Abstract
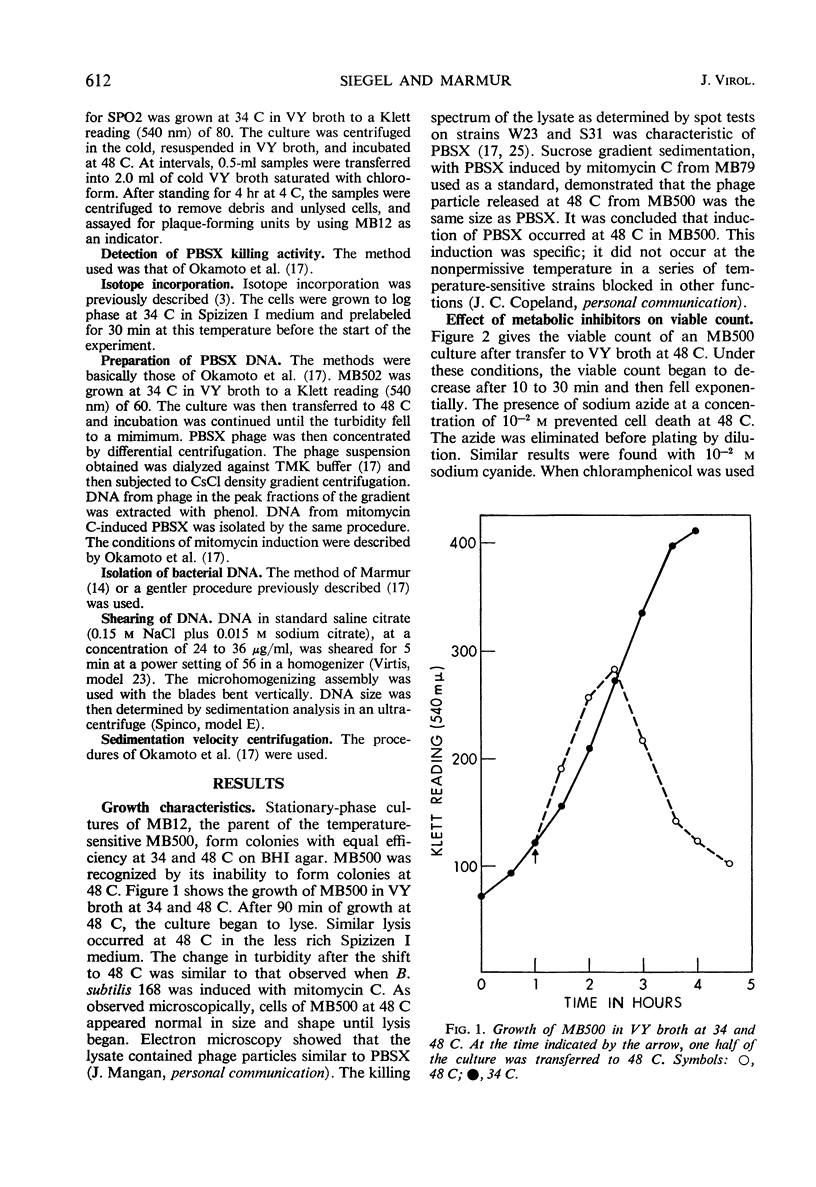
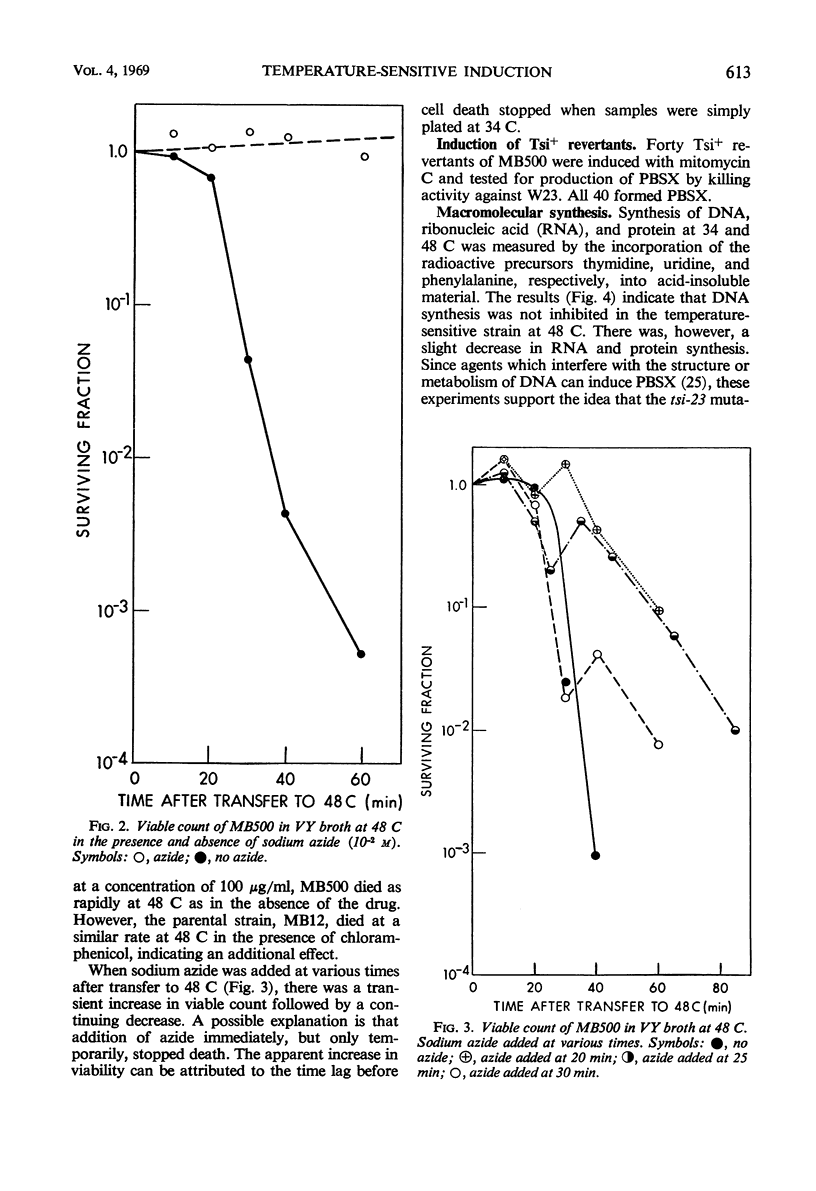
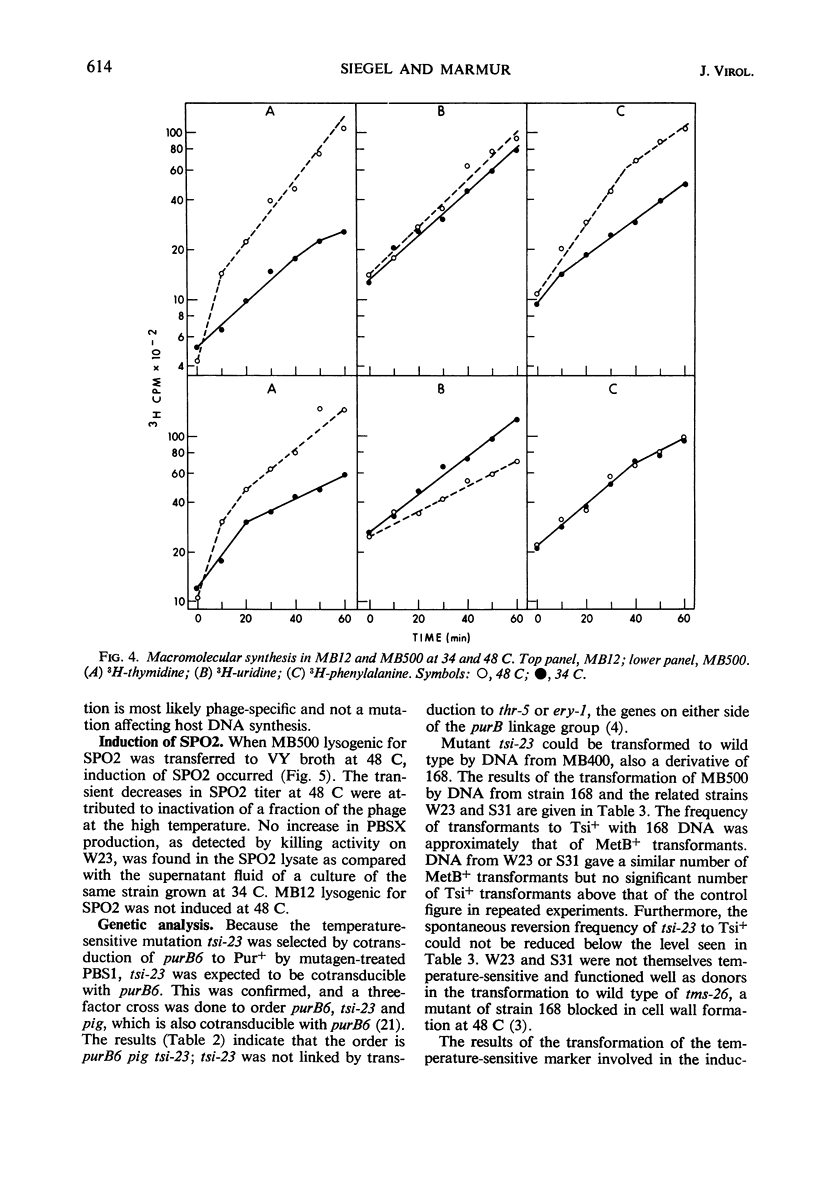
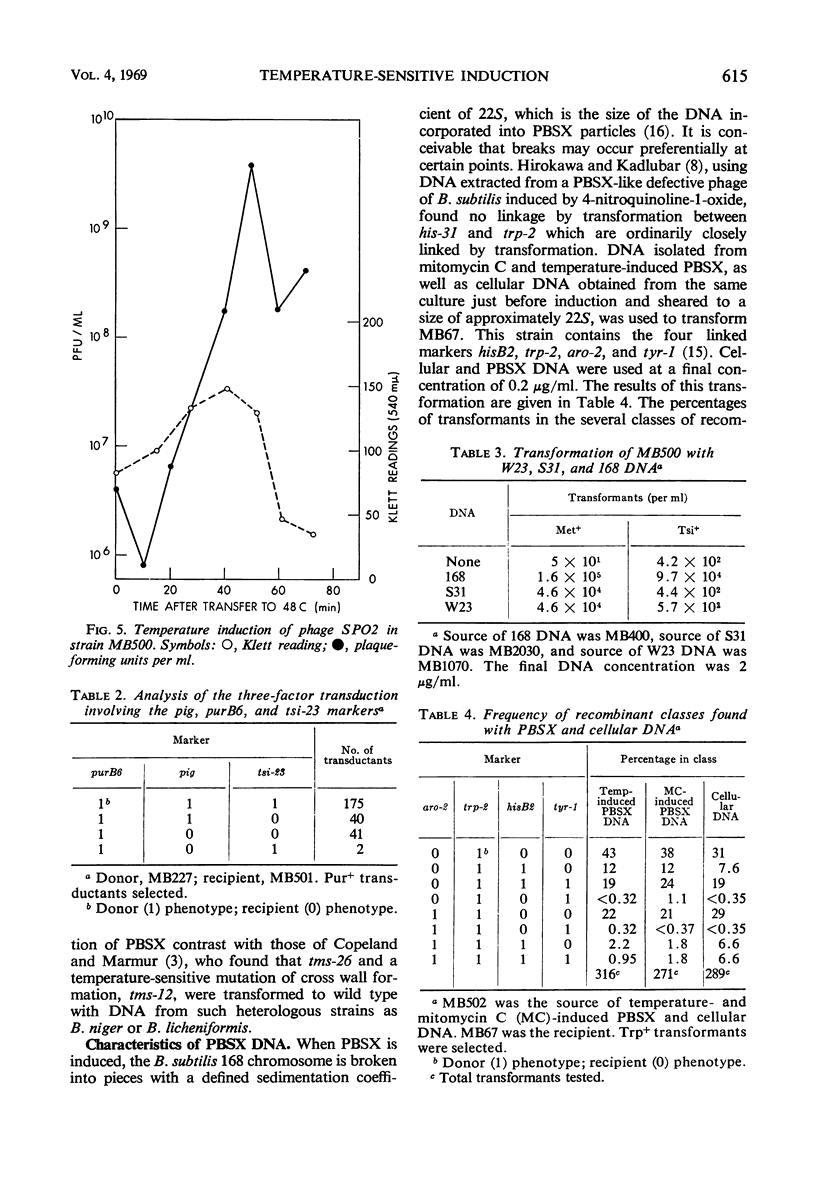
In a temperature-sensitive mutant of Bacillus subtilis 168, induction of the defective phage PBSX occurred at 48 C. Cell lysis began after 90 min of growth at 48 C, and cell viability began to decrease after 10 to 30 min. The loss in viability at the nonpermissive temperature was prevented by azide or cyanide. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic acid, and protein synthesis were not inhibited at 48 C. Temperature induction of the temperate phage SPO2 also occurred in this mutant. The temperature-sensitive mutation, designated tsi-23, was linked by transduction to purB6 and pig, the order being purB6 pig tsi-23. Mutation tsi-23 was transformable to wild type by B. subtilis 168 DNA but not by DNA from the closely related strains W23 or S31. DNA from the latter two strains transformed auxotrophic markers of strain 168 at frequencies close to those found with 168 donor DNA. Upon temperature induction, cellular DNA was broken to a size of 22S, characteristic of DNA in PBSX particles. The DNA isolated from temperature-induced PBSX did not give an increased Ade+/Met+ transformant ratio relative to cellular DNA nor contain preferential break points as determined by transformation of four closely linked markers.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boice L. B. Evidence that Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP02 is temperate and heteroimmune to bacteriophage phi-105. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):47–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.47-49.