Abstract
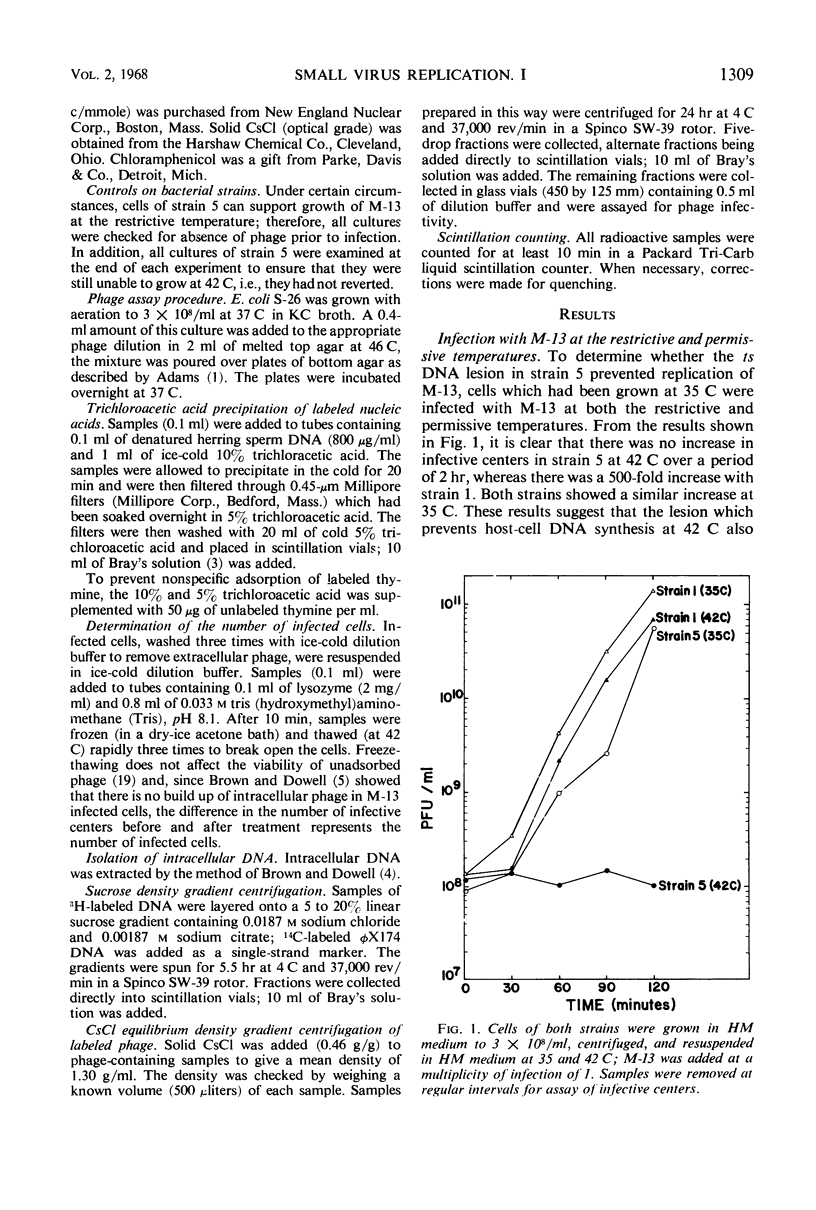
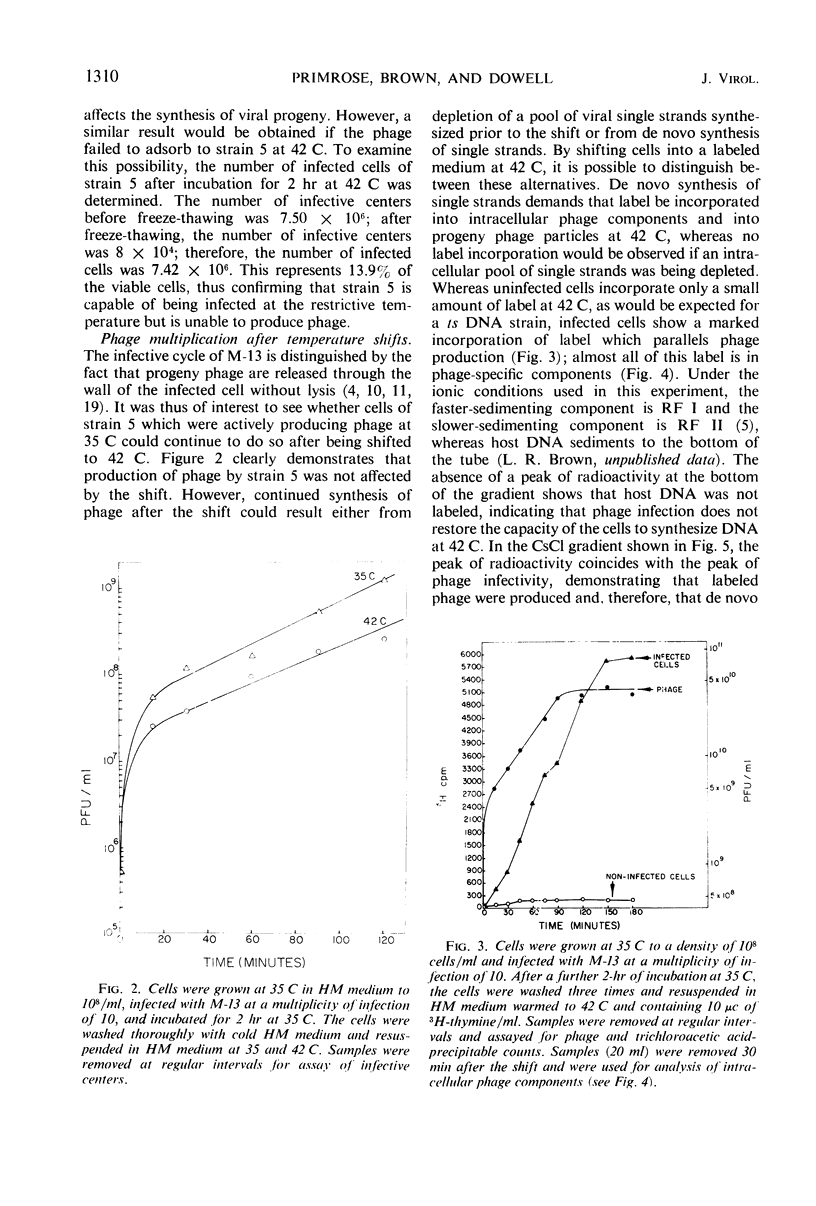
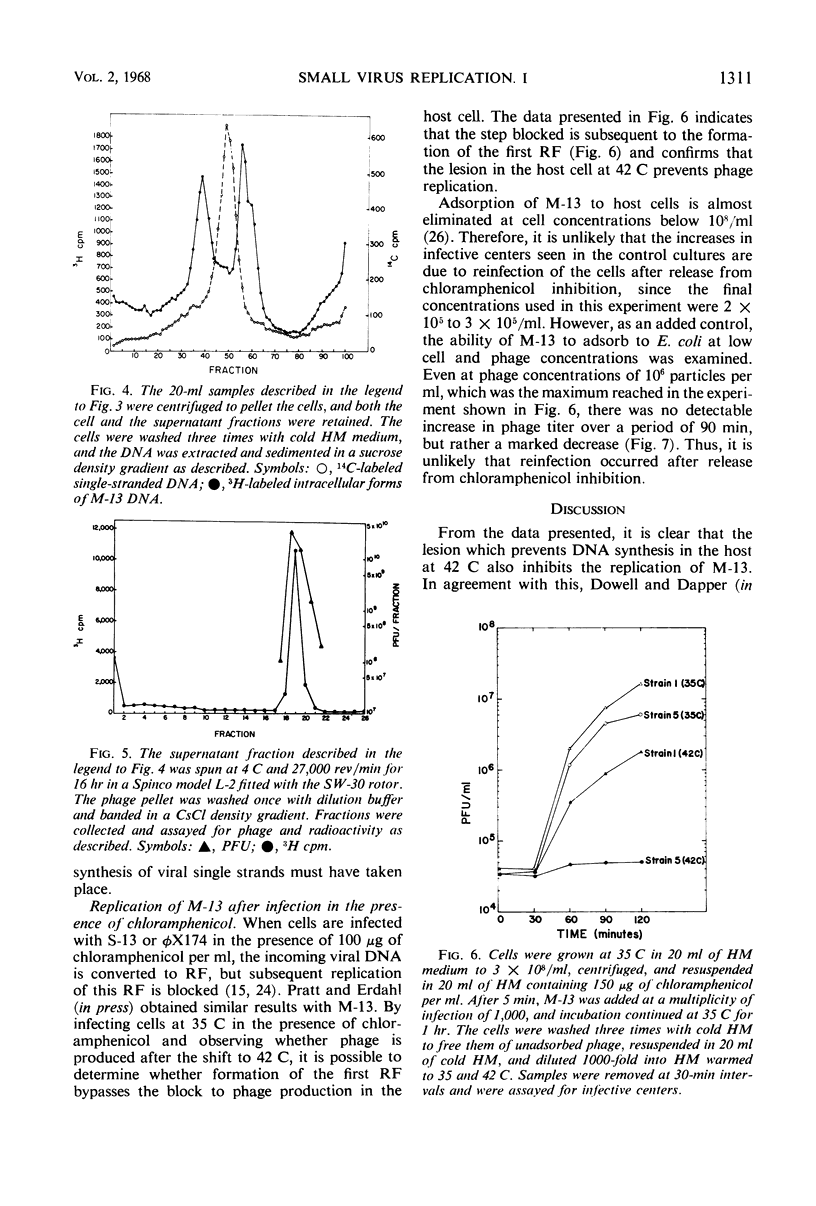
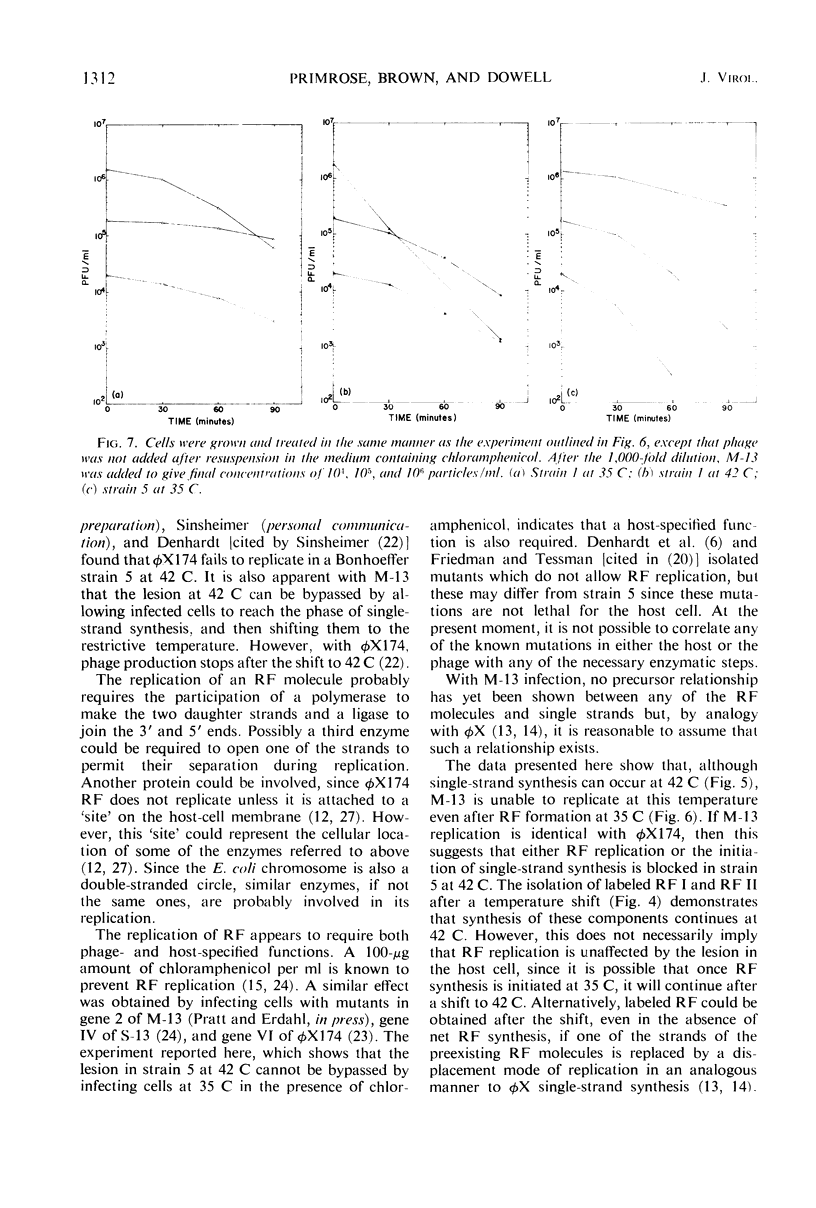
The replication of M-13 in a strain of Escherichia coli with a thermosensitive lesion in deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis was studied. M-13 failed to replicate at the restrictive temperature, even when the parental replicative form was allowed to form at the permissive temperature. When cells which were actively producing phage at the permissive temperature were shifted to the restrictive temperature, phage production continued. The incorporation of radioactive label into phage particles at 42 C indicated that continued single-strand synthesis was unaffected by the lesion in the host cell.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonhoeffer F. DNA transfer and DNA synthesis during bacterial conjugation. Z Vererbungsl. 1966;98(2):141–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00897186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. R., Dowell C. E. Replication of coliphage M-13. I. Effects on host cells after synchronized infection. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1290–1295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1290-1295.