Abstract
Ten Pseudomonas phage were isolated by sewage enrichment. Five psychrophilic and five mesophilic phage were selected for a description of some of their biological properties. In addition to growth on psychrophilic hosts, the psychrophilic phage studied were also able to grow on a mesophilic host within its growth temperature range. Latent periods for psychrophilic phage at 3.5 C were 6 to 12 hr and at 25 C were 30 to 60 min. Mesophilic phage had a latent period of 85 to 190 min at 25 C and 35 to 85 min at 37 C. Psychrophilic phage were significantly more heat-sensitive than the mesophilic phage. Of all the parameters studied, only thermal sensitivity correlated with growth at 3.5 C. Phage used in this study had a deoxyribonucleic acid base composition ranging from 39.6 to 68.2% guanine plus cytosine, deduced from melting temperature measurements.
Full text
PDF
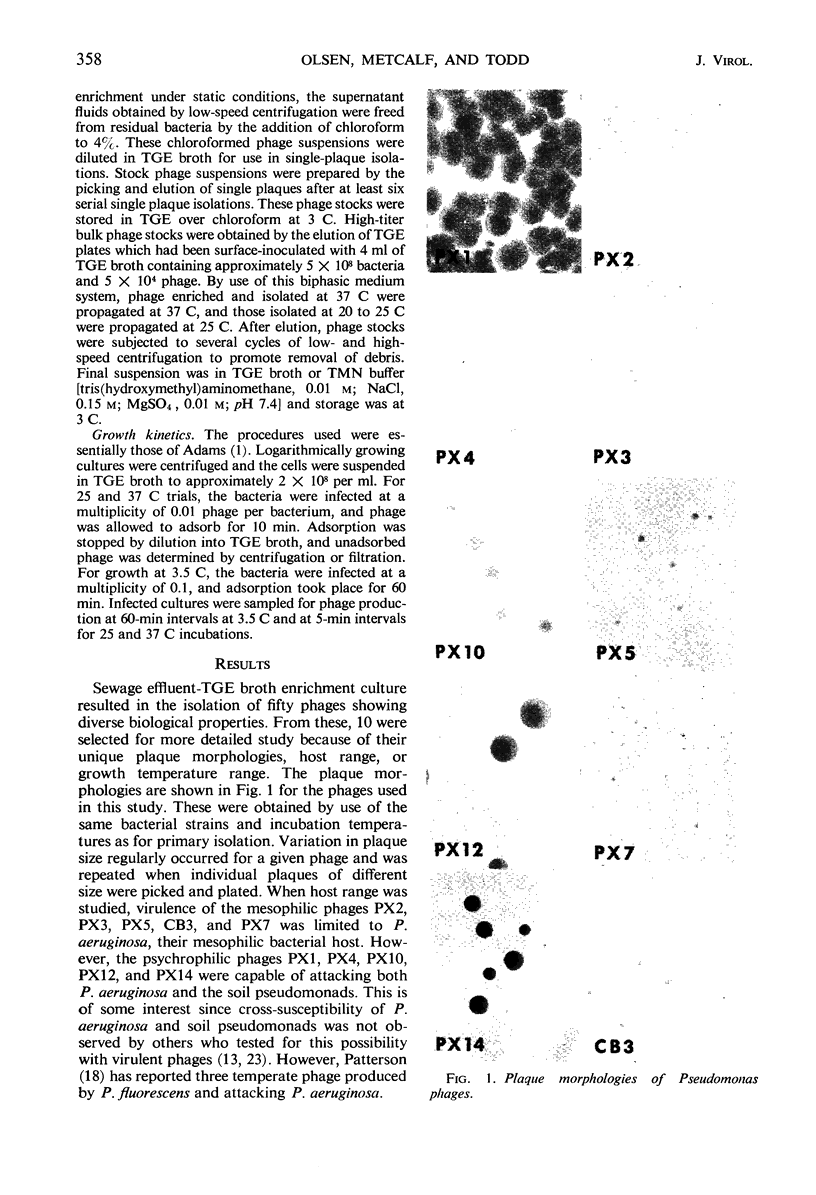

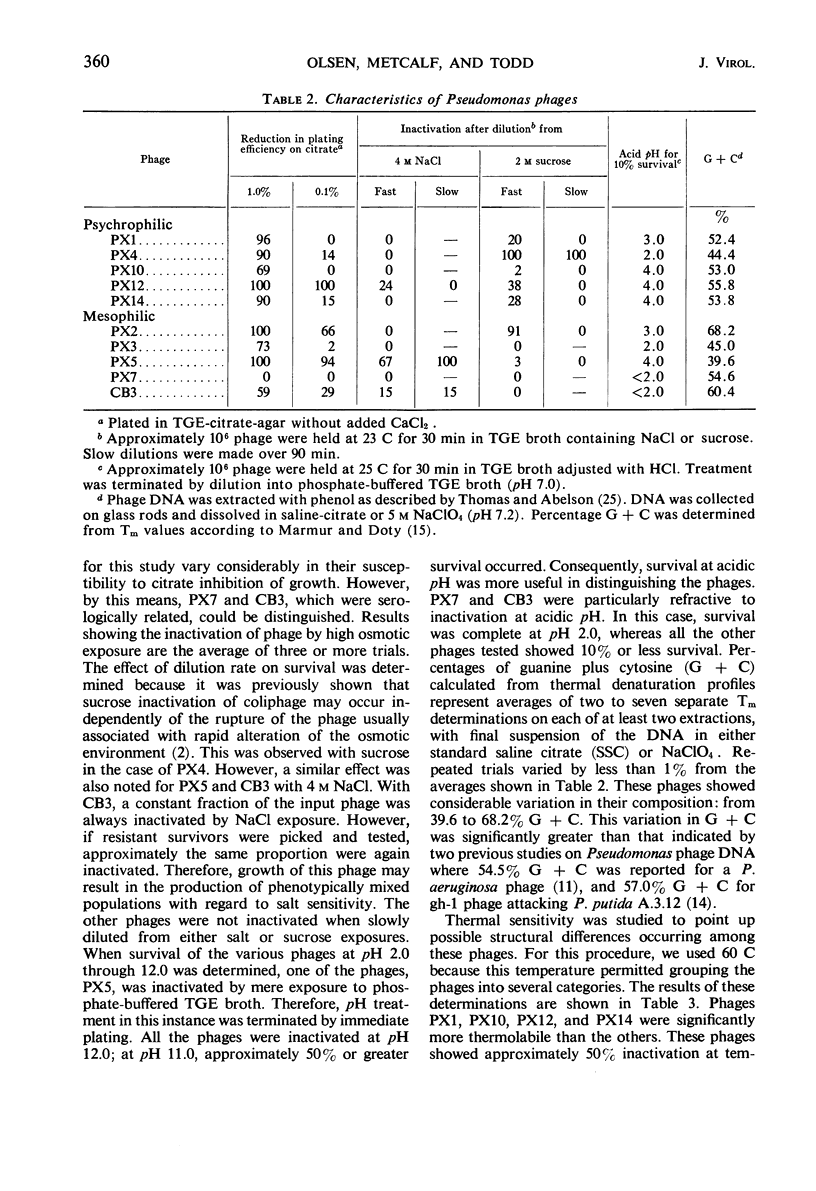



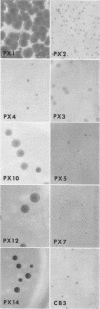
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON T. F., RAPPAPORT C., MUSCATINE N. A. On the structure and osmotic properties of phage particles. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jan;84(1):5–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY D. E. The structure of some Staphylococcus and Pseudomonas phages. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Jun;8:552–565. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)80055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. R., Saul S. H. A cold-sensitive mutant of bacteriophage T1. Virology. 1966 Jul;29(3):497–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90228-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEARY T. W., FISHER E., Jr, FISHER T. N. A small RNA containing Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Mar 5;10:359–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., COWLES P. B. The bacteriophages of Bacillus megaterium. I. Serological, physical, and biological properties. J Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(4):379–385. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.4.379-385.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROGAN J. B., JOHNSON E. J. NUCLEIC ACID COMPOSITION OF A PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA BACTERIOPHAGE. Virology. 1964 Oct;24:235–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham J. L., Stokes J. L. PSYCHROPHILIC BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):97–108. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.97-108.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLINGE K. [Pseudomonas fluorescens, a soil and water microorganism. III. Identification of P. fluorescens strains by bacteriophages]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1959;34:270–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F., Boezi J. A. Characterization of bacteriophage gh-1 for Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1821–1827. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1821-1827.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H. Isolation and growth of psychrophilic bacteriophage. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jan;15(1):198–198. doi: 10.1128/am.15.1.198-.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. C. Bacteriocinogeny and lysogeny in the genus Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jun;39(3):295–303. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., Stokes J. L. Heat-labile enzymes in a psychrophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):199–206. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.199-206.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. F., Campbell L. L. Characterization of a thermophilic bacteriophage for Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):340–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.340-348.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders G. F., Campbell L. L. Ribonucleic acid and ribosomes of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):332–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.332-339.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Amako K. A rod-shaped Pseudomonas phage. Virology. 1966 Jan;28(1):163–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]