Abstract
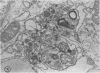
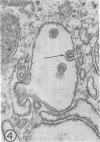
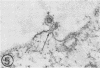
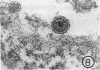
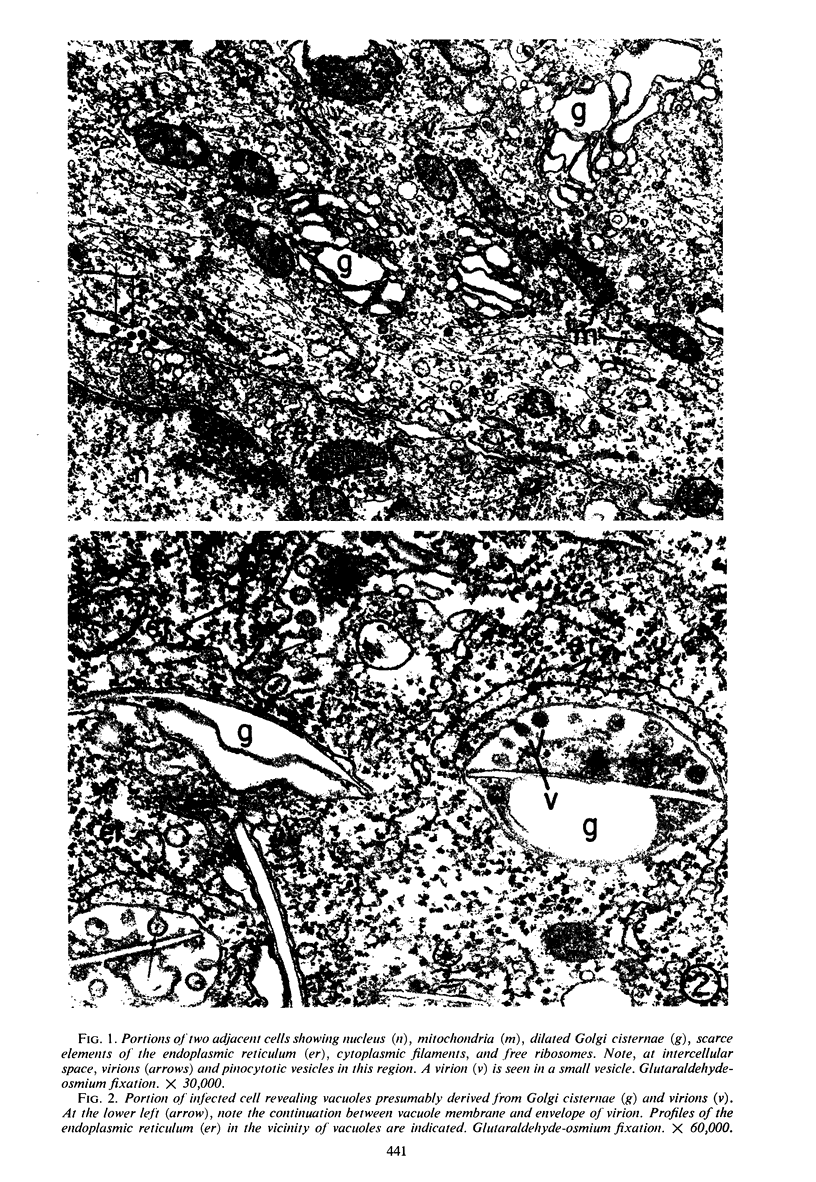
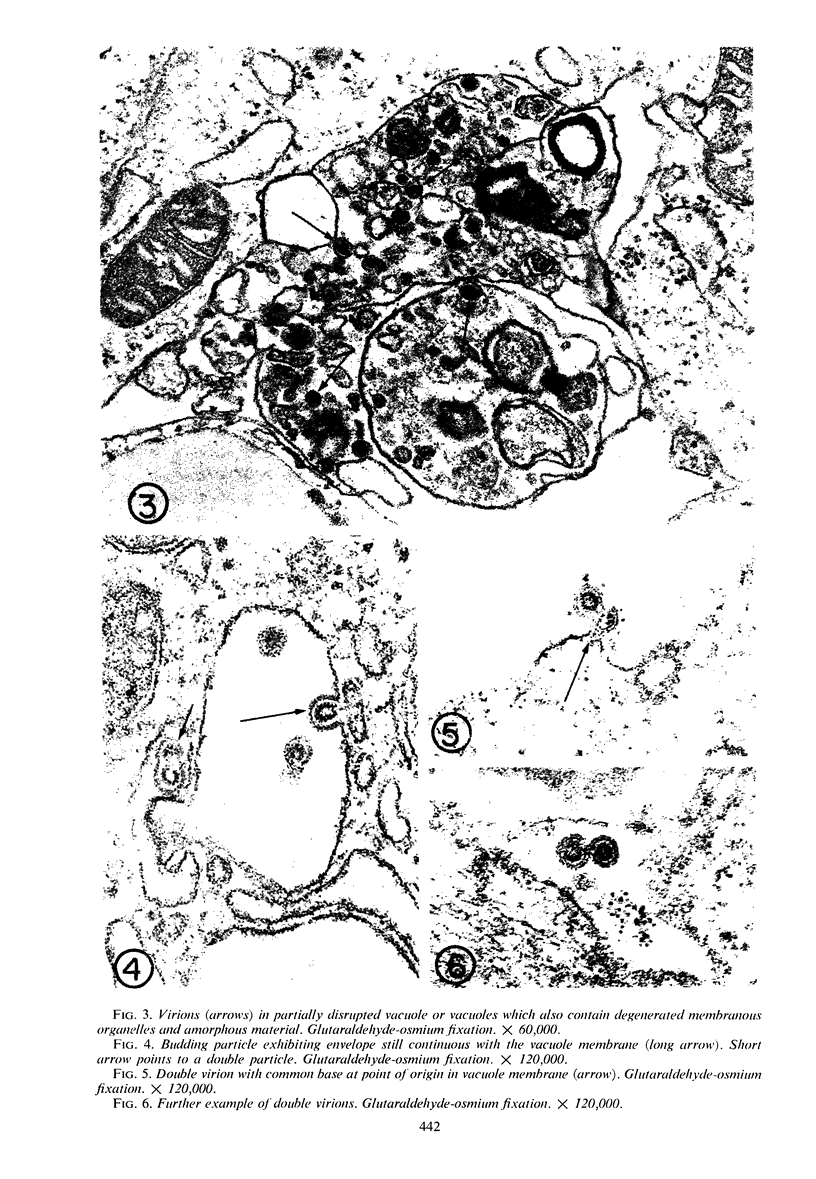
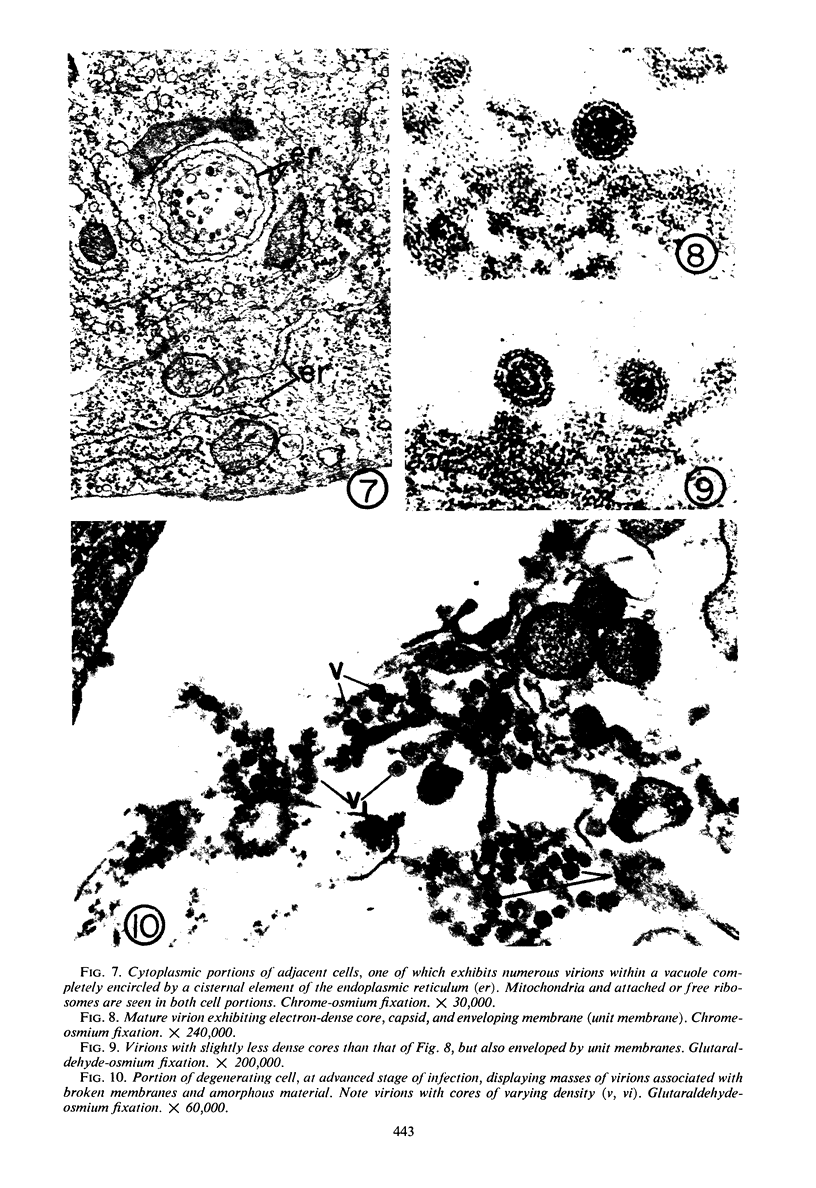
Sequential effects of rubella virus infection in BHK-21 cells were studied by electron microscopy of thin sections of control and infected cells, 2 to 7 days after infection. Vacuolization of cytoplasm in Golgi areas apparently preceded budding of virions from vacuole membranes and involvement of the endoplasmic reticulum. Newly formed endoplasmic reticulum cisternae encircled and segregated virionforming vacuoles together with other cellular elements. Large vacuolar complexes with numerous virus particles developed, and virus release from these areas occurred with disruption at the cell periphery. The viral particles, with a mean diameter of about 56 nm, consisted of an electron-dense core surrounded by a less dense capsid, enveloped by a typical unit membrane derived from the vacuole membrane.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beams H. W., Kessel R. G. The Golgi apparatus: structure and function. Int Rev Cytol. 1968;23:209–276. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibel R., Cohen S. M., Ducharme C. P. Serology of rubella. Virus neutralization, immunofluorescence in BHK21 cells, and hemagglutination inhibition. N Y State J Med. 1968 Jun 1;68(11):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H., Wark M. C., Jack I., Grutzner J. Identification of two possible types of virus particle in rubella-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):37–42. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holms I. H., Warburton M. F. Is rubella an arbovirus? Lancet. 1967 Dec 9;2(7528):1233–1236. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90568-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGNUSSON P., NORRBY E. C. ON THE MORPHOLOGY OF RUBELLA VIRUS. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;16:412–414. doi: 10.1007/BF01253847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCombs R. M., Brunschwig J. P., Rawls W. E. Morphology of rubella virus. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968 Aug;9(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(68)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Halonen P. E., Harrison A. K. Electron microscopy of the development of rubella virus in BHK-21 cells. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1223–1227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1223-1227.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRBY E., MAGNUSSON P., FRIDING B., GARD S. A NOTE ON THE MORPHOLOGY OF RUBELLA VIRUS (BRIEF REPORT). Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1963 May 20;13:421–424. doi: 10.1007/BF01244614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKMAN P. D., BUESCHER E. L., ARTENSTEIN M. S. Recovery of rubella virus from army recruits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Oct;111:225–230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. A., BEHBEHANI A. M., JOHNSON L. W., MELNICK J. L. ISOLATION OF RUBELLA VIRUS: AN EPIDEMIC CHARACTERIZED BY RASH AND ARTHRITIS. JAMA. 1965 Feb 22;191:615–618. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080080005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of cell membranes and their derivatives. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:3–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Delain E., Hollande E. Morphogenèse d'un virus du hamster associé à la souche BHK, ou à des tumeurs. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Jan 30;264(5):785–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]