Abstract
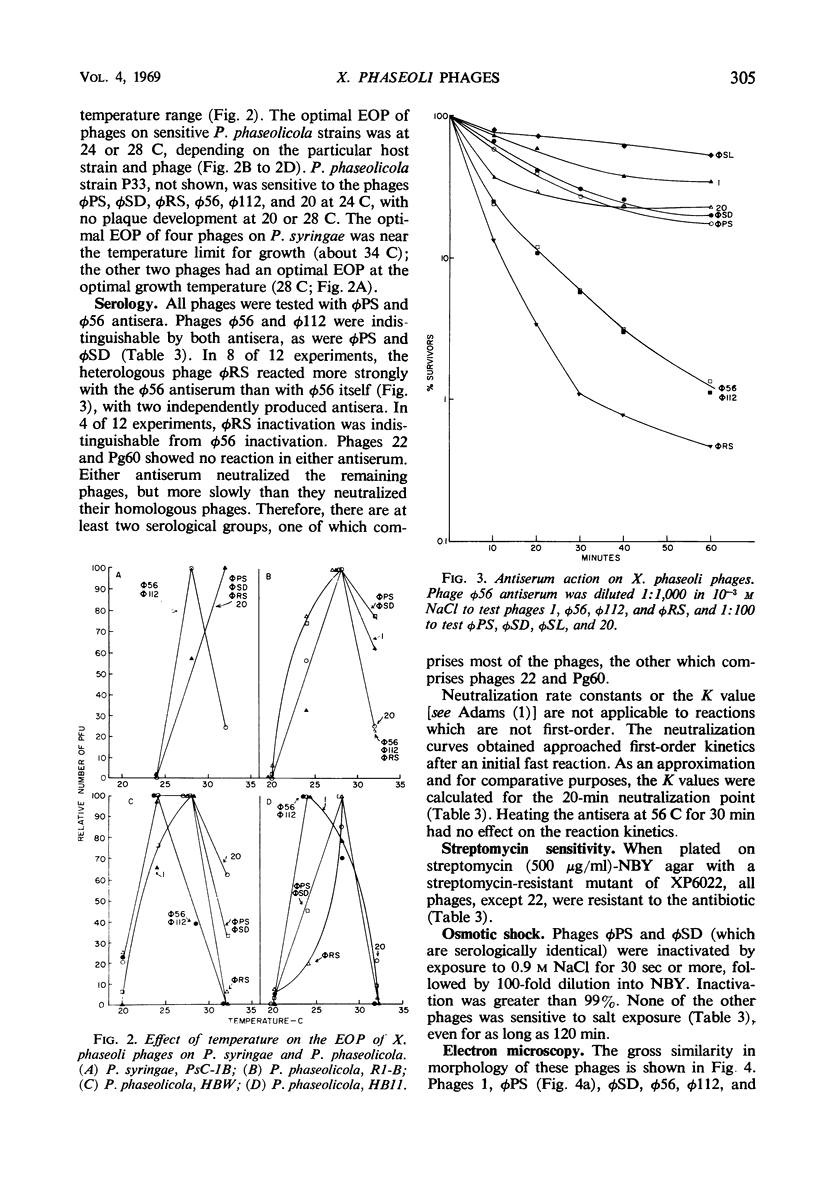
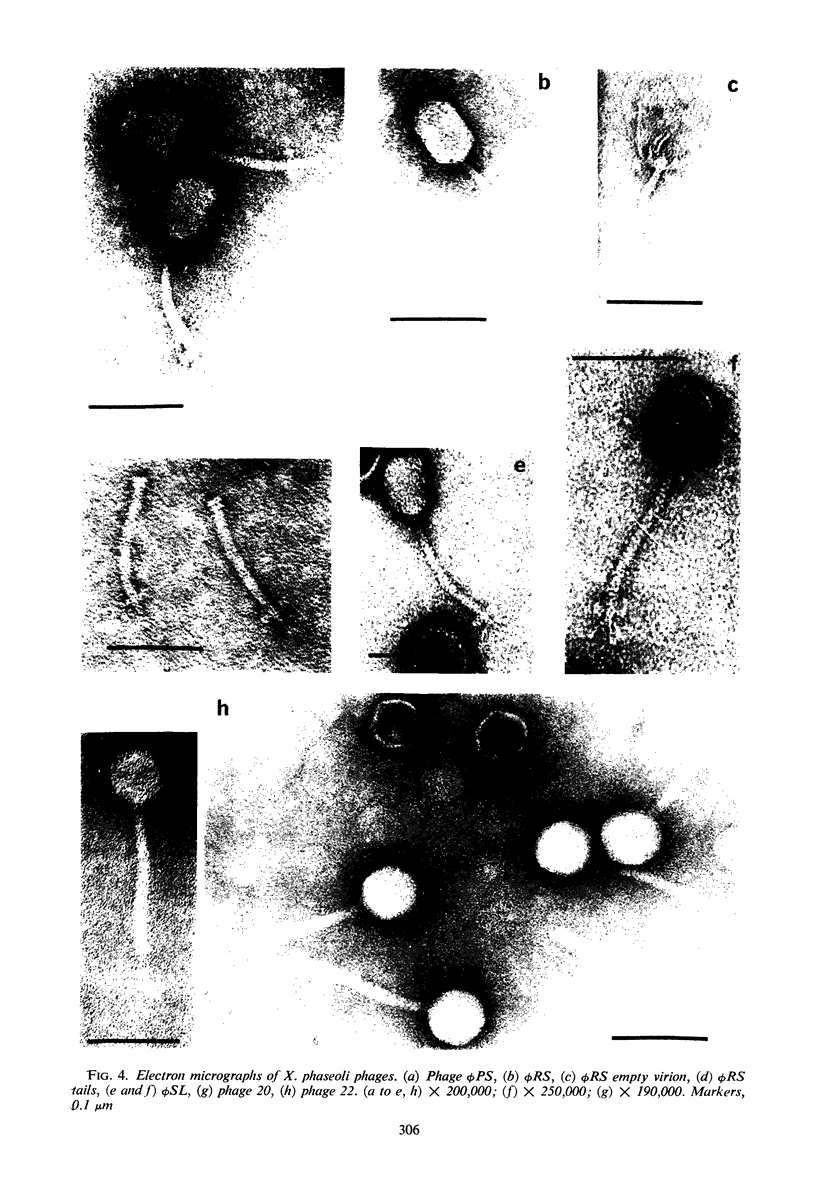
Ten bacteriophages for Xanthomonas phaseoli were characterized. On the basis of adsorption rates, latent period and burst size, plaque morphology, host range, efficiency of plating, ultrastructure, sensitivity to osmotic shock, streptomycin sensitivity, temperature effects on plating efficiency, and serology, the phages were separated into at least