Abstract
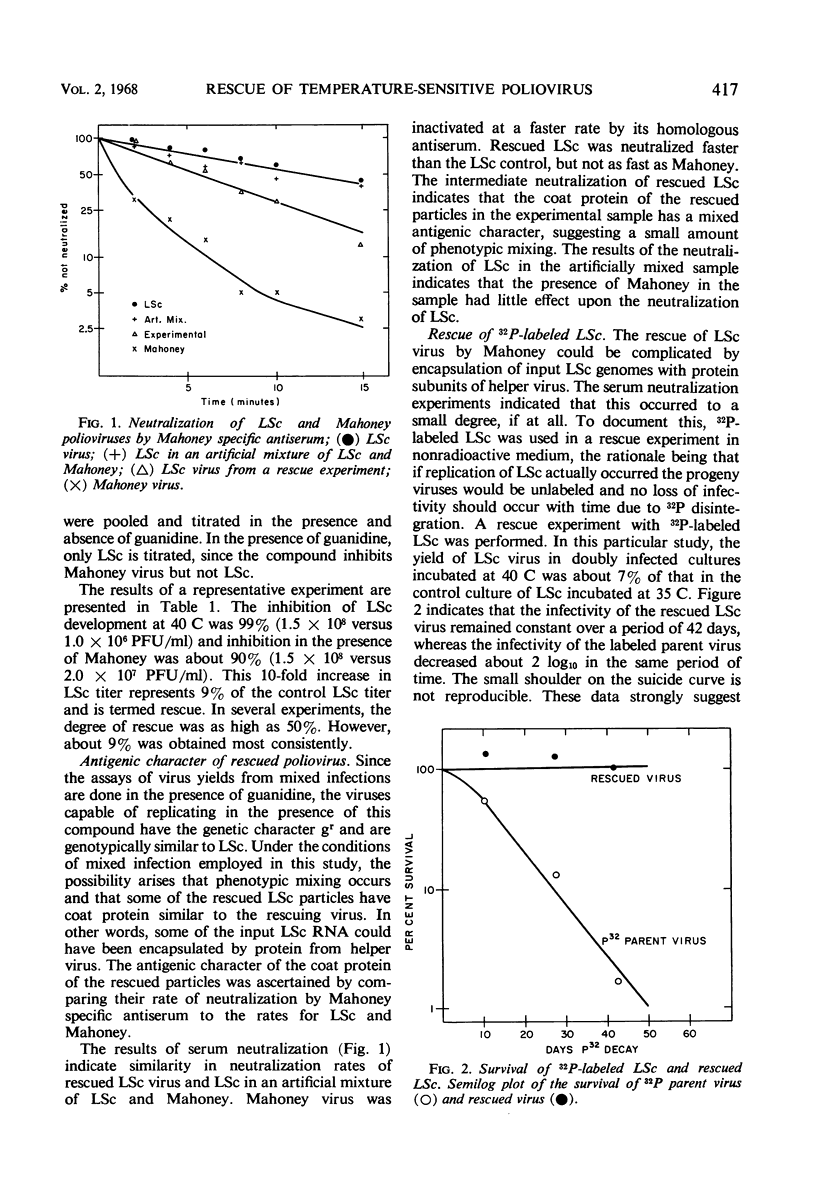
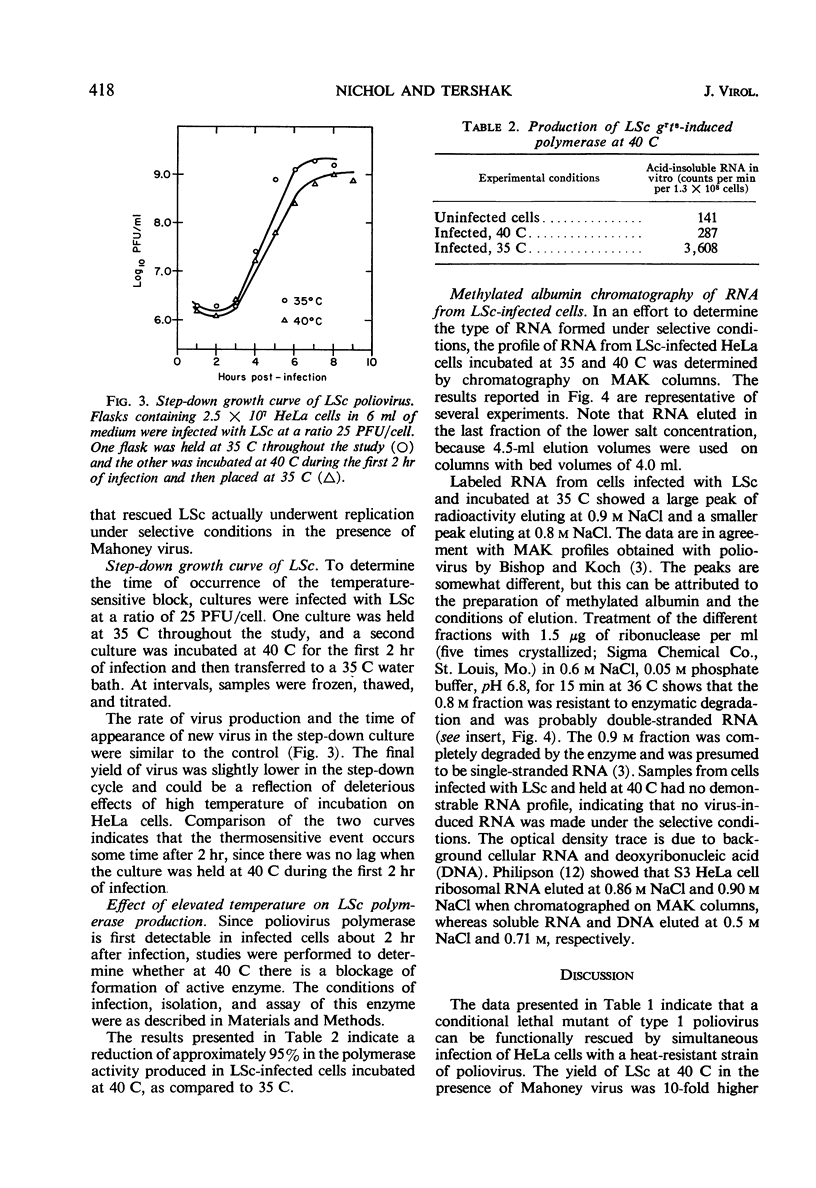
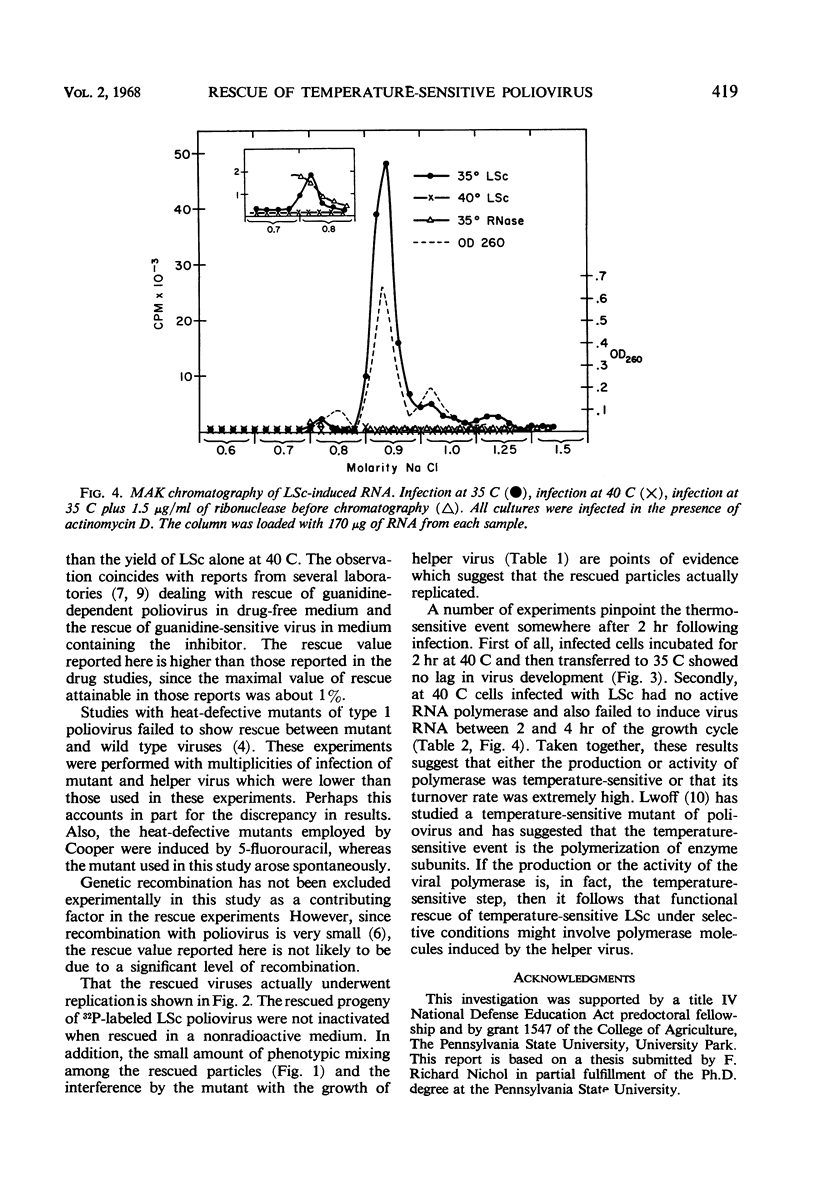
A temperature-sensitive strain of type 1 poliovirus, LSc, was functionally rescued when infected cells were incubated at 40 C in the presence of Mahoney, a temperature-resistant strain of type 1 poliovirus. The rescue value was 9% of the mutant yield obtained under permissive conditions. Rescued virus underwent replication, because the progeny of 32P-labeled LSc were not radiosensitive. Serum inactivation studies with Mahoney specific antiserum indicated that a small amount of phenotypic mixing occurred among the rescued particles. The temperature-sensitive event occurred between 2 and 4 hr postinfection in the developmental cycle of LSc. Neither viral polymerase activity nor virus-induced ribonucleic acid could be demonstrated in infected cells between 2 and 4 hr after infection at 40 C with the temperature-sensitive mutant.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., BECKER Y., DARNELL J. E. VIRUS-SPECIFIC DOUBLE-STRANDED RNA IN POLIOVIRUS-INFECTED CELLS. Science. 