Abstract
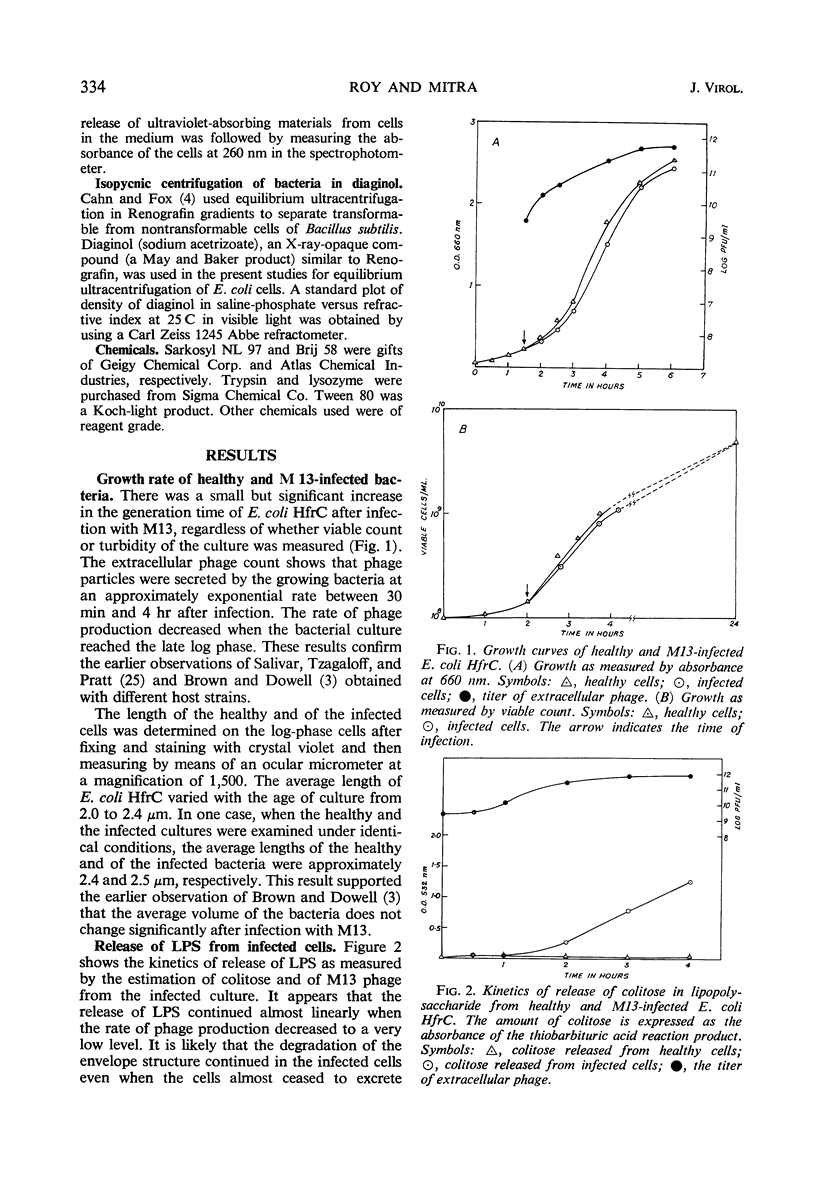
Male strains of Escherichia coli infected with filamentous phage M13 released the progeny phage particles from intact cells. At the same time, the cells continued to grow and multiply at a slightly lower rate than the uninfected cells. Concomitant with the phage release, lipopolysaccharide from the cell wall of the infected cells was also released. The buoyant density of E. coli HfrC in diaginol, 1.25 g/cc, did not change as a result of infection. Detergents like sodium dodecyl sulfate and Sarkosyl specifically lysed the infected cells. The infected cells showed enhanced fragility as indicated by inactivation by various stresses, namely heat, osmotic shock, and freezing and thawing. It is concluded that the infection with M13 causes certain alterations in the surface structure of E. coli, thus making the cells more fragile.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretz H. W., Kocka F. E. Resistance to actinomycin D of Escherichia coli after frozen storage. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jul;13(7):914–917. doi: 10.1139/m67-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown L. R., Dowell C. E. Replication of coliphage M-13. I. Effects on host cells after synchronized infection. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1290–1295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1290-1295.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CYNKIN M. A., ASHWELL G. Estimation of 3-deoxy sugars by means of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. Nature. 1960 Apr 9;186:155–156. doi: 10.1038/186155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahn F. H., Fox M. S. Fractionation of transformable bacteria from ocompetent cultures of Bacillus subtilis on renografin gradients. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.867-875.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falaschi A., Kornberg A. A lipopolysaccharide inhibitor of a DNA methyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1713–1720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH E. C. The isolation of guanosine diphosphate colitose from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 8;39:377–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN-BERLING H., DUERWALD H., BEULKE I. EIN FAEDIGER DNS-PHAGE (FD) UND EIN SPHAERISCHER RNS-PHAGE (FR) WIRTSSPEZIFISCH FUER MAENNLICHE STAEMME VON E. COLI. III. BIOLOGISCHES VERHALTEN VON FD UND FR. Z Naturforsch B. 1963 Nov;18:893–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFSCHNEIDER P. H., PREUSS A. M 13 BACTERIOPHAGE LIBERATION FROM INTACT BACTERIA AS REVEALED BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Mol Biol. 1963 Oct;7:450–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. ACTINOMYCIN SENSITIVITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 4;18:13–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90874-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEB T. Isolation of a bacteriophage specific for the F plus and Hfr mating types of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1960 Mar 25;131(3404):932–933. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3404.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide by EDTA treatment of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvin D. A., Schaller H. The topology of DNA from the small filamentous bacteriophage fd. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80204-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Ashman D. F., Price T. D. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane on release of the acid-soluble nucleotide pool and on breakdown of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1360–1368. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1360-1368.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POSTGATE J. R., HUNTER J. R. On the survival of frozen bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Nov;26:367–378. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-3-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D., Erdahl W. S. Genetic control of bacteriophage M13 DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):181–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REPASKE R. Lysis of gram-negative organisms and the role of versene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Nov;30(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell A. D., Harries D. Damage to Escherichia coli on exposure to moist heat. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1394–1399. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1394-1399.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinskey T. J., Silverman G. J. Characterization of injury incurred by Escherichia coli upon freeze-drying. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):429–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.429-437.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