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. R., Dowell C. E. Replication of coliphage M-13. II. Intracellular deoxyribonucleic acid forms associated with M-13 infection of mitomycin C-treated cells. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1296–1307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1296-1307.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T., Dressler D. H., Hathaway A. THE ABORTIVE REPLICATION OF PhiX174 DNA IN A RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANT OF Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):813–820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowell C. E., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. IX. Studies on the physiology of three phi-X174 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):374–386. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., SIDDIQI O. Suppression of mutations in the alkaline phosphatase structural cistron of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1121–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulian M., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of DNA. 23. Synthesis of circular replicative form of phage phi-X174 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1723–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN-BERLING H., DUERWALD H., BEULKE I. EIN FAEDIGER DNS-PHAGE (FD) UND EIN SPHAERISCHER RNS-PHAGE (FR) WIRTSSPEZIFISCH FUER MAENNLICHE STAEMME VON E. COLI. III. BIOLOGISCHES VERHALTEN VON FD UND FR. Z Naturforsch B. 1963 Nov;18:893–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSCHNEIDER P. H., PREUSS A. M 13 BACTERIOPHAGE LIBERATION FROM INTACT BACTERIA AS REVEALED BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Mol Biol. 1963 Oct;7:450–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knippers R., Komano T., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. XXI. Replication and fate of the replicative form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):577–581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knippers R., Sinsheimer R. L. Process of infection with bacteriophage phiX174. XX. Attachment of the parental DNA of bacteriophage phiX174 to a fast-sedimenting cell component. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komano T., Knippers R., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. XXII. Synthesis of progeny single-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):911–916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist B. H., Sinsheimer R. L. Process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. XIV. Studies on macromolecular synthesis during infection with a lysis-defective mutant. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAALOE O., HANAWALT P. C. Thymine deficiency and the normal DNA replication cycle. I. J Mol Biol. 1961 Apr;3:144–155. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D., Tzagoloff H., Erdahl W. S. Conditional lethal mutants of the small filamentous coliphage M13. I. Isolation, complementation, cell killing, time of cistron action. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALIVAR W. O., TZAGOLOFF H., PRATT D. SOME PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ROD-SHAPED COLIPHAGE M13. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:359–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shleser R., Ishiwa H., Mannes B., Tessman E. S. Early replicative form DNA of bacteriophage S13. I. Sucrose gradient analysis of replicative form made by gene IV mutants. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TZAGOLOFF H., PRATT D. THE INITIAL STEPS IN INFECTION WITH COLIPHAGE M13. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:372–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman I., Ishiwa H., Kumar S., Baker R. Bacteriophage S13: a 7th gene. Science. 1967 May 12;156(3776):824–825. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3776.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M. J., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phiX174. 8. Evidence for an essential bacterial "site". J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):135–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.135-144.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



