Abstract
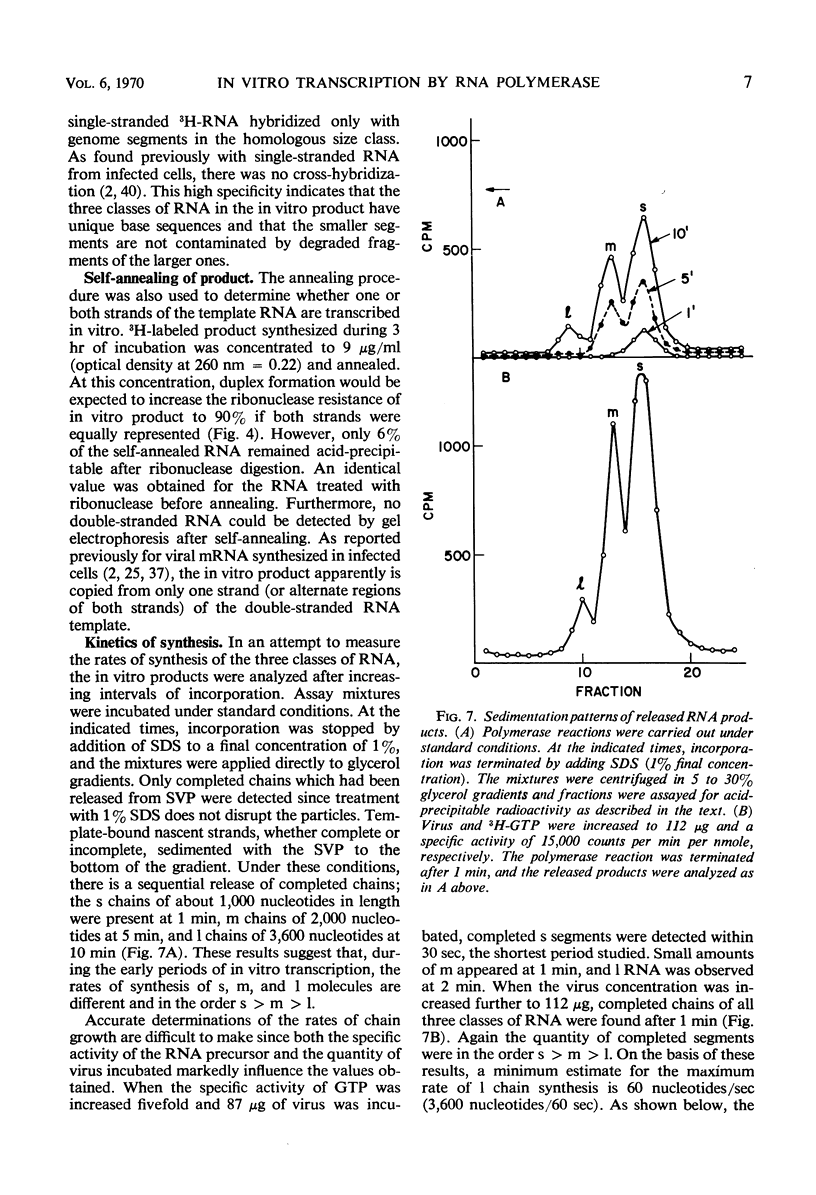
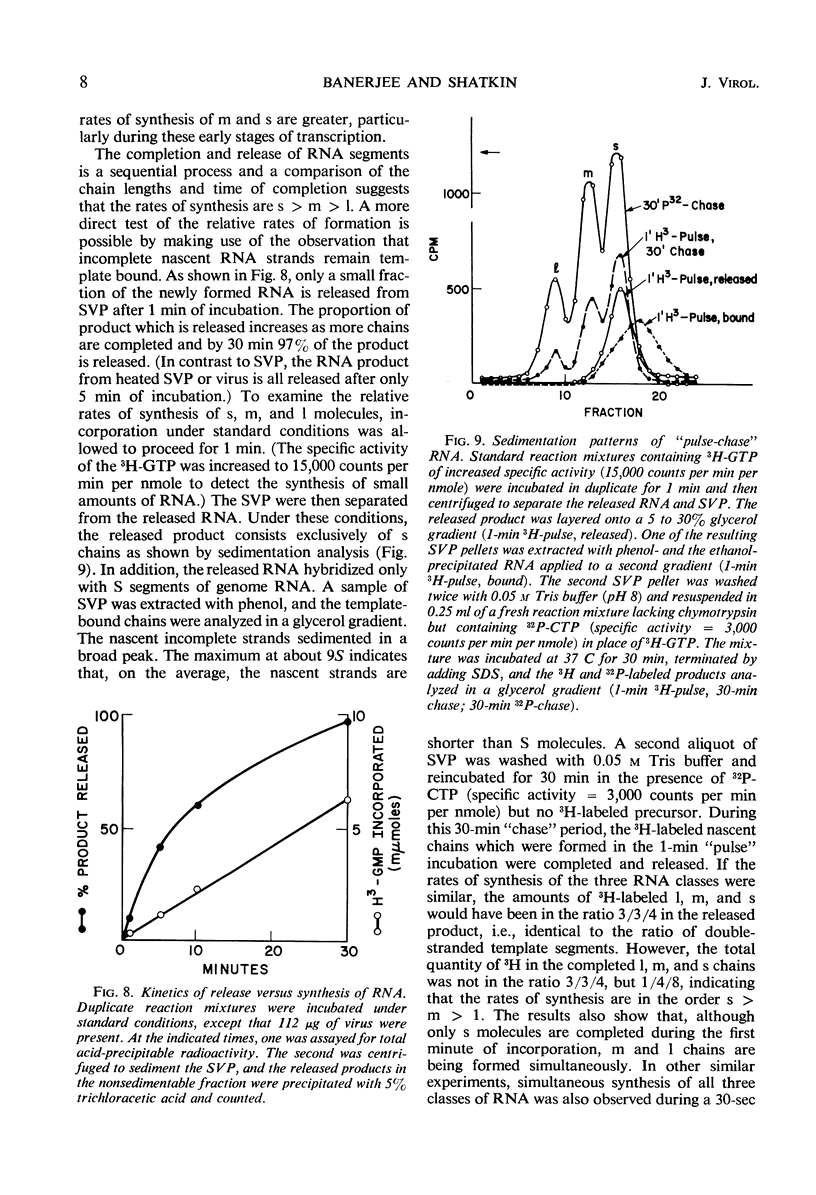
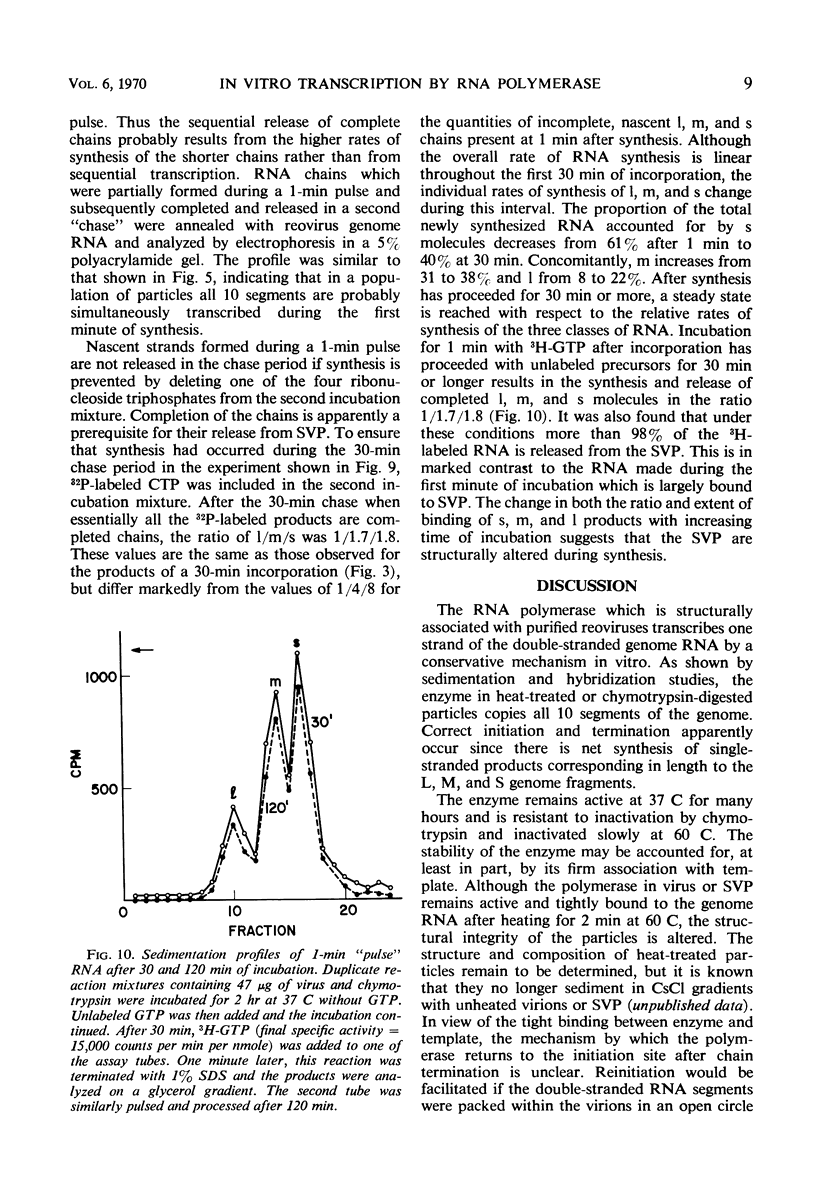
Digestion of purified reovirus type 3 with chymotrypsin degrades 70% of the viral protein and converts the virions to subviral particles (SVP). The SVP contain 3 of the 6 viral structural proteins and all 10 double-stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) genome segments but not adenine-rich, single-stranded RNA. An RNA polymerase which is structurally associated with SVP transcribes one strand of each genome segment by a conservative mechanism in vitro. The single-stranded products include large (1.2 × 106 daltons), medium (0.7 × 106 daltons), and small (0.4 × 106 daltons) molecules which hybridize exclusively with the corresponding genome segments. The enzyme obtained by heating virions at 60 C synthesizes similar products. Kinetic and pulse-chase studies indicate that the different-sized products are synthesized simultaneously but at rates which are in the order: small > medium > large.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellamy A. R., Joklik W. K. Studies on reovirus RNA. II. Characterization of reovirus messenger RNA and of the genome RNA segments from which it is transcribed. