Abstract
Background
With competing interests, limited funding and a socially conservative context, there are many barriers to implementing evidence-informed HIV prevention programmes for sex workers and injection drug users in Pakistan. Meanwhile, the HIV prevalence is increasing among these populations across Pakistan. We sought to propose and describe an approach to resource allocation which would maximise the impact and allocative efficiency of HIV prevention programmes.
Methods
Programme performance reports were used to assess current resource allocation. Population size estimates derived from mapping conducted in 2011 among injection drug users and hijra, male and female sex workers and programme costs per person documented from programmes in the province of Sindh and also in India were used to estimate the cost to deliver services to 80% of these key population members across Pakistan. Cities were prioritised according to key population size.
Results
To achieve 80% population coverage, HIV prevention programmes should be implemented in 10 major cities across Pakistan for a total annual operating cost of approximately US$3.5 million, which is much less than current annual expenditures. The total cost varies according to the local needs and the purchasing power of the local currency.
Conclusions
By prioritising key populations at greatest risk of HIV in cities with the largest populations and limited resources, may be most effectively harnessed to quell the spread of HIV in Pakistan.
Keywords: HIV, POLICY, PREVENTION, EPIDEMIOLOGY (GENERAL)
Introduction
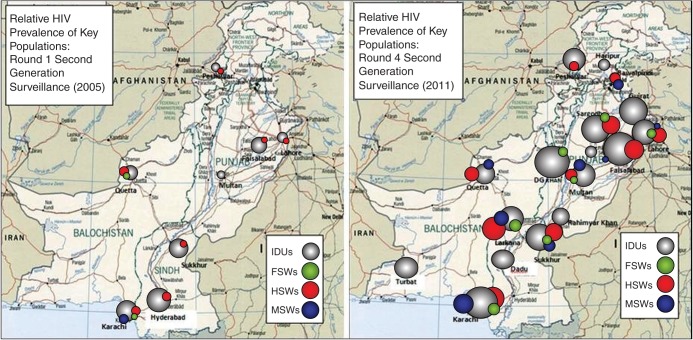
Pakistan's HIV epidemic is concentrated among key populations at greater risk of HIV. In 2011, the HIV prevalence was estimated to be 37.8% among injection drug users (IDUs), and 7.2%, 3.1% and 0.8% among hijra (transgender; HSW), male (MSW), and female (FSW) sex workers, respectively.1 These HIV prevalence estimates are considerably higher than those of the general population (0.1%)1 and of pregnant women attending antenatal clinics (0.05%).2 Given the observed trajectory of the HIV epidemic among these key populations1 3 (figure 1), evidence of potential injection and sexual routes of transmission between IDUs and sex workers, and alarming model projections of prevalence surpassing 70% among IDUs by 2025 in some cities and continuing to increase among sex workers,4 it has become apparent that the window of opportunity to prevent HIV from exploding within IDU populations and becoming firmly established among sex workers and clients may be closing.5 It is therefore imperative to implement effective HIV prevention programmes targeting key populations at high population coverage in Pakistan, and with consideration given to HIV transmission dynamics6–9 within geographically defined areas. Priorities include surveillance, analysis of data, investments in prevention and interventions implemented at high population coverage (table 1).
Figure 1.
Relative HIV prevalence in various cities in Pakistan, 2005 and 2011. FSW, female sex workers; HSW, hijra sex workers; IDU, injection drug users; MSW, men sex workers.
Table 1.
Priorities for the concentrated HIV epidemics of Pakistan
| Factor | Priorities |
|---|---|
| Priorities needed for surveillance, monitoring and evaluation | Emphasis on biological and behavioural surveillance of key populations (male, female and hijra sex workers and injection drug users) |
| Analysis | HIV prevalence, mapping, population-size estimation, behavioural interactions within key populations and between groups, and their sexual or injecting partners |
| Investments | Invest in surveillance, targeted interventions for key populations, and stigma-reduction campaigns for the general population |
| Interventions | Goal is saturation coverage of key populations |
| Key research questions | How to reach key populations with high coverage of high-quality targeted interventions |
Adapted from David Wilson and Daniel T Halperin.9
The Government of Pakistan has indicated its commitment to reducing HIV transmission, and is a signatory to the United Nations Development Programme's Millennium Development Goals, whereby one of the goals is to ‘halt and begin to reverse the HIV/AIDS epidemic by 2015’.10
National-level HIV prevention priorities, resource allocation and implementation strategies are described in the strategic plans prepared and published by the National AIDS Control Program (NACP), and the progress reports to the United Nations General Assembly Special Session on HIV/AIDS.11–14 Since 1986, the national response to HIV/AIDS in Pakistan (figure 2) has been led by NACP, with Provincial AIDS Control Programs (PACPs) largely responsible for implementation, much of which takes place through non-governmental organisations (NGOs).15 16 Coordinated global efforts for HIV prevention prompted the Government of Pakistan to develop its 5-year National Strategic Framework (NSF-I) with UNAIDS support in 2001, which set priorities and aimed to establish a multisectoral response.17 This led to the Enhanced HIV/AIDS Control Program (EHACP) for a 5 year period with financial support from the World Bank, the UK Department for International Development (DFID), and the Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA), with an overall focus on HIV prevention among key populations. The national response was reviewed in 2006, and the Second National Strategic Framework (NSF-II) was developed for 2007–201114 with a total budget of US$99.4 million from the World Bank, DFID and the Government of Pakistan described in the Planning Commission Document 1 (PC-1) of the EHACP. PC-1s describe the programme plan and budget for the subsequent 5 years, and are approved by the executive committee of the National Economic Council (Pakistan). Pakistan also received funding from The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria to scale up prevention and treatment, care and support services for IDUs. Due to devolution of the ministry of health, the provinces are developing their own HIV prevention strategies which will form the Pakistan AIDS Strategy (PAS-III 2012–2016).11
Figure 2.
