Abstract
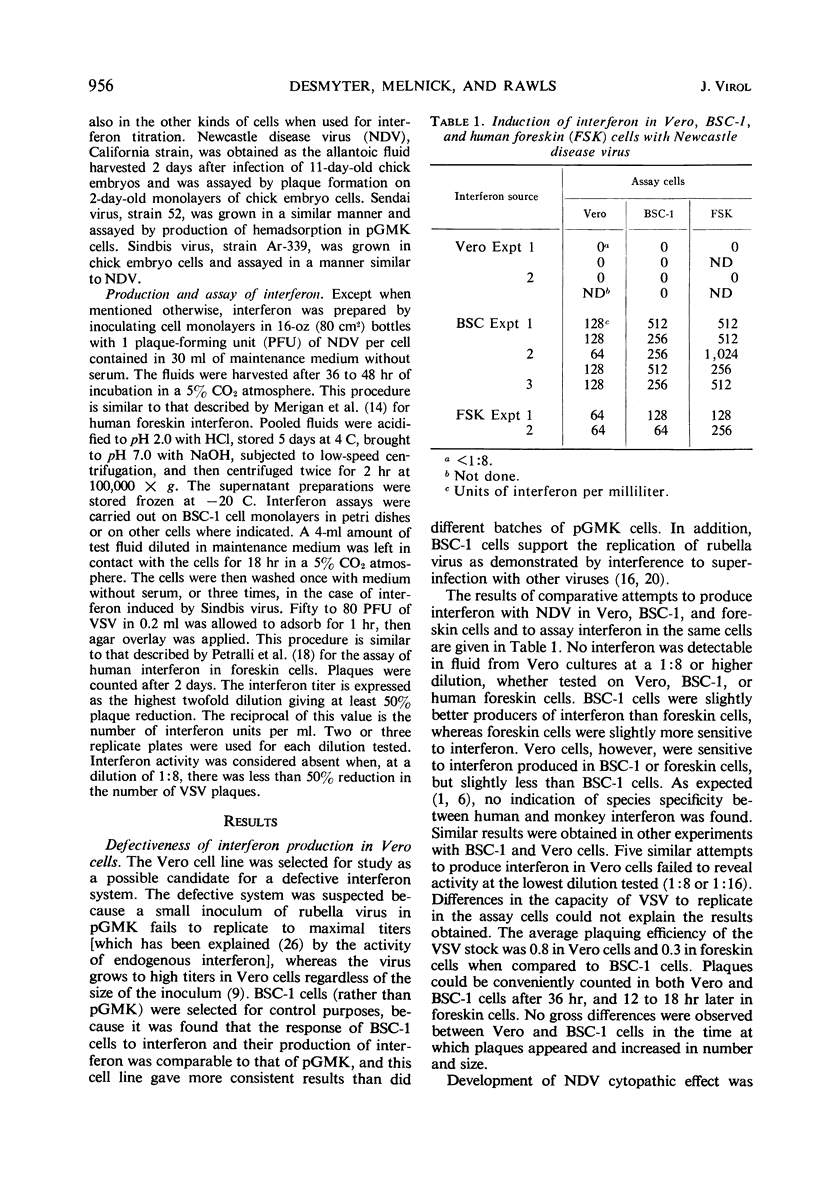
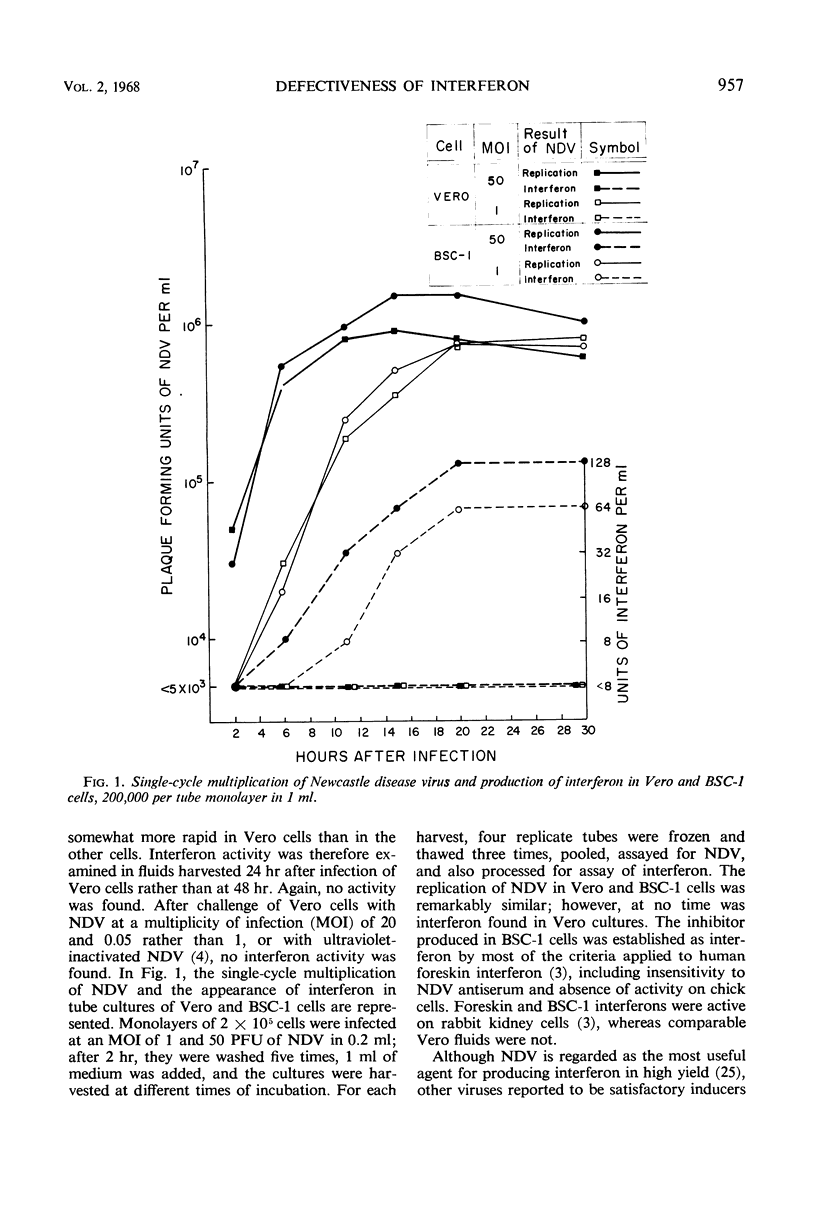
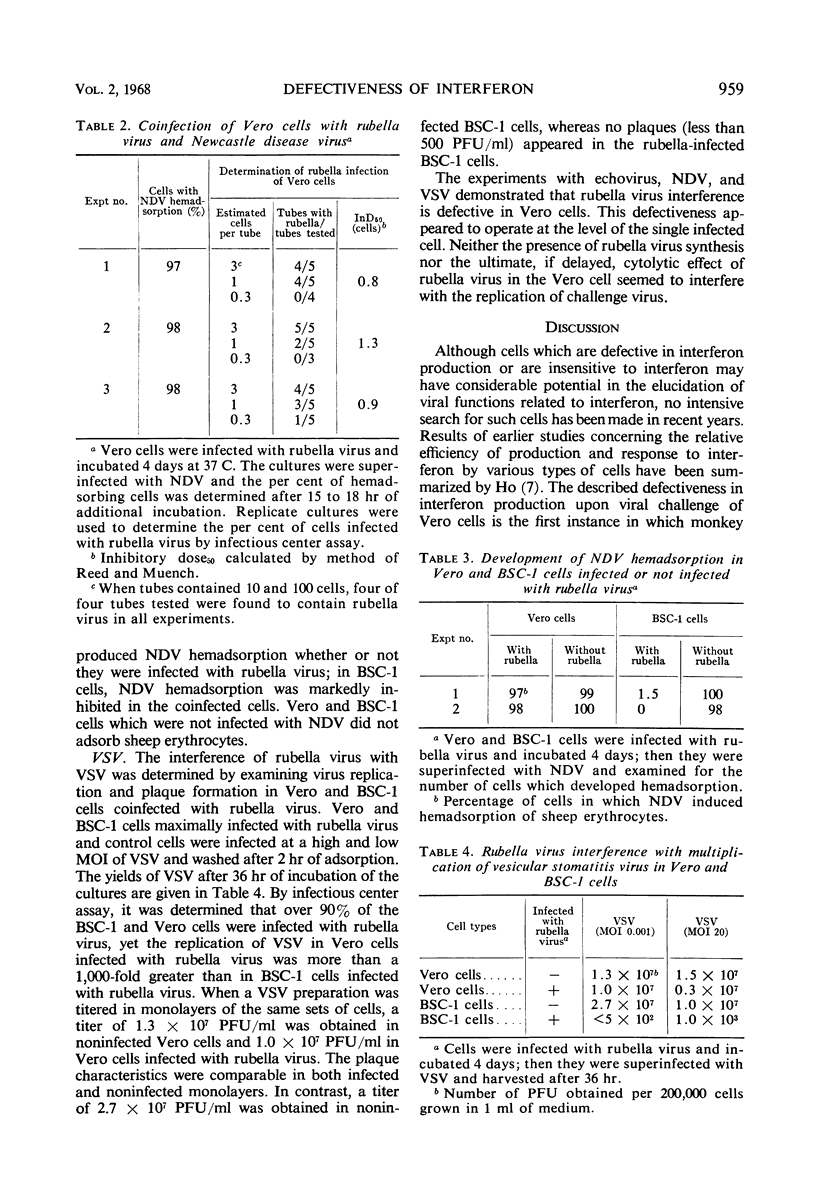
Vero cells, a line of African green monkey kidney cells, failed to produce interferon when infected with Newcastle disease, Sendai, Sindbis, and rubella viruses, although the cells were sensitive to interferon. Further, infection of Vero cells with rubella virus did not result in interference with the replication of echovirus 11, Newcastle disease virus, or vesicular stomatitis virus, even in cultures where virtually every cell was infected with rubella virus. Under the same conditions, BSC-1 cells and other cells of primate origin produced interferon and showed rubella virus interference. The results indicate that the presence of rubella virus in the cell does not in itself exclude multiplication of other viruses and that rubella virus interference appears to be linked to the capability of the cell to produce interferon.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bucknall R. A. "Species specificity" of interferons: a misnomer? Nature. 1967 Dec 9;216(5119):1022–1023. doi: 10.1038/2161022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver D. H., Seto D. S., Migeon B. R. Interferon production and action in mouse, hamster and somatic hybrid mouse-hamster cells. Science. 1968 May 3;160(3827):558–559. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3827.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Somer P., Billiau A., De Clercq E., Schonne E. Rubella virus interference and interferon production. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1967;33(3):237–245. doi: 10.1007/BF02045569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmyter J., Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L. A human interferon that crosses the species line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):69–76. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmyter J., Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L., Yow M. D., Barrett F. F. Interferon in congenital rubella: response to live attenuated measles vaccine. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):771–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff R., Falcoff E., Dubouche P., Chany C. Activité biologique des interférons humains sur l'espèce simienne in vitro et in vivo. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Jan 15;266(3):297–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPS H. E., BERNHEIM B. C., NISALAK A., TJIO J. H., SMADEL J. E. BIOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONTINUOUS KIDNEY CELL LINE DERIVED FROM THE AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY. J Immunol. 1963 Sep;91:416–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber H., Riordan J. T., Horstmann D. M. Replication of rubella virus in a continuous line of African green monkey kidney cells (Vero). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):636–643. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Carver D. H. Hemadsorption-negative plaque test: new assay for rubella virus revealing a unique interference. Science. 1965 Aug 27;149(3687):983–986. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3687.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Carver D. H. Intrinsic interference: a new type of viral interference. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):334–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.334-343.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Gregory D. F., Petralli J. K. Physical properties of human interferon prepared in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1966 Aug;29(4):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVA F. A., WELLER T. H. RUBELLA INTERFERON AND FACTORS INFLUENCING THE INDIRECT NEUTRALIZATION TEST FOR RUBELLA ANTIBODY. J Immunol. 1964 Sep;93:466–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKMAN P. D., BUESCHER E. L., ARTENSTEIN M. S., MCCOWN J. M., MUNDON F. K., DRUZD A. D. STUDIES OF RUBELLA. I. PROPERTIES OF THE VIRUS. J Immunol. 