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Joklik W. K. Studies on the A-rich RNA of reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1389–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Shapiro L., August J. T., Joklik W. K. Studies on reovirus RNA. I. Characterization of reovirus genome RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
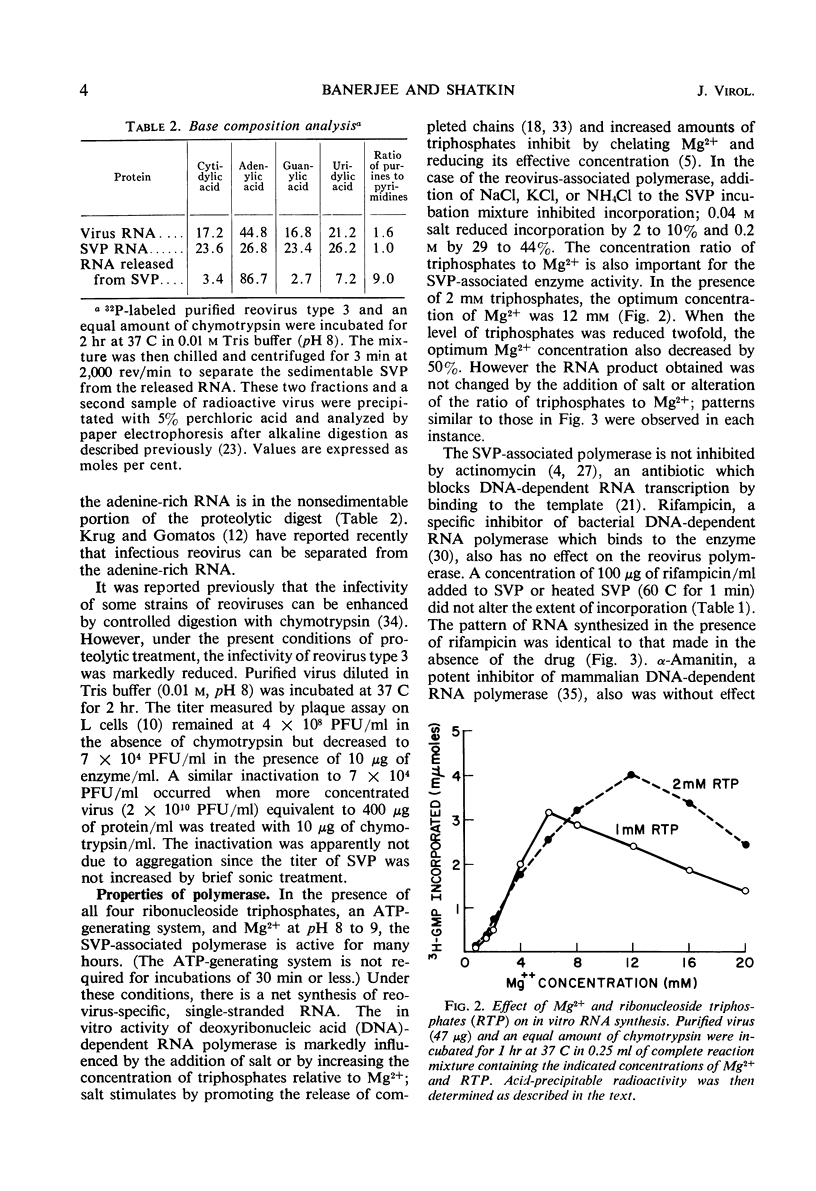
- Boyer P. D. The inhibition of pyruvate kinase by ATP: a Mg++ buffer system for use in enzyme studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 10;34(5):702–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90795-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
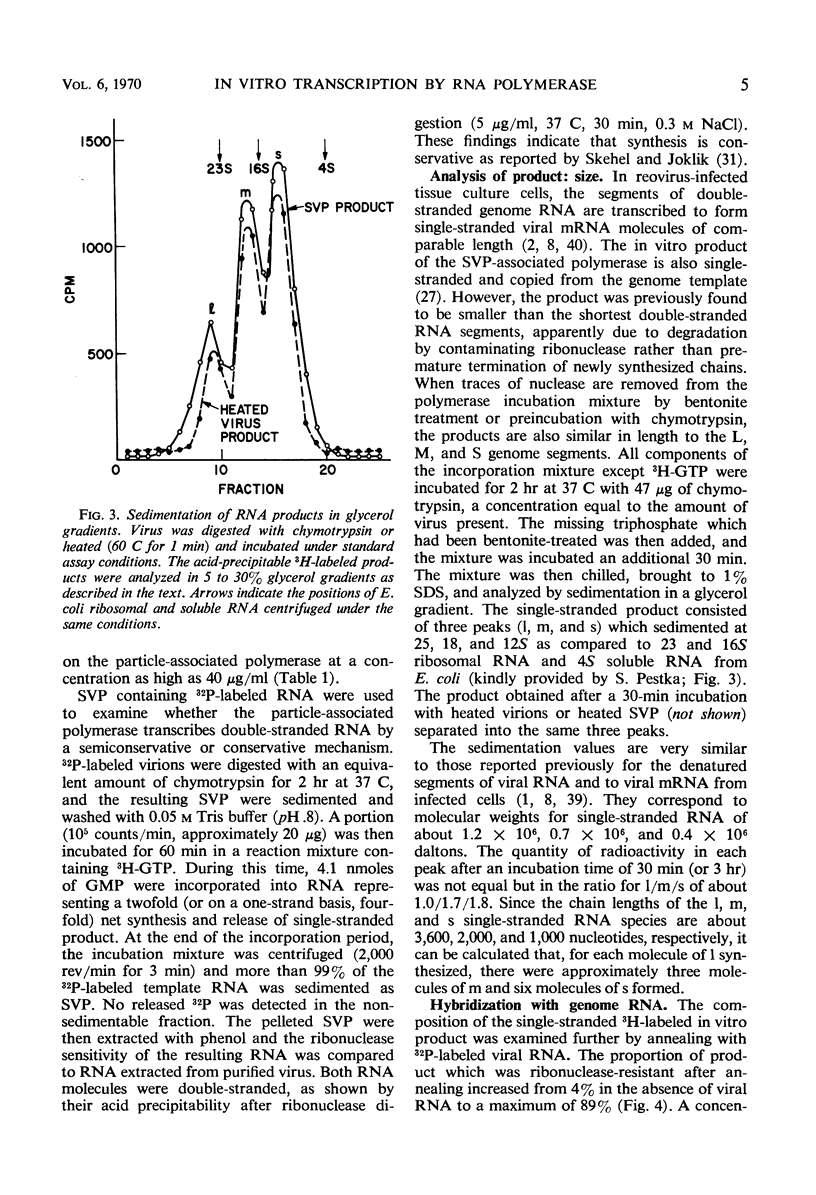
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SINGER B., TSUGITA A. Purification of viral RNA by means of bentonite. Virology. 1961 May;14:54–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMATOS P. J., TAMM I., DALES S., FRANKLIN R. M. Reovirus type 3: physical characteristics and interaction with L cells. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:441–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
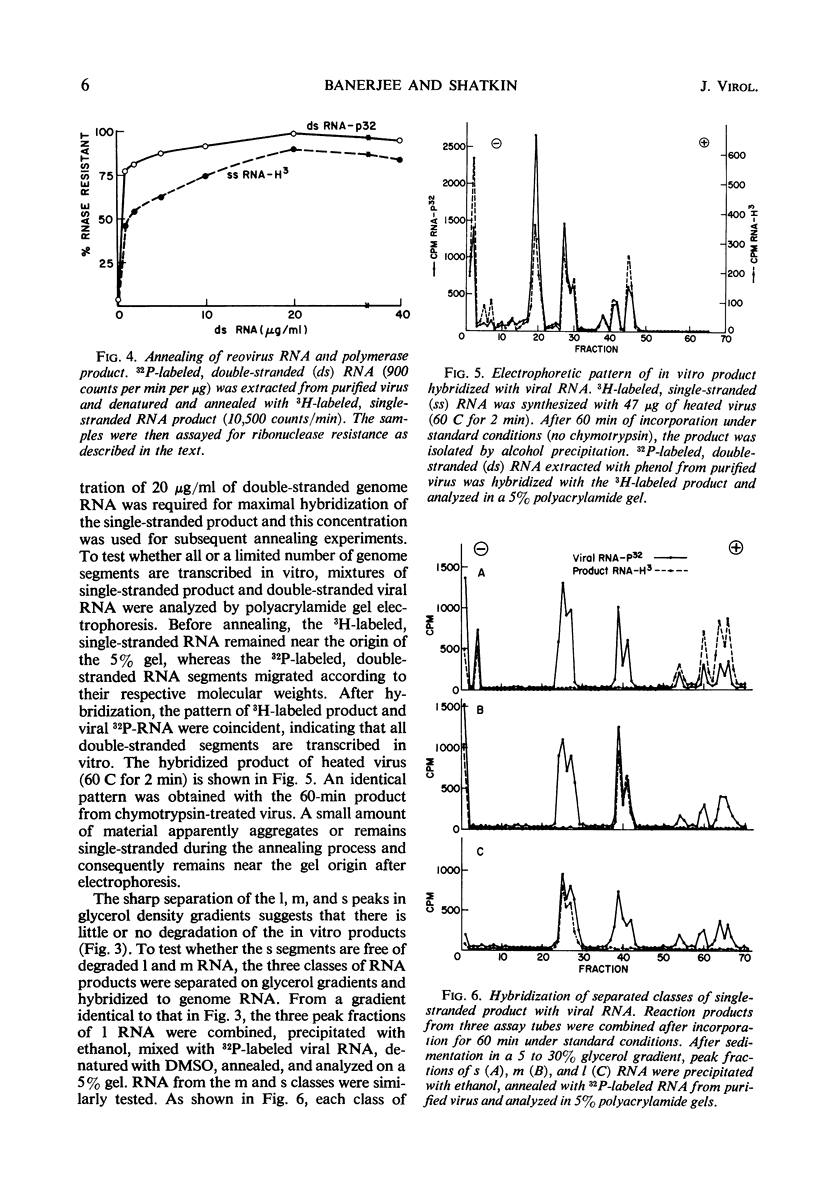
