Abstract
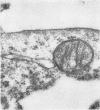
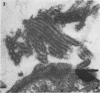
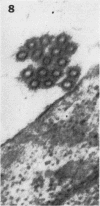
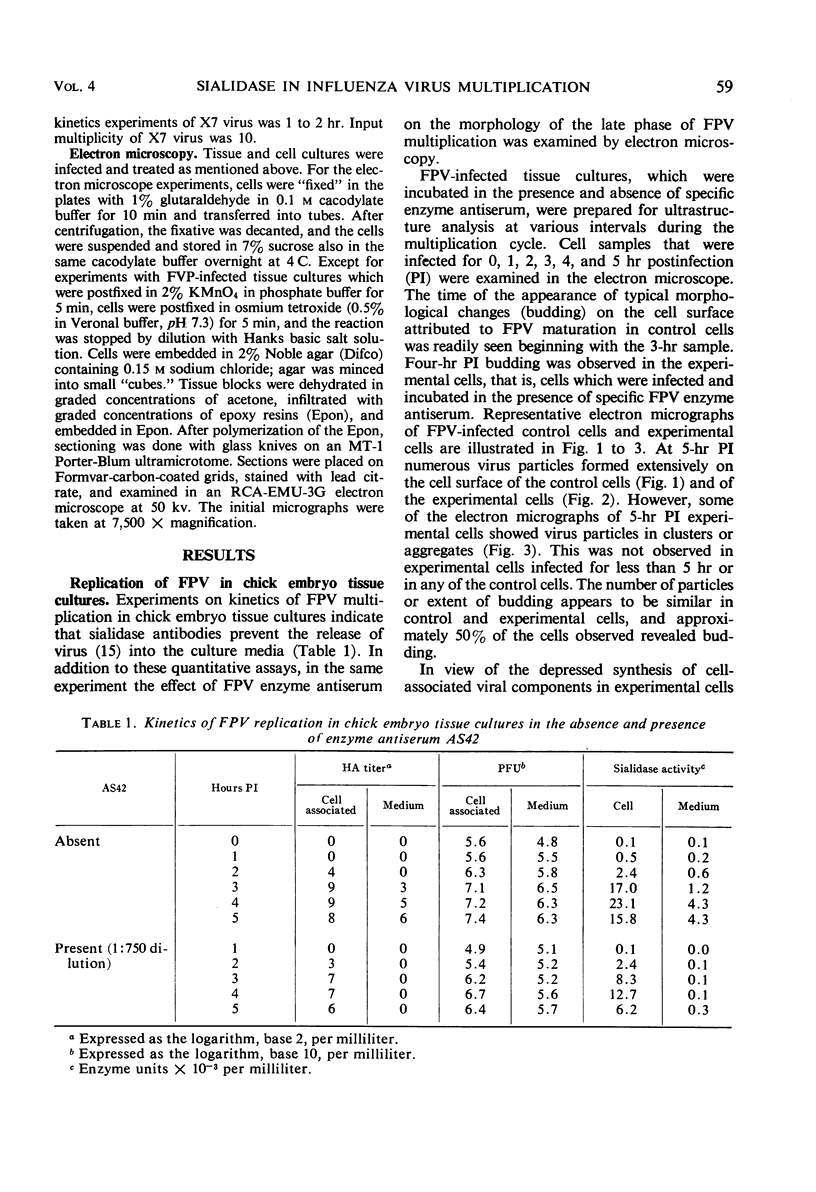
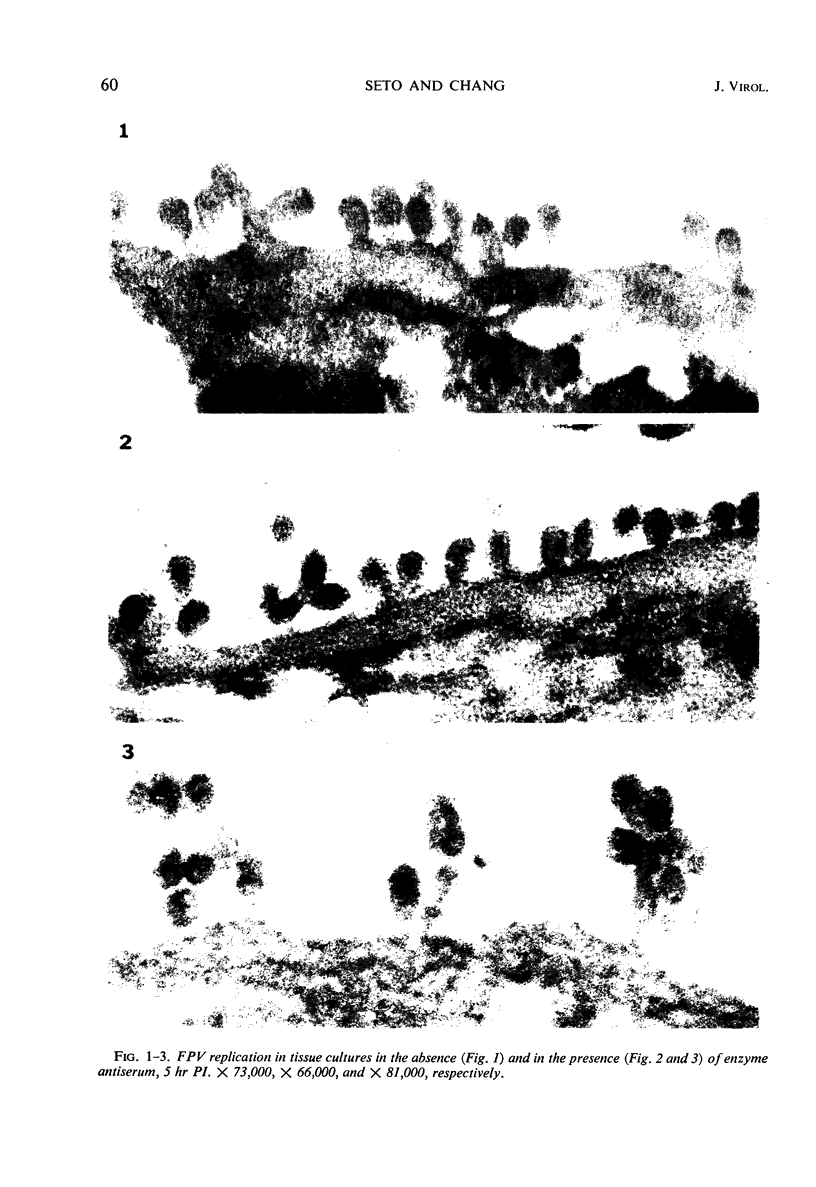
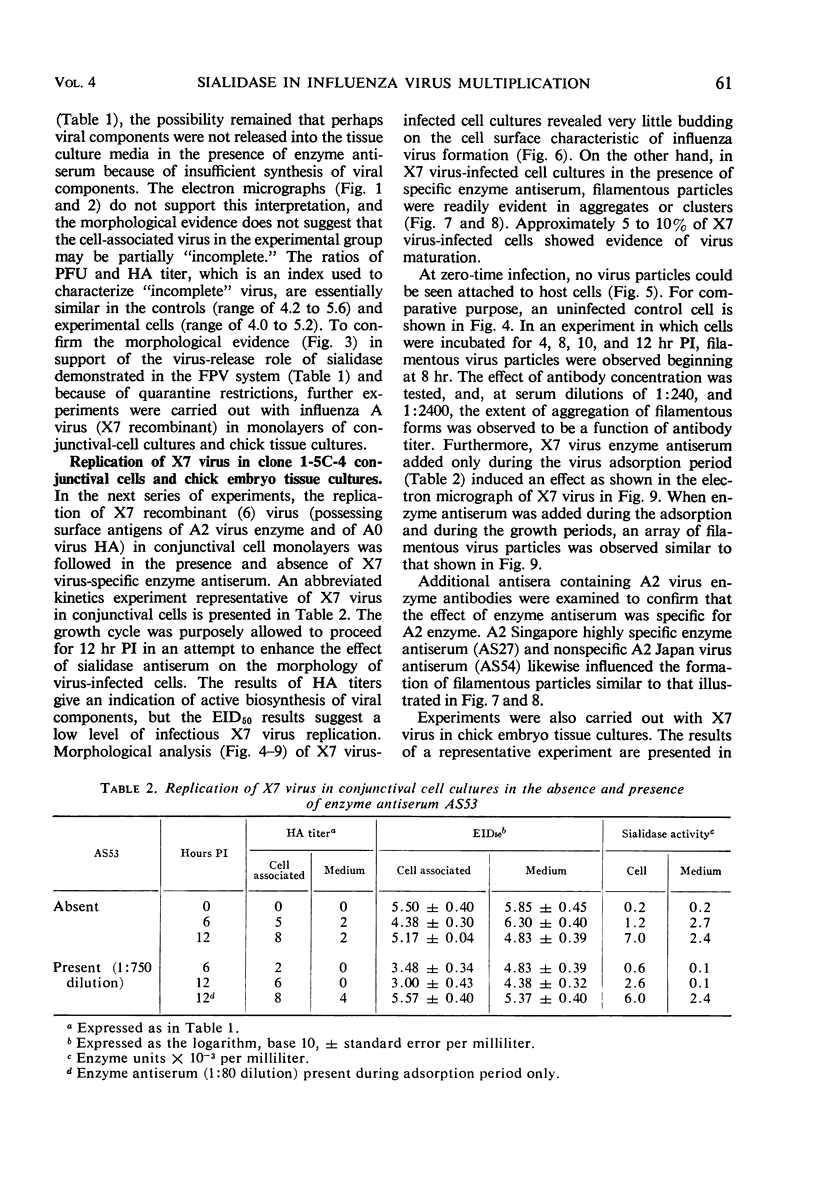
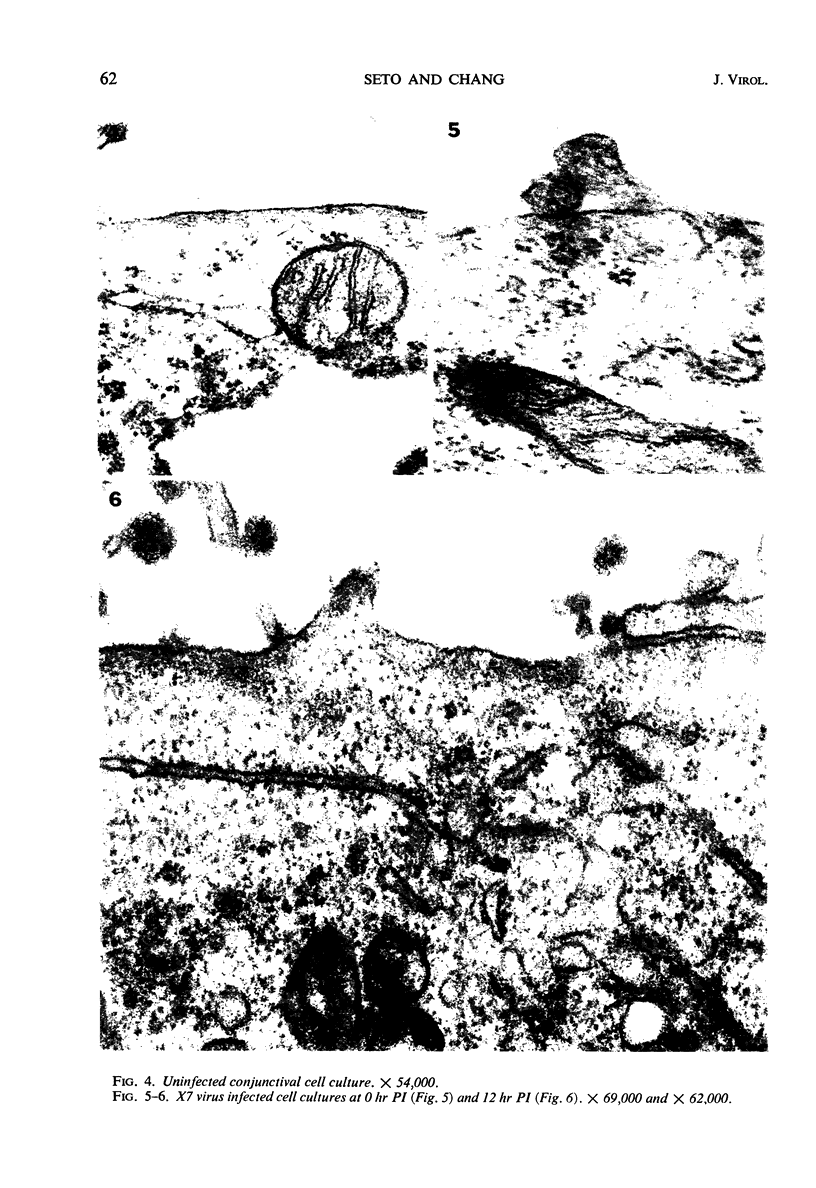
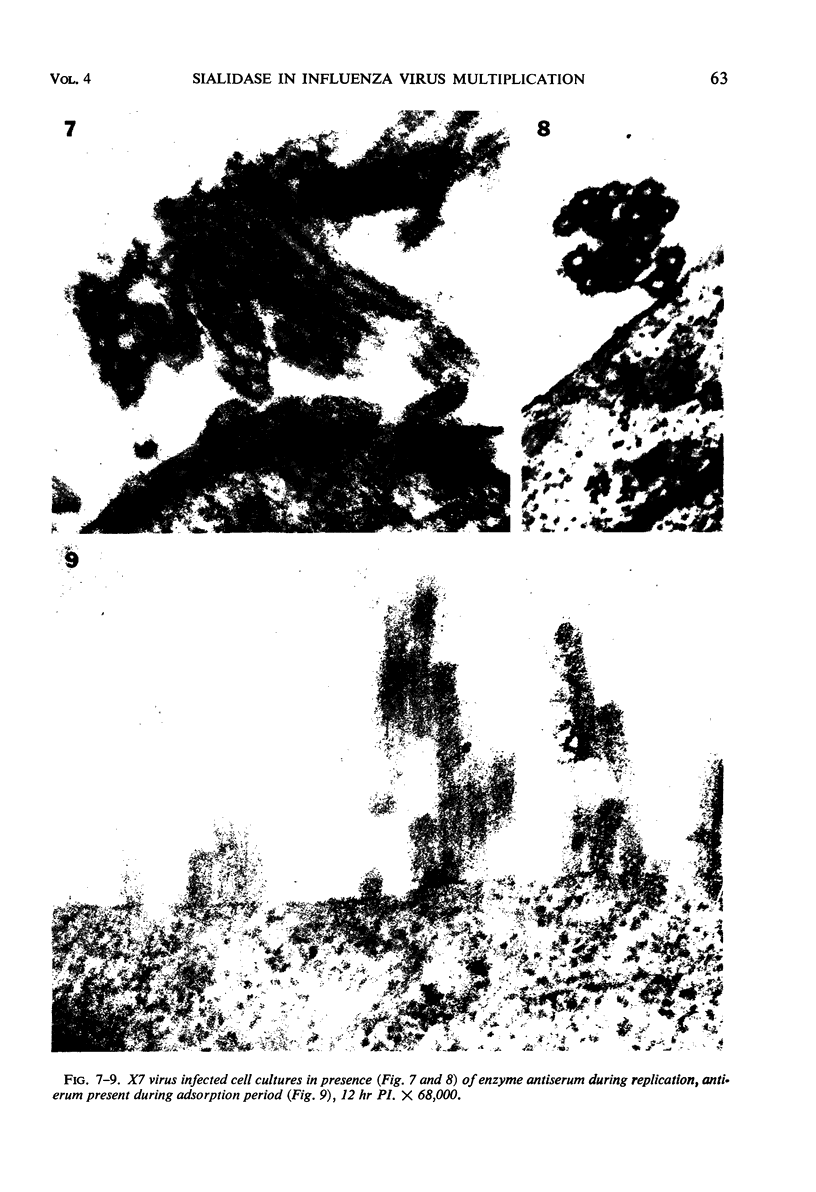
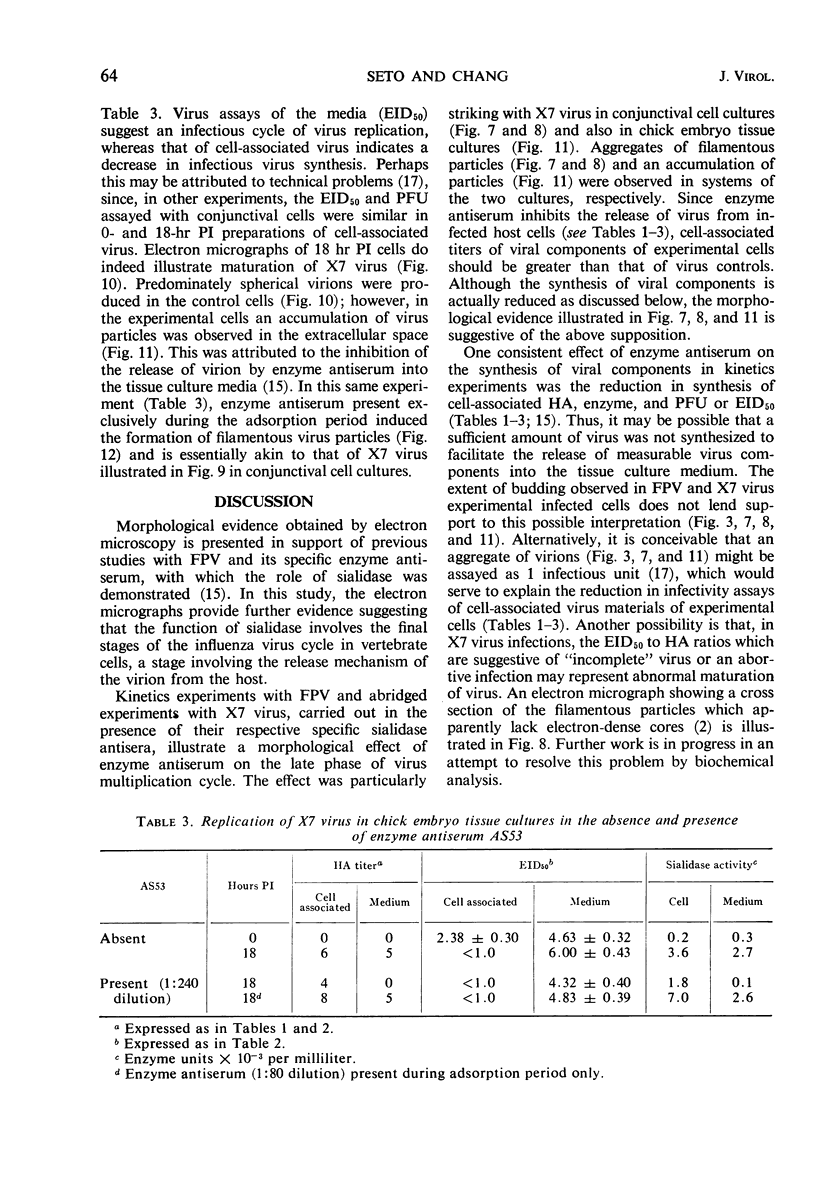
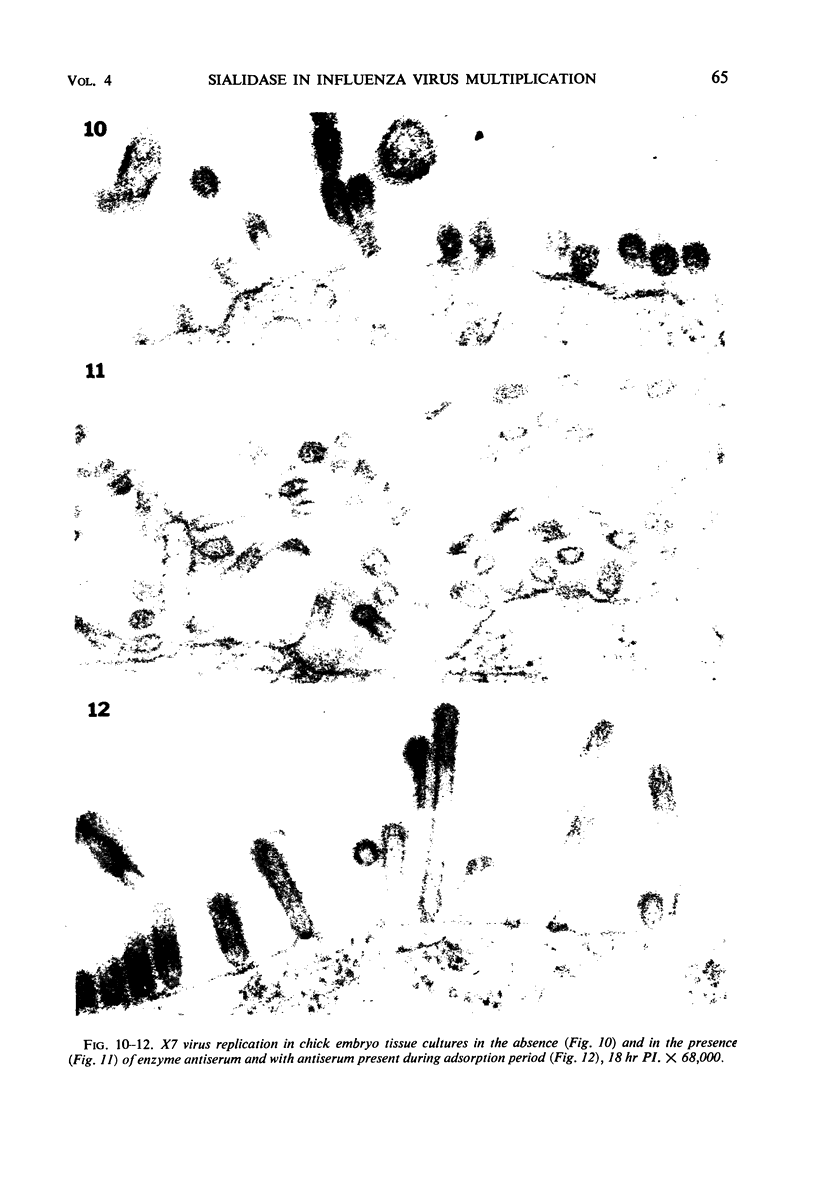
Morphological evidence has been obtained by electron microscopy in support of previous findings that one of the most important functions of sialidase is associated with the release of virus from infected host cells. Highly specific antiserum against fowl plague virus