Abstract
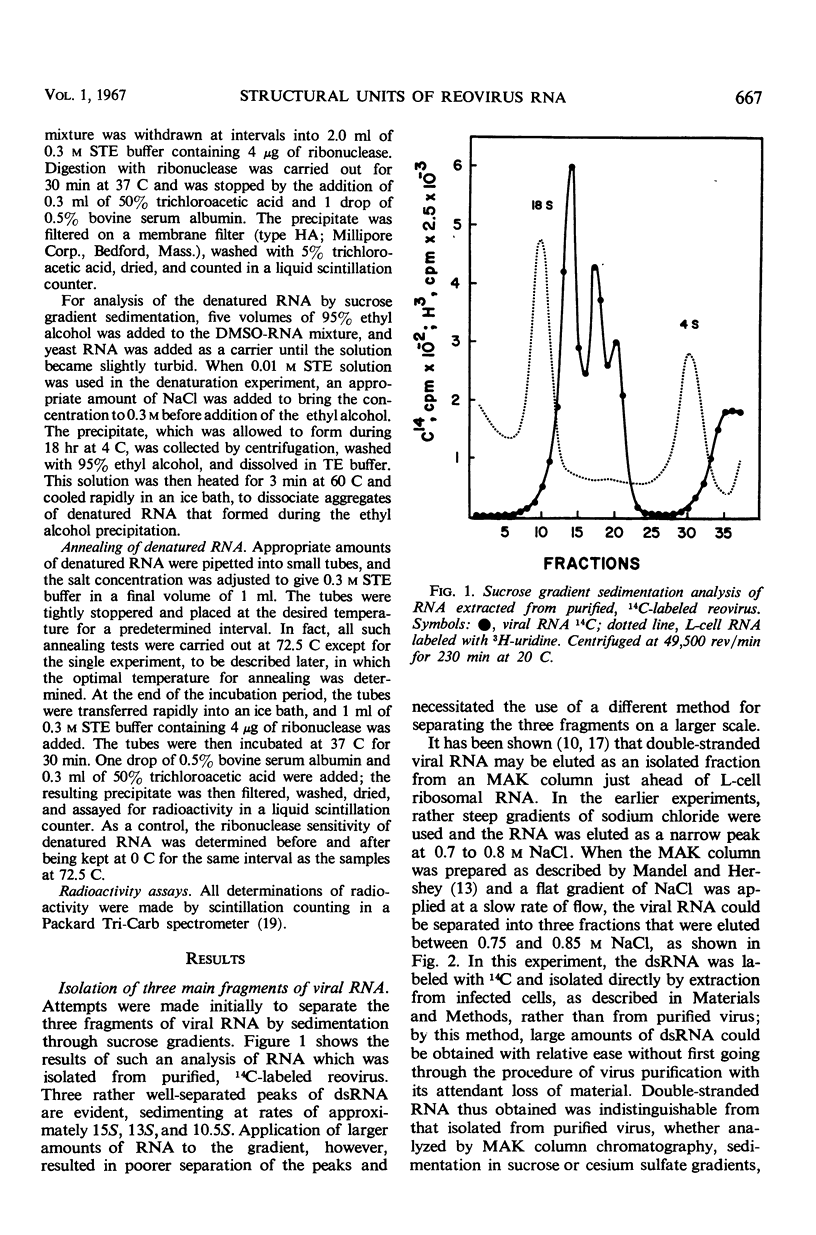
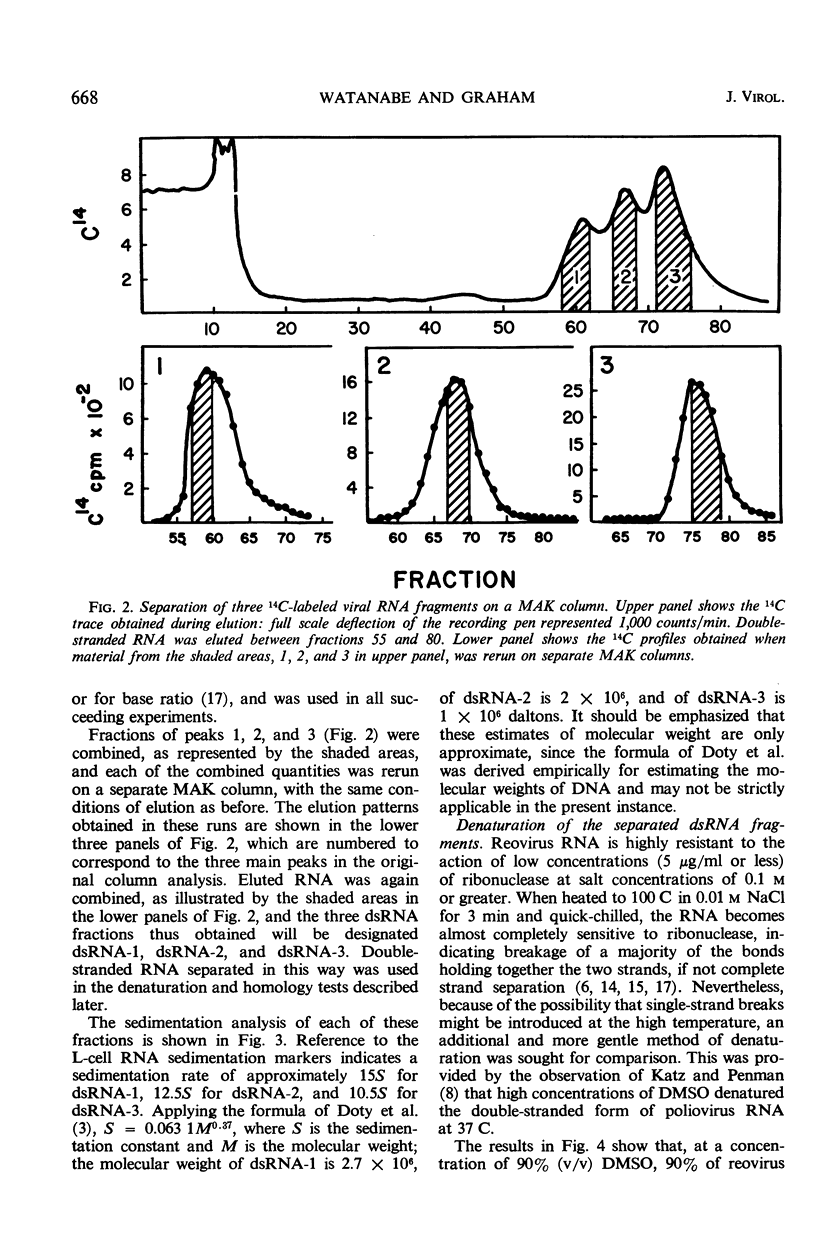
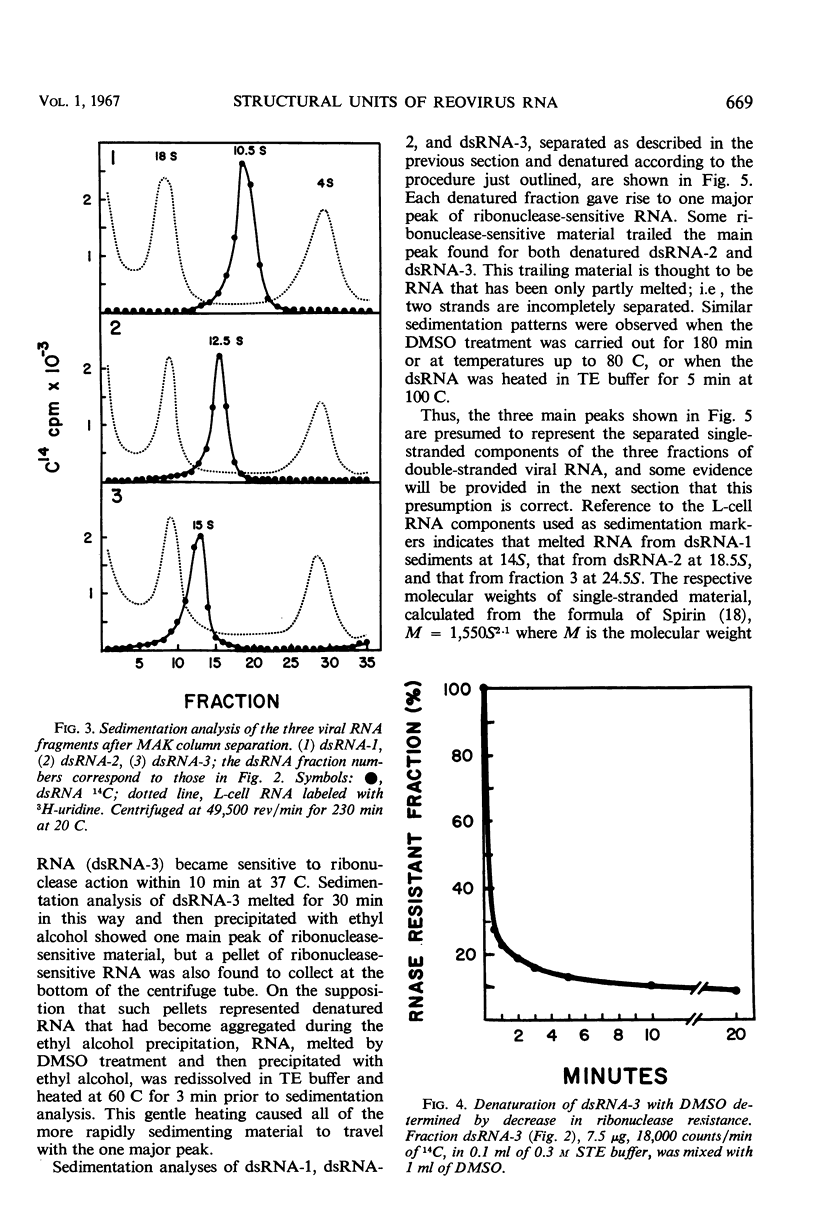
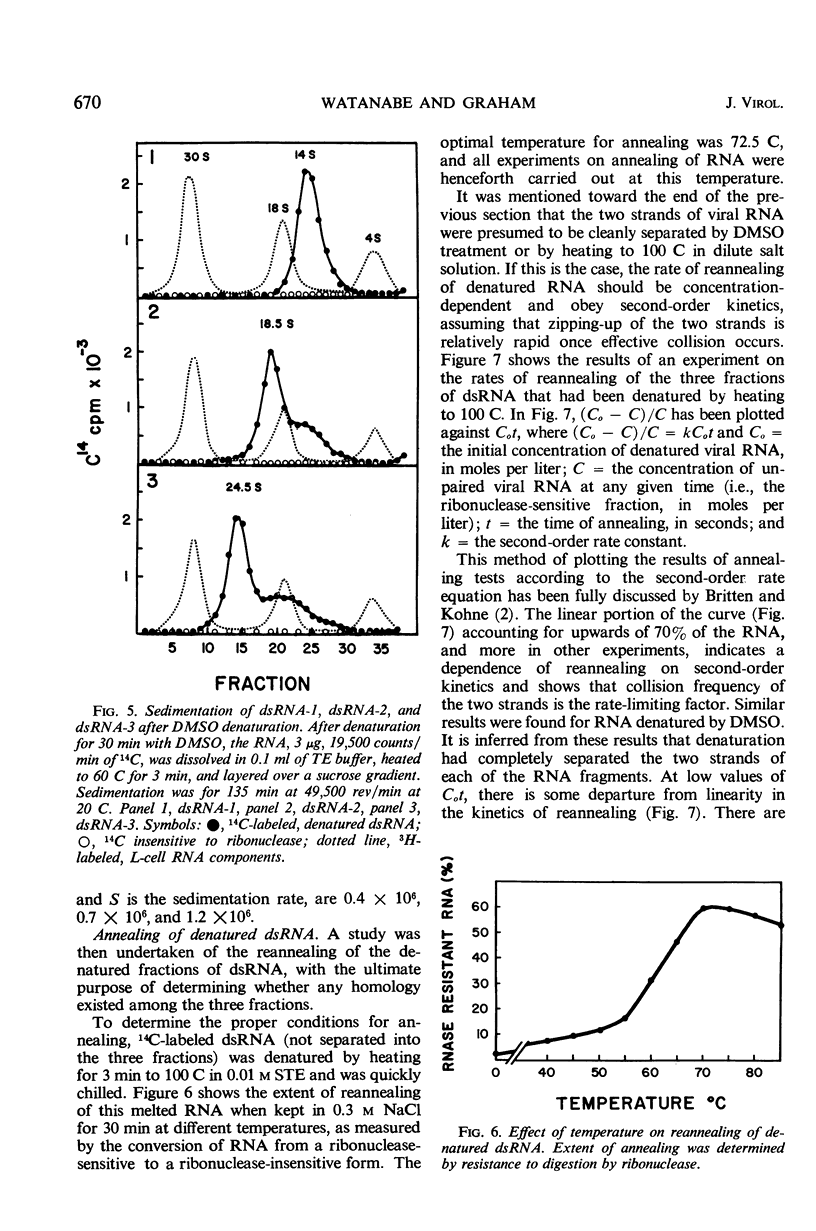
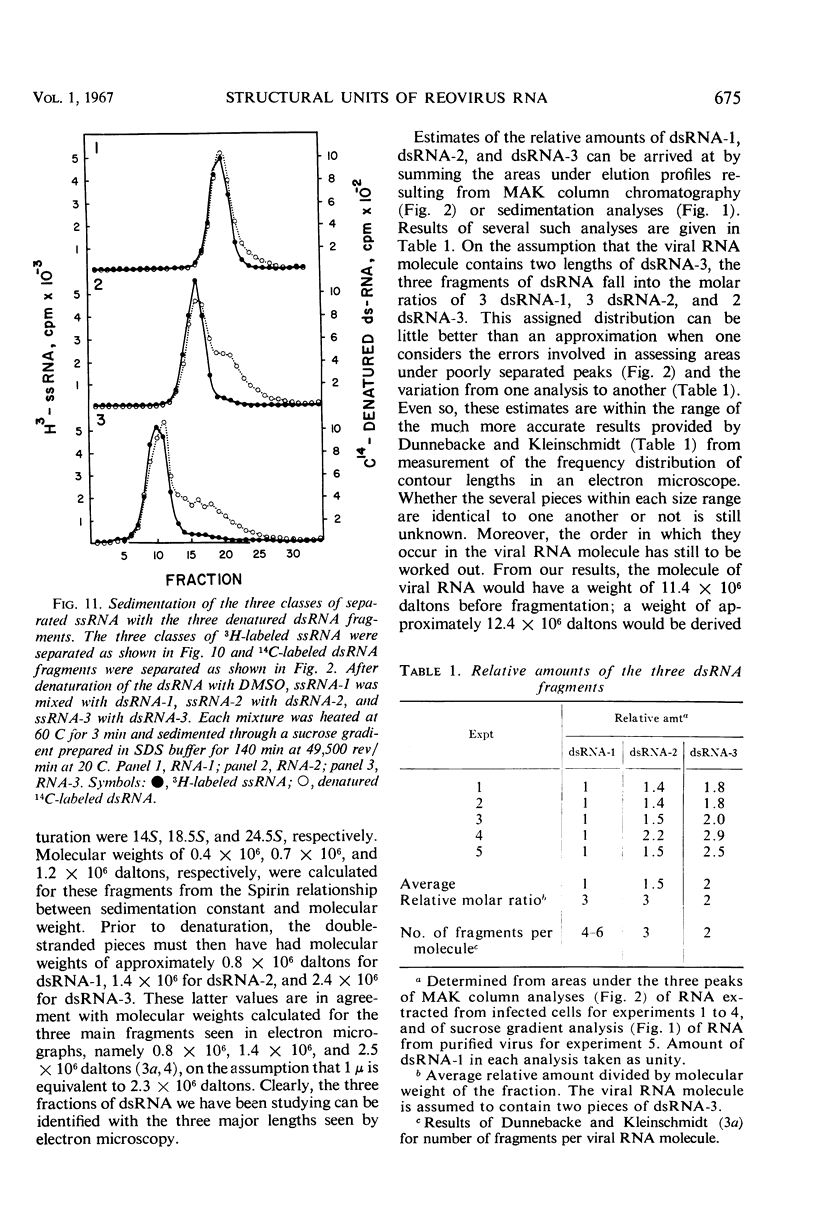
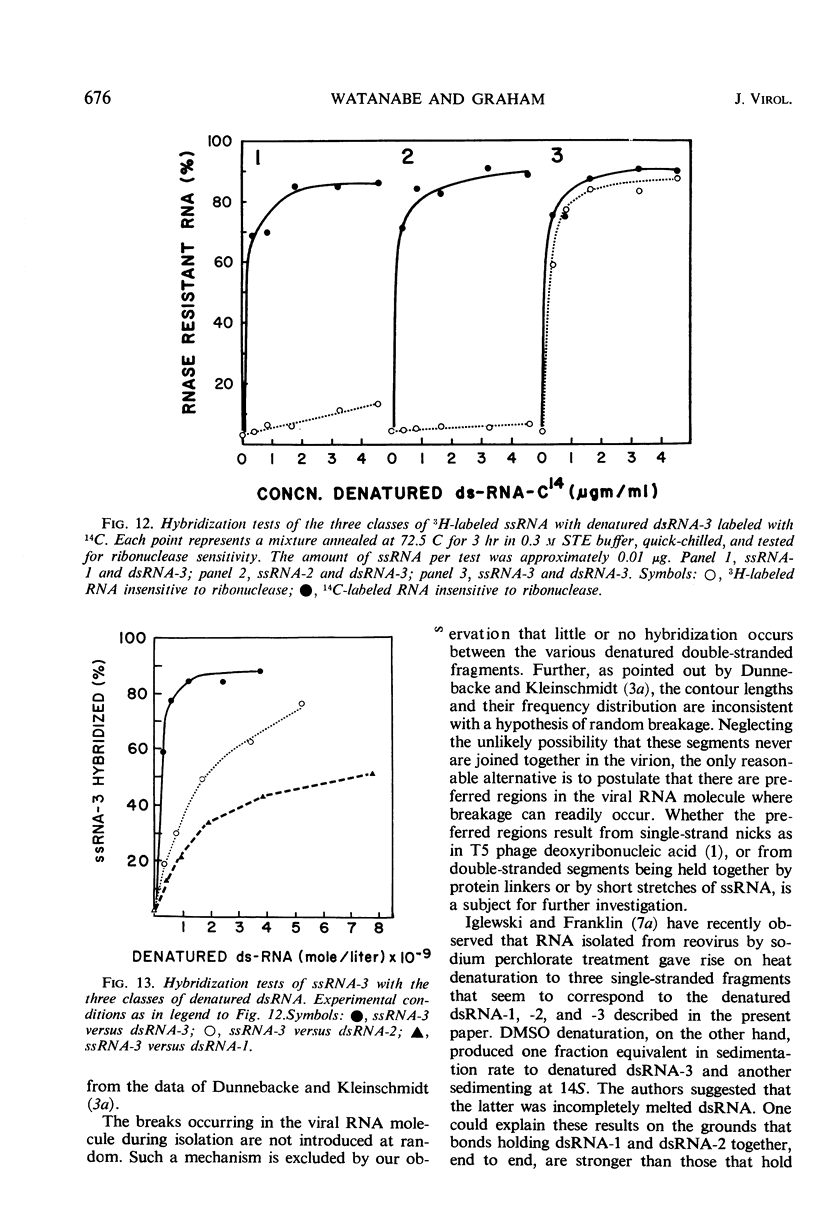
Reovirus contains ribonucleic acid (RNA) equivalent in amount to a molecular weight of approximately 107 daltons. On isolation, this RNA is invariably broken into fragments of three different sizes. The three pieces have been separated from each other by chromatography on methylated albumin-kieselguhr columns. Denaturation of the three fragments of RNA in dimethyl sulfoxide led to separation of the strands, as suggested by sucrose gradient sedimentation patterns and by the second-order kinetics of reannealing. Molecular weights of 0.8 × 106, 1.4 × 106, and 2.4 × 106 were determined for the double-stranded