Abstract
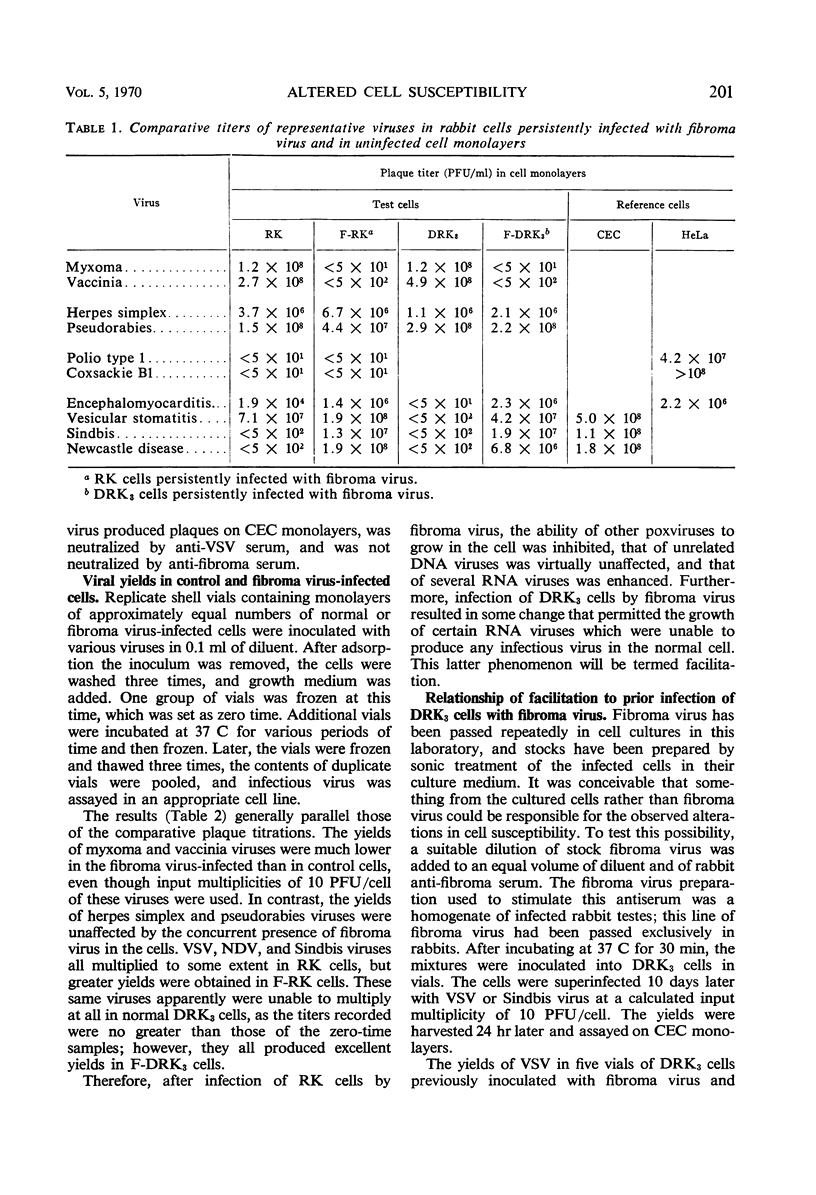
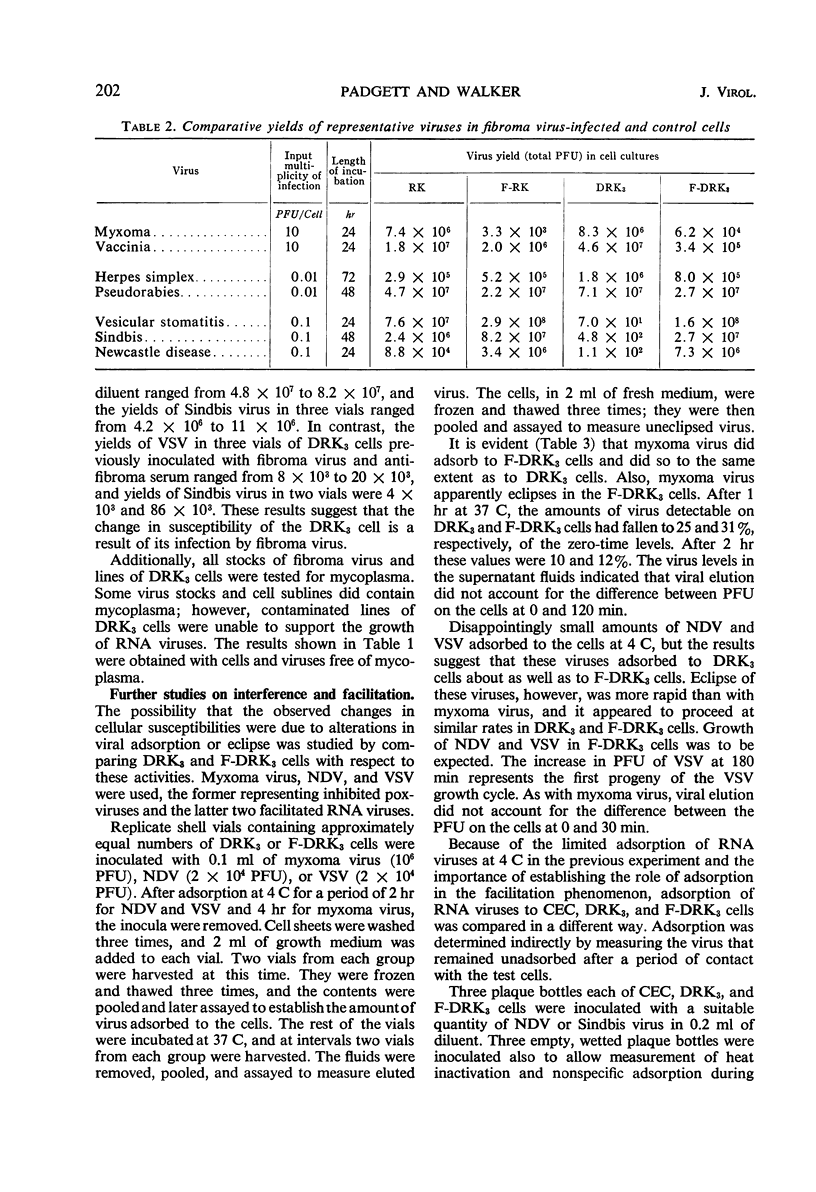
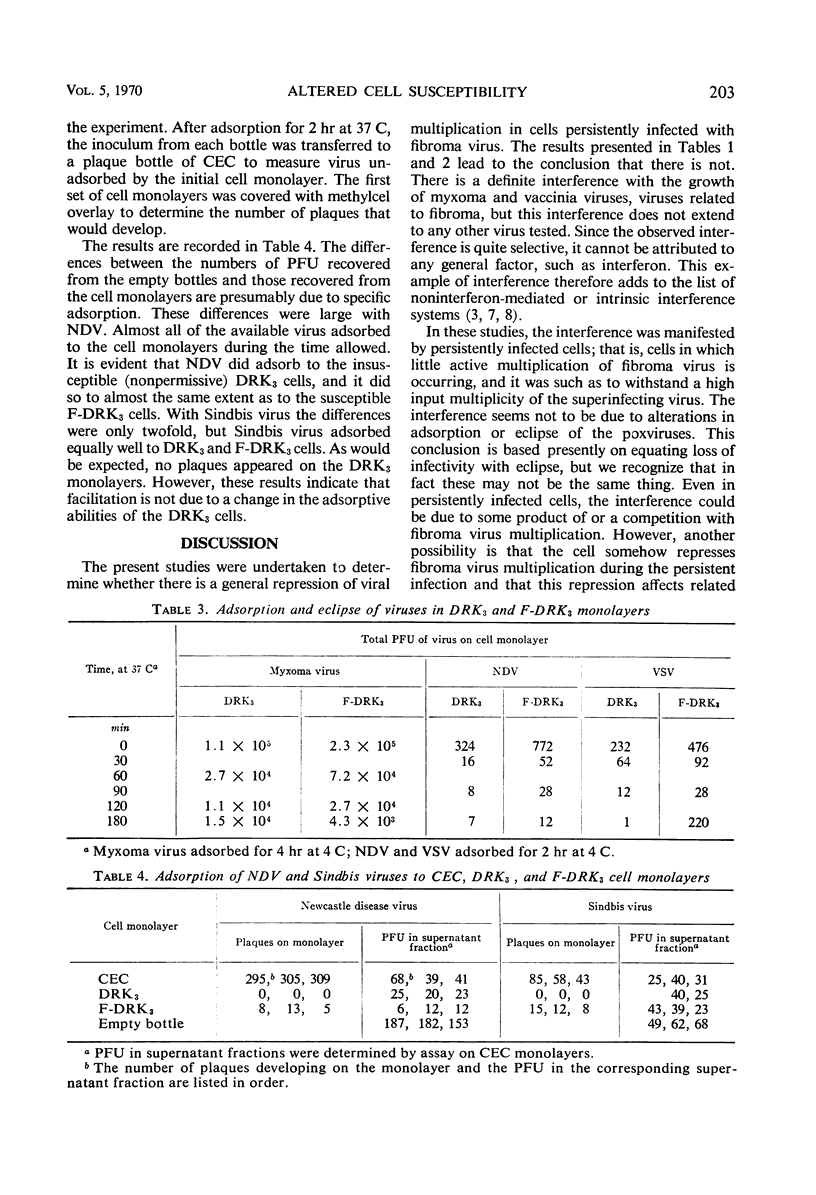
Shope fibroma virus establishes a persistent cytoplasmic infection in primary (RK) and serially cultivated (DRK3) rabbit kidney cells which is accompanied by a morphological alteration of the cells. The response of such cells to superinfection by other viruses was compared with that of control cells by determining plaque production and virus yield of superinfecting viruses. It was found that the growth of other poxviruses, myxoma and vaccinia, was greatly inhibited in the fibroma virus-infected cells, but that of pseudorabies and herpes simplex viruses, which are unrelated deoxyribonucleic acid viruses, was virtually unaffected. The ribonucleic acid (RNA) viruses, poliovirus 1 and coxsackievirus B1, did not produce plaques on either RK or fibroma virus-infected (F-RK) monolayers. However, the growth of several other RNA viruses, vesicular stomatitis virus, encephalomyocarditis virus, Sindbis virus, and Newcastle