Abstract
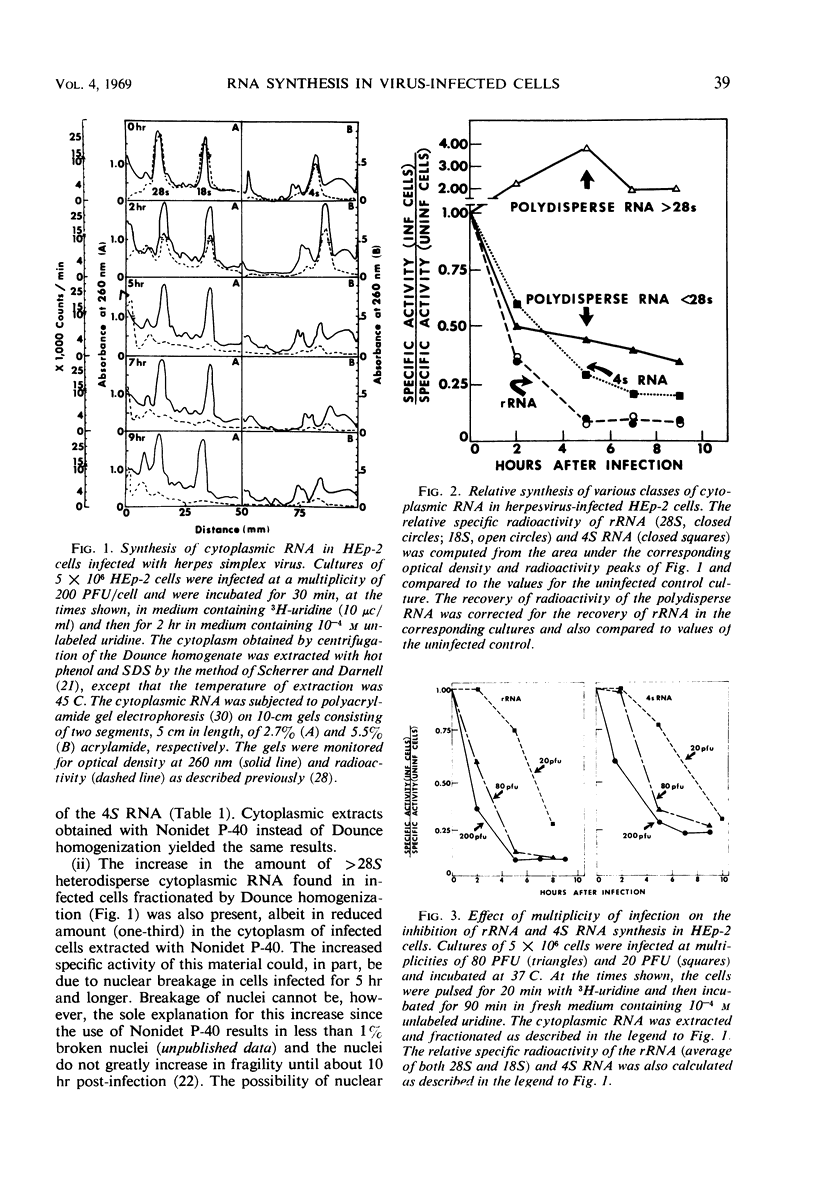
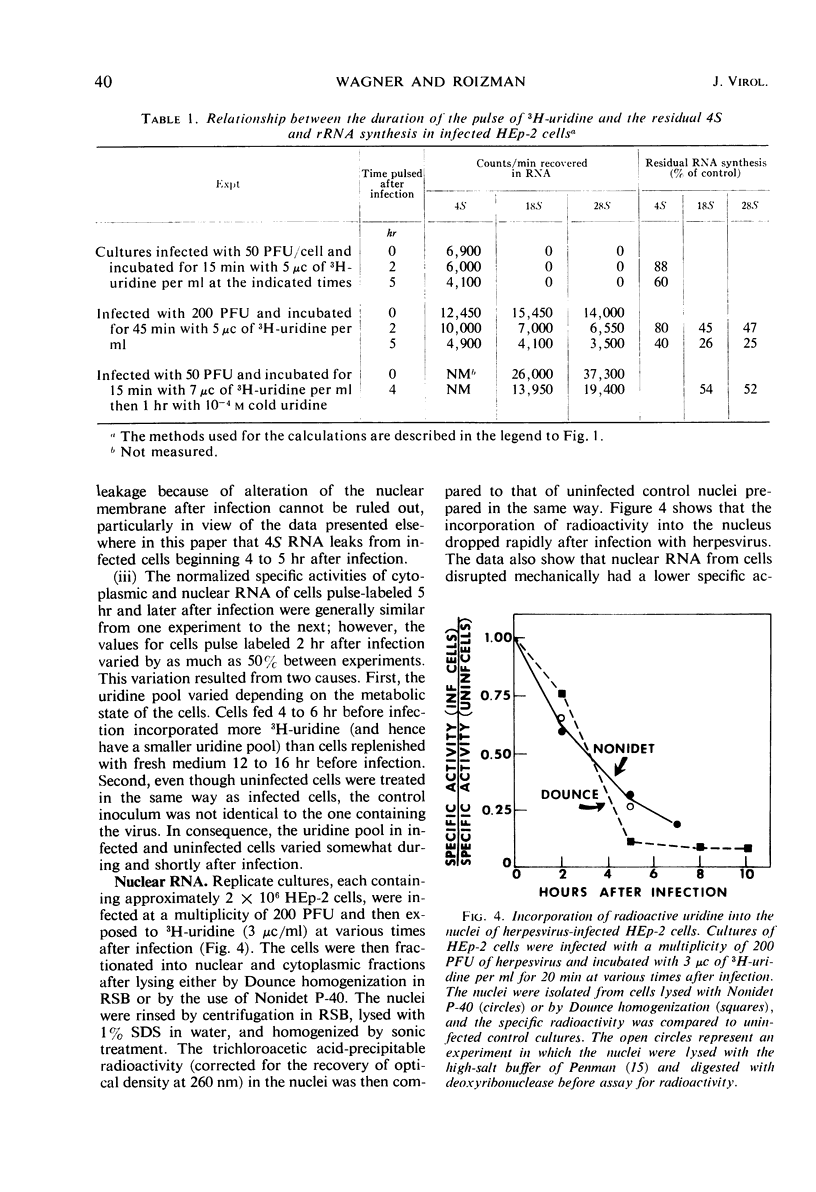
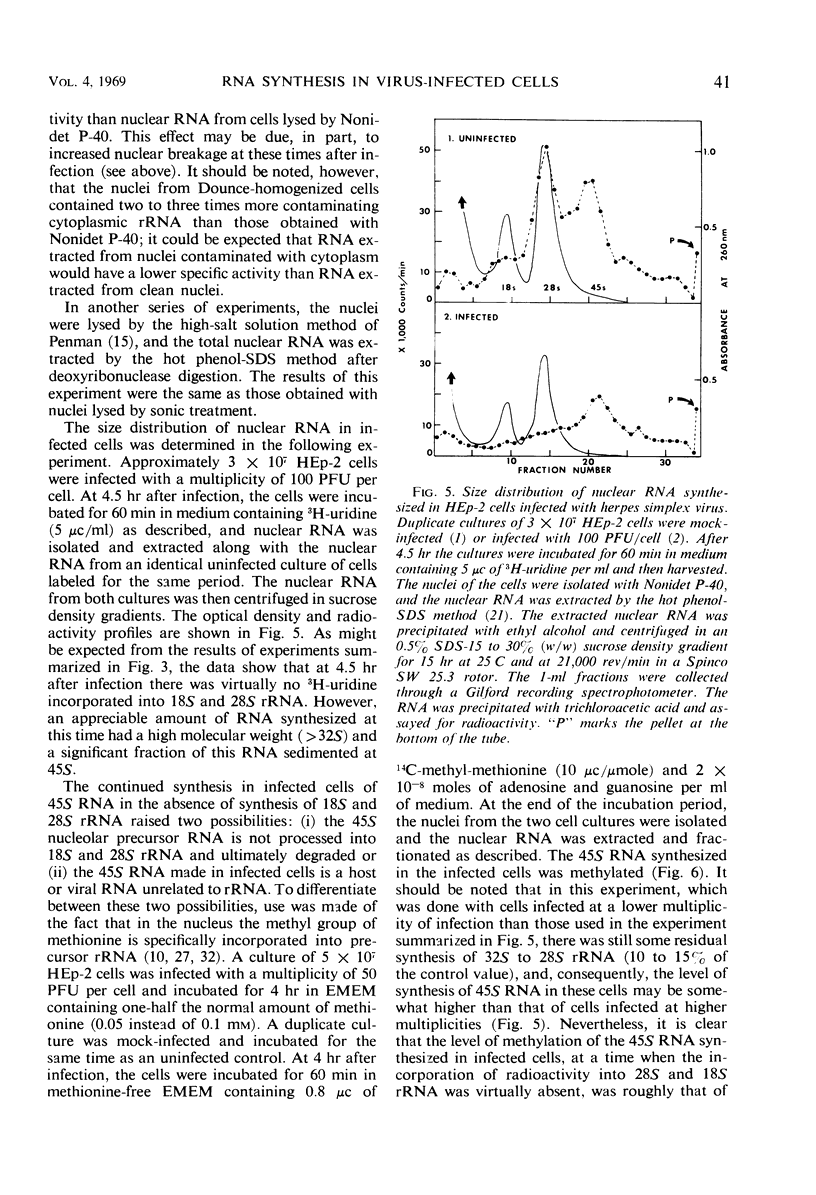
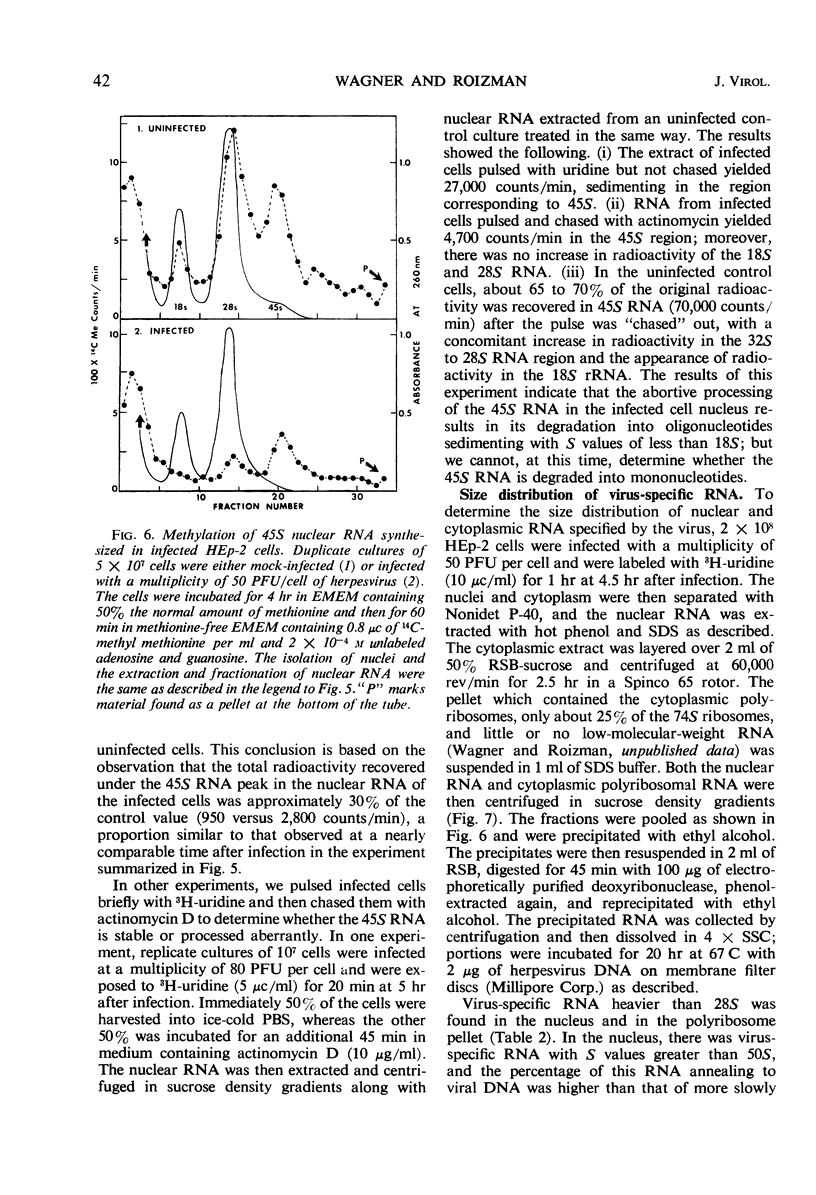
HEp-2 cells were pulse-labeled at different times after infection with herpes simplex virus, and nuclear ribonucleic acid (RNA) and cytoplasmic RNA were examined. The data showed the following: (i) Analysis by acrylamide gel electrophoresis of cytoplasmic RNA of cells infected at high multiplicities [80 to 200 plaque-forming units (PFU)/cell] revealed that ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis falls to less than 10% of control (uninfected cell) values by 5 hr after infection. The synthesis of 4S RNA also declined but not as rapidly, and at its lowest level it was still 20% of control values. At lower multiplicities (20 PFU), the rate of inhibition was slower than at high multiplicities. However, at all multiplicities the rates of inhibition of 18S and 28S rRNA remained identical and higher than that of 4S RNA. (ii) Analysis of nuclear RNA of cells infected at high multiplicities by sucrose density gradient centrifugation showed that the synthesis and methylation of 45S rRNA precursor continued at a reduced but significant rate (ca. 30% of control