Abstract
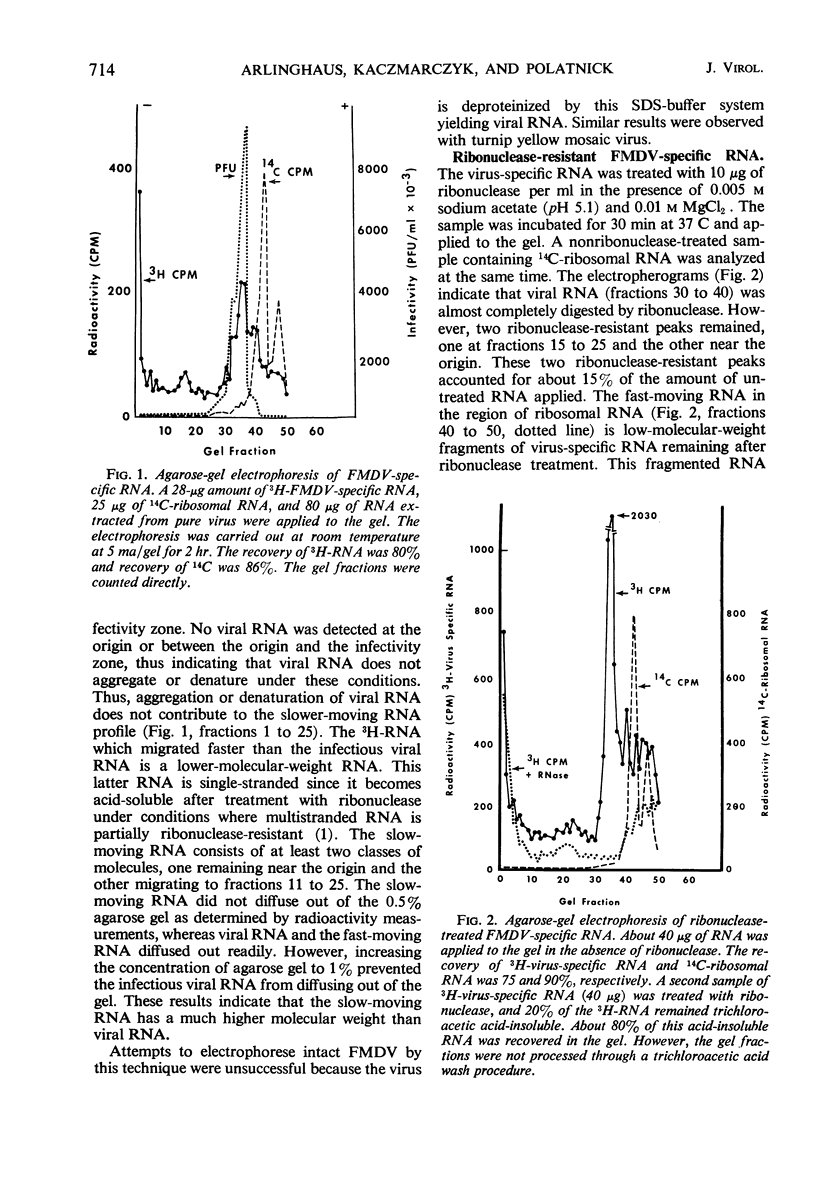
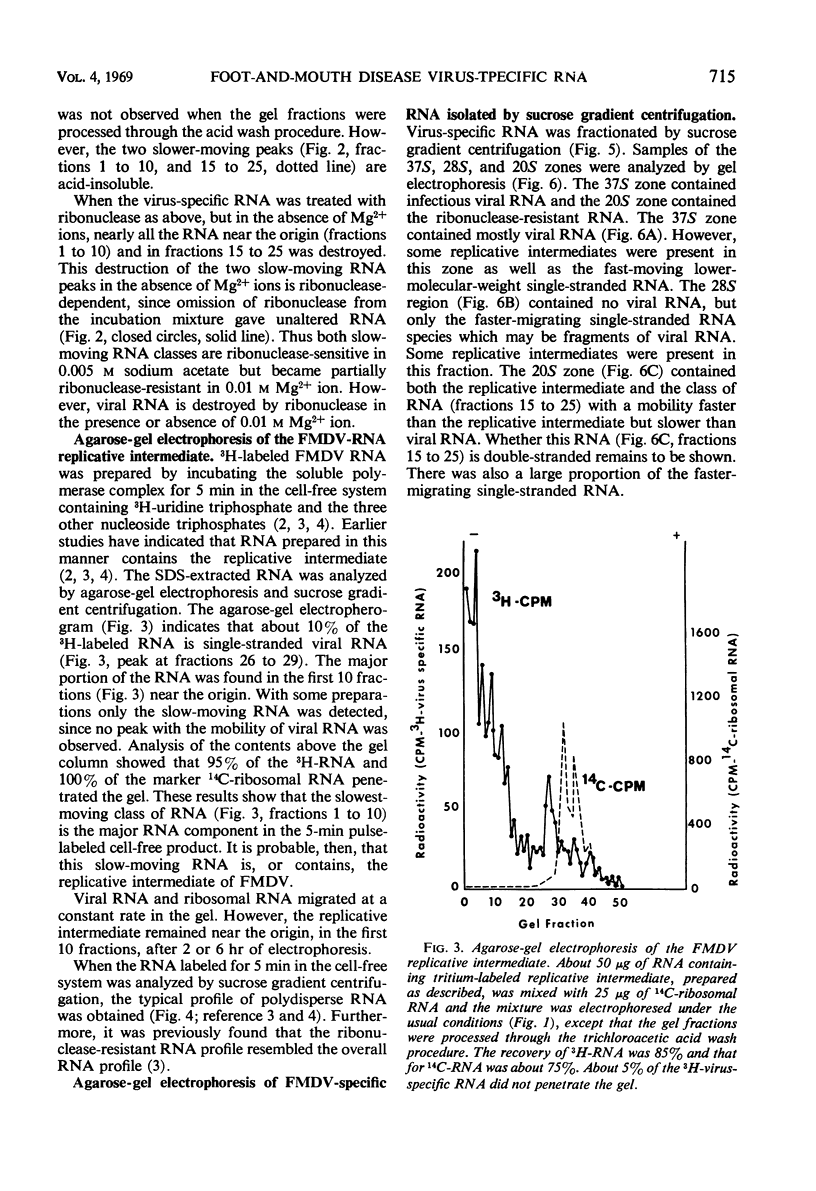
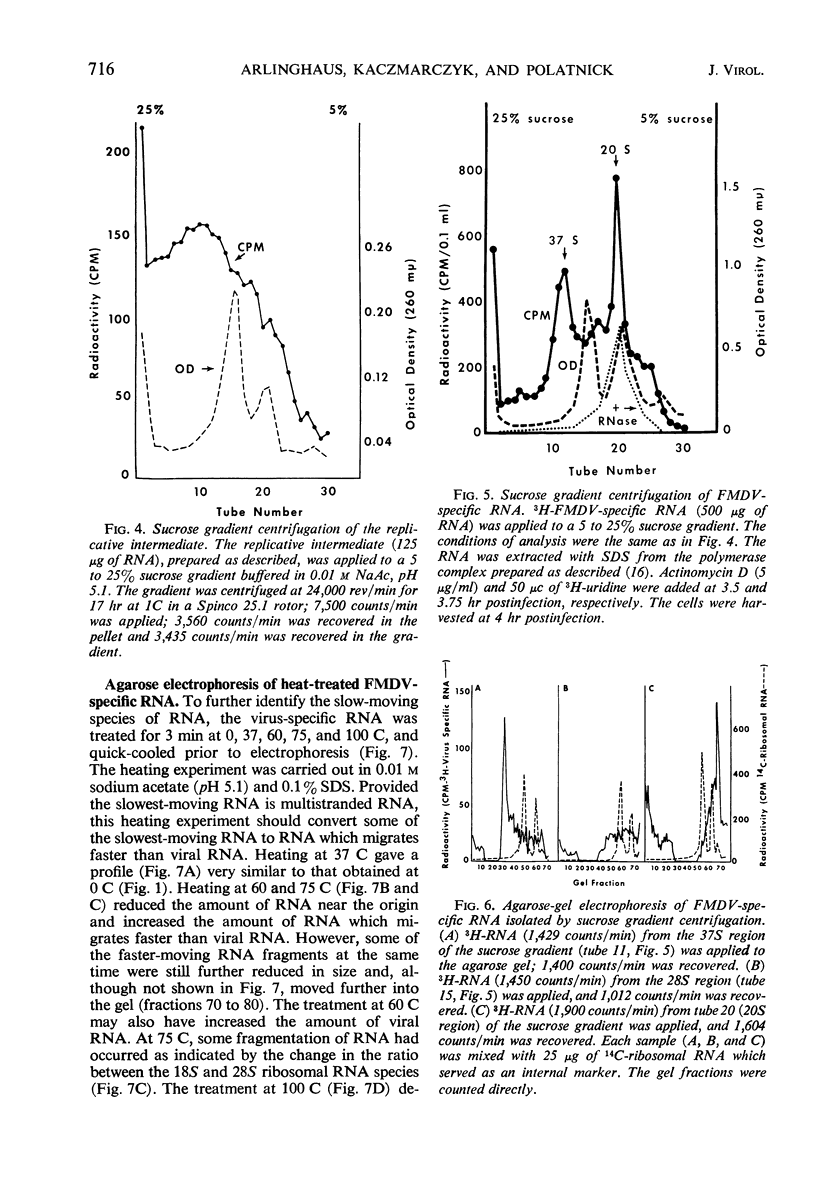
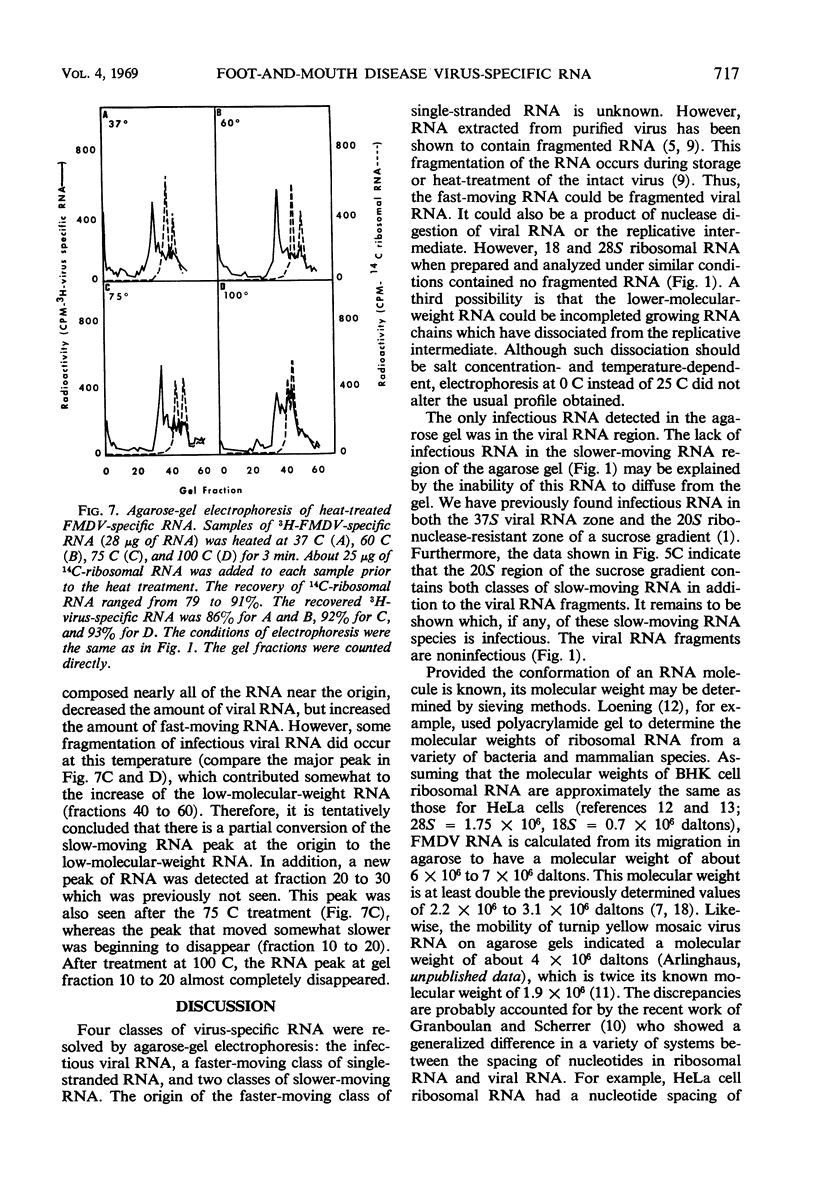
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV)-specific ribonucleic acid (RNA) was analyzed by electrophoresis on 0.5% agarose gels. Four classes of RNA were resolved as a function of mobility in agarose: two classes of slowly migrating multistranded RNA, the infectious viral RNA with intermediate mobility, and a minor fast-moving class of lower-molecular-weight single-stranded RNA. The major RNA species were infectious viral RNA and the slowest migrating class of multistranded RNA. The latter RNA was polydisperse when analyzed by sucrose gradient centrifugation, it was partially ribonuclease resistant, and it was the predominant RNA species labeled during the initial period of 3H-uridine triphosphate incorporation in the cell-free system. Heat treatment studies indicated that part of the slowest-moving RNA was degraded at 60 C and almost complete degradation was detected at 100 C. It was concluded that this RNA is the replicative intermediate in viral RNA synthesis. The second class of multistranded RNA contained both a ribonuclease-resistant RNA and a second RNA peak which was detected only after heat treatment at temperatures above 75 C. Fractions of FMDV-specific RNA isolated by sucrose gradient