Abstract
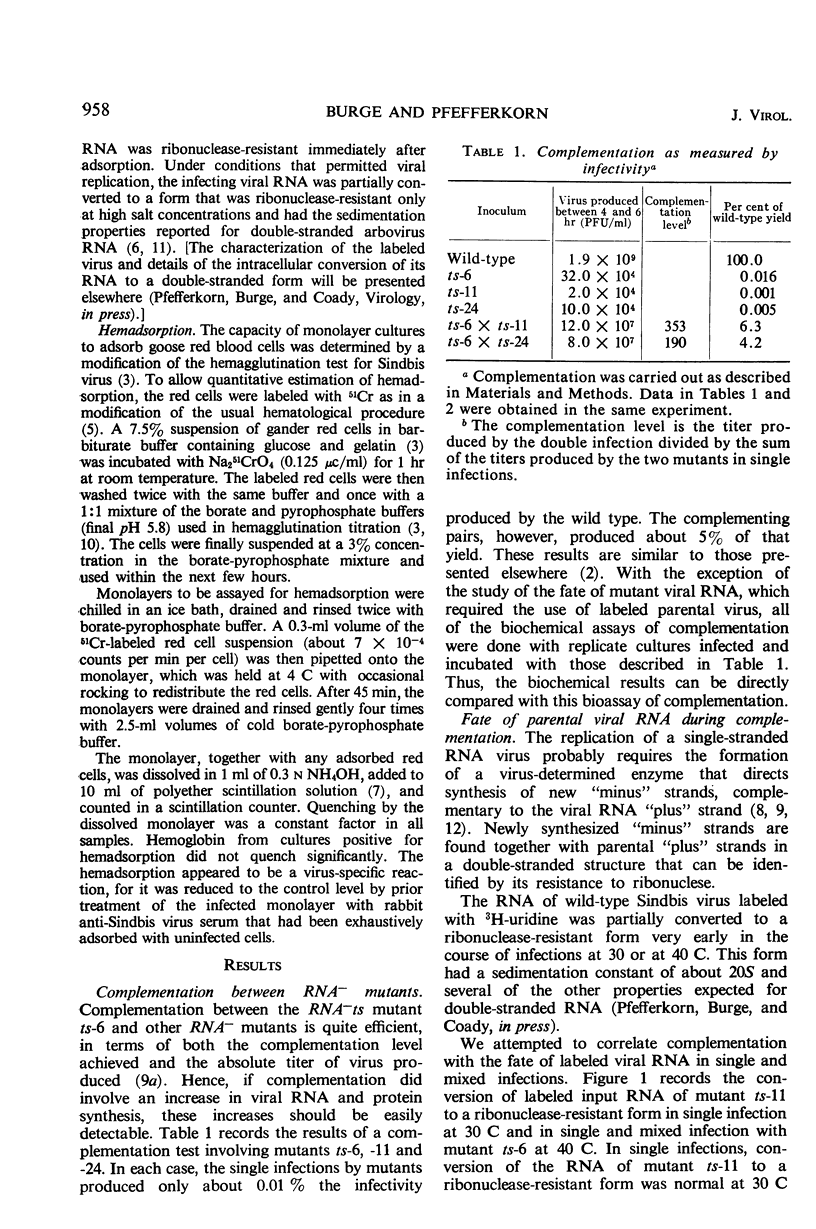
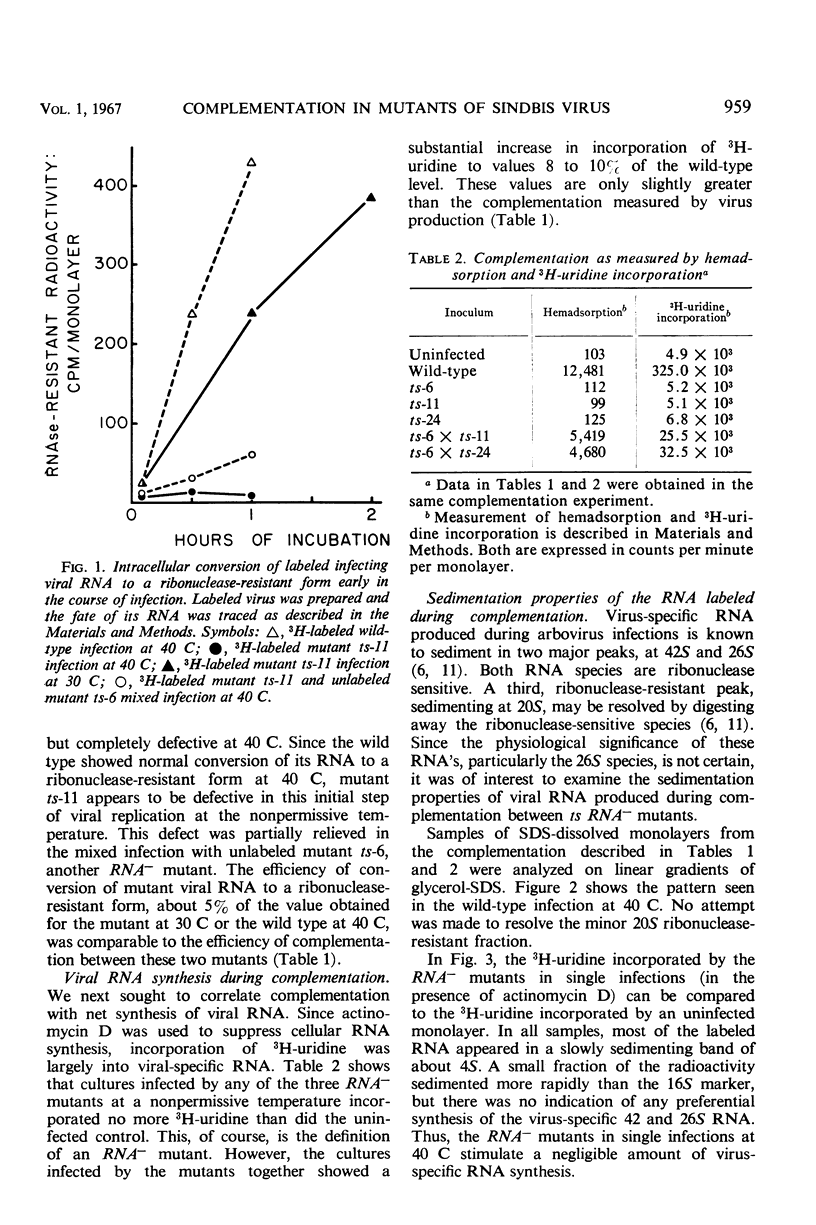
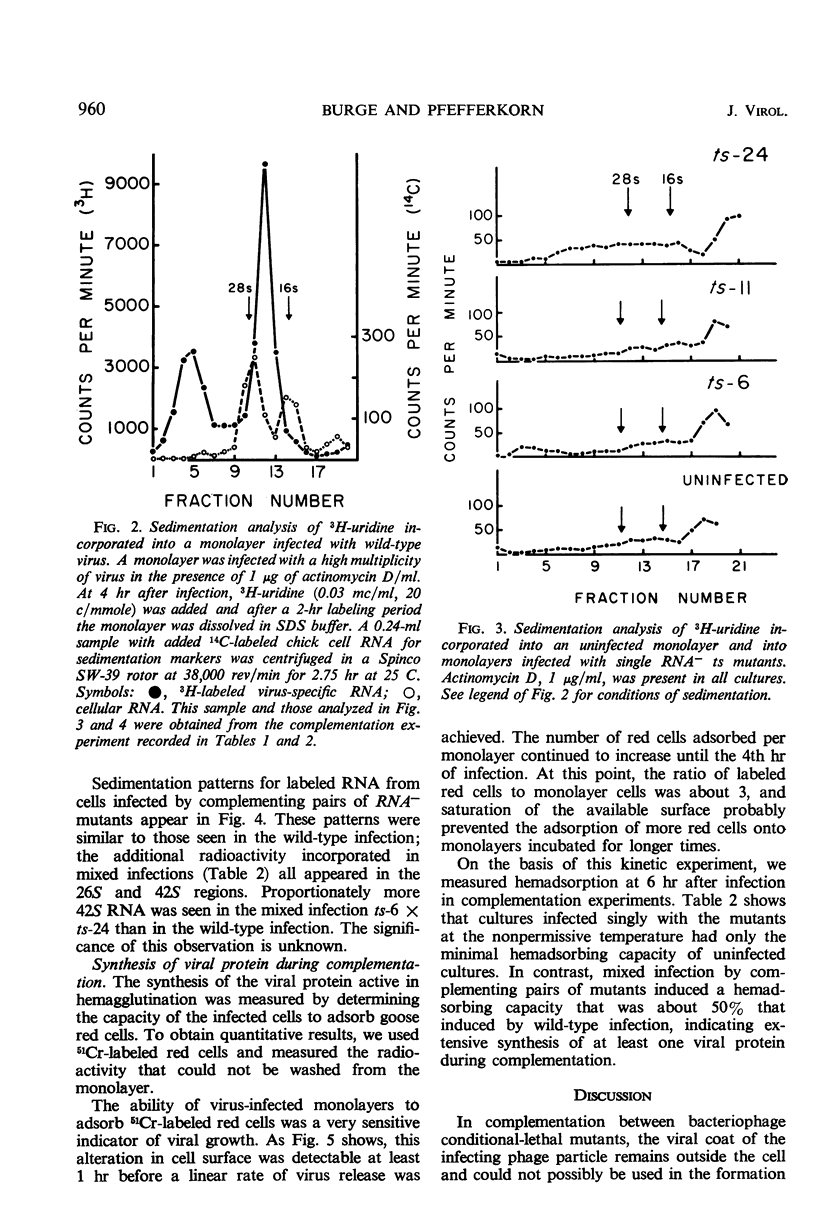
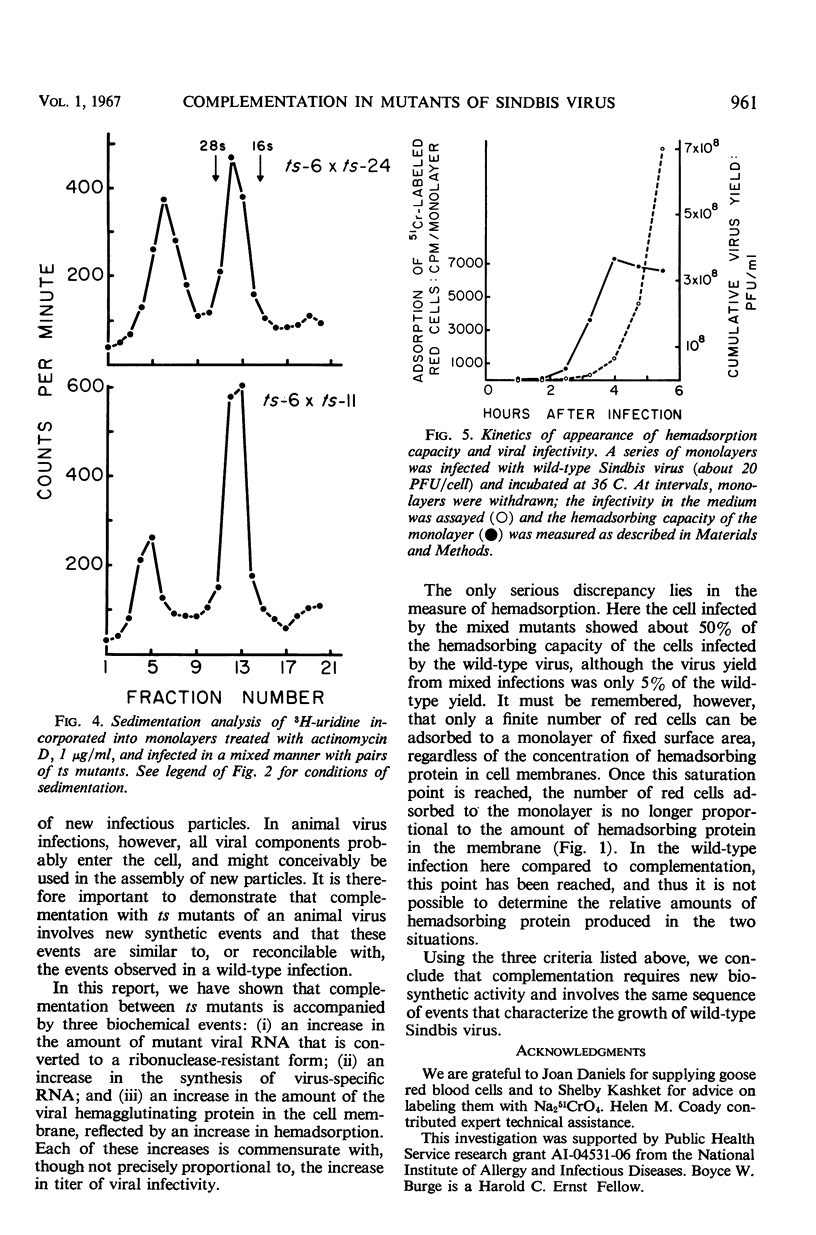
Temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus fail to grow at a temperature that permits growth of the wild type, but when certain pairs of these mutants, mixed together, infect cells at that temperature, viral growth (i.e., complementation) occurs. The yield from this complementation, however, is of the same order of magnitude as the infectivity in the inoculum. Since in animal virus infections the protein components of the virion probably enter the cell with the viral nucleic acid, it was necessary to demonstrate that the observed complementation required synthesis of new viral protein and nucleic acid rather than some sort of rearrangement of the structural components of the inoculum. To demonstrate that complementation does require new biosynthesis, three biochemical events of normal virus growth have been observed during complementation and correlated with the efficiency of viral