Abstract
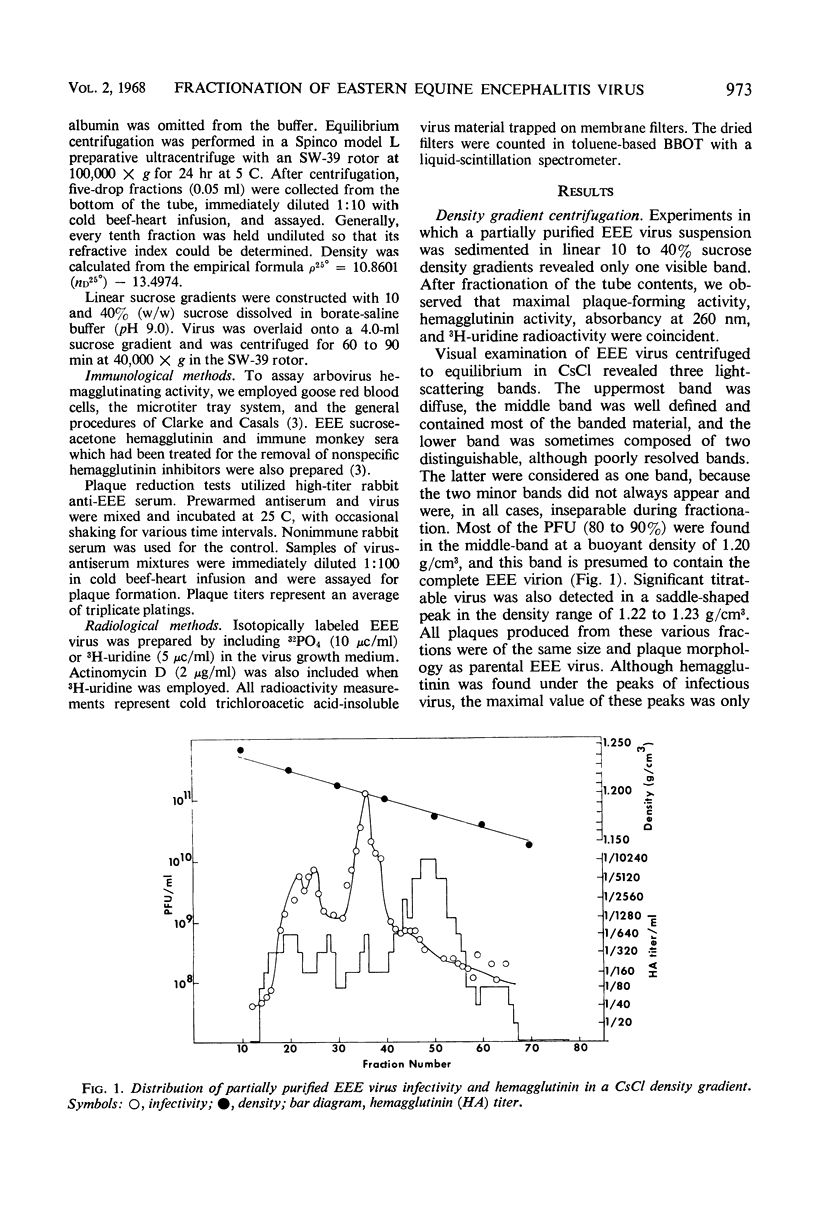
When partially purified Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus was centrifuged to equilibrium in CsCl, three virus specific bands were observed. A hemagglutinin was detected at a buoyant density of 1.18 g/cm3. Infectious EEE virus banded in two positions; most of the virus banded at 1.20 g/cm3 and a lesser amount banded at 1.22 to 1.23 g/cm3. Analysis of radioactive profiles of CsCl-fractionated EEE virus labeled with either 32PO4 or 3H-uridine suggested that the hemagglutinin was stripped from the intact EEE virion. The viral origin of the hemagglutinin was verified by inhibition with specific antiserum. Attempts to differentiate between infectious EEE virus of the different buoyant densities showed that the denser particle was neither a virus contaminant nor a density mutant. No evidence was obtained to indicate that the denser particle was an immature form of EEE virus. The two infectious EEE species obtained after CsCl fractionation were indistinguishable antigenically. Furthermore, unfractionated as well as CsCl-fractionated EEE virus sedimented at about 260S in sucrose gradients. These results together with the results of rebanding experiments suggested that the denser EEE species (1.23 g/cm3) results from a salt (CsCl)-induced alteration or breakdown of the EEE virion (1.20 g/cm3), and that it arises as the hemagglutinin is stripped from the surface of the EEE virion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Tamm I. Replication of Semliki Forest virus: an electron microscopic study. Virology. 1967 May;32(1):128–143. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. DIFFERENCES IN MAXIMUM AND MINIMUM PLAQUE-FORMING TEMPERATURES AMONG SELECTED GROUP A ARBORVIRUSES. Virology. 1963 Nov;21:362–372. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner P., Dobos P. Investigations on the formation and interconversion of Sindbis virus hemagglutinins. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):45–51. doi: 10.1139/m68-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. R., Levine S. I., Karabatsos N., Stim T. B. Antigenic variants of arboviruses. II. Variations in antigen expressions of strains during replication in different hosts. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):925–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSSGAY M. GROWTH CYCLE OF ARBOVIRUSES IN VERTEBRATE AND ARTHROPOD CELLS. Prog Med Virol. 1964;6:193–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mussgay M., Horzinek M. Investigations on complement-fixing subunits of a group A arbo virus (Sindbis). Virology. 1966 Jun;29(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieth P. M., Calberg-Bacq C. M. Changes in morphology, infectivity and haemagglutinating activity of Semliki Forest virus produced by the treatment with caseinase C from Streptomyces albus G. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Apr;43(1):19–30. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEFFERKORN E. R., HUNTER H. S. PURIFICATION AND PARTIAL CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF SINDBIS VIRUS. Virology. 1963 Jul;20:433–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. M., Schlesinger R. W. Studies on the nature of dengue viruses. I. Correlation of particle density, infectivity, and RNA content of type 2 virus. Virology. 1965 Sep;27(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WECKER E. The extraction of infectious virus nucleic acid with hot phenol. Virology. 1959 Feb;7(2):241–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebovitz E., Brown A. Temperature-sensitive steps in the biosynthesis of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.128-134.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