- Gomatos P. J. RNA synthesis in reovirus-infected L929 mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1798–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Tamm I. THE SECONDARY STRUCTURE OF REOVIRUS RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):707–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., McAuslan B. R. Poxvirus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug R. M., Gomatos P. J. Absence of adenine-rich ribonucleic acid from purified infectious reovirus 3. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.642-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus induced RNA in L cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90711-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski L. J., Kalmakoff J., Tanada Y. Characterization of a Ribonucleic Acid Polymerase Activity Associated with Purified Cytoplasmic Polyhedrosis Virus of the Silkworm Bombyx mori. J Virol. 1969 Dec;4(6):857–865. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.6.857-865.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Shatkin A. J. Structural proteins of reoviruses. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1353–1359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1353-1359.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYOR H. D., JAMISON R. M., JORDAN L. E., VANMITCHELL M. REOVIRUSES. II. STRUCTURE AND COMPOSITION OF THE VIRION. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1548–1556. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1548-1556.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra U., Barash F. DNA-dependent synthesis of RNA by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: release and reinitiation of RNA chains from DNA templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):779–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Grace J. T., Jr RNA polymerase activity in purified infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2280–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich E., Goldberg I. H. Actinomycin and nucleic acid function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964;3:183–234. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60742-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEBRING E. D., SALZMAN N. P. AN IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR MEASURING THE DISTRIBUTION OF P32O4--AMONG THE NUCLEOTIDES OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Anal Biochem. 1964 May;8:126–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Inactivity of purified reovirus RNA as a template for E. coli polymerases in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1721–1728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Rada B. Reovirus-directed ribonucleic acid synthesis in infected L cells. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):24–35. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.24-35.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D., Loh P. Separation of ten reovirus genome segments by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.986-991.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. Single-stranded, adenine-rich RNA from purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):246–253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the in vitro transcription of reovirus RNA catalyzed by reovirus cores. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):822–831. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. G., Davie E. W., Epstein R., Tissières A. Effects of cations on DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1739–1746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Fiume L. Studies on the pathogenesis of liver necrosis by alpha-amanitin. Effect of alpha-amanitin on ribonucleic acid synthesis and on ribonucleic acid polymerase in mouse liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):779–782. doi: 10.1042/bj1050779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASQUEZ C., TOURNIER P. The morphology of reovirus. Virology. 1962 Aug;17:503–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90149-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Graham A. F. Structural units of reovirus ribonucleic acid and their possible functional significance. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):665–677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.665-677.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):36–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.36-44.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Millward S., Graham A. F. Regulation of transcription of the Reovirus genome. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 28;36(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Prevec L., Graham A. F. Specificity in transcription of the reovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1040–1046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]