Number of reported HIV cases in Pakistan, and Pakistan Government's response to HIV from 1985 to 2011.
By the end of 2009, HIV/AIDS interventions reached more than 30 000 IDUs, 25 000 MSW/HSWs, 12 000 FSWs and 50 000 long-distance truckers. According to the National AIDS Spending Assessment, a total of US$34.19 million was spent in 2008 and 2009.12 For fiscal year 2009–2010, it was reported that 43% of HIV/AIDS funds were spent on prevention, with another 38% spent on programme management.11 Within the prevention category, the majority of the ∼US$5.7 million in funding was spent on harm reduction activities among IDUs and their partners (US$3.8 million), sex workers (∼US$0.8 million), with the remainder spent on prevention among ‘vulnerable and accessible populations’, men who have sex with men (MSM), blood safety and behaviour change communication.11 Pakistan's 2010 UNGASS report presents how US$13.88 million were allocated for HIV prevention among specific population groups over two fiscal years (2008–2009 and 2009–2010). According to this breakdown, 54% was spent on IDUs, 21.6% spent on FSWs, 11% spent on MSW/HSWs and the remaining 13.3% (US$1.85 million) was spent on jail inmates, truck drivers and women and their partners.12
Although there have been efforts to implement a comprehensive multisectoral approach for the prevention and treatment of HIV in Pakistan, there have been significant barriers to implementation, including conflict and insecurity, funding gaps, competing priorities and lack of capacity.11 18–20 This has undermined Pakistan's political commitment to HIV prevention, and has coincided with an increasing HIV prevalence. Moreover, the prevailing conservative social norms render the provision of services and protection of rights for marginalised populations, particularly those related to HIV prevention, politically unfavourable.20 This challenging context has been further exacerbated by the devolution of Pakistan's Ministry of Health in June 2011 as part of the 18th constitutional amendment,21 and natural disasters, such as the 2010 floods which killed more than 2000 people and internally displaced nearly 2.5 million more, resulted in substantial reallocation of funds from EHACP.22 Now, in the context of devolution, the provinces are engaged in a process to redefine their roles. With the prospect of a rapidly spreading epidemic among key populations, there is an urgent need to re-engage and redefine efforts for HIV prevention. With its wealth of data gathered among key populations through the Canada–Pakistan HIV/AIDS Surveillance Project (HASP) from 2004 to 2011, Pakistan is well positioned to design a comprehensive and evidence-based HIV prevention programme.
In this paper, we provide an assessment of the prevention initiatives undertaken to date, and present estimates of the cost to implement comprehensive HIV prevention programmes at high coverage in cities across Pakistan.
Methods
Population size estimates
Mapping data collected as part of the Canada–Pakistan HIV/AIDS Surveillance Project between March and September 20118 was used to locate, enumerate and characterise populations of IDUs and female, male and hijra sex workers in each of the cities included in the mapping. In mapping, secondary key informants, such as taxi drivers, were interviewed to identify locations where members of these key populations congregate. This step is followed by interviewing key population members themselves to get more detailed information about locations. The cities in which mapping was conducted are considered to be the most important cities in terms of presence and size of key populations. Data collection and analysis as part of HASP was approved by the institutional ethical review boards of HOPE International in Pakistan and the Public Health Agency of Canada. Our approach identified priority cities across Pakistan in which to implement targeted HIV prevention programmes for particular key populations in order to achieve high programme coverage.