disease virus, was enhanced in F-RK cells. None of these latter RNA viruses produced any infectious progeny in DRK3 cells, but they all plaqued on and produced good yields in DRK3 cells persistently infected with fibroma virus. This phenomenon is termed facilitation. Facilitation results from the infection of DRK3 cells by fibroma virus. Neither interference nor facilitation were due to changes in the adsorption or eclipse of the superinfecting virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen V., Sueltmann S., Lawson C. Laboratory diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumonia in a public health laboratory. Health Lab Sci. 1967 Apr;4(2):90–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORDS C. E., HOLLAND J. J. INTERFERENCE BETWEEN ENTEROVIRUSES AND CONDITIONS EFFECTING ITS REVERSAL. Virology. 1964 Feb;22:226–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINDER D. R., FRIEDEWALD W. F. Effect of Semliki Forest virus on rabbit fibroma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Jun;77(2):272–276. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINZE H. C., WALKER D. L. RESPONSE OF CULTURED RABBIT CELLS TO INFECTION WITH THE SHOPE FIBROMA VIRUS. I. PROLIFERATION AND MORPHOLOGICAL ALTERATION OF THE INFECTED CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1185–1194. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1185-1194.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDINKO N. An analysis of interference between active polioviruses types 1 and 2 in HeLa cells. Virology. 1963 May;20:29–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Carver D. H. Intrinsic interference: a new type of viral interference. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):334–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.334-343.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADGETT B. L., MOORE M. S., WALKER D. L. Plaque assays for myxoma and fibroma viruses and differentiation of the viruses by plaque form. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:462–469. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



