Abstract
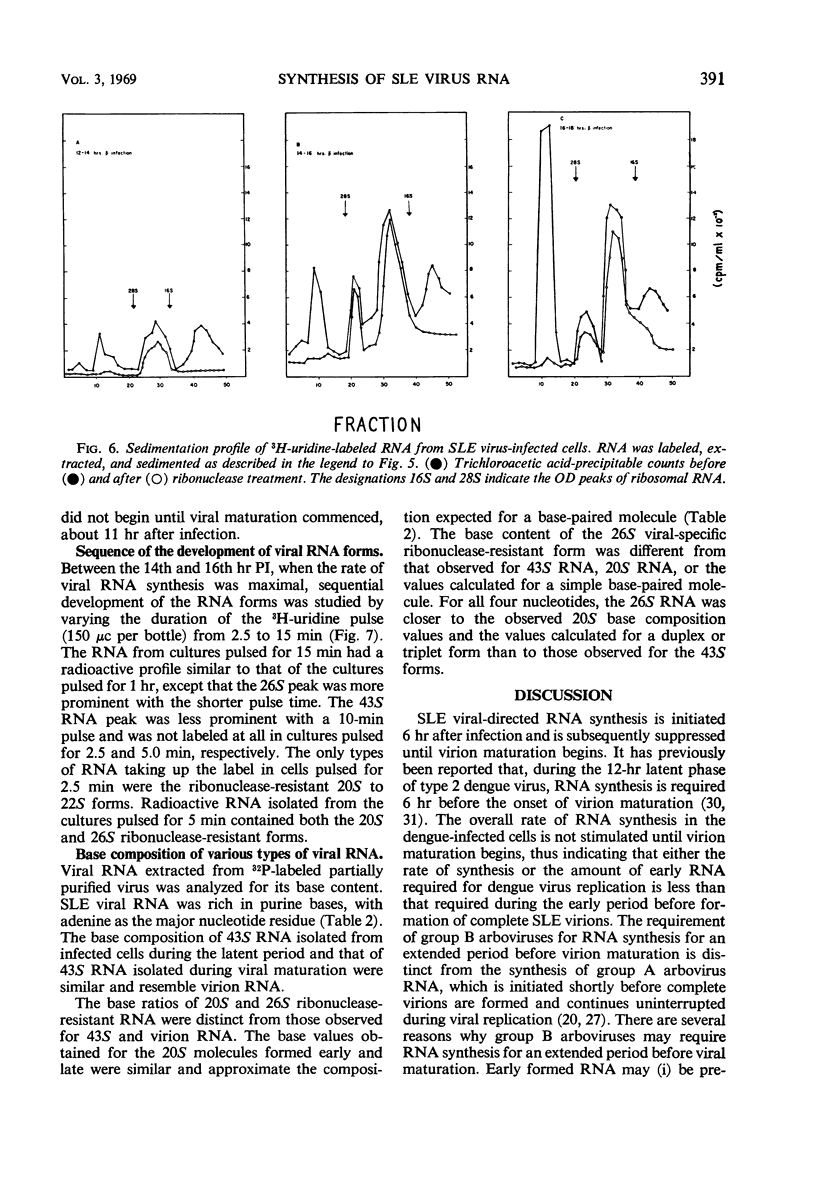
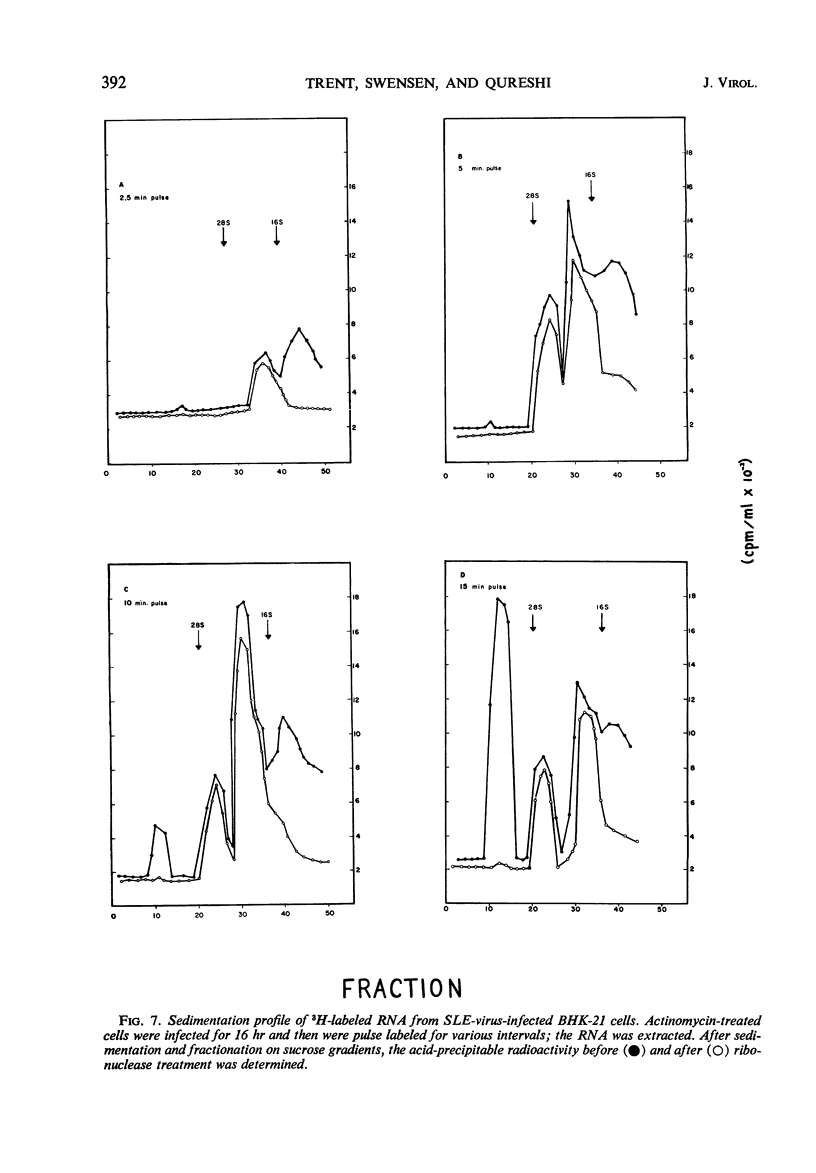
Infection of baby hamster kidney cells (BHK-21/13) with Saint Louis encephalitis (SLE) virus depressed the rate of protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis until viral RNA synthesis began 6 hr postinfection (PI). Virus-directed RNA synthesis was subsequently inhibited until 12 hr PI when virion maturation began. The rate of protein synthesis reached a peak 6 hr PI and was subsequently depressed until just before the onset of virion maturation. Density gradient analysis of phenol-extracted RNA from actinomycin-treated infected cells indicated that, at 6 to 8 hr and again at 12 to 20 hr PI, three species of viral-specific RNA were synthesized. The most rapid sedimenting form (43S) was ribonuclease-sensitive and had a base composition similar to the RNA isolated from mature virions. The 20S RNA species was ribonuclease-resistant and had a sedimentation coefficient and base composition similar to the replicative form associated with other arbovirus infections. The 26S RNA was ribonuclease-resistant (0.2 μg/ml, 0.1 m NaCl, 25 C, 30 min) and had a nucleotide base composition closer to the 20S form than to the values for 43S RNA. Five-minute pulse labeling of infected cultures during the period viral RNA synthesis was maximal resulted in labeling of only the 20S to 22S RNA fractions. With pulse-labeling periods of 10 min, both the 20S and 26S RNA species were radioactive. Periods of radioactive labeling of as long as 15 min were required before the 43S form was radioactively labeled. These results suggest that the 20S and 26S RNA may be intermediate forms in the synthesis of 43S viral RNA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Berezesky I. K. Cytoplasmic fractions associated with Semliki Forest virus ribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):374–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.374-383.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Replication of semliki forest virus: three forms of viral RNA produced during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):440–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Replicative intermediate of an arbovirus. J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):547–552. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.547-552.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOMMA M., GRAHAM A. F. SYNTHESIS OF RNA IN L CELLS INFECTED WITH MENGO VIRUS. J Cell Physiol. 1963 Oct;62:179–192. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030620207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBERT R. B., SCHMITZ H., BRUMM A. F., POTTER V. R. Nucleotide metabolism. II. Chromatographic separation of acid-soluble nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jul;209(1):23–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO H., INOUE Y. K. Studies on Japanese B encephalitis virus. IV. Plaque assay of Japanese B encephalitis virus in a stable line of porcine kidney cells. Virology. 