Program cost estimates
We used two methods to convert the costs to US dollars: the effective exchange rate and the purchasing power-adjusted exchange rate. Actual costs to implement service delivery programmes for these key populations in Sindh Province23 in 2009 were used to calculate an estimated cost to achieve 80% programme coverage, according to the population size estimates derived from the 2011 round of mapping and surveillance. We include these estimates for 80% population coverage because impact evaluations of programmes in India with coverage at this level have shown a reversal of the epidemic among FSWs, clients and the general population.24 25 The 2009 annual cost of Pakistani rupees 1675 (PKR; 2011, US$21.14) for each female sex worker, and 1450 PKRs (2011 US$18.30) for each male or hijra sex worker was used for this calculation. This cost includes six visits to a primary health clinic, sexually transmitted infection treatment costs, 240 condoms, 12 visits with a peer educator, and costs to train programme staff, conduct a baseline survey and annual evaluation, and 25% management charges for the NGO host. The annual cost of 2875 PKRs (2011 US$36.28) per IDU includes 12 visits to a primary health clinic, 300 disposable 5cc syringes with a needle, STI treatment costs, 50 condoms, 12 visits with a peer educator, and costs to train programme staff, conduct a baseline survey and annual evaluation, and 25% management charges for the NGO.
Cost sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis was conducted using different per-client programme cost estimates. Programme cost data from India were used to calculate alternative costs for HIV prevention for key population members in the same cities of Pakistan. To facilitate comparison, all costs were converted to 2011 currency values using the real effective exchange rate index, and then converted to US dollars using 2011 purchasing power-adjusted market exchange rate conversion factors.26 27 The 1 January 2011 exchange rates used were PKR85.61, and `44.7. The 2011 purchasing power-adjusted market exchange rate conversion factors used were 37.17 and 19.67, for Pakistan and India, respectively.
The annual budgeted costs to deliver targeted interventions in India in 2007 (including office infrastructure, programme management and programme delivery) were `1800 (2011, US$41.30) per FSW, `1850 (2011, US$42.45) per MSM and `2900 (2011, US$66.54) per IDU.28
Results
High population coverage for a strategic response to Pakistan's concentrated HIV epidemics
Key population size estimates derived from the mapping conducted in 2011 indicated 46 351 IDUs in the 19 cities included in the mapping, 42 436 MSWs and HSWs in 14 cities, and 89 178 FSWs in 15 cities included in the mapping. The estimated size of each population in each city is provided in table 2.
Table 2.
Estimated annual costs of large-scale HIV prevention programme implementation for injection drug users, male/hijra sex workers and female sex workers
| Total annual cost per city using Pakistan costs | Cumulative annual cost using Pakistan costs | Cumulative annual cost using India costs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | City | Est. pop. size | % of total | Cum. % of total | 2011 PKR | 2011 US$ | 2011 PPP US$ | 2011 PKR | 2011 US$ | 2011 PPP US$ | 2011 US$ | 2011 PPP US$ |
| IDU | Karachi | 16 544 | 35.7 | 35.7 | 51 382 676 | 600 195 | 1 382 370 | 51 382 676 | 600 195 | 1 382 370 | 1 100 872 | 2 501 728 |
| Faisalabad | 7907 | 17.1 | 52.8 | 24 557 714 | 286 856 | 660 686 | 75 940 390 | 887 050 | 2 043 056 | 1 627 021 | 3 697 398 | |