1964 Oct;93:595–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETRALLI J. K., MERIGAN T. C., WILBUR J. R. CIRCULATING INTERFERON AFTER MEASLES VACCINATION. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 22;273:198–201. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507222730405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman P. D., Meyer H. M., Jr, Kirschstein R. L., Hopps H. E. Attenuated rubella virus. I. Development and laboratory characterization. N Engl J Med. 1966 Sep 15;275(11):569–574. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196609152751101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F. PLAQUE DIFFERENTIATION AND REPLICATION OF VIRULENT AND ATTENUATED STRAINS OF MEASLES VIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1448–1458. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1448-1458.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Desmyter J., Melnick J. L. Rubella virus neutralization by plaque reduction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):167–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L. Rubella virus carrier cultures derived from congenitally infected infants. J Exp Med. 1966 May 1;123(5):795–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim J. S., Schell K. Cytopathic and plaque assay of rubella virus in a line of African green monkey kiency cells (Vero). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):602–606. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truden J. L., Sigel M. M., Dietrich L. S. An interferon antagonist: its effect on interferon action in mengo-infected Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Sedwick W. D., Plotkin S. A., Maes R. Cytopathic effect of rubella virus in RHK21 cells and growth to high titers in suspension culture. Virology. 1965 Oct;27(2):239–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. T., Baron S., Ward T. G. Rubella virus: role of interferon during infection of African green monkey kidney tissue cultures. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1140–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



