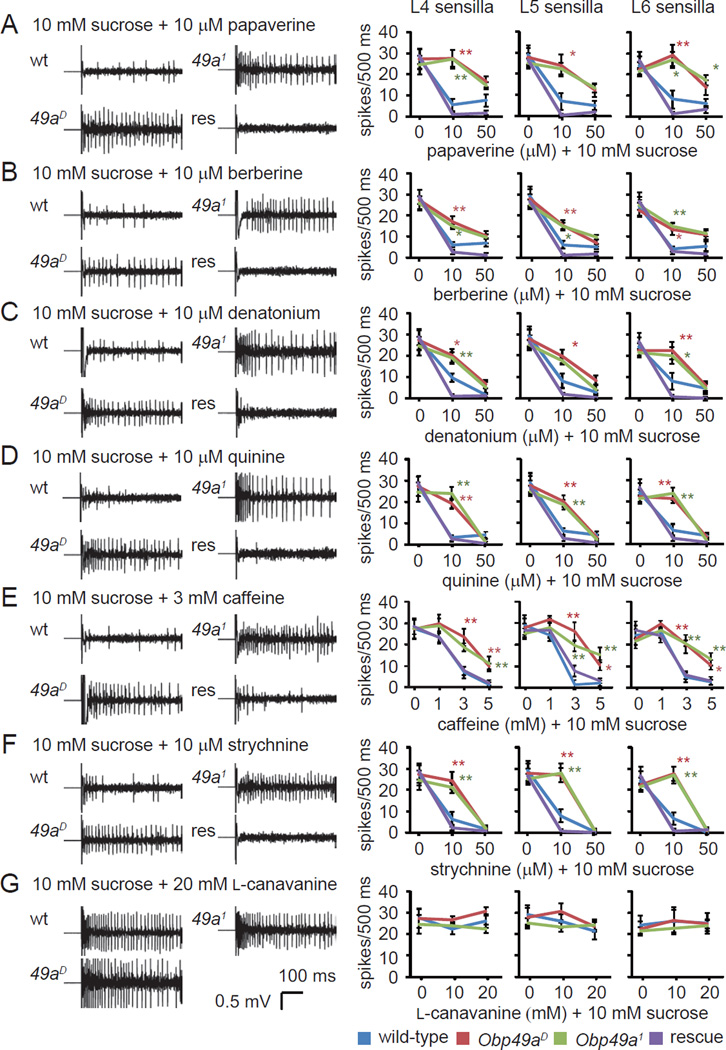
Figure 5. Requirement for Obp49a for inhibition of sucrose-induced action potentials by aversive chemicals.
Tip recordings of L-type sensilla (L4, L5, and L6) showing representative traces and the mean action potentials induced by 10 mM sucrose combined with aversive chemicals. Each stimulant contained 10 mM sucrose, 1 mM KCl as the electrolyte and the indicated concentrations of bitter chemicals. The tip recordings were performed using the indicated sensilla and the following bitter chemicals. (A) Papaverine. (B) Berberine. (C) Denatonium. (D) Quinine. (E) Caffeine. (F) Strychnine. (G) L-canavanine. Shown are the means ±SEM (n=5—13). The genotype of the rescue flies was Obp49aD;nompA-GAL4/UASObp49a. The asterisks denote statistically significant differences (*p<0.05, **p<0.01) from wild-type flies (see also Figure S3).