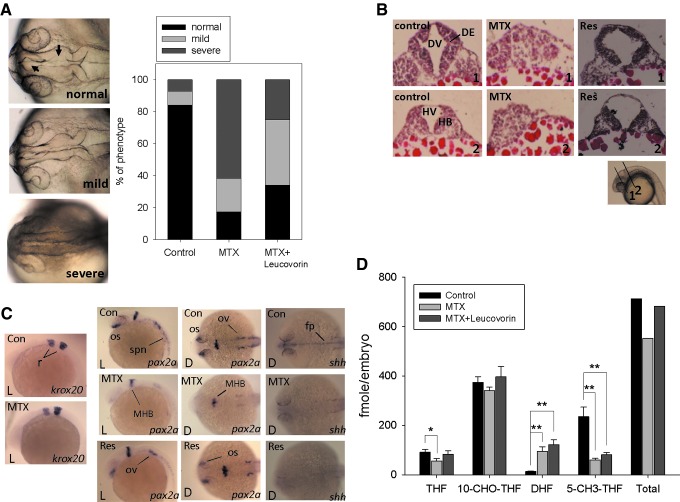
FIG. 5.
Methotrexate-induced morphological abnormality and altered folate composition in embryos are partly reversed by leucovorin. Methotrexate (with or without leucovorin) was added to the wells containing embryos at 6 hpf to 1.5 mM and collected at indicated time points for characterization. (A) Embryos were collected at 24 hpf and evaluated for gross morphology under light a dissecting microscope. Embryonic phenotype is categorized into normal, mild, and severe groups mainly based on brain ventricle formation. A total of ∼80 embryos were included for each group in three separate and independent trials. (B) Embryos were subjected to cryo-sectioning and HE stain for examining the brain ventricular cavity. Inset shows the position of cross-sections. Res, rescue (by adding methotrexate and leucovorin simultaneously); DE, diencephalon; DV, diencephalic ventricle; HB, hindbrain; HV, hindbrain ventricle. (C) The development of embryonic neural tissues was characterized at 24 hpf with in-situ hybridization using neural tissue specific probes krox20(rhombomere), shh (floor plate), and pax2a (mid-hindbrain boundary and spinal cord); Con, control, embryos without any treatment; MTX, methotrexate treated; Res, rescue; L, lateral view; D, dorsal view; r, rhombomere; os, optical stalk; ov, otic vesicle; spn, spinal cord; MHB, mid-hindbrain boundary; fp, floor plate. (D) Embryos were collected at 12 hpf and subjected to folate composition analysis with HPLC. The data presented are the averages of at least three independent experiments with different batches of embryos. “Total” refers to the sum of the four folate adducts examined in the study. *p<0.05, **p<0.005. hpf, hour postfertilization.