centrifugation were analyzed by agarose-gel electrophoresis. Infectious viral RNA was detected only in the 37S zone and was the major species of RNA in this part of the gradient. The ribonuclease-resistant RNA (the 20S zone) contained about equal amounts of multistranded RNA (both classes) and the low-molecular-weight single-stranded RNA. All sucrose gradient fractions between 20 and 40S were found to contain the replicative intermediate, although the major portion was detected in the 20 to 25S region.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlinghaus R. B., Bachrach H. L., Polatnick J. Site of foot-and-mouth disease virus-ribonucleic acid synthesis and some properties of its double-stranded ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. Detergent-solubilized RNA polymerase from cells infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Science. 1967 Dec 8;158(3806):1320–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3806.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. In vitro products of a membrane-free foot-and-mouth disease virus ribonucleic acid polymerase. Virology. 1969 Feb;37(2):252–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. The isolation of two enzyme-ribonucleic acid complexes involved in the synthesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus ribonucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):821–828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J., Vande Woude G. F. Studies on foot-and-mouth disease virus ribonucleic acid synthesis. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L. Foot-and-mouth disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:201–244. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L. Ribonucleic acid of foot-and-mouth disease virus: an ultrasensitive plaque assay. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):939–945. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Pace N. R., Spiegelman S. An analysis by gel electrophoresis of Q-beta-RNA complexes formed during the latent period of an in vitro synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1474–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Wild T. F. The effect of heat on the structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus and the viral ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 19;119(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granboulan N., Scherrer K. Visualisation in the electron microscope and size of RNA from animal cells. Eur J Biochem. 1969 May 1;9(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Longley W., Leberman R. Arrangement of protein subunits and the distribution of nucleic acid in turnip yellow mosaic virus. I. X-ray diffraction studies. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):315–343. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H., Hopkins J. W. Molecular weights of some HeLa ribosomal RNA's. J Mol Biol. 1969 Feb 14;39(3):545–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLATNICK J., BACHRACH H. L. PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION OF MILLIGRAM AMOUNTS OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS FROM BABY HAMSTER KIDNEY CELL CULTURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:368–373. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.368-373.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Bishop D. H., Spiegelman S. Examination of the Qbeta-replicase reaction by sucrose gradient and gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.771-778.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Arlinghaus R. B. Foot-and-mouth disease virus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase in baby hamster kidney cells. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROHMAIER K., MUSSGAY M. Bestimmung der Sedimentationskonstante eines infektiösen Prinzips mit Nucleinsäurecharakter aus dem Virus der Maul- und Klauenseuche mit Hilfe der Gradienten-Zentrifugation. Z Naturforsch B. 1959 Mar;14B(3):171–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Ogino T., Baba K. Estimation of relative molecular length of DNA by electrophoresis in agarose gel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



