Abstract
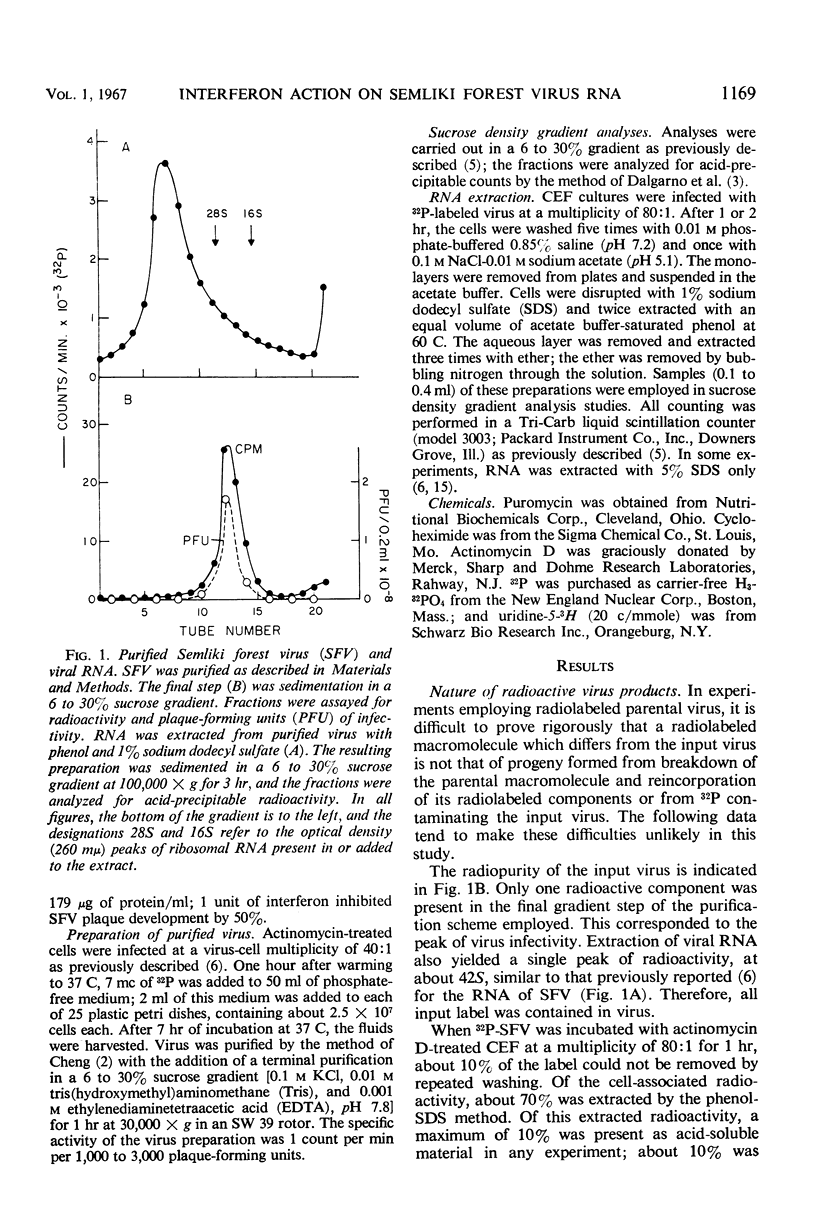
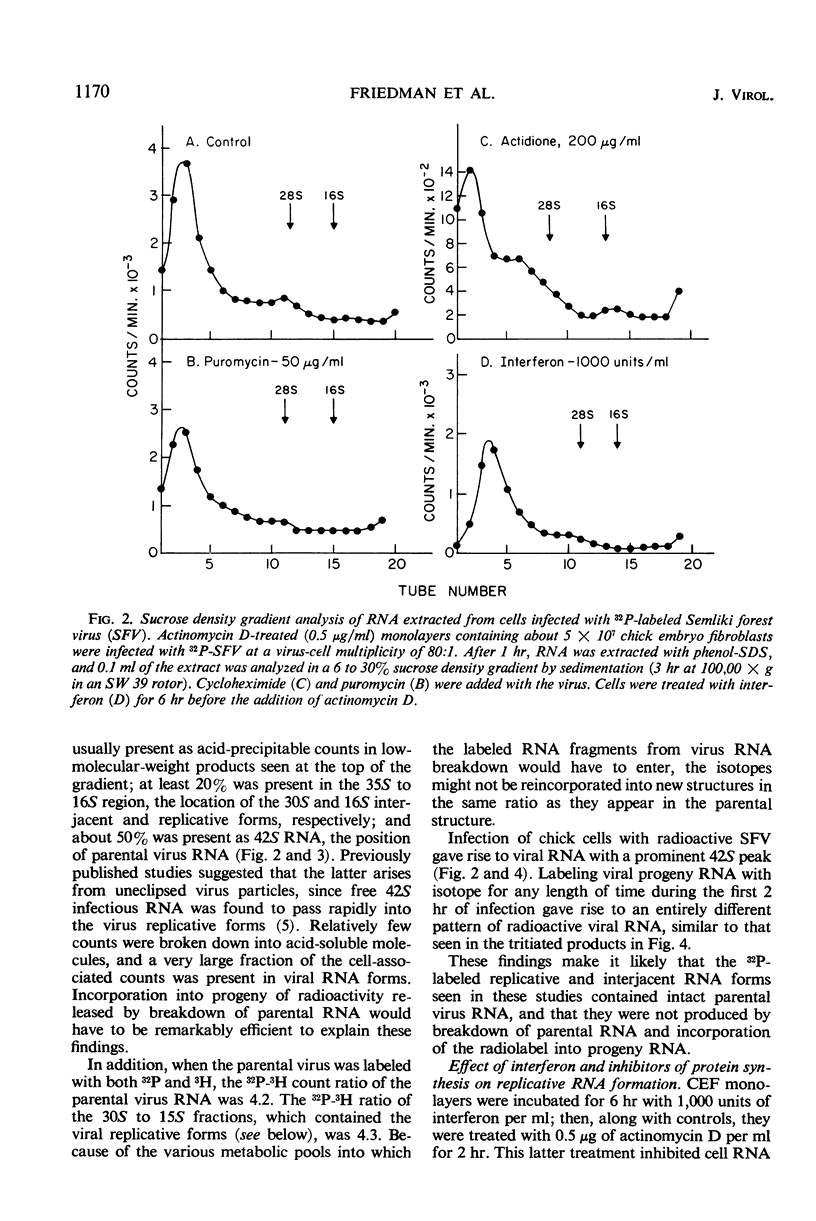
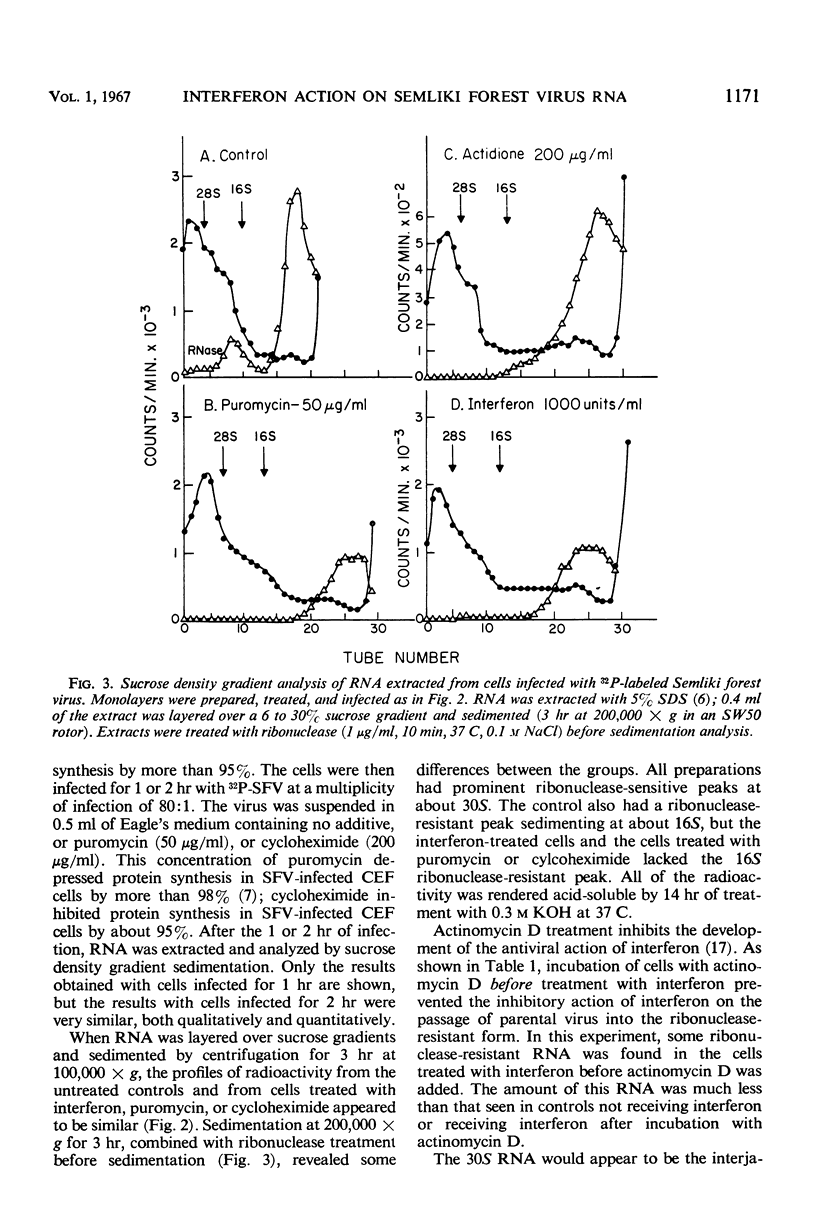
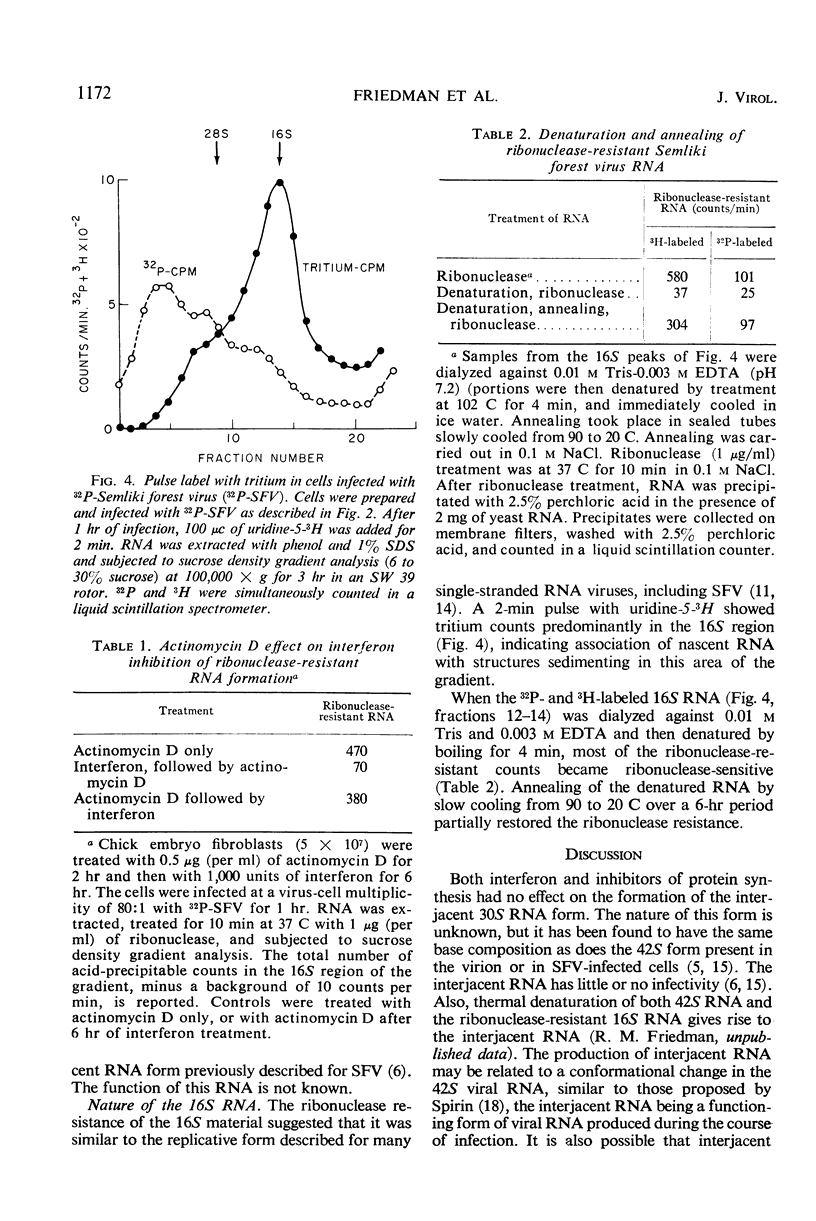
Actinomycin D-treated chick fibroblasts were infected with purified 32P-labeled Semliki forest virus, and ribonucleic acid (RNA) was extracted after 1 or 2 hr. Within 1 hr, viral RNA forms sedimenting in sucrose gradients at 42S, 30S, and 16S were present. The 42S form corresponded to the RNA of the virion. The 16S form appeared to be a double-stranded template for the formation of new viral RNA, since nascent RNA was associated with it and the molecule could be heat-denatured and subsequently reannealed by slow cooling. Interferon treatment before infection, or puromycin (50 μg/ml) or cycloheximide (200 μg/ml) added at the time of virus infection, had no effect on the formation of the 30S RNA but inhibited the production of the 16S form. Several findings made it unlikely that these results were due to breakdown of parental RNA and reincorporation of 32P into progeny structures. The results suggested