Abstract
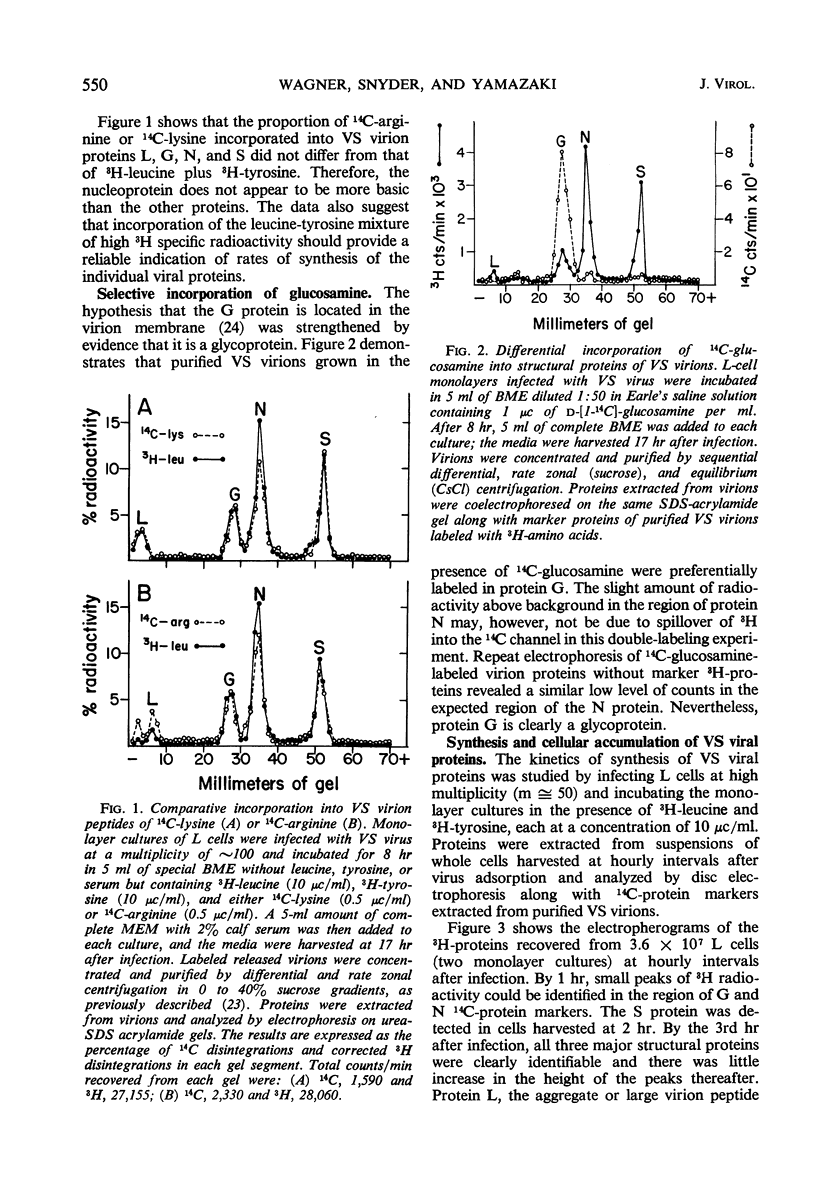
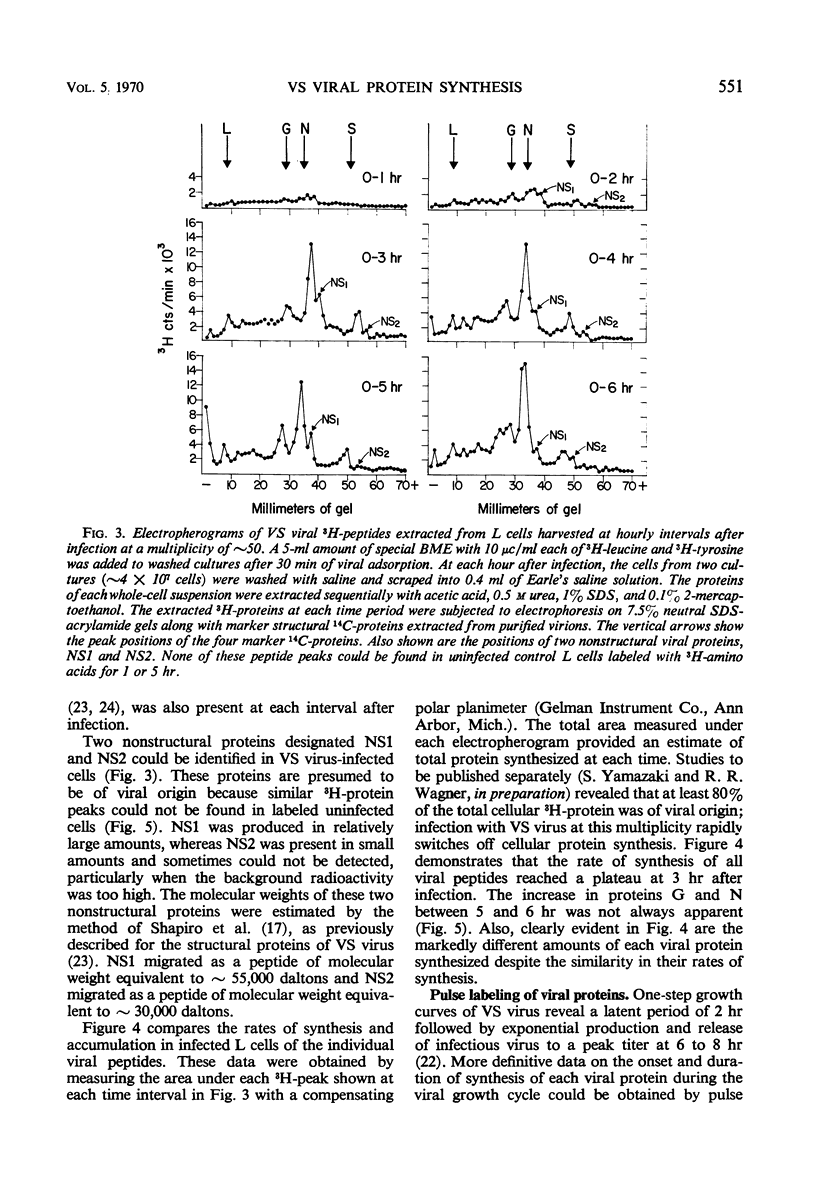
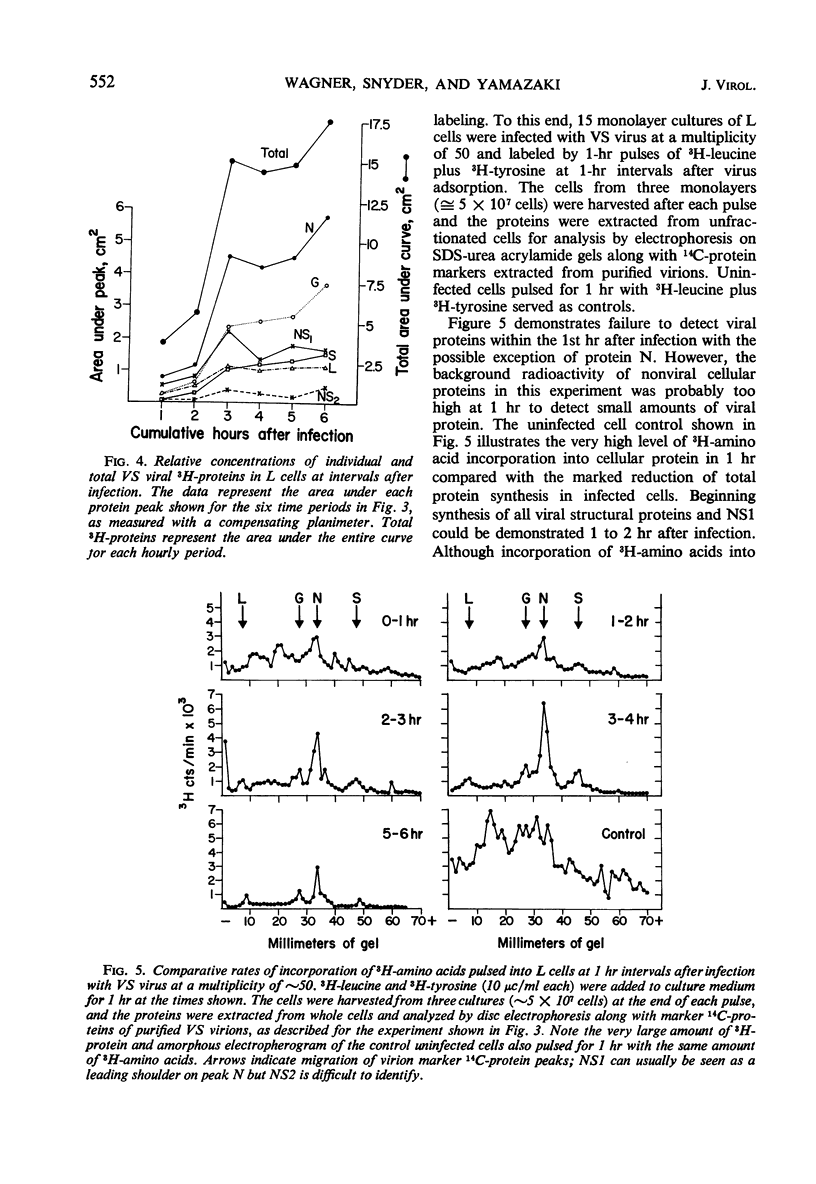
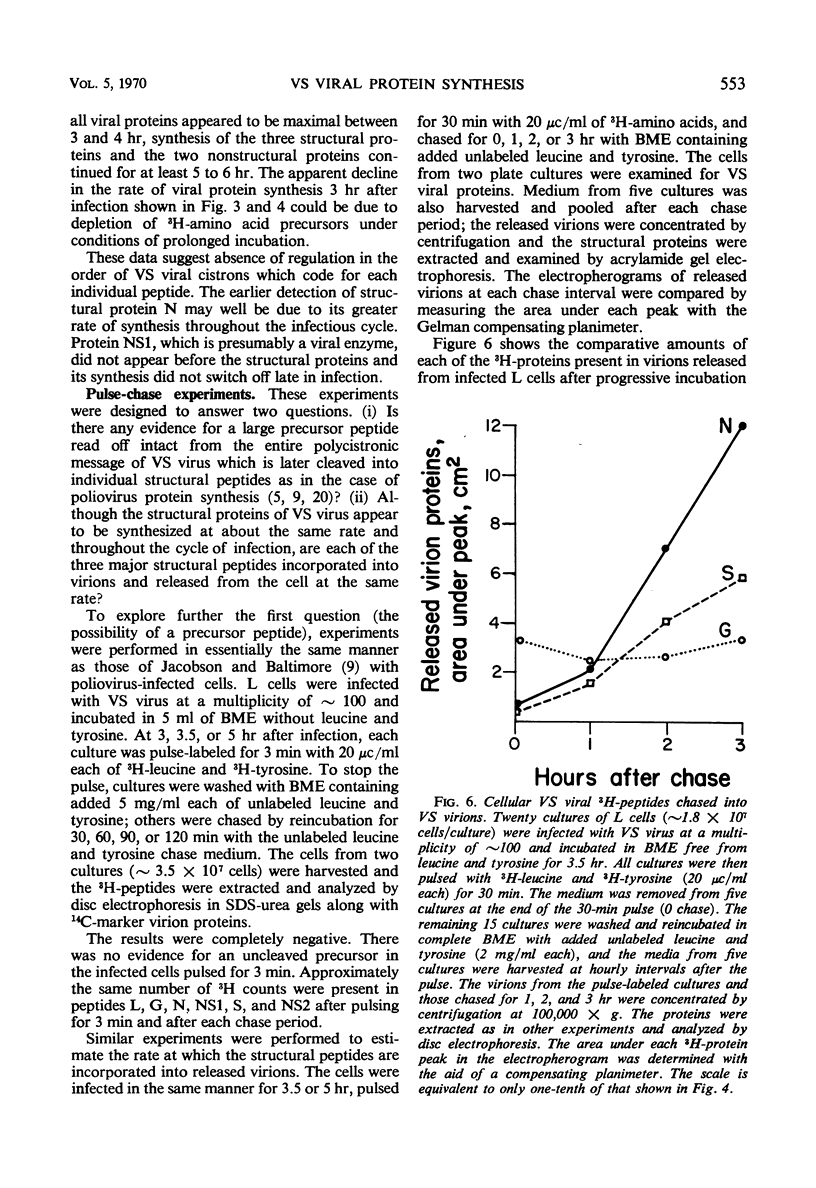
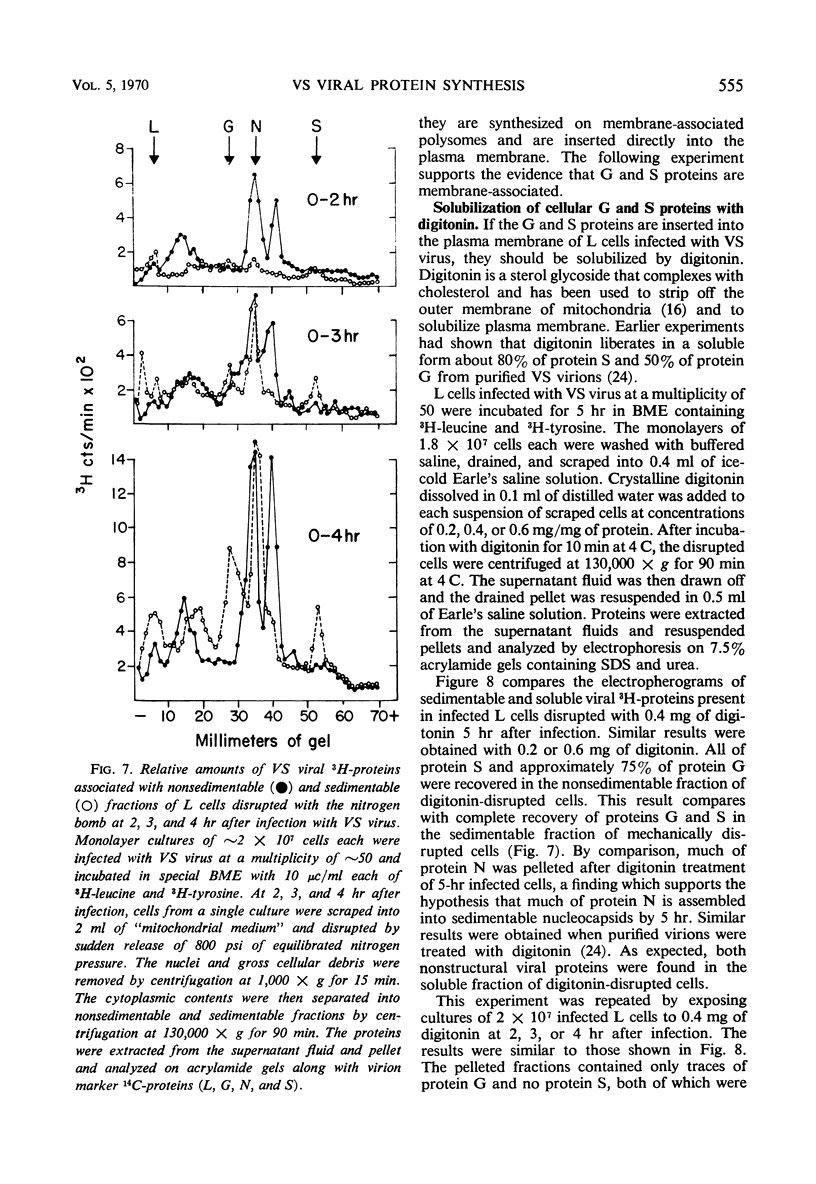
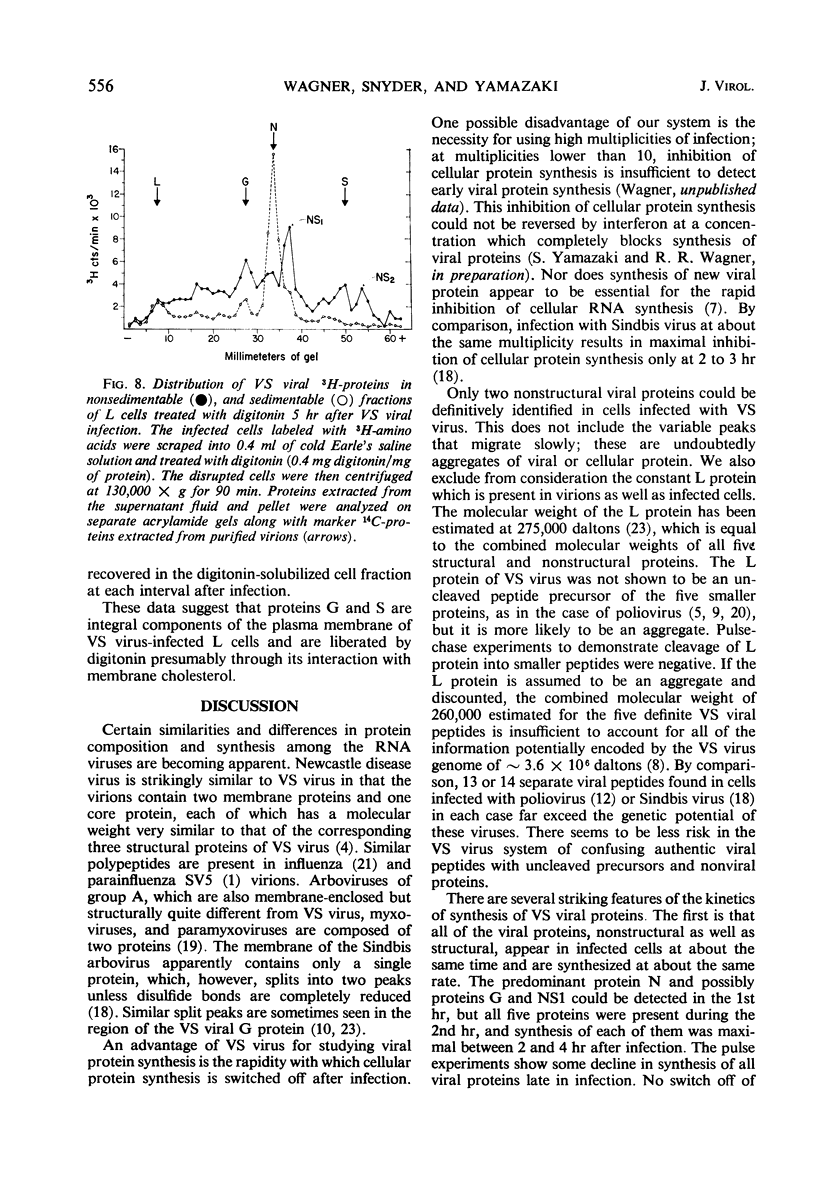
Five viral peptides synthesized in L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis (VS) virus were identified by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and designated as follows: nucleoprotein N, a membrane glycoprotein G, a membrane surface protein S, and two nonstructural proteins NS1 and NS2. A slowly migrating minor structural protein L also present in infected cells is probably an aggregate. Incorporation of 3H-amino acids into each viral protein could be detected by the 2nd hr after infection and even earlier for protein N which is synthesized in the greatest amount. There was no evidence of regulation of viral protein synthesis at the transcriptive level; nonstructural and structural proteins were synthesized throughout the cycle of infection. Short pulses of 3H-amino acids revealed no uncleaved precursor peptides that could be chased into structural peptides. Proteins N and S were chased into released virions but protein G was apparently incorporated into