values) at times after infection when no radioactive uridine was incorporated or could be chased into 28S and 18S rRNA. This indicates that the inhibition of rRNA synthesis after herpesvirus infection is a result of two processes: a decrease in the rate of synthesis of 45S RNA and a decrease in the rate of processing of that 45S RNA that is synthesized. (iii) Hybridization of nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA of infected cells with herpesvirus DNA revealed that a significant proportion of the total viral RNA in the nucleus has a sedimentation coefficient of 50S or greater. The sedimentation coefficient of virus-specific RNA associated with cytoplasmic polyribosomes is smaller with a maximum at 16S to 20S, but there is some rapidly sedimenting RNA (> 28S) here too. (iv) Finally, there was leakage of low-molecular weight (4S) RNA from infected cells, the leakage being approximately three-fold that of uninfected cells by approximately 5 hr after infection.
Full text
PDF


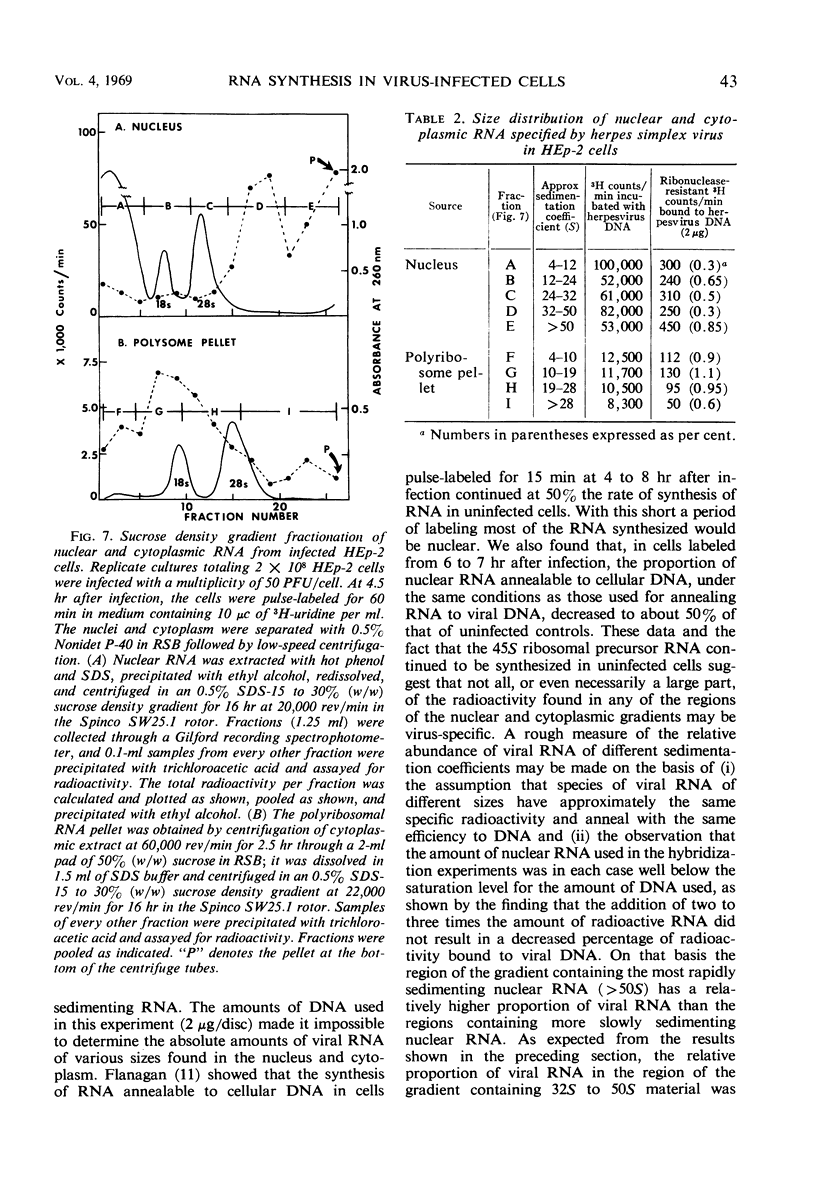
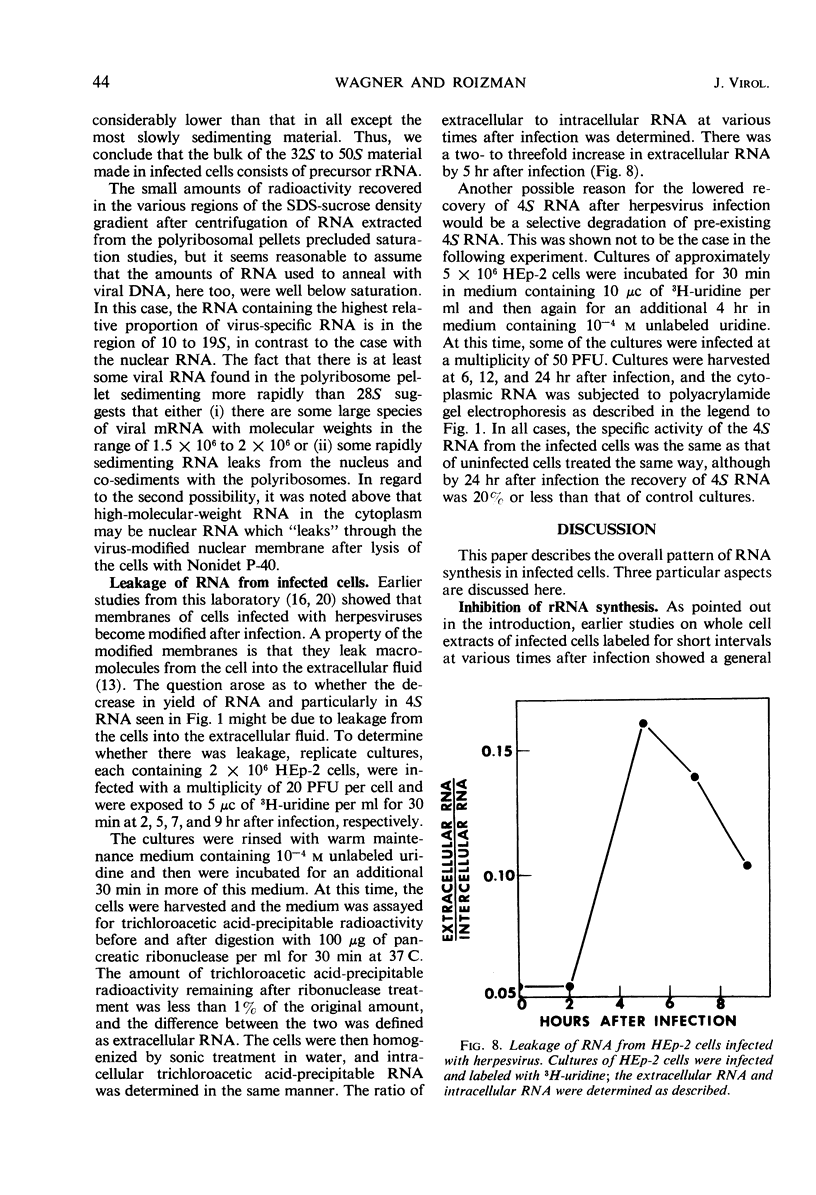


