Abstract
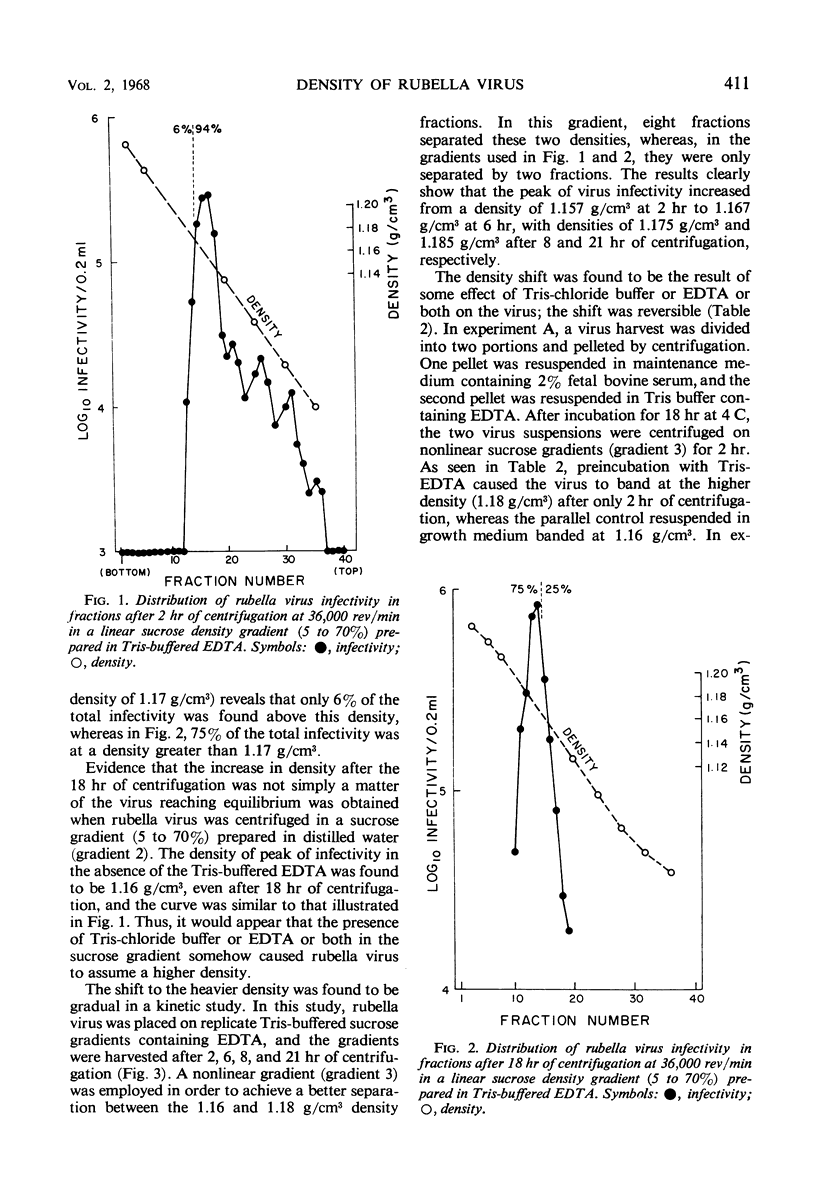
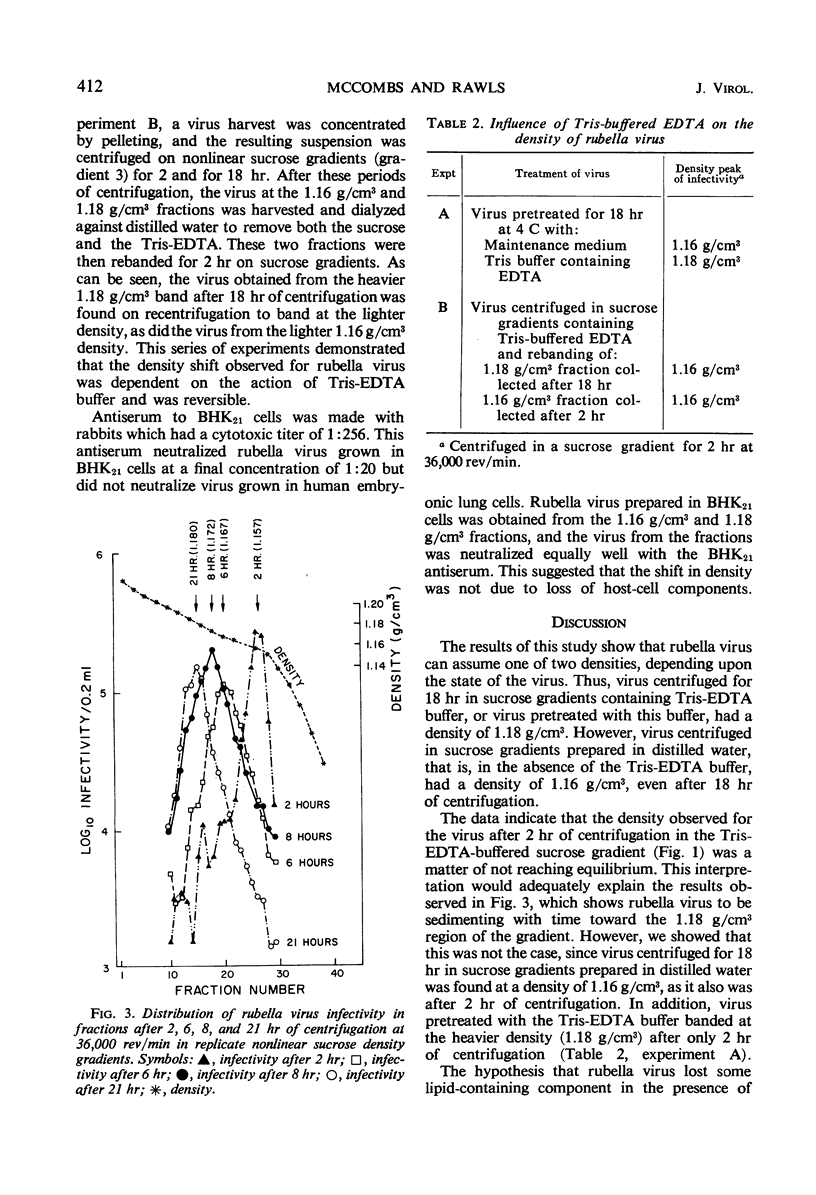
Rubella virus was centrifuged in sucrose density gradients. One of two densities could be ascribed to the virus, depending upon the suspending medium used. The virus was found at a density of 1.16 g/cm3 after centrifugation for 18 hr in sucrose gradients prepared in distilled water. By contrast, when the sucrose gradients were prepared in tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris)buffer containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), the virus was found at a density of 1.18 g/cm3 after 18 hr of centrifugation. The virus banded at this higher density after only 2 hr of centrifugation when pretreated by overnight incubation in the Tris-EDTA buffer. A kinetic study showed that, in sucrose gradients containing this buffer, the virus gradually migrated as a single peak of infectivity from a density of 1.16 g/cm3 after 2 hr of centrifugation to the higher 1.18 g/cm3 density after 18 hr. The density change was shown to be reversible; after the removal of the Tris-EDTA buffer, rebanding of virus harvested at the heavy density resulted in its banding at the lower 1.16 g/cm3 density. The data indicate that density change could not be explained on the basis of the loss of some component from the virus or on the basis of the failure of the virus to reach equilibrium. However, it is possible that the two densities observed were a reflection of the existence of rubella virus in different hydration states in the presence and absence of Tris buffer containing EDTA.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATCHISON R. W., CASTO B. C., HAMMON W. M. ADENOVIRUS-ASSOCIATED DEFECTIVE VIRUS PARTICLES. Science. 1965 Aug 13;149(3685):754–756. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3685.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusumano C. L. Density gradient centrifugation studies of rubella virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jun;122(2):461–465. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Plotkin S., Sedwick D., Profeta M. Haemagglutinin of rubella virus. Nature. 1967 Jul 8;215(5097):172–173. doi: 10.1038/215172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPS H. E., BERNHEIM B. C., NISALAK A., TJIO J. H., SMADEL J. E. BIOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONTINUOUS KIDNEY CELL LINE DERIVED FROM THE AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY. J Immunol. 