Abstract
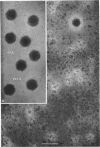
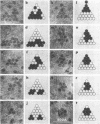
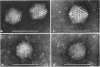
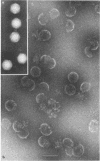
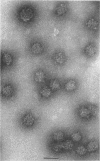
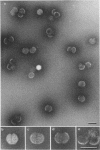
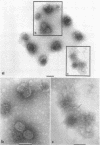
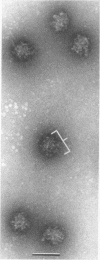
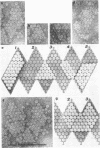
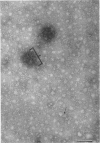
Treatment of adenovirus types 4 and 7 with formamide disrupted the virions, degrading the capsids into predominantly single capsomers. As shown by electron microscopic observation, disruption proceeded in the following sequence: (i) reduction of the electron density of the virions, suggesting release of an internal component; (ii) progressive cleavage of the capsid into two or more segments and the formation (type 7 only) of capsomer “sheets”; (iii) final cleavage of the capsid into single or groups of a few capsomers. The sequence appeared similar for both adenoviruses; for both types, the rate and extent of disruption were dependent on the formamide concentration, but type 7 was more easily disrupted than type 4 by short-term (5 to 10 sec) treatment at the low (10%) concentration. At 30% formamide, the intercapsomer bonds of either type were fully cleaved, and the capsids were completely degraded into predominantly single capsomers. Pretreatment with formaldehyde did not prevent this degradation. Under suitable conditions, virus-derived remnants can be observed among the breakdown products. These remnants have been shorn of capsomers and presumably represent intact internal nucleoprotein.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lawrence W. C., Ginsberg H. S. Intracellular uncoating of type 5 adenovirus deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):851–867. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.851-867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Rubin B. A., Stasny J. T. Cleavage by formamide of intercapsomer bonds in adenovirus types 4 and 7 virions and hemagglutinins. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1086–1095. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1086-1095.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L. Attachment and eclipse of adenovirus. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):868–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.868-875.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse H. C., Schlesinger R. W. An arginine-dependent step in the maturation of type 2 adenovirus. Virology. 1967 Nov;33(3):513–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Valentine R. C., Pereira H. G. The effect of heat on the anatomy of the adenovirus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Oct;1(4):509–522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-4-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Gehle W. D., Trousdale M. D. Architecture of the Adenovirus Capsid. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):254–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.254-261.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G., Norrby E., Schönning U. Ultrastructure of soluble antigens and the virion of adenovirus type 4. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;21(2):234–242. doi: 10.1007/BF01241447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]