virions as it was being synthesized. VS viral proteins of infected cells were released by mechanically disrupting cytoplasmic membrane by nitrogen decompression and fractionated by high-speed centrifugation. Protein NS1 was present in the nonsedimentable cytoplasmic fraction throughout the cycle of infection. The nucleoprotein N was recovered primarily from the nonsedimentable fraction early in infection but aggregated into a sedimentable component, presumably the nucleocapsid, later in infection. Proteins G and S were always present in the sedimentable fraction of mechanically disrupted infected cells, presumably in association with plasma membrane. Exposure of infected cells to the membrane-dissolving agent, digitonin, resulted in solubilization of most of protein G and all of protein S but not of protein N. These experiments are compatible with the hypothesis that VS viral proteins G and S are synthesized at and inserted into plasma membrane which envelopes a nucleocapsid core to form the VS virion.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caliguiri L. A., Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. The proteins of the parainfluenza virus SV5. 1. Separation of virion polypeptides by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Grimley P. M. Inhibition of arbovirus assembly by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):292–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.292-299.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett A. J., Zee Y. C., Schaffer F. L., Talens L. Electron microscopic study of the morphogenesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1154–1162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1154-1162.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam E. A., Cheyne I. M., White D. O. The structural proteins of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):118–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90353-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Kiehn E. D. Specific cleavage of viral proteins as steps in the synthesis and maturation of enteroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Comparative sedimentation coefficients of RNA extracted from plaque-forming and defective particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of cellular RNA synthesis by nonreplicating vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Polyacrylamide gel analysis of viral antigens. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):404–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.404-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr Acrylamide-gel electrophorograms by mechanical fractionation: radioactive adenovirus proteins. Science. 1966 Feb 25;151(3713):988–990. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3713.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Summers D. F. Evidence for differences in size and composition of the poliovirus-specific polypeptides in infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):48–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, White D. O., Scharff M. D. The polypeptides of adenovirus. II. Soluble proteins, cores, top components and the structure of the virion. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):126–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Howatson A. F. The fine structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):268–281. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele C. M., Pfefferkorn E. R. Kinetics of incorporation of structural proteins into Sindbis virions. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):369–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.369-375.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C., Erwin V. G., Greenawalt J. W. The submitochondrial localization of monoamine oxidase. An enzymatic marker for the outer membrane of rat liver mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):719–735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Jr, Burge B. W., Darnell J. E. Sindbis virus infection of chick and hamster cells: synthesis of virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Jr, Burge B. W., Pfefferkorn E. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Identification of the membrane protein and "core" protein of Sindbis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Evidence for large precursor proteins in poliovirus synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):966–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Hampson A. W., White D. O. The polypeptides of influenza virus. 1. Cytoplasmic synthesis and nuclear accumulation. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVEY A. H., SNYDER R. M., RATCLIFF G. A., Jr, HYATT D. F. BIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF TWO PLAQUE VARIANTS OF VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS (INDIANA SEROTYPE). J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:112–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACH D. F., KAMAT V. B. PLASMA AND CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE FRAGMENTS FROM EHRLICH ASCITES CARCINOMA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:721–728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. A., Snyder R. M. Structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):395–403. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.395-403.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. C., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the structural components of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):611–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.611-618.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. O., Scharff M. D., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. 3. Synthesis in infected cells. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Meezan E., Black P. H., Robbins P. W. Comparative studies on the carbohydrate-containing membrane components of normal and virus-transformed mouse fibroblasts. I. Glucosamine-labeling patterns in 3T3, spontaneously transformed 3T3, and SV-40-transformed 3T3 cells. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2509–2517. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



