Abstract
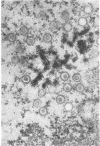
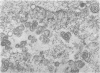
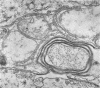
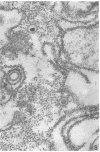
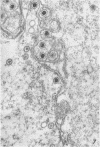
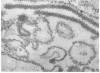
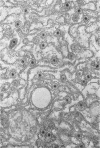
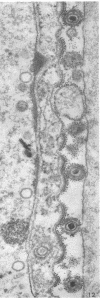
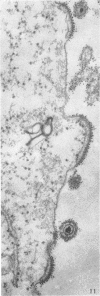
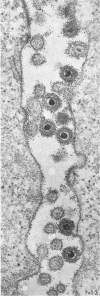
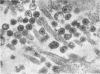
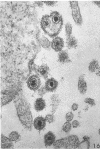
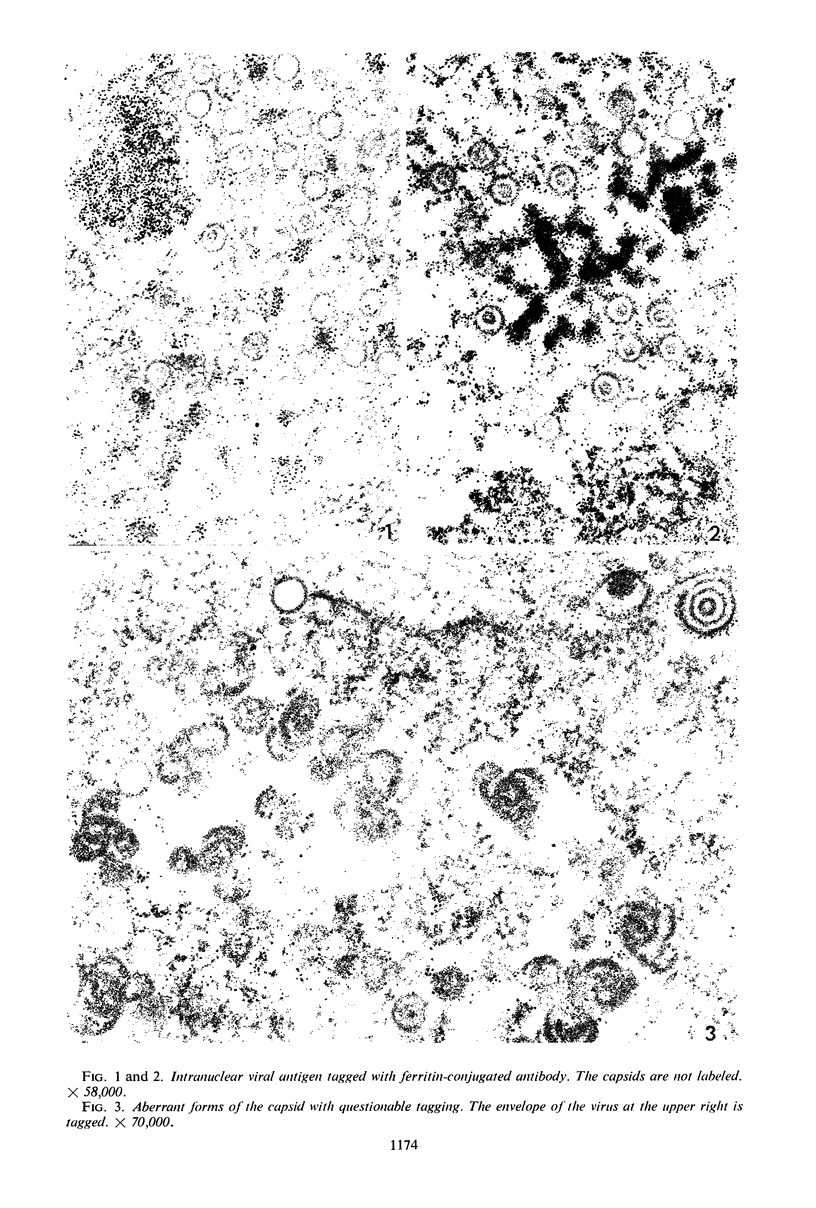
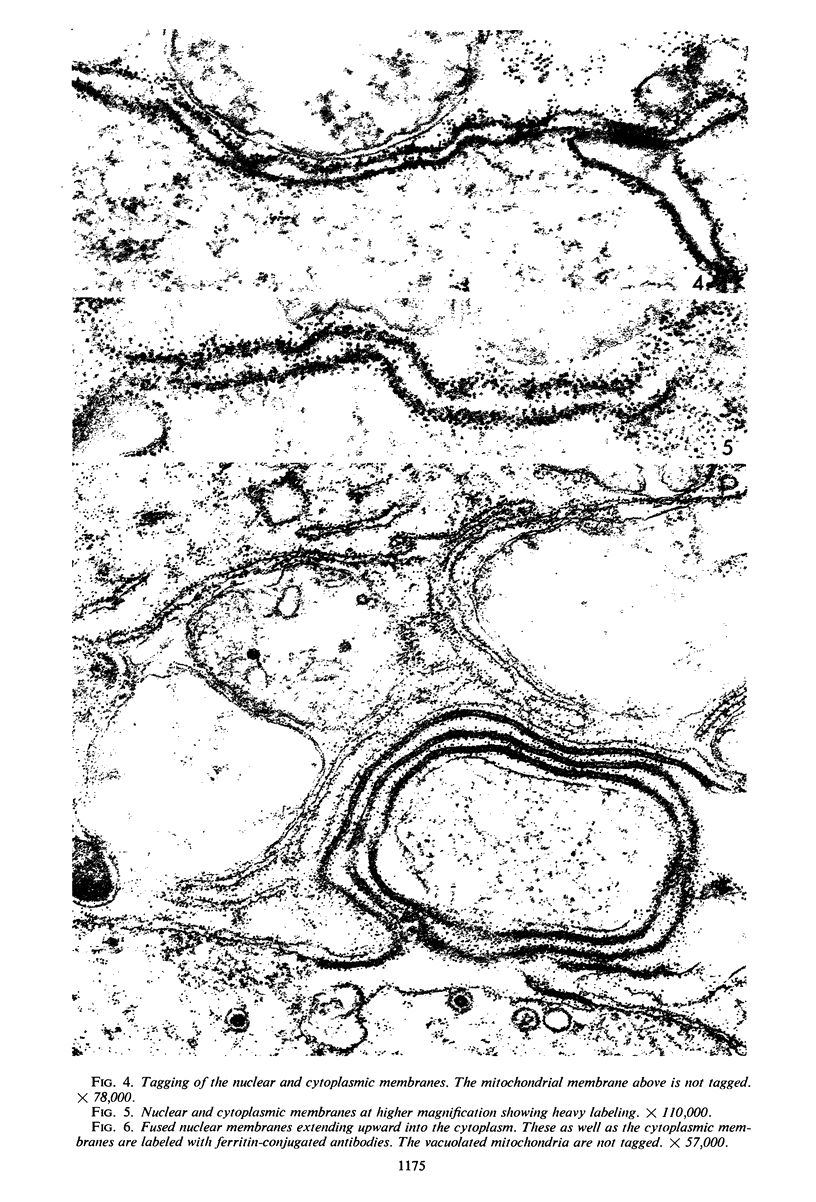
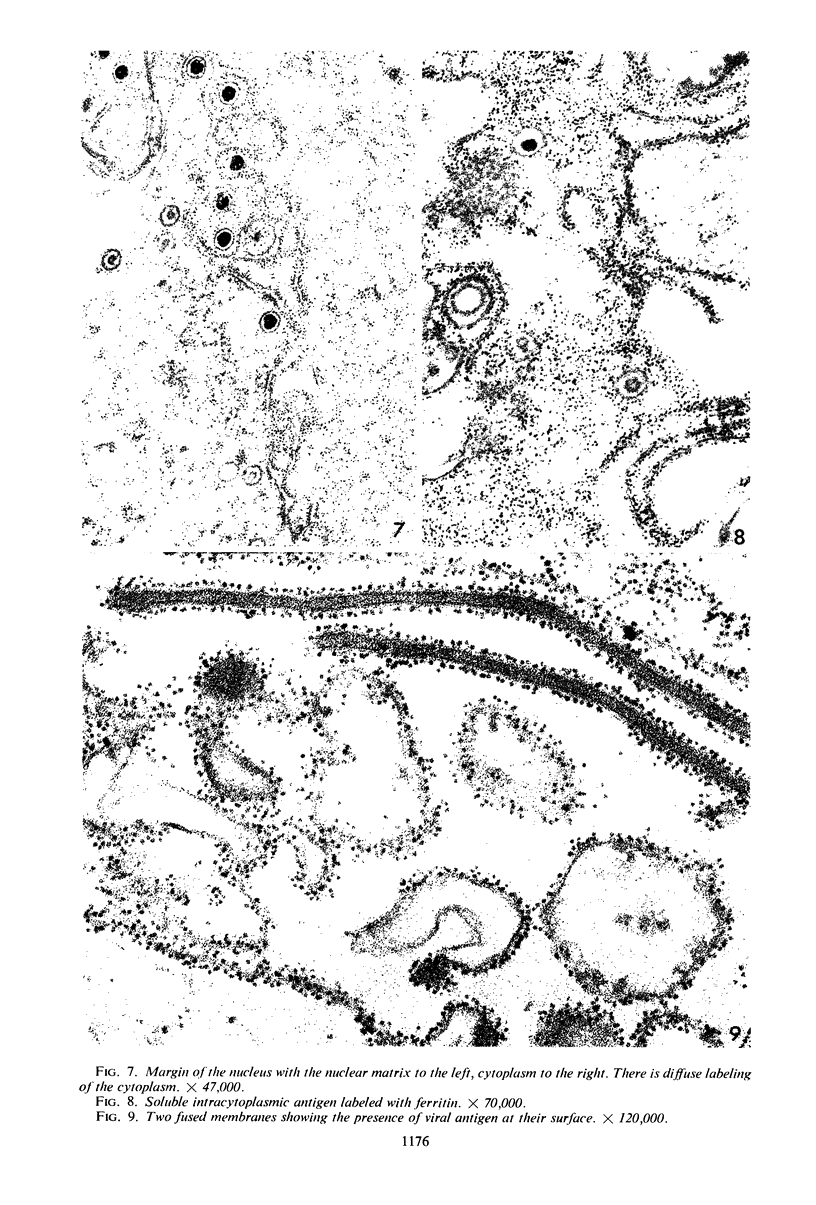
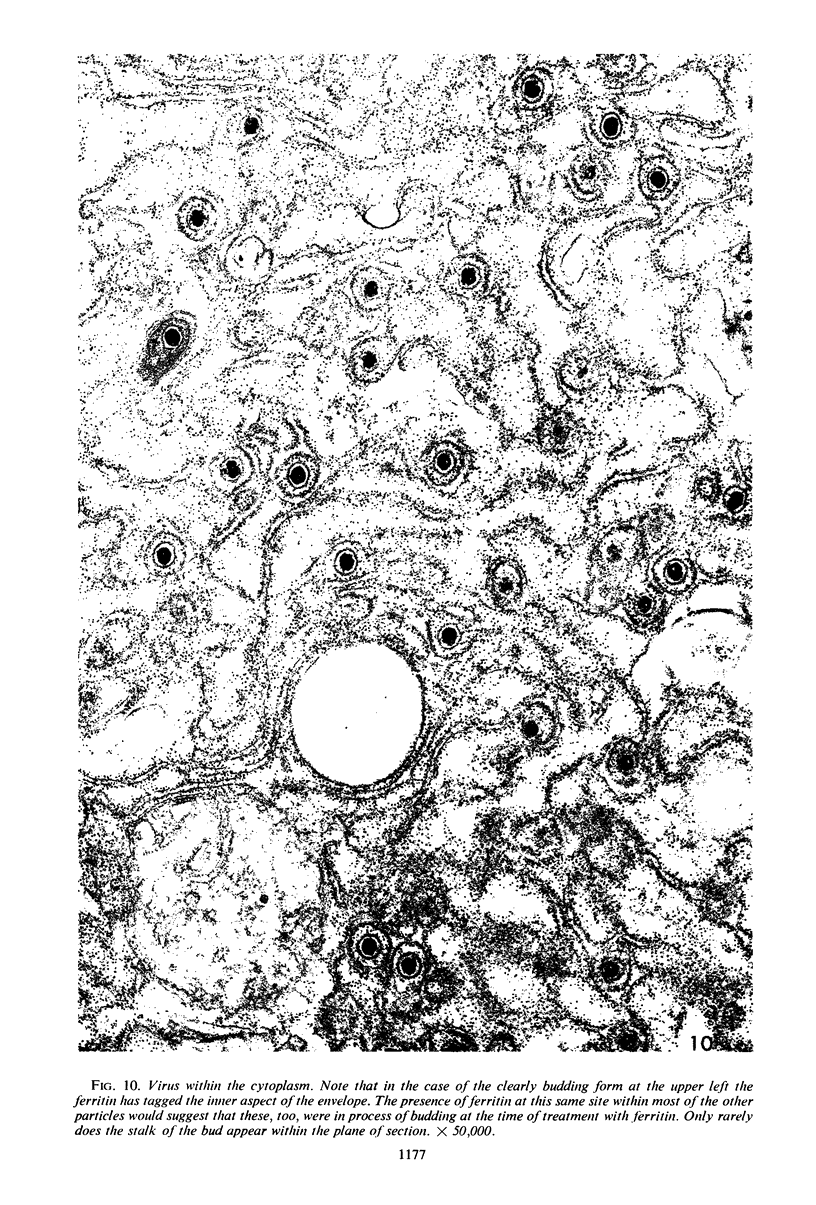
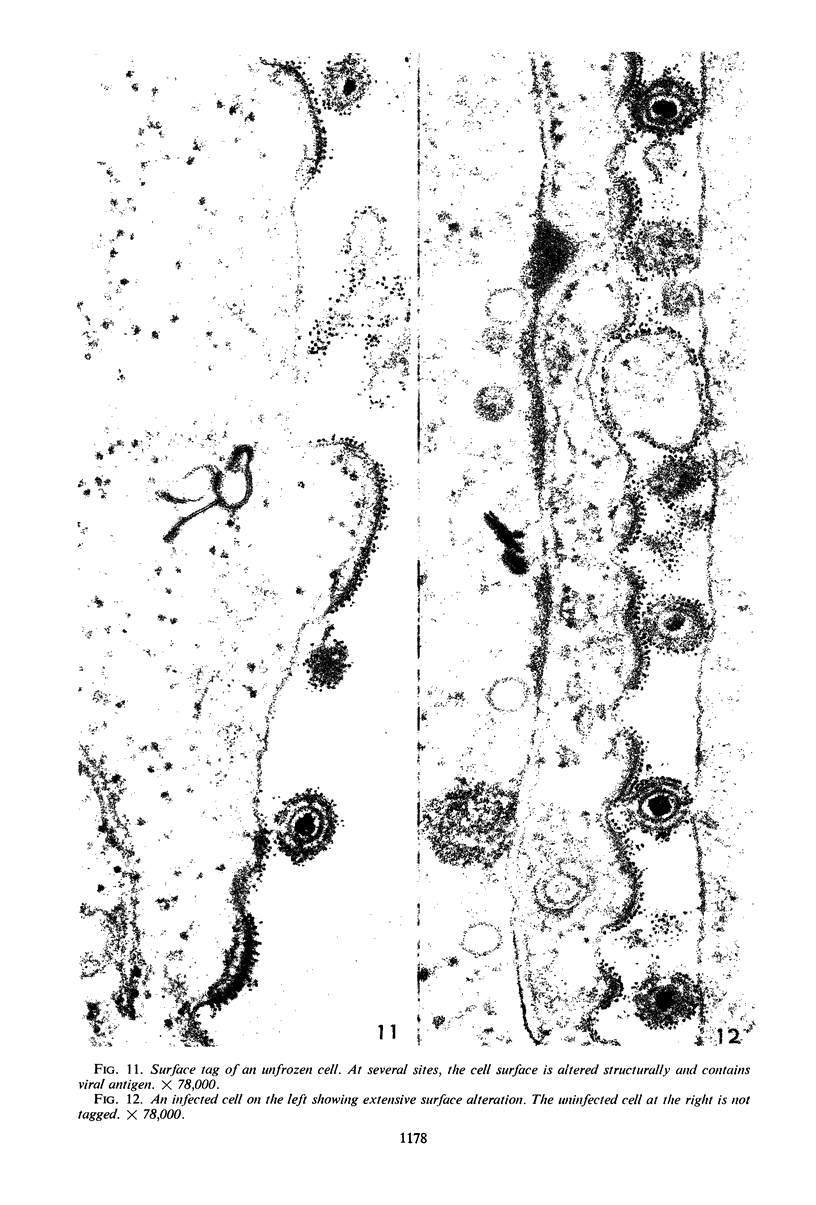
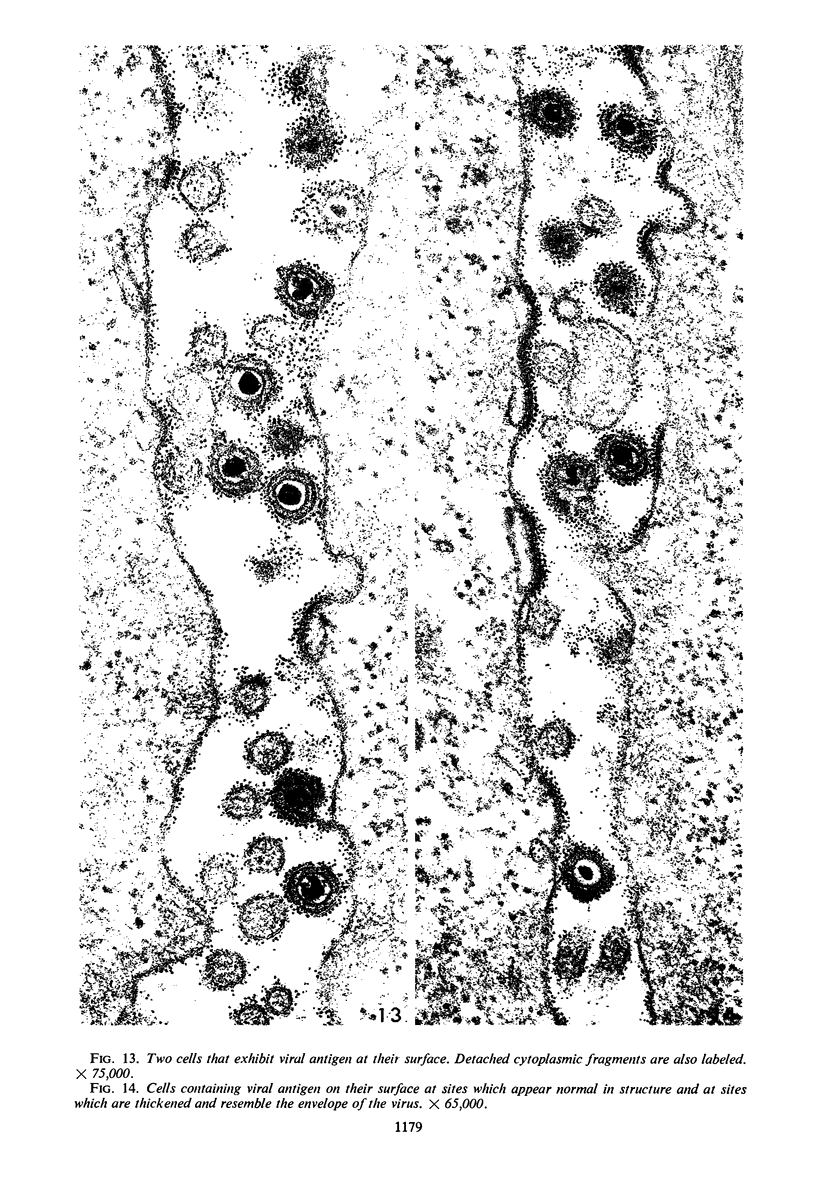
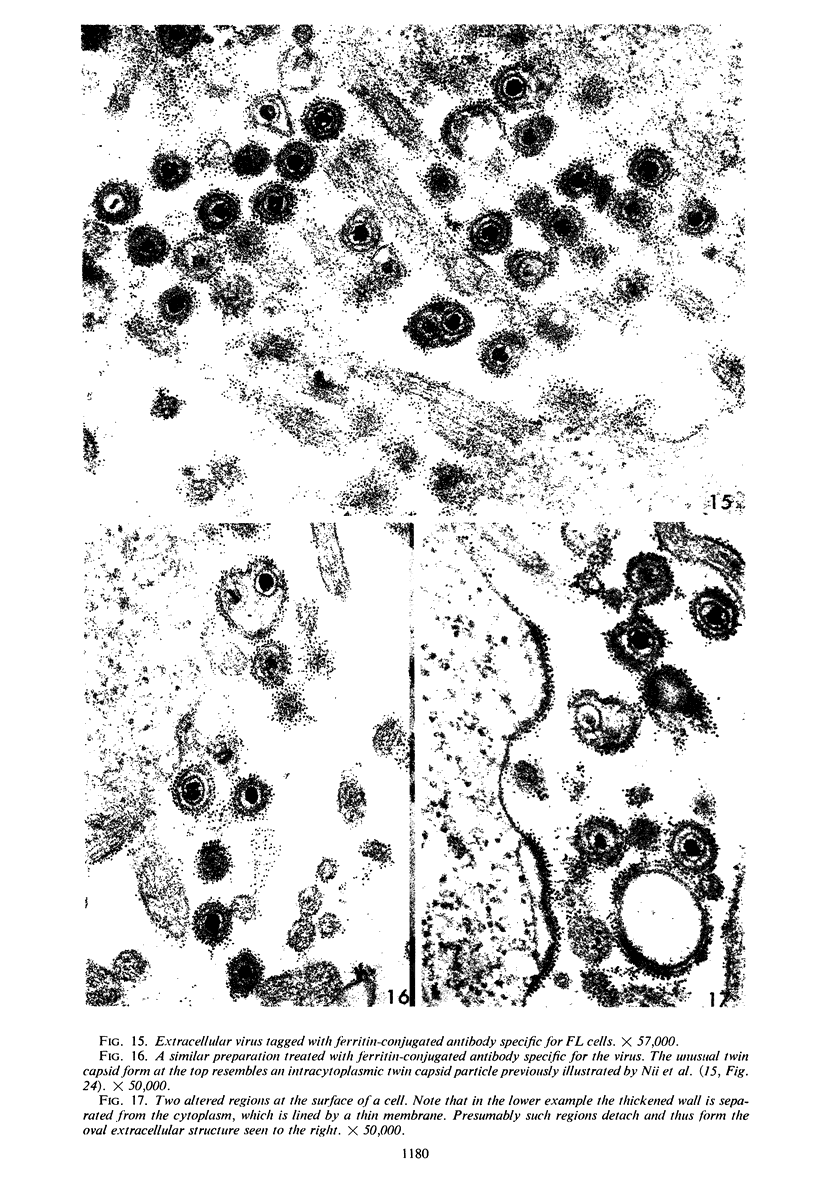
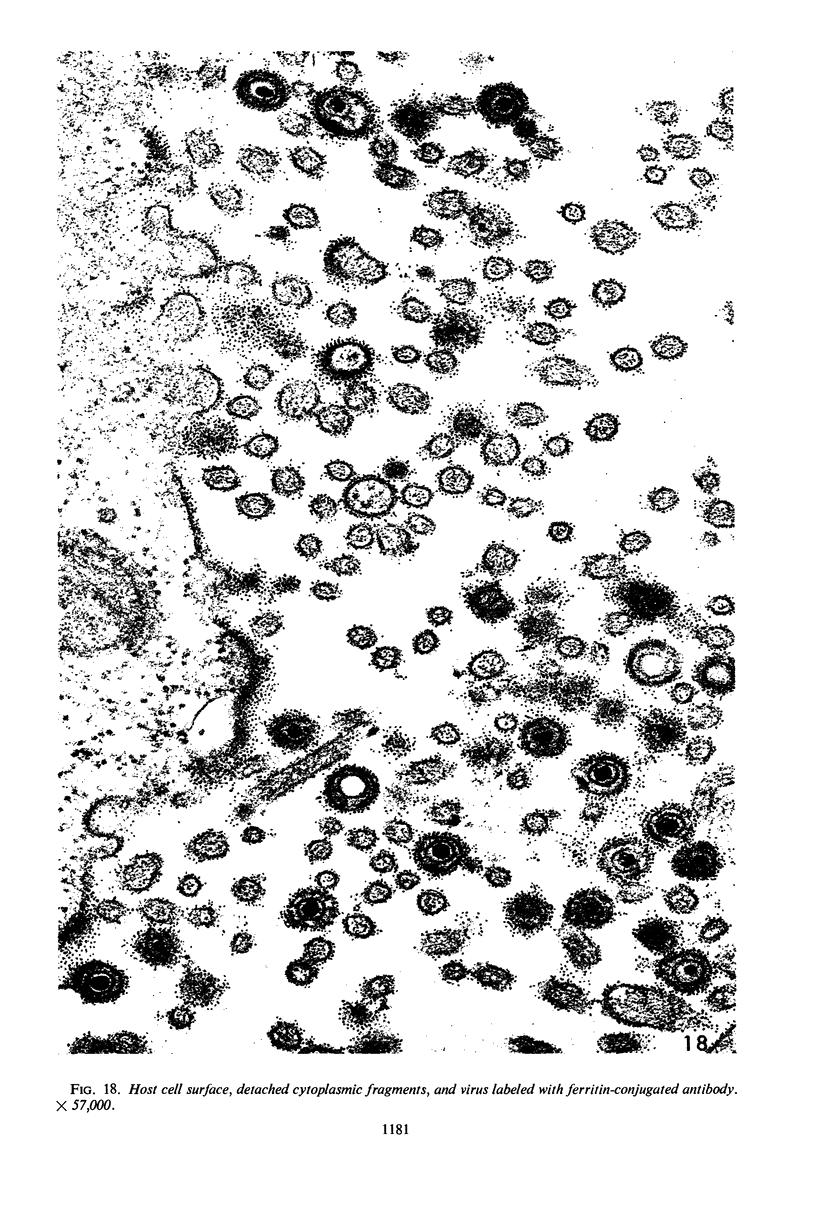