enzyme and specific antiserum against X7 recombinant influenza virus enzyme were shown to influence the morphology of cells infected with their homologous virus. In the presence of enzyme antiserum, an accumulation and aggregation of virus particles were evident on the cell surface and in the extracellular space of infected host cells. The aggregation of virus particles was interpreted to result from the inhibition of the release of virus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRCH-ANDERSEN A., PAUCKER K. Studies on the structure of influenza virus. II. Ultrathin sections of infectious and noninfectious particles. Virology. 1959 May;8(1):21–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILBOURNE E. D., MURPHY J. S. Genetic studies of influenza viruses. I. Viral morphology and growth capacity as exchangeable genetic traits. Rapid in ovo adaptation of early passage Asian strain isolates by combination with PR8. J Exp Med. 1960 Mar 1;111:387–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D., Laver W. G., Schulman J. L., Webster R. G. Antiviral activity of antiserum specific for an influenza virus neuraminidase. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):281–288. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.281-288.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R. Untersuchungen über die Feinstruktur des infektiösen Partikels der Newcastle Disease und über die neben ihm auftretenden, nichtinfektiösen, virusspezifischen Einheiten Ein Beitray zur Klassifizierung der Myxoviren. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1965 Feb;12(1):74–contd. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOLTISSEK C., ROTT R. BEHAVIOR OF VIRUS-SPECIFIC ACTIVITIES IN TISSUE CULTURES INFECTED WITH MYXOVIRUSES AFTER CHEMICAL CHANGES OF THE VIRAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Virology. 1964 Feb;22:169–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETO J. T., HICKEY B. J., RASMUSSEN A. F., Jr Sialidase activity and related properties of influenza A2 viruses. Virology. 1959 Dec;9:598–611. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETO J. T., HOKAMA Y. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS ANALYSIS OF SIALIDASE FROM INFLUENZA VIRUS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:640–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIURA A., KILBOURNE E. D. GENETIC STUDIES OF INFLUENZA VIRUSES. II. PLAQUE FORMATION BY INFLUENZA VIRUSES IN A CLONE OF A VARIANT HUMAN HETEROPLOID CELL LINE. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:478–488. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto JT BRZENIEK R., Rott R. Isolation of a low molecular weight sialidase (neuraminidase) from influenza virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):402–404. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto J. T., Rott R. Functional significance of sialidose during influenza virus multiplication. Virology. 1966 Dec;30(4):731–737. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Virus aggregation as the cause of the non-neutralizable persistent fraction. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.478-488.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G. Preparation and properties of antibody directed specifically against the neuraminidase of influenza virus. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):49–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]