1964 Mar 6;143(3610):1034–1036. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3610.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. A NEW RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE APPEARING AFTER MENGOVIRUS INFECTION OF L-CELLS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3395–3400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Purification and characterization of poliovirus-induced infectious double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1736–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. RESCUE OF ONE PHENOTYPE IN MIXED INFECTIONS WITH HEAT-DEFECTIVE MUTANTS OF TYPE 1 POLIOVIRUS. Virology. 1965 Mar;25:431–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREYFUSS J. CHARACTERIZATION OF A SULFATE- AND THIOSULFATE-TRANSPORTING SYSTEM IN SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2292–2297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRST G. K. Genetic recombination with Newcastle disease virus, polioviruses, and influenza. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:303–309. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., CORDS C. E. MATURATION OF POLIOVIRUS RNA WITH CAPSID PROTEIN CODED BY HETEROLOGOUS ENTEROVIRUSES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1082–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIUNG G. D., MELNICK J. L. Plaque formation with poliomyelitis, Coxsackie, and orphan (echo) viruses in bottle cultures of monkey epithelial cells. Virology. 1955 Dec;1(5):533–535. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKEGAMI N., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. RESCUE OF DRUG-REQUIRING AND DRUG-INHIBITED ENTEROVIRUSES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1419–1426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LWOFF A. The thermosensitive critical event of the viral cycle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:159–174. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPSON L. Chromatographic separation, and characteristics of nucleic acids from HeLa cells. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May;44:899–910. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



