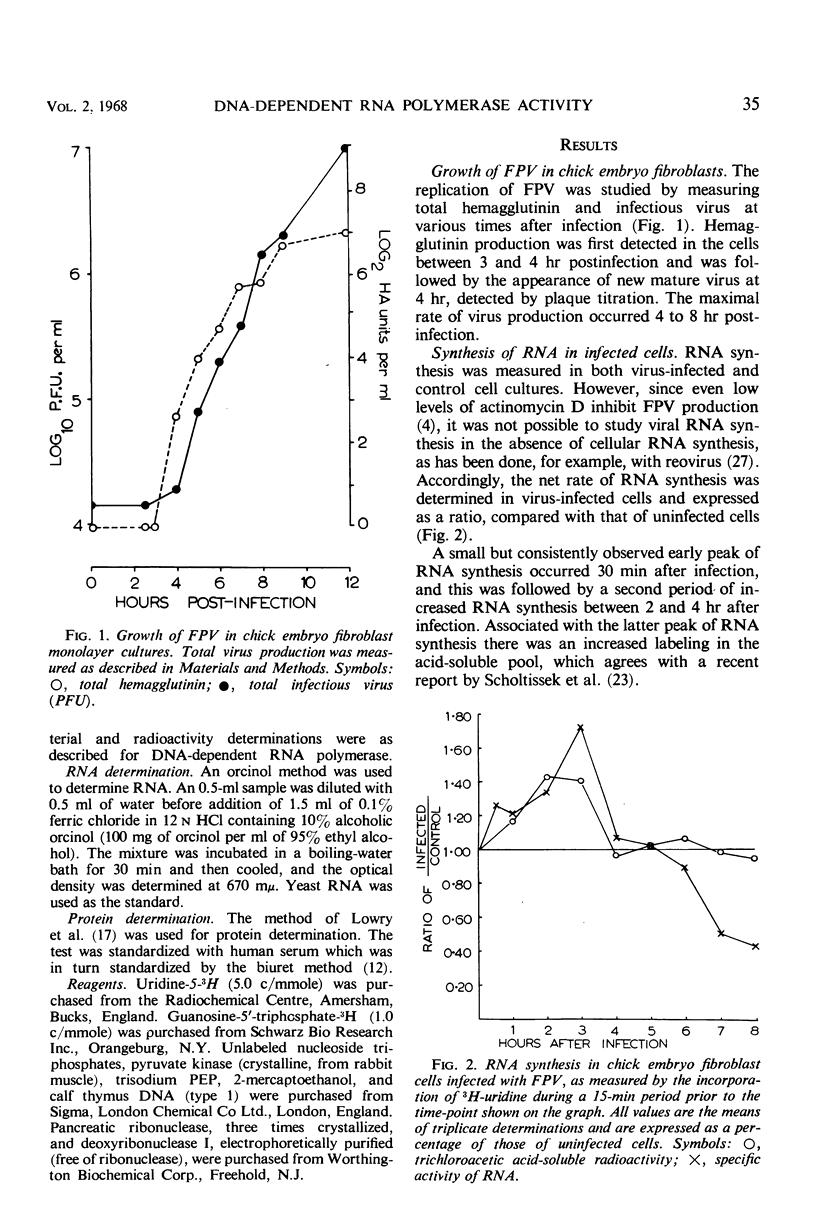
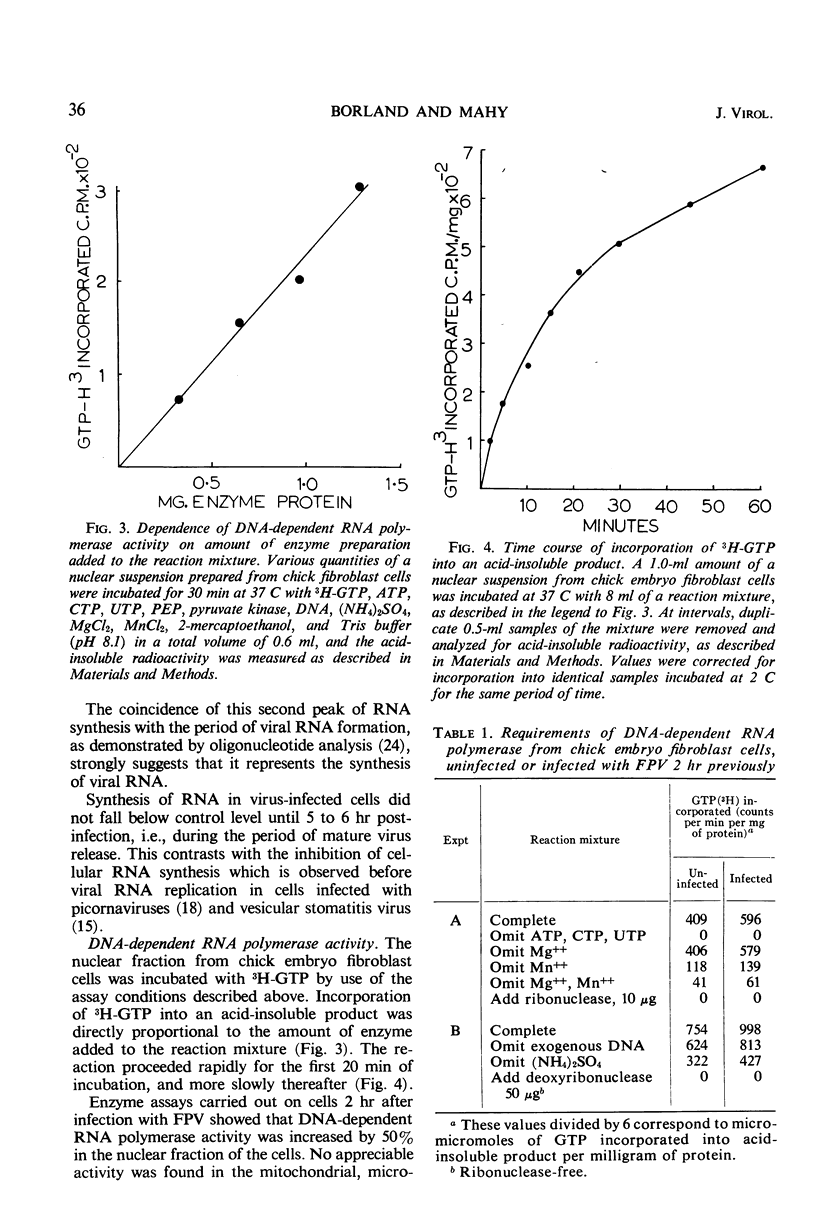
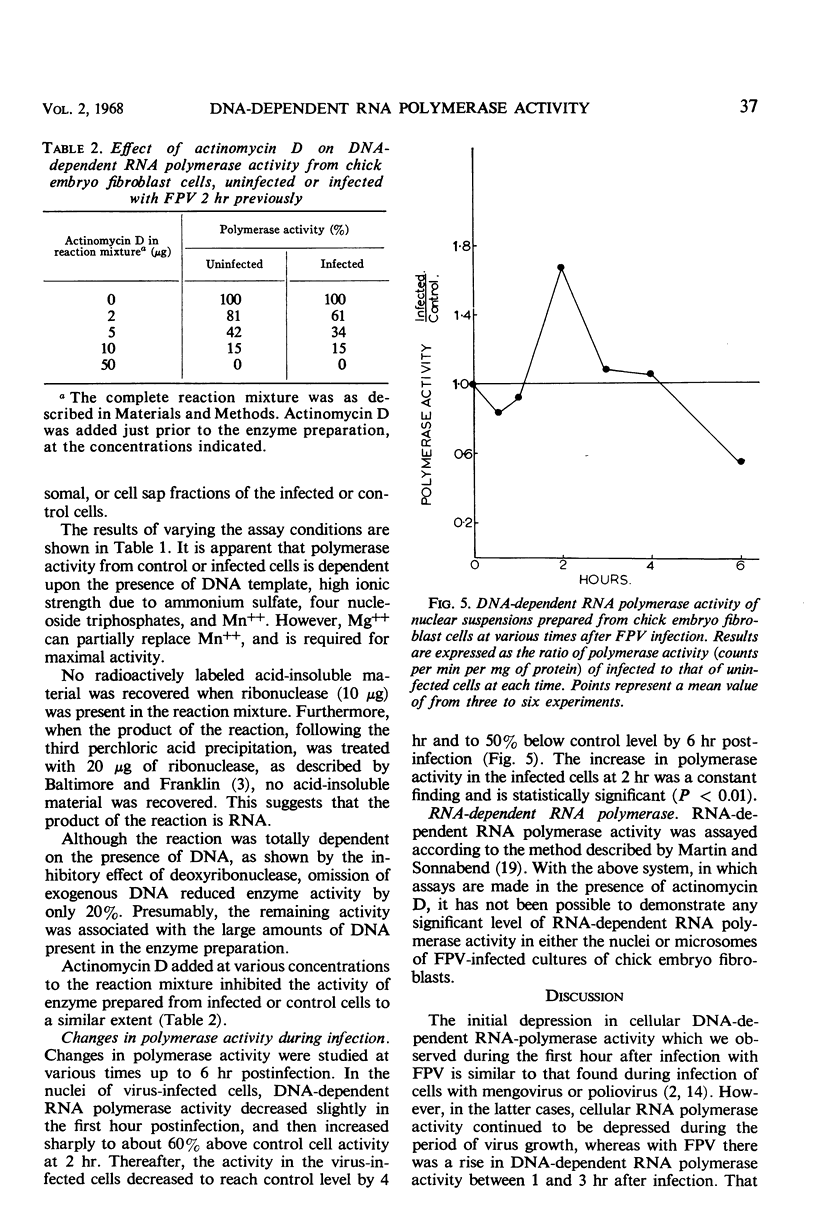
Abstract
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-dependent ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase activity was assayed on nuclear preparations of chick embryo fibroblast cells at various times after infection with an influenza A virus (fowl plague virus) and was compared with the activity of uninfected cells. Polymerase activity was increased by about 60% by 2 hr after infection, and this increase coincided with an increase in RNA synthesis in infected cells, as determined by pulse-labeling with uridine. No difference could be detected between the polymerases of infected and uninfected cells as to their requirements for DNA primer, divalent cations, and nucleoside triphosphates, and they were equally sensitive to addition of actinomycin D to the reaction mixture. It is possible that host cell DNA-dependent RNA polymerase is involved in the replication of influenza virus RNA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. A NEW RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE APPEARING AFTER MENGOVIRUS INFECTION OF L-CELLS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3395–3400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. The effect of Mengovirus infection on the activity of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of L-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1383–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY R. D. THE EFFECTS OF ACTINOMYCIN D AND ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATION ON THE PRODUCTION OF FOWL PLAGUE VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Dec;24:563–569. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREITENFELD P. M., SCHAFER W. The formation of fowl plague virus antigens in infected cells, as studied with fluorescent antibodies. Virology. 1957 Oct;4(2):328–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader J. P. Metabolic requirements for infection by Rous sarcoma virus. I. The transient requirement for DNA synthesis. Virology. 