| Hyderabad | 3857 | 8.3 | 61.1 | 11 979 145 | 139 927 | 322 280 | 87 919 535 | 1 026 977 | 2 365 336 | 1 883 673 | 4 280 641 | |
| Lahore | 3596 | 7.8 | 68.9 | 11 168 526 | 130 458 | 300 472 | 99 088 061 | 1 157 436 | 2 665 807 | 2 122 959 | 4 824 416 | |
| Sukkur | 1979 | 4.3 | 73.2 | 6 146 417 | 71 796 | 165 360 | 105 234 478 | 1 229 231 | 2 831 167 | 2 254 646 | 5 123 674 | |
| Nawabshah | 1865 | 4 | 77.2 | 5 792 353 | 67 660 | 155 834 | 111 026 831 | 1 296 891 | 2 987 001 | 2 378 747 | 5 405 693 | |
| Peshawar | 1850 | 4 | 81.2 | 5 745 766 | 67 116 | 154 581 | 116 772 597 | 1 364 007 | 3 141 582 | 2 501 849 | 5 685 443 | |
| Sargodha | 1621 | 3.5 | 84.7 | 5 034 533 | 58 808 | 135 446 | 121 807 130 | 1 422 814 | 3 277 028 | 2 609 714 | 5 930 566 | |
| Mirpurkhas | 1229 | 2.7 | 87.4 | 3 817 052 | 44 587 | 102 692 | 125 624 182 | 1 467 401 | 3 379 720 | 2 691 494 | 6 116 411 | |
| Larkana | 1096 | 2.4 | 89.8 | 3 403 978 | 39 761 | 91 579 | 129 028 160 | 1 507 162 | 3 471 298 | 2 764 425 | 6 282 144 | |
| Multan | 870 | 1.9 | 91.7 | 2 702 063 | 31 562 | 72 695 | 131 730 223 | 1 538 725 | 3 543 993 | 2 822 316 | 6 413 703 | |
| Quetta | 626 | 1.4 | 93.1 | 1 944 243 | 22 710 | 52 307 | 133 674 466 | 1 561 435 | 3 596 300 | 2 863 972 | 6 508 364 | |
| DG Khan | 596 | 1.3 | 94.4 | 1 851 068 | 21 622 | 49 800 | 135 525 534 | 1 583 057 | 3 646 100 | 2 903 631 | 6 598 490 | |
| Pakpattan | 487 | 1.1 | 95.5 | 1 512 534 | 17 668 | 40 692 | 137 038068 | 1 600 725 | 3 686 792 | 2 936 037 | 6 672 132 | |
| Haripur | 493 | 1.1 | 96.6 | 1 531 169 | 17 885 | 41 194 | 138 569 237 | 1 618 610 | 3 727 986 | 2 968 842 | 6 746 682 | |
| Dadu | 470 | 1 | 97.6 | 1 459 735 | 17 051 | 39 272 | 140 028 972 | 1 635 661 | 3 767 258 | 3 000 117 | 6 817 754 | |
| Gujrat | 431 | 0.9 | 98.5 | 1 338 608 | 15 636 | 36 013 | 141 367 580 | 1 651 298 | 3 803 271 | 3 028 796 | 6 882 928 | |
| Rahim Yar Khan | 426 | 0.9 | 99.4 | 1 323 079 | 15 455 | 35 595 | 142 690 660 | 1 666 752 | 3 838 866 | 3 057 143 | 6 947 346 | |
| Turbat | 408 | 0.9 | 100.3 | 1 267 174 | 14 802 | 34 091 | 143 957 834 | 1 681 554 | 3 872 958 | 3 084 292 | 7 009 043 | |
| MSW/HSW | Karachi | 15 811 | 37.3 | 37.3 | 24 766 560 | 289 295 | 666 305 | 24 766 560 | 289 295 | 666 305 | 671 165 | 1 525 221 |
| Lahore | 5004 | 11.8 | 49.1 | 7 838 332 | 91 559 | 210 878 | 32 604 892 | 380 854 | 877 183 | 883 581 | 2 007 935 | |
| Faisalabad | 3329 | 7.8 | 56.9 | 5 214 590 | 60 911 | 140 290 | 37 819 482 | 441 765 | 1 017 473 | 1 024 895 | 2 329 070 | |
| Multan | 2725 | 6.4 | 63.3 | 4 268 476 | 49 860 | 114 837 | 42 087 958 | 491 624 | 1 132 310 | 1 140 569 | 2 591 939 | |
| Hyderabad | 2566 | 6 | 69.4 | 4 019 416 | 46 950 | 108 136 | 46 107 374 | 538 575 | 1 240 446 | 1 249 494 | 2 839 471 | |
| Quetta | 2399 | 5.7 | 75 | 3 757 825 | 43 895 | 101 098 | 49 865 199 | 582 469 | 1 341 544 | 1 351 330 | 3 070 892 | |
| Sukkur | 2338 | 5.5 | 80.5 | 3 662 274 | 42 779 | 98 528 | 53 527 474 | 625 248 | 1 440 072 | 1 450 576 | 3 296 429 | |
| Larkana | 1698 | 4 | 84.5 | 2 659 770 | 31 068 | 71 557 | 56 187 243 | 656 316 | 1 511 629 | 1 522 655 | 3 460 228 | |
| Peshawar | 1564 | 3.7 | 88.2 | 2 449 870 | 28 617 | 65 910 | 58 637 114 | 684 933 | 1 577 539 | 1 589 046 | 3 611 100 | |
| Sargodha | 1338 | 3.2 | 91.4 | 2 095 861 | 24 481 | 56 386 | 60 732 975 | 709 414 | 1 633 925 | 1 645 843 | 3 740 172 | |
| Haripur | 1187 | 2.8 | 94.2 | 1 859 333 | 21 719 | 50 022 | 62 592 307 | 731 133 | 1 683 947 | 1 696 230 | 3 854 677 | |
| Rawalpindi | 980 | 2.3 | 96.5 | 1 535 085 | 17 931 | 41 299 | 64 127 392 | 749 064 | 1 725 246 | 1 737 830 | 3 949 213 | |
