Abstract
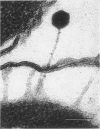
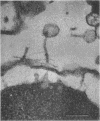
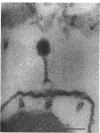
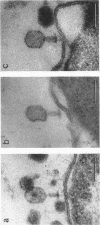
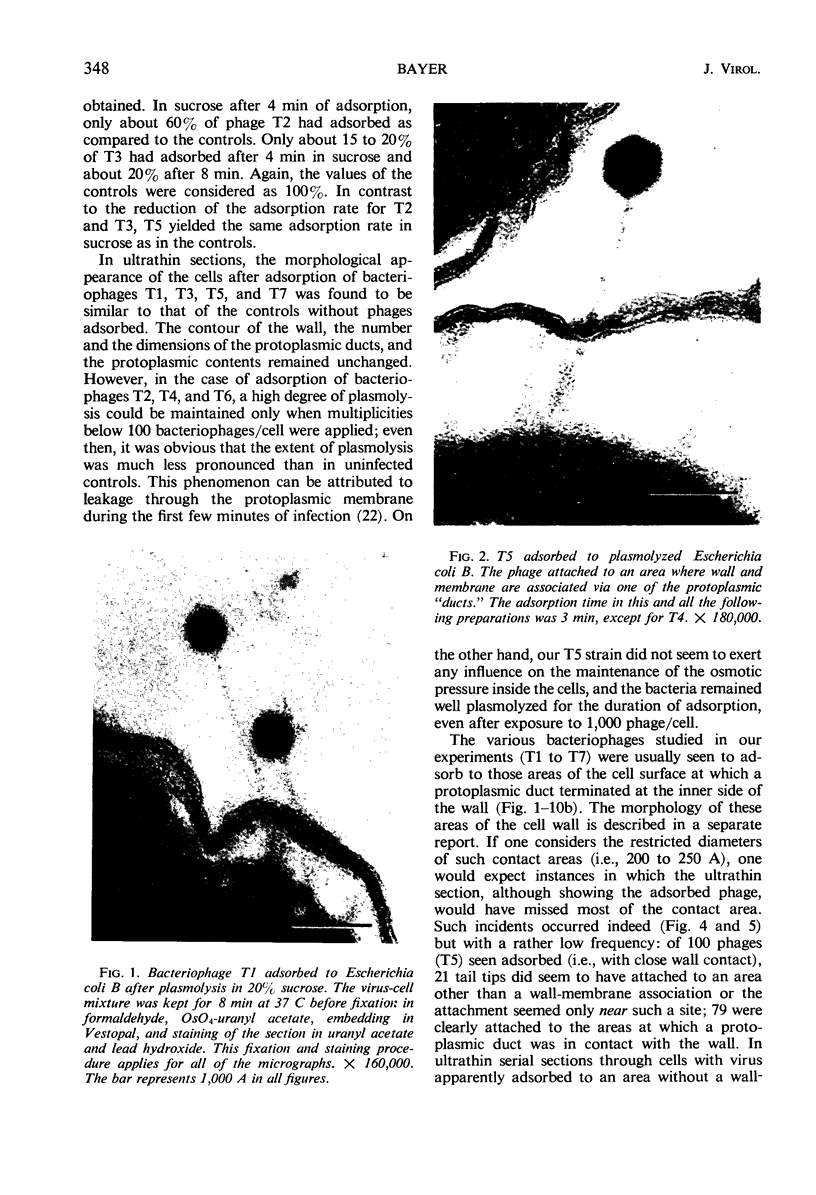
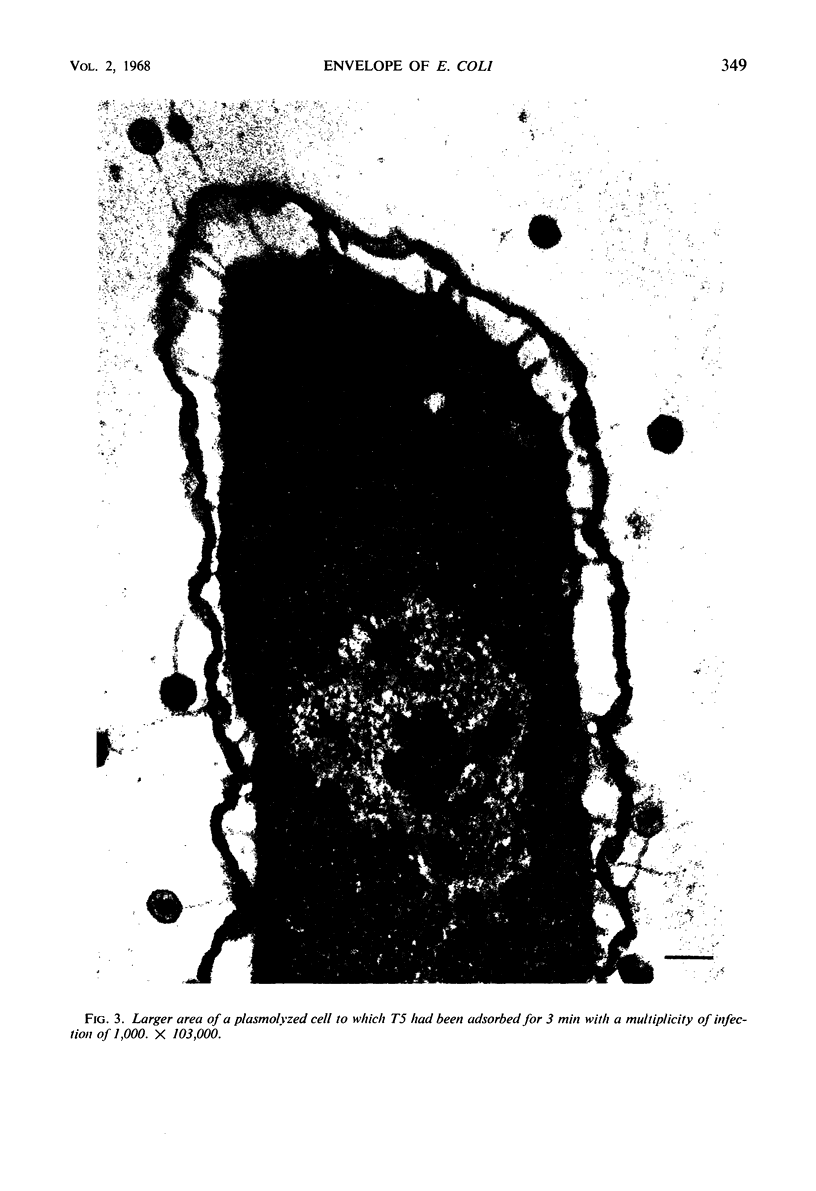
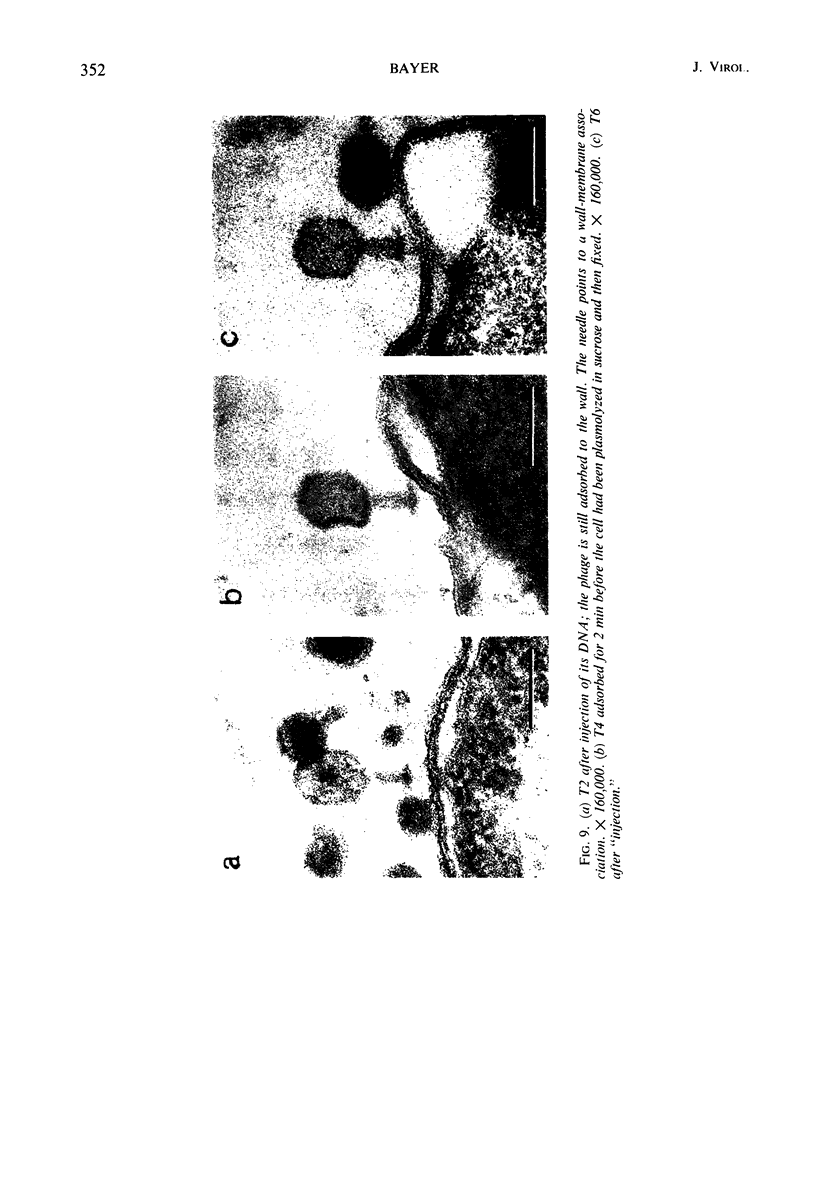
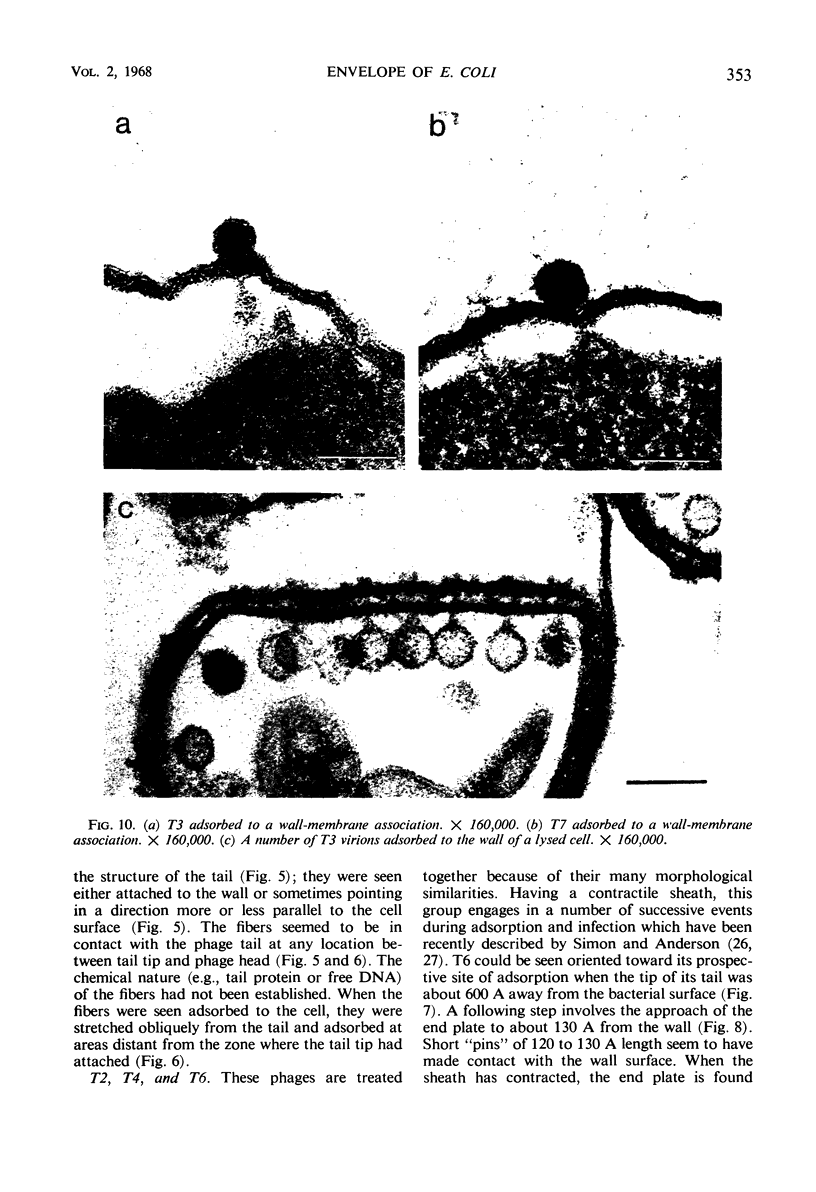
In plasmolyzed Escherichia coli, wall and membrane adhered to one another at 200 to 400 localized areas. This number of specialized wall areas per cell was of the same order of magnitude as the total number of bacteriophage receptors. When bacteriophages T1 to T7 were adsorbed to the bacteria, they were seen to attach almost exclusively to these areas. Comparisons of the number of adsorbed phage particles observed in ultrathin sections and the expected number of phages per cell were in agreement. These results suggest a sharing of receptive areas by the various phages. Adsorption to the wall-membrane associations would permit the virus to release its nucleic acid at an area closest to the cell's protoplasmic contents.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON T. F. The morphology and osmotic properties of bacteriophage systems. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1953;18:197–203. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1953.018.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINTON C. C., Jr, GEMSKI P., Jr, CARNAHAN J. A NEW TYPE OF BACTERIAL PILUS GENETICALLY CONTROLLED BY THE FERTILITY FACTOR OF E. COLI K 12 AND ITS ROLE IN CHROMOSOME TRANSFER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:776–783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Response of Cell Walls of Escherichia coli to a Sudden Reduction of the Environmental Osmotic Pressure. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1104–1112. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1104-1112.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER D., JERREL E. A. The amino acid composition of T3 bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross L. Active membranes for active transport. J Theor Biol. 1967 Jun;15(3):298–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSHEY A. D., CHASE M. Independent functions of viral protein and nucleic acid in growth of bacteriophage. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;36(1):39–56. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel J. V., Anderson T. F., Levine M. in vitro MORPHOGENESIS OF PHAGE P22 FROM HEADS AND BASE-PLATE PARTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):284–291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., SECHAUD J. Electron microscopical studies of phage multiplication. II. Production of phage-related structures during multiplication of phages T2 and T4. Virology. 1957 Apr;3(2):256–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Anderson T. F. The Identification and Characterization of Bacteriophages with the Electron Microscope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1942 Apr;28(4):127–130.1. doi: 10.1073/pnas.28.4.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M., Anderson T. F. Electron Microscope Studies of Bacterial Viruses. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):57–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.57-77.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL E. W. A phage, phi chi, which attacks motile bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:253–290. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., GAREN A., CLINE J. The mechanism of virus attachment to host cells. I. The role of ions in the primary reaction. J Exp Med. 1951 Jan;93(1):65–88. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., LEE H. H. Mechanism of cell wall penetration by viruses. I. An increase in host cell permeability induced by bacteriophage infection. J Exp Med. 1954 May 1;99(5):481–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.5.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. I. Attachment and penetration. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. II. Structure and function of the baseplate. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D. The properties of x-ray inactivated bacteriophage. I. Inactivation by direct effect. J Bacteriol. 1950 Dec;60(6):697–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.6.697-718.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W. Phage receptor systems of E. coli B. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1953;18:155–157. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1953.018.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILDY P., ANDERSON T. F. CLUMPING OF SUSCEPTIBLE BACTERIA BY BACTERIOPHAGE TAIL FIBRES. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Feb;34:273–283. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. C., FRASER D. Morphology of the seven T-bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(4):458–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.4.458-464.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]