growth seen in complementation. These events include: (i) entrance of parental viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) into a double-stranded form; (ii) subsequent synthesis of viral RNA; and (iii) synthesis and subsequent incorporation of viral protein(s) into cell membranes where they were detected by hemadsorption. Although the infecting single-stranded RNA genome of the wild type was converted to a ribonuclease-resistant form, the genome of a mutant (ts-11) incapable of RNA synthesis at a nonpermissive temperature was not so converted. However, during complementation with another mutant also defective in viral RNA synthesis, some of the RNA of mutant ts-11 was converted to a ribonuclease-resistant form, and total synthesis of virus-specific RNA was markedly enhanced. The virus-specific alteration of the cell surface, detected by hemadsorption, was also extensively increased during complementation. These observations support the view that complementation between temperature-sensitive mutants and replication of wild-type virus are similar processes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burge B. W., Pfefferkorn E. R. Complementation between temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):214–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge B. W., Pfefferkorn E. R. Isolation and characterization of conditional-lethal mutants of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):204–213. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. One-step growth curve of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus on chicken embryo cells grown in vitro and analysis of virus yields from single cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):183–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBAUGH F. G., Jr, EMERSON C. P., ROSS J. F. The use of radioactive chromium 51 as an erythrocyte tagging agent for the determination or red cell survival in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1953 Dec;32(12):1260–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI102855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Replication of semliki forest virus: three forms of viral RNA produced during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):440–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Zinder N. D. Replication of the RNA of Bacteriophage f2. Science. 1966 Apr 15;152(3720):372–377. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3720.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Pace N. R., Spiegelman S. The in vitro synthesis of a noninfectious complex containing biologically active viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1778–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEFFERKORN E. R., HUNTER H. S. PURIFICATION AND PARTIAL CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF SINDBIS VIRUS. Virology. 1963 Jul;20:433–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E. Viral specific RNAs in infected cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):365–367. doi: 10.1038/213365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C., Feix G. Replication of viral RNA. XI. Synthesis of viral "minus" strands in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