fragments from the sedimentation rates of the single-stranded RNA obtained by denaturation. There was little or no homology among the three classes of denatured RNA when taken in pairs in hybridization tests. The three pieces of double-stranded RNA, therefore, did not result from random breaks in the original viral RNA molecule. Virusspecific single-stranded RNA formed in infected cells, and previously found to be largely if not entirely messenger RNA transcribed from the viral genome, was also separated into three size classes by sedimentation through sucrose gradients. Each class of single-stranded RNA corresponded in size to one of the three fragments of double-stranded RNA. The largest piece of single-stranded RNA hybridized uniquely with the largest fragment of denatured viral RNA. By whatever means this fragment of double-stranded RNA may be joined into the viral RNA molecule, it seems to act as a specific unit for transcription of an uninterrupted messenger RNA of equivalent length.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doty P., McGill B. B., Rice S. A. THE PROPERTIES OF SONIC FRAGMENTS OF DEOXYRIBOSE NUCLEIC ACID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 May;44(5):432–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.5.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnebacke T. H., Kleinschmidt A. K. Ribonucleic acid from reovirus as seen in protein monolayers by electron microscopy. Z Naturforsch B. 1967 Feb;22(2):159–164. doi: 10.1515/znb-1967-0210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMATOS P. J., STOECKENIUS W. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON REOVIRUS RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1449–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMATOS P. J., TAMM I. ANIMAL AND PLANT VIRUSES WITH DOUBLE-HELICAL RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:878–885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Tamm I. THE SECONDARY STRUCTURE OF REOVIRUS RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):707–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski W. J., Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of reovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.302-307.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT A. K., DUNNEBACKE T. H., SPENDLOVE R. S., SCHAFFER F. L., WHITCOMB R. F. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF RNA FROM REOVIRUS AND WOUND TUMOR VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Nov;10:282–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Penman S. The solvent denaturation of double-stranded RNA from poliovirus infected HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):557–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90765-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus induced RNA in L cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90711-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo H., Graham A. F. Synthesis of reovirus ribonucleic acid in L cells. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):936–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.936-945.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGRIDGE R., GOMATOS P. J. The structure of RNA. Reovirus RNA and transfer RNA have similar three-dimensional structures, which differ from DNA. Science. 1963 Aug 23;141(3582):694–698. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3582.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevec L., Graham A. F. Reovirus-specific polyribosomes in infected L-cells. Science. 1966 Oct 28;154(3748):522–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHATKIN A. J. ACTINOMYCIN AND THE DIFFERENTIAL SYNTHESIS OF REOVIRUS AND L CELL RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:506–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Inactivity of purified reovirus RNA as a template for E. coli polymerases in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1721–1728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Rada B. Reovirus-directed ribonucleic acid synthesis in infected L cells. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.24-35.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):36–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.36-44.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