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland J. C., Marmur J. Identification of conserved genetic functions in Bacillus by use of temperature-sensitive mutants. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):302–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Goldthwaite C., Smith I., Marmur J. Genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):163–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDTHWAIT D., JACOB F. SUR LE M'ECANISME DE L'INDUCTION DU D'EVELOPPEMENT DU PROPHAGE CHEZ LES BACT'ERIES LYSOG'ENES. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1964 Jul 20;259:661–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Yoshikawa H. Defective bacteriophage PBSH in Bacillus subtilis. I. Induction, purification, and physical properties of the bacteriophage and its deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):233–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.233-247.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Yoshikawa H. Defective bacteriophage PBSH in Bacillus subtilis. II. Intracellular development of the induced prophage. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):248–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.248-260.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa H., Kadlubar F. Length of deoxyribonucleic acid of PBSX-like particles of Bacillus subtilis induced by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):205–209. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.205-209.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan E. A genetic study of temperature-sensitive mutants of the subtilis phage SP82. Virology. 1966 Dec;30(4):650–660. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby E. P., Jacob F., Goldthwait D. A. Prophage induction and filament formation in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1903–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEB M. ULTRAVIOLET SENSITIVITY OF ESCHERICHIA COLI CONTAINING HEAT-INDUCIBLE LAMBDA PROPHAGES. Science. 1964 Jul 10;145(3628):175–176. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3628.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb M. Studies of heat-inducible lambda bacteriophage. I. Order of genetic sites and properties of mutant prophages. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nester E W, Schafer M, Lederberg J. Gene Linkage in DNA Transfer: A Cluster of Genes Concerned with Aromatic Biosynthesis in Bacillus Subtilis. Genetics. 1963 Apr;48(4):529–551. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Mudd J. A., Mangan J., Huang W. M., Subbaiah T. V., Marmur J. Properties of the defective phage of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):413–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Mudd J. A., Marmur J. Conversion of Bacillus subtilis DNA to phage DNA following mitomycin C induction. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Romig W. R. Comparison of ultraviolet sensitivity of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO2 and its infectious DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):130–142. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Hopkins N. The operators controlled by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1282–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. ISOLATION OF THE lambda PHAGE REPRESSOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):306–313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Genetic mapping of a locus which regulates the production of pigment associated with spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2426–2427. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2426-2427.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romig W. R. Infectivity of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acids extracted from mature particles and from lysogenic hosts. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):349–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAMAN E., TARMY E., MARMUR J. INDUCIBLE PHAGES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:607–613. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN R., JACOB F. [On a thermosensitive repression system in the Escherichia coli lambda bacteriophage]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1962 Feb 19;254:1517–1519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS R. ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE GENETIC SEGMENT CONTROLLING IMMUNITY IN TEMPERATE BACTERIOPHAGES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:247–253. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland B. C., Szybalski W., Ris H. Mapping of deletions and substitutions in heteroduplex DNA molecules of bacteriophage lambda by electron microscopy. Science. 1969 Mar 21;163(3873):1343–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3873.1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