1966 Jul;29(3):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Barry R. D. Nucleic acid of influenza virus. Nature. 1966 Jul 23;211(5047):384–387. doi: 10.1038/211384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusberg P. H., Robinson W. S. On the structure and replication of influenza virus. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):383–405. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90193-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Franklin R. M. Symposium on replication of viral nucleic acids. I. Formation and properties of a replicative intermediate in the biosynthesis of viral ribonucleic acid. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):267–278. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.267-278.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., REICH E. ACTINOMYCIN INHIBITION OF RNA SYNTHESIS DIRECTED BY DNA. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:958–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in nuclear extracts of mammalian cells grown in suspension culture; effect of ionic strength and surface-active agents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jul 22;51:201–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)91042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Inhibition of DNA-primed RNA synthesis during poliovirus infection of human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Dec 19;9:556–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. P., Walters C. P. Influenza virus-induced ribonucleic acid nucleotidyltransferase and the effect of actinomycin D on its formation. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):231–235. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU C. Studies of influenza infection in ferrets by means of fluorescein-labelled antibody. I. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of the disease. J Exp Med. 1955 Jun 1;101(6):665–676. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.6.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. M., Sonnabend J. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase catalyzing synthesis of double-stranded arbovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):97–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.97-109.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Symposium on replication of viral nucleic acids. 3. Replication of mengovirus ribonucleic acid. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):288–308. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.288-308.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons M. W. Studies on influenza virus ribonucleic acid. Virology. 1967 Mar;31(3):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., SHATKIN A. J., TATUMEL Action of actinomycin D on animal cells and viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1238–1245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOLTISSEK C., ROTT R. [Relation between the synthesis of ribonucleic acid and protein in the propagation of a virus of the influenza group (fowlplague virus)]. Z Naturforsch B. 1961 Oct;16B:663–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHATKIN A. J. ACTINOMYCIN AND THE DIFFERENTIAL SYNTHESIS OF REOVIRUS AND L CELL RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:506–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Becht H., Drzeniek R. Biochemical studies on the cytopathic effect of influenza viruses. J Gen Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):219–225. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Rada B. Reovirus-directed ribonucleic acid synthesis in infected L cells. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.24-35.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMIN H. M. THE EFFECTS OF ACTINOMYCIN D ON GROWTH OF ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS IN VITRO. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:577–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIGIER P., GOLDE A. EFFECTS OF ACTINOMYCIN D AND OF MITOMYCIN C ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Aug;23:511–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. G., Bader J. P. Viral ribonucleic acid polymerase: chick-embryo cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus or Rous-associated virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 10;103(4):549–557. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



