Abstract
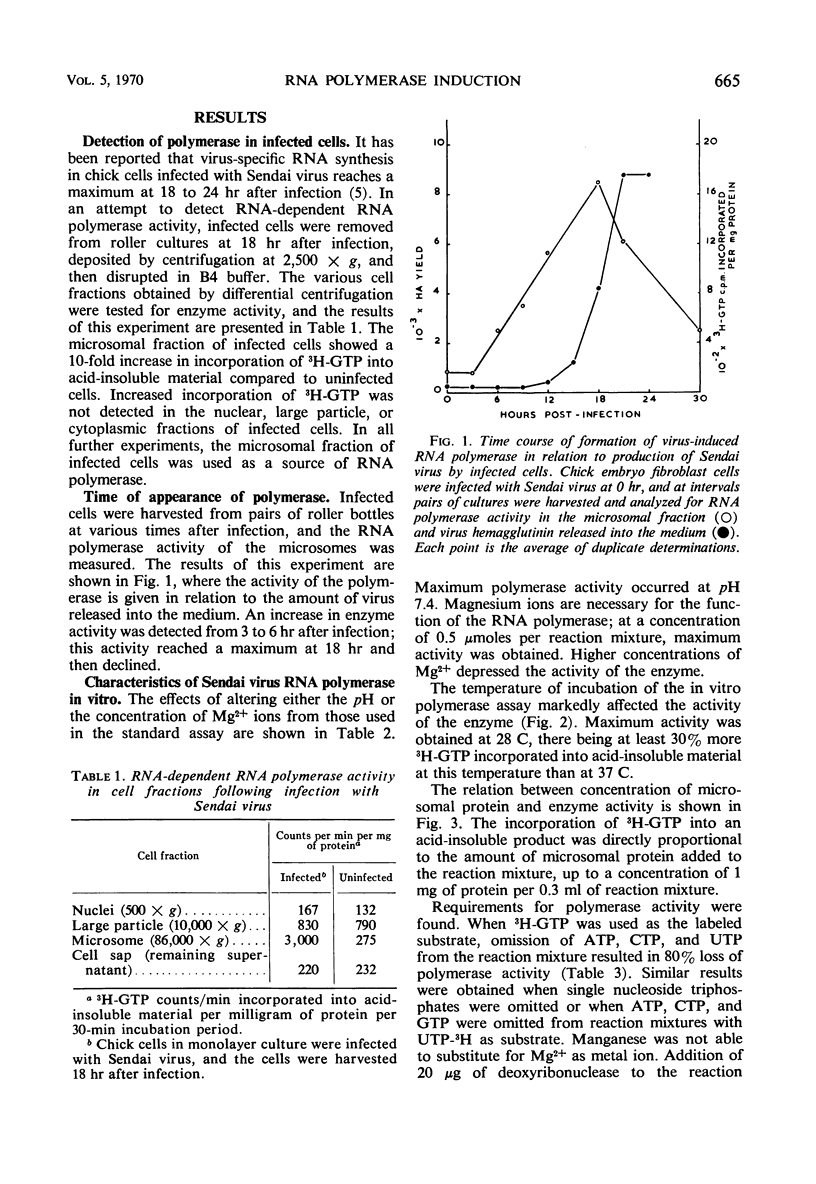
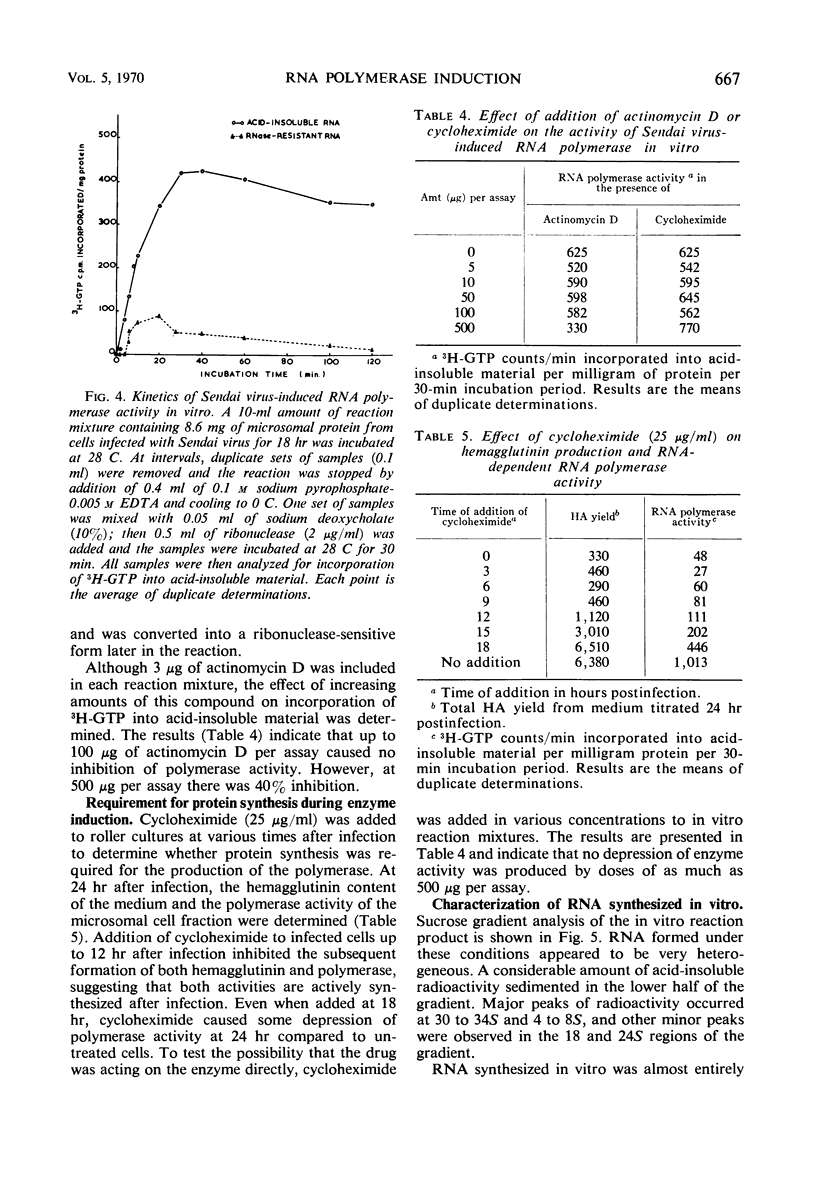
A ribonucleic acid (RNA)-dependent RNA polymerase was induced in chick embryo fibroblast cells after infection with Sendai virus (parainfluenza 1 virus). The enzyme was associated with the microsomal fraction of infected cells and reached maximum detectable activity at 18 hr after virus infection. The activity of the enzyme in vitro was dependent on the presence of added magnesium ions and all four nucleoside triphosphates and was not inhibited by actinomycin D. The RNA synthesized by the enzyme in vitro was sensitive to ribonuclease and consisted of a complex mixture of RNA species including 34S, 24S, and 18S components. Similar RNA components were detected in the microsomal fraction of Sendai virus-infected cells by labeling with 3H-uridine from 17 to 18 hr postinfection in the presence of actinomycin D. Of the RNA synthesized by Sendai virus-induced RNA polymerase in vitro, 98% became insensitive to ribonuclease after annealing with RNA extracted from purified Sendai virus particles.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M. A NEW RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE APPEARING AFTER MENGOVIRUS INFECTION OF L-CELLS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3395–3400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY R. D. FACTORS WHICH AFFECT THE RELEASE OF NEWCASTLE DISEASE AND SENDAI VIRUSES FROM INFECTED ALLANTOIC CELLS. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 May;39:229–238. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-2-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY R. D., IVES D. R., CRUICKSHANK J. G. Participation of deoxyribonucleic acid in the multiplication of influenza virus. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1139–1140. doi: 10.1038/1941139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry R. D., Bukrinskaya A. G. The nucleic acid of Sendai virus and ribonucleic acid synthesis in cells infected by Sendai virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):71–79. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair C. D., Robinson W. S. Replication of Sendai virus. I. Comparison of the viral RNA and virus-specific RNA synthesis with Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASKY A. J., SIMON L., HOLPER J. C. INTERFERONS: SELECTIVITY AND SPECIFICITY OF ACTION IN CELL-FREE SYSTEMS. Science. 1964 Jun 26;144(3626):1581–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3626.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasky A. J., Roderick W. R., Holper J. C. Viral synthetase inhibitors as antiviral agents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 30;130(1):412–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb12577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J. Reovirus-specific, single-stranded RNA's synthesized in vitro with enzyme purified from reovirus-infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):423–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. P., Walters C. P. Influenza virus-induced ribonucleic acid nucleotidyltransferase and the effect of actinomycin D on its formation. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):231–235. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E., Liu S. L., Martin E. M., Work T. S. Properties of a virus-induced RNA polymerase in ascites cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):62–76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W. Newcastle disease virus RNA. II. Preferential synthesis of RNA complementary to parental viral RNA by chick embryo cells. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):204–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahy B. W., Bromley P. A. Synthesis of ribonuclease-resistant ribonucleic acid by fowl-plague-virus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):64P–64P. doi: 10.1042/bj1140064pa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. M., Sonnabend J. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase catalyzing synthesis of double-stranded arbovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):97–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.97-109.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Reversible inhibition of induction of mengovirus RNA polymerase and of virus maturation in Novikoff rat hepatoma cells by phenethyl alcohol. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Replication of mengovirus. II. General properties of the viral-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2327–2332. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2327-2332.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Arlinghaus R. B. Foot-and-mouth disease virus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase in baby hamster kidney cells. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruck B. J., Brammer K. W., Page M. G., Coombes J. D. The detection and characterization of an induced RNA polymerase in the chorioallantoic membranes of embryonated eggs infected with influenza A2 virus. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90345-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Rott R. Ribonucleic acid nucleotidyl transferase induced in chick fibroblasts after infection with Newcastle disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jun;4(4):565–570. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-4-4-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Burke D. C. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in chick embryo cells infected with fowl-plague virus. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):429–438. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.429-438.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Yin F. H. Sindbis virus-induced viral ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):599–604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.599-604.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):36–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.36-44.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. G., Bader J. P. Viral ribonucleic acid polymerase: chick-embryo cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus or Rous-associated virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 10;103(4):549–557. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