that the mechanism of interferon action involves inhibition of protein synthesis by parental viral RNA, since a specific viral RNA polymerase had previously been demonstrated to be necessary for production of 16S RNA. No protein synthesis appears necessary for formation of 30S RNA from parental virus RNA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHENG P. Y. Purification, size, and morphology of a mosquitoborne animal virus, Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1961 May;14:124–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Levy H. B. Ribosomes: effect of interferon on their interaction with rapidly labeled cellular and viral RNA's. Science. 1967 Mar 10;155(3767):1254–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3767.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno L., Martin E. M., Liu S. L., Work T. S. Characterization of the products formed by the RNA polymerases of cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes K. H. Further purification of chick interferon. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1298–1298. doi: 10.1038/2071298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Berezesky I. K. Cytoplasmic fractions associated with Semliki Forest virus ribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):374–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.374-383.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Replication of semliki forest virus: three forms of viral RNA produced during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):440–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Sonnabend J. A. Inhibition by interferon of production of double-stranded Semliki forest virus ribonucleic acid. Nature. 1965 May 1;206(983):532–532. doi: 10.1038/206532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K., Merigan T. C. Concerning the mechanism of action of interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):558–565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. M., Sonnabend J. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase catalyzing synthesis of double-stranded arbovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):97–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.97-109.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner N., Ray W. J., Jr, Simon E. H. Effect of interferon on the production and action of viral RNA polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHOA S., WEISSMANN C., BORST P., BURDON R. H., BILLETER M. A. REPLICATION OF VIRAL RNA. Fed Proc. 1964 Nov-Dec;23:1285–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E., Fantes K. H. The effect of interferon on the synthesis and activity of an RNA polymerase isolated from chick cells infected with Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jan;1(1):41–48. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E. Viral specific RNAs in infected cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):365–367. doi: 10.1038/213365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF INTERFERON. I. INTERFERON ACTION AND RNA SYNTHESIS IN CHICK EMBRYO FIBROBLASTS INFECTED WITH SEMLIKI FOREST VIRUS. Virology. 1965 Mar;25:340–349. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



