Abstract
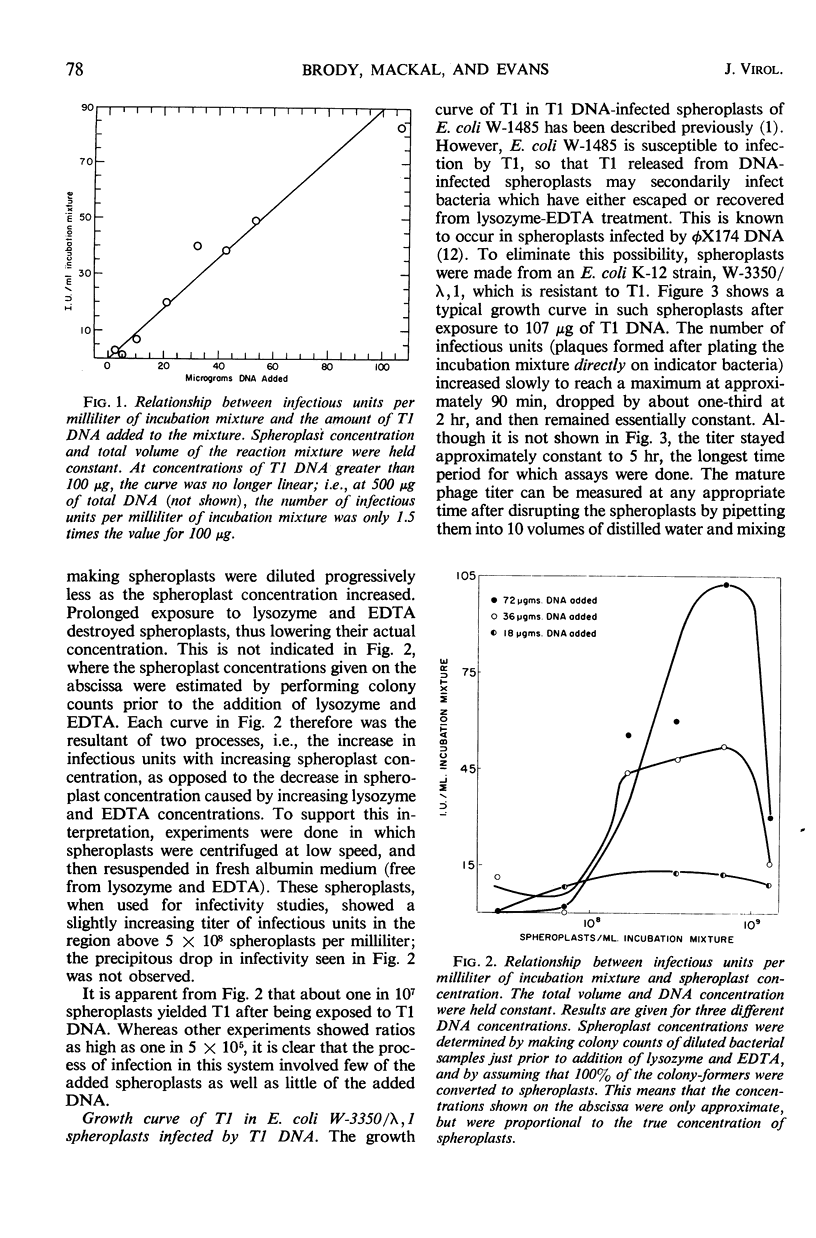
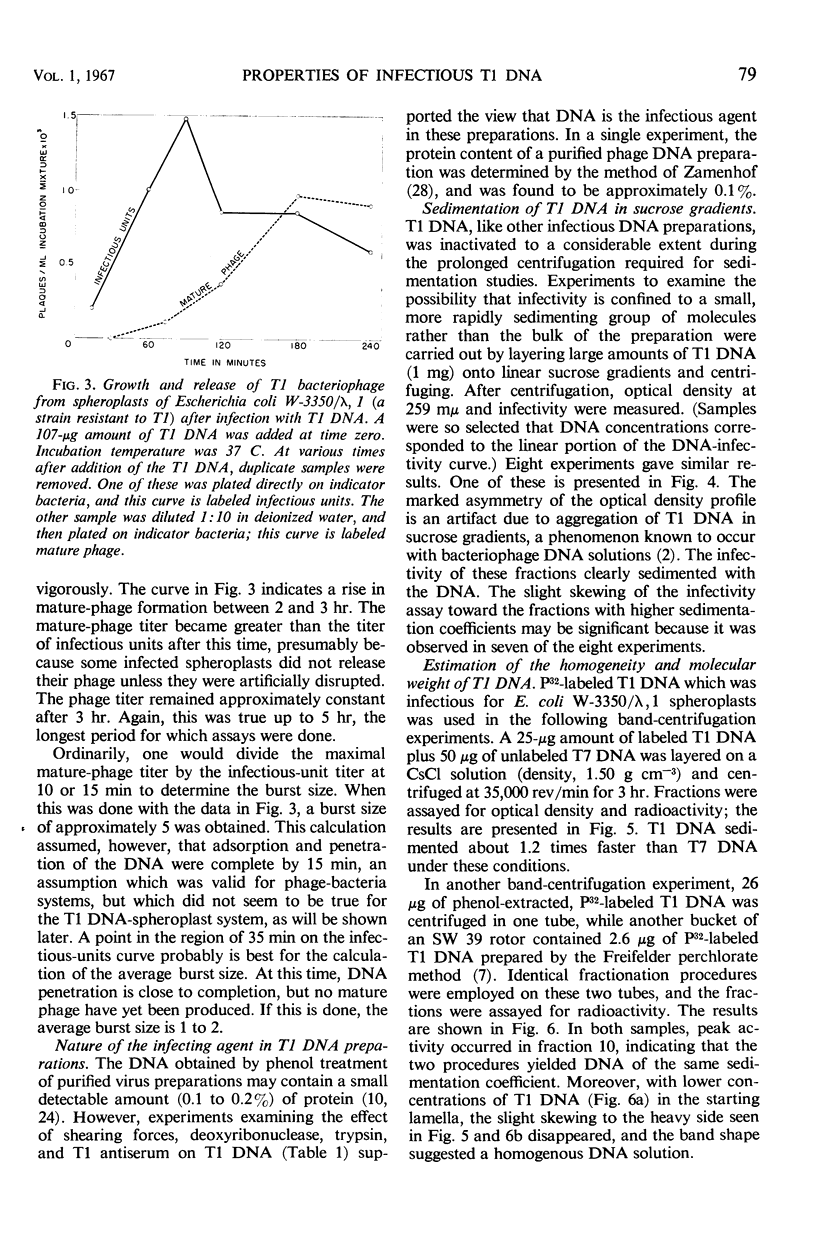
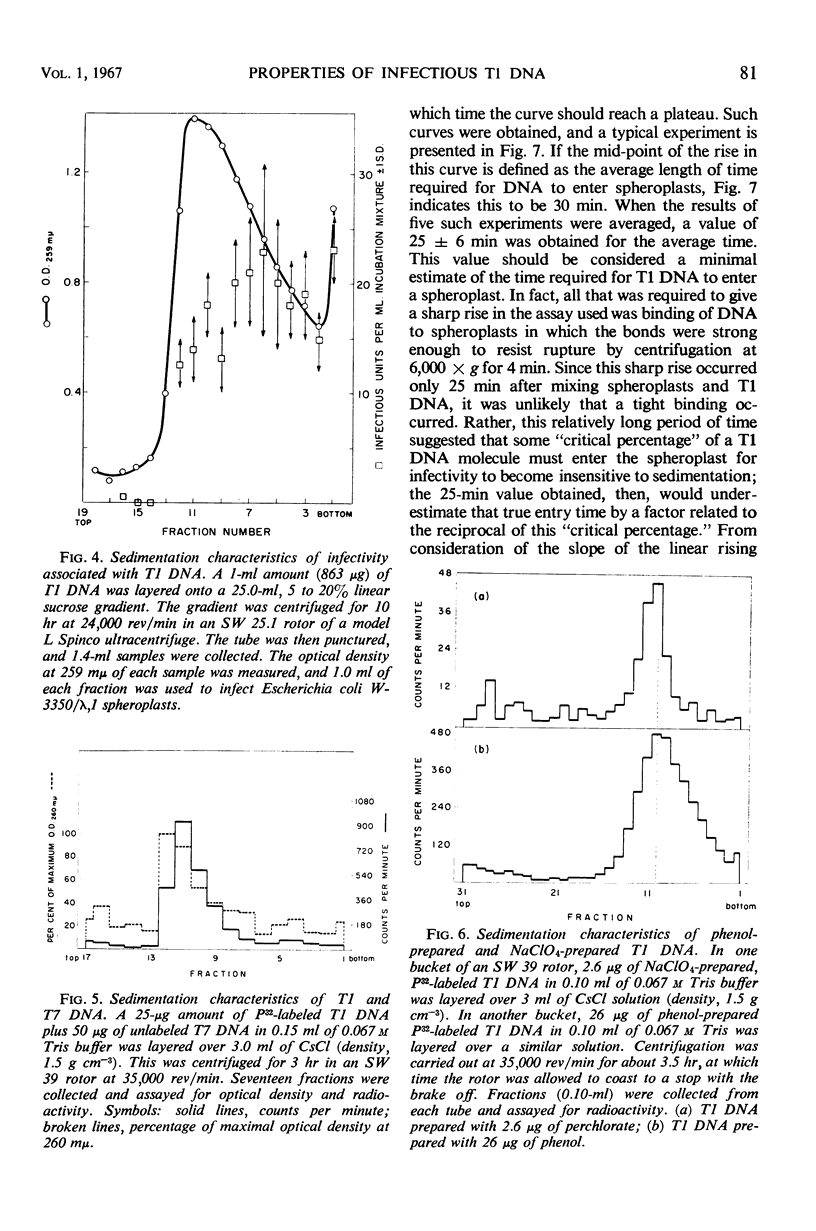
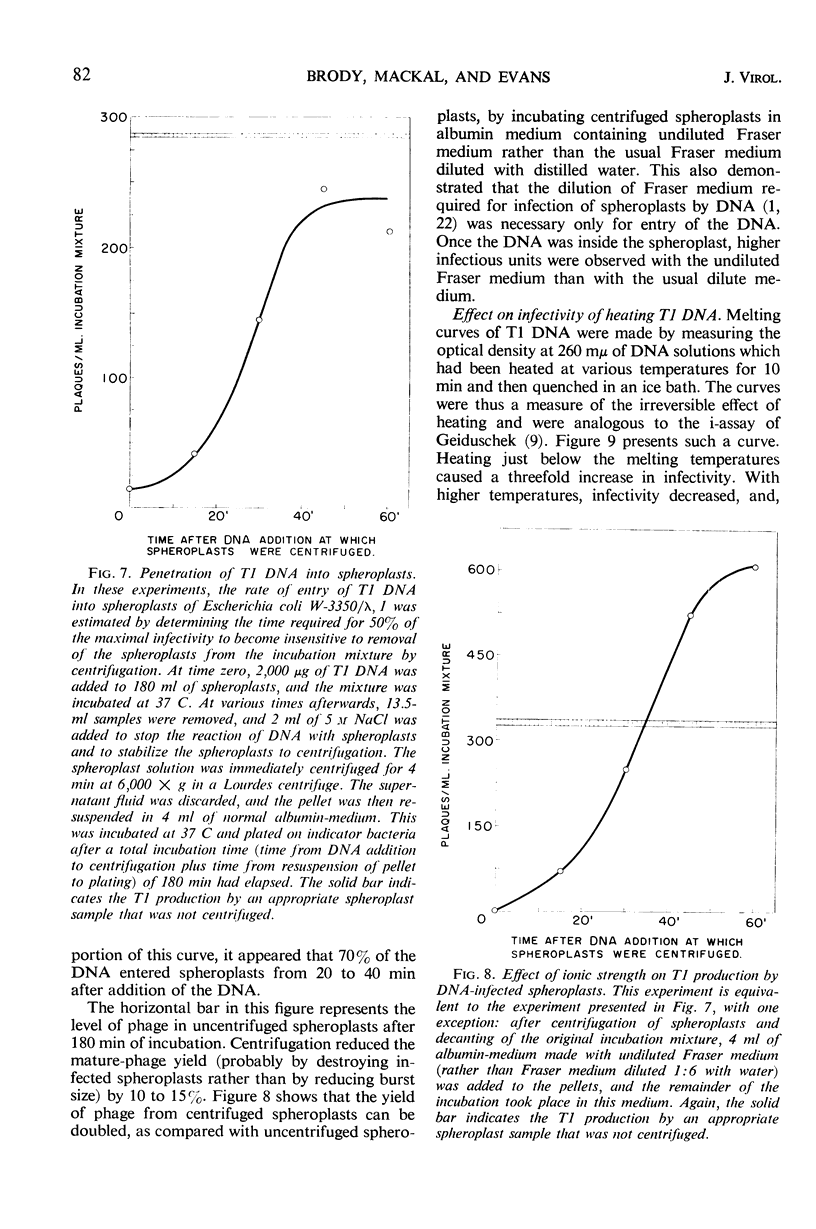
T1 deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) infection of spheroplasts was characterized by the following. A small number of the DNA molecules initiated infectious centers, and a small number of the spheroplasts were infected by T1 DNA. Once a favorable encounter of T1 DNA with spheroplast occurred, a minimum of 20 to 30 min was required for T1 DNA to enter the spheroplast. The mature T1 particles produced in the infection of spheroplasts by T1 DNA were released in a burst, but the average burst size was quite small compared with a normal burst of the phage-infected bacteria. T1 DNA preparations, capable of causing viral growth in spheroplasts, did not require detectable amounts of protein for infectivity, were homogeneous in band and boundary sedimentation, and had a guanine plus cytosine content of 48% and a minimal molecular weight of 35 × 106. Denatured T1 DNA, like denatured λDNA, did not infect spheroplasts. Renatured T1 DNA was not infectious; this was in marked contrast to renatured λDNA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODY E., COLEMAN L., MACKAL R. P., WERNINGHAUS B., EVANS E. A., Jr PROPERTIES OF INFECTIOUS DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM T1 AND LAMBDA BACTERIOPHAGE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:285–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. Sedimentation rate as a measure of molecular weight of DNA. Biophys J. 1963 Jul;3:309–321. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86823-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON P. F., FREIFELDER D. The physical properties of the deoxyribonucleic acid from T7 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1962 Dec;5:643–649. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENSTARK A., MAALOE O., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. Genetic variants of phage T3. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:56–64. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigner J., Doty P. The native, denatured and renatured states of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):549–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER D., JERREL E. A. The amino acid composition of T3 bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREIFELDER D. A NOVEL METHOD FOR THE RELEASE OF BACTERIOPHAGE DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:141–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90897-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P. On the factors controlling the reversibility of DNA denaturation. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:467–487. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. M. INFECTIVITY OF DNA ISOLATED FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS BACTERIOPHAGE, SP82. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:438–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHRIE G. D., SINSHEIMER R. L. Observations on the infection of bacterial protoplasts with the deoxyribonucleic acid of bacteriophage phi X174. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 25;72:290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D., Burgi E., Ingraham L. COHESION OF DNA MOLECULES ISOLATED FROM PHAGE LAMBDA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):748–755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D., HOGNESS D. S. The transformation of Escherichia coli with deoxyribonucleic acid isolated from bacteriophage lambda-dg. J Mol Biol. 1960 Dec;2:392–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(60)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. D., Inman R. B. Cohesion and the biological activity of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):78–91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S., TOLMACH L. J. Genetic transformation. II. The significance of damage to the DNA molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jun;33(2):371–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACHATTIE L. A., THOMAS C. A., Jr DNA FROM BACTERIOPHAGE LAMBDA: MOLECULAR LENGTH AND CONFORMATION. Science. 1964 May 29;144(3622):1142–1144. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3622.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAL R. P., WERNINGHAUS B., EVANS E. A., Jr THE FORMATION OF LAMBDA BACTERIOPHAGE BY LAMBDA DNA IN DISRUPTED CELL PREPARATIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1172–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER F., MACKAL R. P., TAO M., EVANS E. A., Jr Infectious deoxyribonucleic acid from gamma bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1141–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., FUERST C. R. Inactivation of bacteriophages by decay of incorporated radioactive phosphorus. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Mar 20;38(4):441–458. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.4.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINOGRAD J., BRUNER R., KENT R., WEIGLE J. Band-centrifugation of macromolecules and viruses in self-generating density gradients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:902–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