1963 Sep;91:416–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Blacklow N. R., Rowe W. P. Studies of small DNA viruses found in various adenovirus preparations: physical, biological, and immunological characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1467–1474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGNUSSON P., NORRBY E. C. ON THE MORPHOLOGY OF RUBELLA VIRUS. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;16:412–414. doi: 10.1007/BF01253847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCAIG N., RENDI R. WATER EXTRUSION IN ISOLATED SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS. II. PRESENCE OF A ME2+EDTA DEPENDENT WATER EXTRUSION SYSTEM IN VARIOUS SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 30;79:416–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L. Tissue culture techniques and their application to original isolation, growth, and assay of poliomyelitis and orphan viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Sep 27;61(4):754-72; discussion, 772-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb42532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson P., Skaaret P. Purification studies of rubella virus. Distribution of infectivity in equilibrium centrifugation of potassium citrate density gradients and after chromatography on anion exchanger. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(3):374–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Carver D. H. Hemadsorption-negative plaque test: new assay for rubella virus revealing a unique interference. Science. 1965 Aug 27;149(3687):983–986. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3687.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs R. M., Melnick M. B., Brunschwig J. P. Biophysical studies of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):803–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.803-812.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Mayor H. D., Smith K. O., Rapp F. Association of 20-Millimicron Particles with Adenoviruses. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):271–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.271-274.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRBY E., MAGNUSSON P., FRIDING B., GARD S. A NOTE ON THE MORPHOLOGY OF RUBELLA VIRUS (BRIEF REPORT). Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1963 May 20;13:421–424. doi: 10.1007/BF01244614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'CONNOR T. E., RAUSCHER F. J., ZEIGEL R. F. DENSITY GRADIENT CENTRIFUGATION OF A MURINE LEUKEMIA VIRUS. Science. 