three groups. Some of the phages were infectious for Pseudomonas phaseolicola (four strains) and P. syringae (one strain) in a narrow temperature range. The taxonomic and ecological significance of this finding is discussed.
Full text
PDF
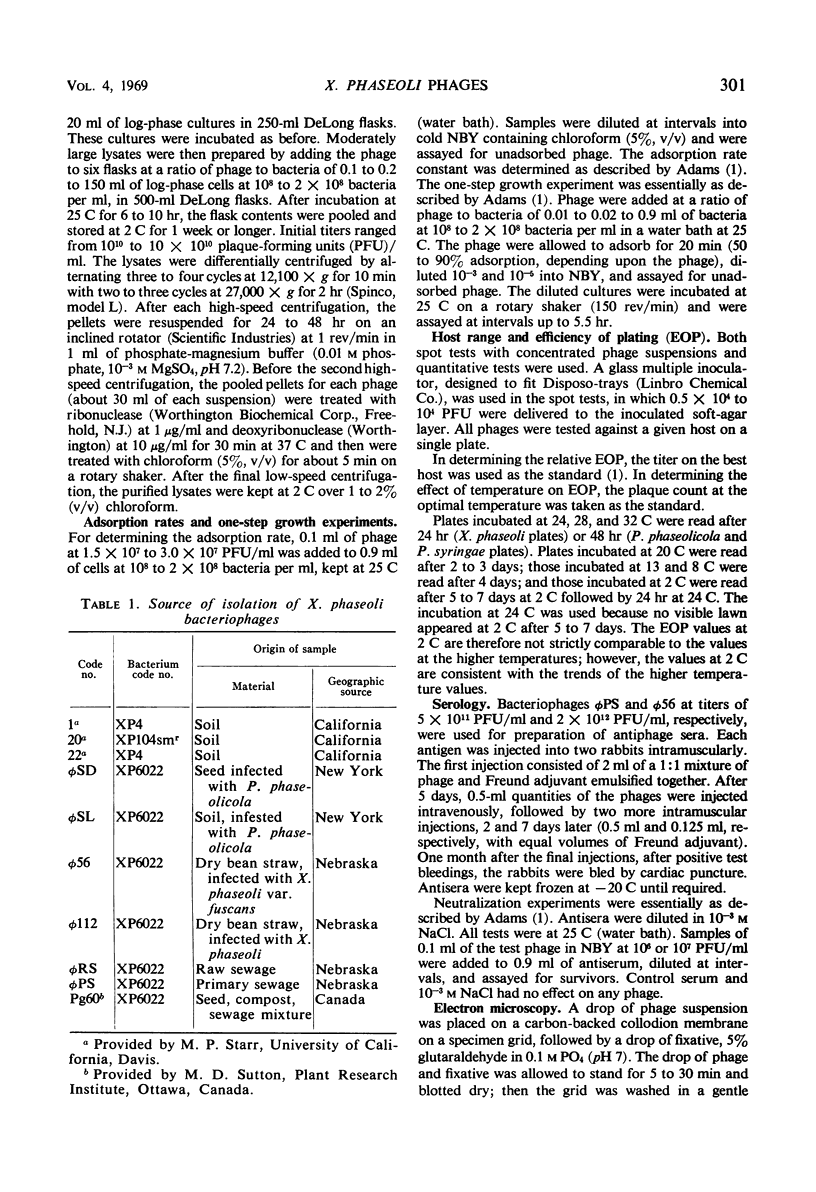

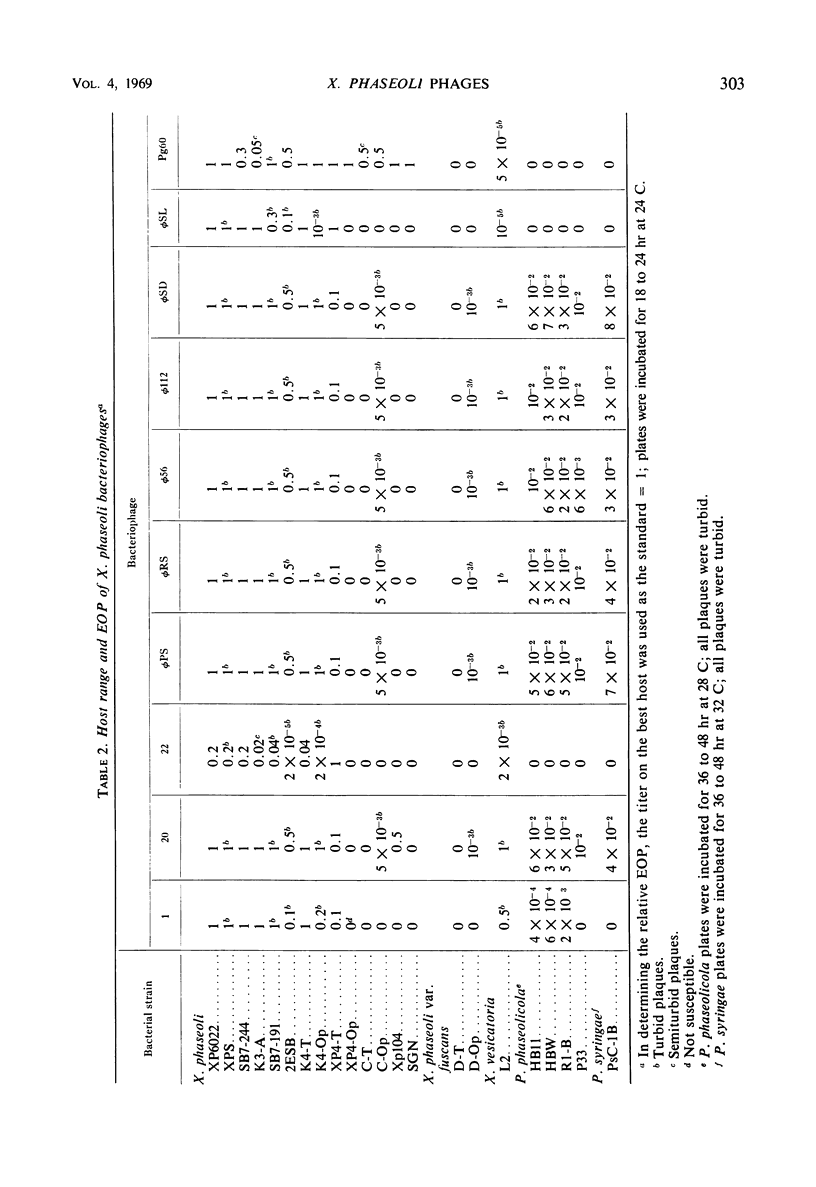
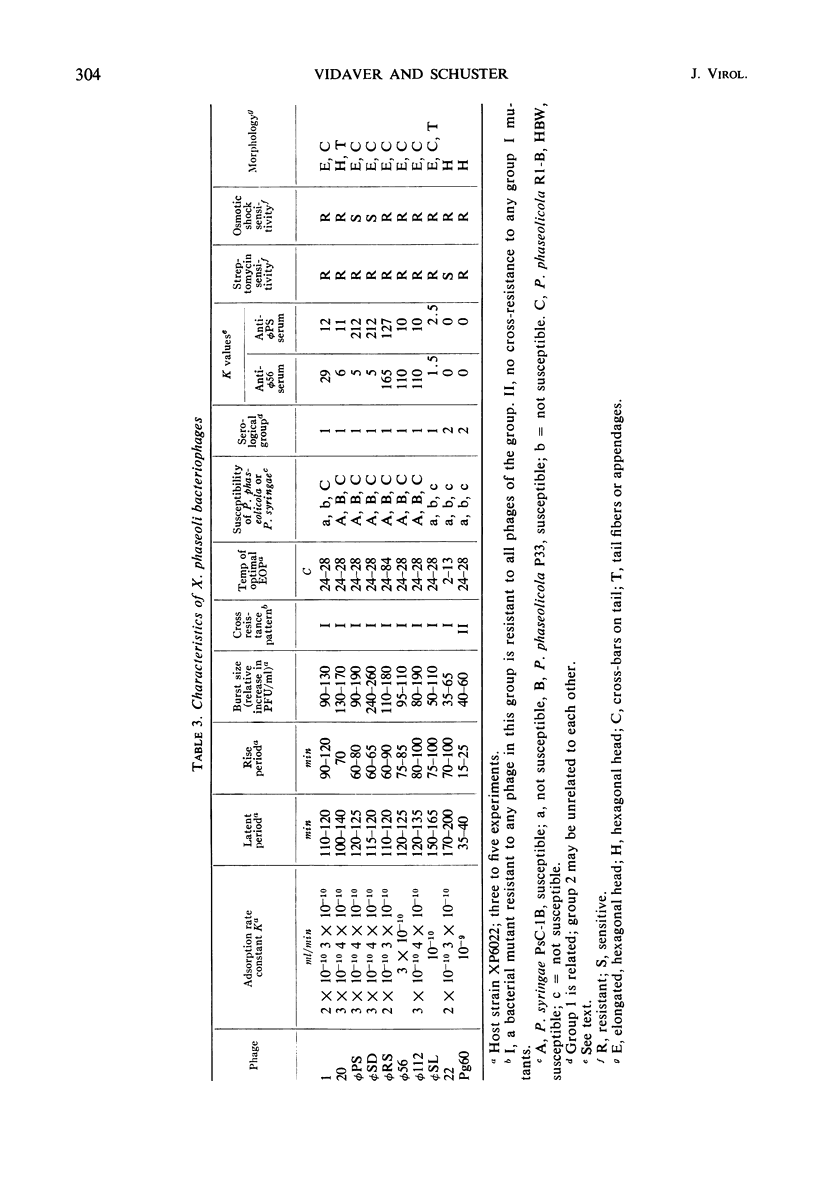


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLAHAN W. P., HORNER J. A. THE USE OF VANADIUM AS A STAIN FOR ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Feb;20:350–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley J., Park I. W., Tijtgat R., Van Ermengem J. DNA homology and taxonomy of Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jan;42(1):43–56. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZNELSON H., SUTTON M. D., BAYLEY S. T. The use of bacteriophage of Xanthomonas phaseoli in detecting infection in beans, with observation on its growth and morphology. Can J Microbiol. 1954 Aug;1(1):22–29. doi: 10.1139/m55-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTTON M. D., KATZNELSON H., QUADLING C. A bacteriophage that attacks numerous phytopathogenic Xanthomonas species. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Oct;4(5):493–497. doi: 10.1139/m58-053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]