| Nawabshah | 807 | 1.9 | 98.4 | 1 264 095 | 14 766 | 34 008 | 65 391 488 | 763 830 | 1 759 254 | 1 772 087 | 4 027 061 | |
| Mirpurkhas | 690 | 1.6 | 100 | 1 080 825 | 12 625 | 29 078 | 66 472 313 | 776 455 | 1 788 332 | 1 801 377 | 4 093 622 | |
| FSW | Karachi | 25 399 | 28.5 | 28.5 | 45 958 916 | 536 841 | 1 236 452 | 45 958 916 | 536 841 | 1 236 452 | 1 049 029 | 2 383 915 |
| Lahore | 23 766 | 26.7 | 55.2 | 43 004 039 | 502 325 | 1 156 956 | 88 962 955 | 1 039 165 | 2 393 407 | 2 030 612 | 4 614 558 | |
| Multan | 5308 | 6 | 61.2 | 9 604 706 | 112 191 | 258 399 | 98 567 661 | 1 151 357 | 2 651 807 | 2 249 843 | 5 112 760 | |
| Faisalabad | 4846 | 5.4 | 66.6 | 8 768 727 | 102 426 | 235 909 | 107 336 388 | 1 253 783 | 2 887 716 | 2 449 993 | 5 567 599 | |
| Hyderabad | 4566 | 5.1 | 71.7 | 8 262 074 | 96 508 | 222 278 | 115 598 462 | 1 350 292 | 3 109 994 | 2 638 577 | 5 996 157 | |
| Sargodha | 3898 | 4.4 | 76.1 | 7 053 343 | 82 389 | 189 759 | 122 651 805 | 1 432 681 | 3 299 753 | 2 799 573 | 6 362 018 | |
| Quetta | 3710 | 4.2 | 80.3 | 6 713 161 | 78 416 | 180 607 | 129 364 966 | 1 511 096 | 3 480 360 | 2 952 803 | 6 710 233 | |
| Rawalpindi | 3635 | 4.1 | 84.4 | 6 577 450 | 76 830 | 176 956 | 135 942 416 | 1 587 927 | 3 657 315 | 3 102 936 | 7 051 409 | |
| Peshawar | 3317 | 3.7 | 88.1 | 6 002 036 | 70 109 | 161 475 | 141 944 453 | 1 658 036 | 3 818 791 | 3 239 934 | 7 362 738 | |
| Haripur | 2994 | 3.4 | 91.5 | 5 417 575 | 63 282 | 145 751 | 147 362 028 | 1 721 318 | 3 964 542 | 3 363 592 | 7 643 751 | |
| Sukkur | 2317 | 2.6 | 94.1 | 4 192 559 | 48 973 | 112 794 | 151 554 587 | 1 770 291 | 4 077 336 | 3 459 289 | 7 861 221 | |
| Nawabshah | 2011 | 2.3 | 96.4 | 3 638 859 | 42 505 | 97 898 | 155 193 446 | 1 812 796 | 4 175 234 | 3 542 347 | 8 049 971 | |
| DG Khan | 1413 | 1.6 | 98 | 2 556 792 | 29 866 | 68 786 | 157 750 238 | 1 842 661 | 4 244 020 | 3 600 707 | 8 182 593 | |
| Larkana | 1114 | 1.2 | 99.2 | 2 015 758 | 23 546 | 54 231 | 159 765 995 | 1 866 207 | 4 298 251 | 3 646 718 | 8 287 152 | |
| Mirpurkhas | 884 | 1 | 100.2 | 1 599 578 | 18 684 | 43 034 | 161 365 573 | 1 884 892 | 4 341 285 | 3 683 229 | 8 370 123 | |
| Grand total for 80% coverage | 3 500 351 | 8 062 013 | 6 905 229 | 15 692 106 | ||||||||
FSW, female sex workers; HSW, hijra sex workers; IDUs, injection drug users; PKR, Pakistani rupees; MSW, male sex workers.
Previous evidence has suggested that 80% key population programme coverage may effectively stem HIV transmission among sex workers, clients and the general population.24 25 This may be approached in two ways: by reaching 100% of key population members in 80% of the cities in which these key population members live, or to reach 80% of key population members in all the cities in which they live. By applying the first approach to the cities included in this study, programmes would only have to be implemented in 10 cities to reach 80% of the population. Faisalabad, Hyderabad and Lahore were included in the prioritised cities for all three key population groups and should, therefore, have programmes targeting all three groups. Based on the system of prioritising the cities with 80% of the key population members, programmes targeting two of the key populations should be implemented in Karachi (IDU and MSW/HSW), Sukkur (IDU and MSW/HSW), Multan (FSW and MSW/HSW), and Quetta (FSW and MSW/HSW). Finally, programmes targeting one key population should be implemented in Nawabshah (IDU), Peshawar (IDU), and Sargodha (FSW) to achieve 80% population coverage, for a total annual cost of US$3.5 million (US$8.06 million adjusted for purchasing power) (table 2).