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AURELIAN L., ROIZMAN B. ABORTIVE INFECTION OF CANINE CELLS BY HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. II. ALTERNATIVE SUPPRESSION OF SYNTHESIS OF INTERFERON AND VIRAL CONSTITUENTS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:539–548. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEN-PORAT T., KAPLAN A. S. MECHANISM OF INHIBITION OF CELLULAR DNA SYNTHESIS BY PSEUDORABIES VIRUS. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:22–29. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Scharff M. D., Robbins E. Preparation of mammalian polyribosomes with the detergent Nonidet P-40. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 21;149(1):302–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90715-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Ribonucleic acids from animal cells. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Sep;32(3):262–290. doi: 10.1128/br.32.3.262-290.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. F. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid synthesis in KB cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.583-590.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J., Koteles G. J., Keir H. M., Subak Sharpe H. Herpes virus specified ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1966 Apr 23;210(5034):387–390. doi: 10.1038/210387b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamiya T., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Control of certain aspects of the infective process by progeny viral DNA. Virology. 1965 Aug;26(4):577–589. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D. J., Cheevers W. P., Gentry G. A., Randall C. C. Kinetics of cellular and viral DNA synthesis in equine abortion (herpes) virus infection of L-M cells. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):104–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., AURELIAN L. ABORTIVE INFECTION OF CANINE CELLS BY HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. I. CHARACTERIZATION OF VIRAL PROGENY FROM CO-OPERATIVE INFECTION WITH MUTANTS DIFFERING IN CAPACITY TO MULTIPLY IN CANINE CELLS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:528–538. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B. Polykaryocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:327–342. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Borman G. S., Rousta M. K. Macromolecular synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1965 Jun 26;206(991):1374–1375. doi: 10.1038/2061374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Spear P. G. Preparation of herpes simplex virus of high titer. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):83–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.83-84.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERRER K., DARNELL J. E. Sedimentation characteristics of rapidly labelled RNA from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:486–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., CHENG T. Y. Fractionation of nucleic acids with the methylated albumin column. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring S. B., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus products in productive and abortive infection. 3. Differentiation of infectious virus derived from nucleus and cytoplasm with respect to stability and size. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):979–985. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.979-985.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subak-Sharpe H. An animal virus with DNA of high guanine + cytosine content which codes for S-RNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):924–928. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80339-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subak-Sharpe H., Shepherd W. M., Hay J. Studies on sRNA coded by herpes virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:583–594. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sydiskis R. J., Roizman B. Polysomes and protein synthesis in cells infected with a DNA virus. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):76–78. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER J. R., KNOPF P. M., RICH A. A multiple ribosomal structure in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Roizman B. Effect of the Vinca alkaloids on RNA synthesis in human cells in vitro. Science. 1968 Nov 1;162(3853):569–570. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3853.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Loening U., Willems M., Penman S. Acrylamide gel electrophoresis of HeLa cell nucleolar RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1088–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. B., Hsu W. T., Foft J. W., Scherberg N. H. Transfer RNA coded by the T4 bacteriophage genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):114–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman E. F., Holler B. W. Methylation of 45 s ribosomal RNA precursor in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jan 28;23(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