1964 May 29;144(3622):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3622.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKMAN P. D., BUESCHER E. L., ARTENSTEIN M. S., MCCOWN J. M., MUNDON F. K., DRUZD A. D. STUDIES OF RUBELLA. I. PROPERTIES OF THE VIRUS. J Immunol. 1964 Oct;93:595–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTKIN S. A., BOUE A., BOUE J. G. THE IN VITRO GROWTH OF RUBELLA VIRUS IN HUMAN EMBRYO CELLS. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Jan;81:71–85. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENDI R. WATER EXTRUSION IN ISOLATED SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS. 3. THE IMPORTANCE OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN THE ME2+-EDTA DEPENDENT REACTION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 2;84:694–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L., Rosenberg H. S., Bayatpour M. Spontaneous virus carrier cultures and postmortem isolation of virus from infants with congenital rubella. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Dec;120(3):623–626. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L. Rubella virus carrier cultures derived from congenitally infected infants. J Exp Med. 1966 May 1;123(5):795–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Pitkanen A., Rubin H. The nucleic acid of the Bryan strain of Rous sarcoma virus: purification of the virus and isolation of the nucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):137–144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell B., Selzer G., Goetze H. The particle size of rubella virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jul;1(3):305–310. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-3-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M., MACPHERSON I. SYRIAN HAMSTER FIBROBLAST CELL LINE BHK21 AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Nature. 1964 Sep 26;203:1355–1357. doi: 10.1038/2031355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell K., Wong K. T. Stability and storage of rubella complement fixing antigen. Nature. 1966 Nov 5;212(5062):621–622. doi: 10.1038/212621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H., Dennis J. Density gradient centrifugation studies on rubella complement-fixing antigens. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