By population group, this is an annual cost of US$1.36 million (11.6 crore Pakistani rupees) for IDUs, US$625 248 (5.4 crore rupees) for MSW/HSW, and US$1.51 million (12.9 crore rupees) for FSWs (table 2). This represents a proportional allocation of 39% to IDU programmes, 18% to MSW/HSW programmes, and 43% to FSW programmes.
The Pakistan and India rupee are particularly undervalued in relation to the US dollar, resulting in the large change in the cost estimate upon adjusting for purchasing power. Incorporating the purchasing power adjustment to the cost estimates derived from three different countries effectively eliminates differences in the purchasing power of their respective currencies, rendering these cost estimates comparable.
Discussion
Pakistan is to be commended for its HIV surveillance programme (2004–2011), its efforts to provide services to key populations despite complex social and political challenges, and recent changes to its prevention targets to reflect the reality of a concentrated epidemic by prioritising prevention among key populations. Pakistan is rare in terms of its wealth of scientific data available which could be used to better set priorities. We have a rich understanding of the key populations, the current distribution of HIV infections, and the behaviours that drive transmission. Pakistan's HIV epidemic is concentrated among key populations, with geographic heterogeneity, very few infections in the general population, and modelling results project an increase in HIV prevalence if current trends continue.4 In this epidemiological context, HIV prevention programmes should target IDUs and male, hijra and female sex workers at high population coverage.9 Although the prevalence is relatively low among sex workers, the prevalence was close to zero until recently, suggesting that HIV may have recently been introduced to sex work networks.1 Considering the behavioural risks and large size of sex worker populations, there is significant potential for rapid transmission of HIV within these networks, and it is therefore imperative to rapidly implement HIV prevention interventions for sex workers and IDUs. Given the present economic and development situation, it is essential that available resources are put to optimal use.
Considering key population sizes in Pakistan's major cities, and the costs to implement these services in Pakistan, we estimate an annual cost of US$3.5 or 7 million over 2 years, to achieve 80% population coverage. This is considerably lower than the funding that was made available for HIV prevention in Pakistan in the last several fiscal years, suggesting that it is feasible to fund programmes at sufficient coverage to stem HIV transmission. According to the 2010 UNGASS report, more than twice this amount was spent on prevention efforts targeting specific populations.12 This cost may be reduced by eliminating the 13.3% that was spent on women, truckers and jail inmates who are of low HIV prevalence and risk, and rather strategically allocate costs according to local key population sizes and their needs (eg, client volume, frequency of injection).
Considering the behavioural risk of HIV acquisition among FSWs, continued low service coverage leaves that segment of the population highly vulnerable. If the HIV prevalence begins to increase among FSWs, the wider impact will be large due to the very large bridge population formed by the clients of FSWs. To maximise efficient use of limited resources, HIV prevention programmes should be implemented in the geographic locations with large key population sizes, and designed specifically for the local key population characteristics. As the priority cities we identified are in multiple provinces, a national coordinating body would be useful to ensure a coordinated response with strategic allocation of funds to the provinces and provide technical support and capacity-building opportunities to the provinces. Provincial strategic plans should focus prevention resources on saturating programme coverage among IDUs and sex workers according to the local context, characteristics and needs of the local key populations. Engaging NGOs as implementation partners contributes to the success of a programme because many have already established rapport with key population members. Capacity building within these organisations provides staff with the skills to implement, manage and monitor local programmes.
Our analysis sought to demonstrate an approach to maximising the population coverage of HIV prevention programmes for a given budget. Our cost estimates might well be underestimates for a full package of programmes and services, and are intended to demonstrate an approach to determine how to allocate HIV prevention funds to achieve high population coverage. For example, the programmes from which these costs are derived provide 240 condoms per FSW annually, which may not be sufficient if her client volume is higher than 240 per year. Further, costs for structural interventions have not been included. The estimated costs to deliver these programmes using cost estimates from India are indeed higher. Cost estimates per key population member vary according to the purchasing power of national currencies and, therefore, it is important to adjust for purchasing power parity in order to make comparisons across countries. Local costs will also vary according to the particular components and configuration of HIV prevention programmes required for the local context. Overall costs will vary according to the particular size of key populations in the local context.