1962 Nov;18:500–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN J. F., MORTON H. J., PARKER R. C. Nutrition of animal cells in tissue culture; initial studies on a synthetic medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Jan;73(1):1–8. doi: 10.3181/00379727-73-17557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mécs E., Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Fantes K. H. The effect of interferon on the synthesis of RNA in chick cells infected with Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jan;1(1):25–40. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGAI K., SATHER G., HAMMON W. M. PLAQUE STUDIES WITH CERTAIN GROUP B ARBOVIRUSES. 3. ST. LOUIS VIRUS ON CHICK EMBRYO TISSUE CULTURE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Apr;118:1065–1069. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-30047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEFFERKORN E. R., HUNTER H. S. PURIFICATION AND PARTIAL CHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF SINDBIS VIRUS. Virology. 1963 Jul;20:433–445. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLATNICK J., BACHRACH H. L. PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION OF MILLIGRAM AMOUNTS OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS FROM BABY HAMSTER KIDNEY CELL CULTURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:368–373. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.368-373.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEBRING E. D., SALZMAN N. P. AN IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR MEASURING THE DISTRIBUTION OF P32O4--AMONG THE NUCLEOTIDES OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Anal Biochem. 1964 May;8:126–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schito G. C. A rapid procedure for the purification of bacterial viruses. Virology. 1966 Sep;30(1):157–159. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(66)81023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E. Viral specific RNAs in infected cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):365–367. doi: 10.1038/213365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Lockart R. Z., Jr, Dodson M. L., Jr, Hartman K. A. Replication of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus. I. Some chemical and physical characteristics of viral ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):558–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.558-566.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Lockart R. Z., Jr Heterogeneous RNA's occurring during the replication of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):974–981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar V., Stevens T. M., Schlesinger R. W. Studies on the nature of dengue viruses. II. Characterization of viral RNA and effects of inhibitors of RNA synthesis. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Graham A. F. Structural units of reovirus ribonucleic acid and their possible functional significance. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):665–677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.665-677.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Assessment and application of a cell line from pig kidney for plaque assay and neutralization tests with twelve group B arboviruses. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Nov;84(3):439–456. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