Small aggregates of viral antigen were encountered in the nuclear matrix. The capsids did not tag with antibodies specific for the virus or for the host cell. This observation remains unexplained. Nuclear and cytoplasmic membranes, as well as the envelope of the virus, reacted with both types of antibodies and appear, therefore, to contain host cell and viral protein. Large amounts of viral antigen are synthesized within the cytoplasm. This antigen was either diffusely spread or localized at the surface of membranes. The surface of infected cells contains viral antigen, which accumulates as infection progresses. At circumscribed sites, the cell wall becomes altered antigenically and structurally so as to resemble the envelope of the virus. Hypotheses are presented regarding the manner in which cell fusion occurs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Compans R. W., Holmes K. V., Dales S., Choppin P. W. An electron microscopic study of moderate and virulent virus-cell interactions of the parainfluenza virus SV5. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):411–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Kaplan A. S. Site of protein synthesis in cells infected with pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1967 May;32(1):60–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Morgan C., de Vaux St Cyr C., Hsu K. C., Rose H. M. Morphogenesis of type 2 parainfluenza virus examined by light and electron microscopy. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):215–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.215-237.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN H. E. The diagnosis of corneal herpes simplex infection by fluorescent antibody staining. Arch Ophthalmol. 1960 Sep;64:382–384. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1960.01840010384009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBRUN J. Cellular localization of Herpes simplex virus by means of fluorescent antibody. Virology. 1956 Aug;2(4):496–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiselman N., Kohn A., Danon D. Electron microscopic study of penetration of Newcastle disease virus into cells leading to formation of polykaryocytes. J Cell Sci. 1967 Mar;2(1):71–76. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rose H. M., Mednis B. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. I. Entry. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):507–516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.507-516.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASTUK W. L., PLESCIA O. J., OSSERMAN K. E. Changes in serum complement activity in patients with myasthenia gravis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Oct;105:177–184. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NII S., KAMAHORA J. Cytopathic changes induced by herpes simplex virus. Biken J. 1961 Dec;4:255–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NII S., KAMAHORA J. LOCATION OF HERPETIC VIRAL ANTIGEN IN INTERPHASE CELLS. Biken J. 1963 Jul;6:145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nii S., Morgan C., Rose H. M. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. II. Sequence of development. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):517–536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.517-536.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro L. S., Rose H. M., Morgan C., Hsu K. C. Electron microscopic study of the development of simian virus 40 by use of ferritin-labeled antibodies. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):384–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.384-399.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIFKIND R. A., HSU K. C., MORGAN C. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STAINING FOR ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Feb;12:131–136. doi: 10.1177/12.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B. Polykaryocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:327–342. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS R. W., ORLANS E. The redistribution of nucleic acid and the appearance of specific antigen in HeLa cells infected with herpes virus. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(2):393–402. doi: 10.1002/path.1700760208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Spring S. B., Roane P. R., Jr Cellular compartmentalization of herpesvirus antigens during viral replication. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):181–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.181-192.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMINOFF P. THE EFFECT OF 5-BROMODEOXYURIDINE ON HERPES SIMPLEX INFECTION OF HELA CELLS. Virology. 1964 Sep;24:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E., Harris H. An ultrastructural study of inter-specific cell fusion induced by inactivated Sendai virus. J Cell Sci. 1966 Dec;1(4):401–406. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Buoyant density of herpes simplex virus in solutions of caesium chloride. Nature. 1967 May 13;214(5089):713–714. doi: 10.1038/214713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sydiskis R. J., Roizman B. Polysomes and protein synthesis in cells infected with a DNA virus. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):76–78. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOZZA R., BALDUCCI D. The technique of fluorescent antibodies in opthalmology. A study of herpes simplex and vaccine keratoconjunctivitis and human trachomatous infection. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961 Jul;52:72–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. H., WILDY P. SOME SEROLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF HERPES VIRUS PARTICLES STUDIED WITH THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. Virology. 1963 Sep;21:100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. H., Shedden W. I., Elliot A., Tetsuka T., Wildy P., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D., Gold E. Virus specific antigens in mammalian cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Immunology. 1966 Oct;11(4):399–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]