The government must change the way it prioritises HIV/AIDS, first by approaching HIV as an urgent public health issue and, second, by addressing the underlying socioeconomic determinants of the epidemic as well as stigma, misconceptions and the influence of religious and societal pressures which shape the opportunities, behaviours and vulnerabilities faced by key populations at greater risk of HIV. Fostering a sense of accountability for HIV incidence may reduce the barriers to programme implementation and re-energise decision makers. There are many challenges to the uptake and delivery of comprehensive HIV prevention programmes for IDUs and sex workers in Pakistan, which affects the ability to achieve high population coverage.29 30 However, strategies also exist that may be used to reduce the barriers to accessing such programmes, such as the implementation of carefully planned outreach services delivered by trained community members, and designing fixed service delivery sites to ensure the accessibility, safety, confidentiality and privacy of patrons. Involving community members in programme planning and implementation increases the likelihood that programmes will be acceptable and accessible to members of these highly marginalised populations, and sensitisation of local authorities to improve the ability of such services to exist without disruption. Given the presence of epidemiological, behavioural and structural differences in different cities across Pakistan, data specific to local contexts should also be used when determining the best ways to deliver HIV prevention programmes.4
The cost estimates reported in this paper were derived from key population mapping conducted in major cities across Pakistan and are, therefore, limited by the mapping methodology. The system we used for prioritising cities for HIV prevention interventions targeting key populations was intended as a simplistic demonstration, and only included population-size data. In order to achieve 80% population coverage across the major cities in Pakistan, 100% population coverage would have to be achieved in the prioritised cities, and this is likely not feasible. It did not incorporate data about the prevalence of HIV and risk behaviours among key populations in different cities. We did not incorporate data about the reported frequency of sex, condom use and the sharing of drug injection equipment or information about local social, cultural and political factors which may affect health, behaviours, stigma, social and economic opportunities and access to services. These factors impact the probability of HIV transmission and should be considered in a more comprehensive prioritisation scheme to determine how to allocate HIV prevention resources most efficiently. Also, projections of future HIV prevalence and incidence may inform prioritisation.
Key messages.
Given competing interests, limited funding, socially conservative context and increasing HIV prevalence, it is important to maximise the impact of HIV prevention programmes.
Cities with relatively large key population sizes may be prioritised for the implementations of targeted HIV prevention programmes.
To achieve 80% population coverage, HIV prevention programmes could be implemented in 10 major cities across Pakistan for a total annual operating cost of approximately US$3.5 million which is much less than current annual expenditures.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Canada–Pakistan HIV/AIDS Surveillance Project (HASP) team for their efforts in mapping, data collection, specimen collection, data entry and knowledge translation. We also thank study participants for their time and willingness to answer sensitive questions. We thank Dr Tahira Reza (HASP) for her assistance with data management. We thank Dr Evelyn Forget for providing helpful guidance for the cost adjustments.
Handling editor: Jackie A Cassell.
Contributors: FE conducted the surveillance project that generated the mapping data used for the calculations presented in this paper. FE wrote the first draft of this manuscript and contributed to interpretation of results and manuscript revisions. LHT contributed to analysis, manuscript writing and interpretation of results. MS, NA, TER, HH and SA contributed to the surveillance project and data collection, and critically reviewed the manuscript. JFB provided direction for the development of this manuscript, critically reviewed the manuscript, and led the development of special supplement strategy.
Funding: The Canada–Pakistan HIV/AIDS Surveillance Projected was funded by the Canadian International Development Agency (CIDA PK 30849).
Competing interests: None.
Ethics approval: HOPE International in Pakistan and the Public Health Agency of Canada.
Provenance and peer review: Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.National AIDS Control Program. HIV Second Generation Surveillance in Pakistan 2011. Round Four Report. 17 Dec, 2012. http://www.nacp.gov.pk/surveillance_and_research/
- 2.National AIDS Control Program Antenatal sero-surveillance for HIV/AIDS in Pakistan 2012 http://www.nacp.gov.pk/surveillance_and_research/ (accessed 17 Dec 2012).
- 3.National AIDS Control Program HIV Second Generation Surveillance in Pakistan 2005. Round One Report. http://www.nacp.gov.pk/surveillance_and_research/ (accessed 17 Dec 2012).
