin: a virus-induced lysin from staphylococcal phage lysates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Aug;89(4):502–507. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REITER B., ORAM J. D. GROUP N STREPTOCOCCAL PHAGE LYSIN. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jul;32:29–32. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STREISINGER G., MUKAI F., DREYER W. J., MILLER B., HORIUCHI S. Mutations affecting the lysozyme of phage T4. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:25–30. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutow A. B., Welker N. E. Chemical composition of the cell walls of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1452–1457. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1452-1457.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELKER N. E., CAMPBELL L. L. INDUCTION AND PROPERTIES OF A TEMPERATURE BACTERIOPHAGE FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:175–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.175-184.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORK E. The action of a lytic enzyme from spores of a bacillus on various species of bacteria. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1959 Apr;96(4):468–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]