- 4.Reza T, Melesse DY, Shafer LA, et al. Patterns and trends in Pakistan's heterogeneous HIV epidemic. Sex Transm Infect 2013;89:ii4–10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zaheer HA, Hawkes S, Buse K, et al. STIs and HIV in Pakistan: from analysis to action. Sex Transm Infect 2009;85(Suppl 2):ii1–2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.IWW Baseline Survey Report: Best practice Models of Integrated Prevention care and Support with Key Vulnerable communities in Multan & Kasur, Punjab. Interact Worldwide. Islamabad, Pakistan, 2008
- 7.United Nations Population Fund Sex Work and HIV in Pakistan; A Situation and Response Analysis. UNFPA Pakistan, 2008
- 8.Canada-Pakistan HIV-AIDS Surveillance Project. Mapping of key populations at risk of HIV. HIV Second Generation Surveillance in Pakistan. National AIDS Control Program. Govt of Pakistan. Islamabad, 2012
- 9.Wilson D, Halperin DT. "Know your epidemic, know your response": a useful approach, if we get it right. Lancet 2008;372:423–6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.United Nations Development Programme—Pakistan. MDGs in Pakistan. 17 Dec 2012. http://undp.org.pk/mdgs-in-pakistan.html
- 11.United Nations General Assembly UNGASS Pakistan Report: Progress report on the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS for the United Nations General Assembly Special Session on HIV/AIDS, 2012
- 12.United Nations General Assembly UNGASS Pakistan Report: Progress report on the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS for the United Nations General Assembly Special Session on HIV/AIDS, 2010
- 13.National AIDS Control Program Country Progress Report: Pakistan. Global AIDS Response Progress Report 2012. http://www.unaids.org/en/dataanalysis/monitoringcountryprogress/progressreports/2012countries/ce_PK_Narrative_Report%5B1%5D.pdf (accessed 14 Jun 2012).
- 14.National AIDS Control Program Report of the Mid Term Review-Enhanced HIV AIDS Control Program. National AIDS Control Program. Govt of Pakistan. Islamabad, 2009
- 15.Zaidi S, Mayhew SH, Cleland J, et al. Context matters in NGO-government contracting for health service delivery: a case study from Pakistan. Health Policy Plan 2012;27:570–81 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Husain S, Kadir M, Fatmi Z. Resource allocation within the National AIDS Control Program of Pakistan: a qualitative assessment of decision maker's opinions. BMC Health Serv Res 2007;7:11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.National AIDS Control Program. National Strategic Framework for HIV/AIDS. Govt of Pakistan. Islamabad, 2000
- 18.Rai MA, Warraich HJ, Ali SH, et al. HIV/AIDS in Pakistan: the battle begins. Retrovirology 2007;4:22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rai MA, Rajabali A, Khan MN, et al. Educating the power: HIV/AIDS and parliamentarians of Pakistan. Health Res Policy Syst 2009;7:20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Buse K, Lalji N, Mayhew SH, et al. Political feasibility of scaling-up five evidence-informed HIV interventions in Pakistan: a policy analysis. Sex Transm Infect 2009; 85(Suppl 2):ii37–42 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Malik AU, Khalil M, Ulikpan A, et al. A tale of devolution, abolition, and performance. Lancet 2012;379:409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Asian Development Bank, The World Bank and the National Disaster Management Authority. Pakistan Floods 2010: Preliminary Damage and Needs Assessment. http://www.gfdrr.org/gfdrr/sites/gfdrr.org/files/publication/Pakistan_DNA.pdf (accessed 17 Dec 2012).
- 23.Abbas SQ. Unit costs for HIV/AIDS prevention project component/activity wise unit cost along with assumptions. Sindh AIDS Control Program, 2009
- 24.Verma R, Shekhar A, Khobragade S, et al. Scale-up and coverage of Avahan: a large-scale HIV-prevention programme among female sex workers and men who have sex with men in four Indian states. Sex Transm Infect 2010;86(Suppl 1): i76–82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boily MC, Pickles M, Lowndes CM, et al. Positive impact of a large-scale HIV prevention program among female sex workers and clients in Karnataka state, India. AIDS. Published Online First: 3 Mar 2013. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e32835fba81 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Reserve Bank of India. Indices of Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) and Nominal Effective Exchange Rate (NEER) of the Indian Rupee. http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AnnualReportPublications.aspx?Id=1065 (accessed 31 Dec 2012).
- 27.The World Bank. PPP conversion factor, GDP (LCU per international $). http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/PA.NUS.PPP (accessed 31 Dec 2012).
- 28.National AIDS Control Organization & Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. Government of India. Targeted Interventions Under NACP III. Operational Guidelines, Volume 1, Core High Risk Groups, 2007
- 29.Emmanuel F. Sex work and HIV in Pakistan: situation and response analysis. Islamabad, Pakistan: United Nations Population Fund, 2012 [Google Scholar]
- 30.Thompson LH, Salim M, Baloch CR, et al. Heterogeneity of characteristics, structure, and dynamics of male and hijra sex workers in selected cities of Pakistan. Sex Transm Infect 2013;89:ii43–7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]