Abstract
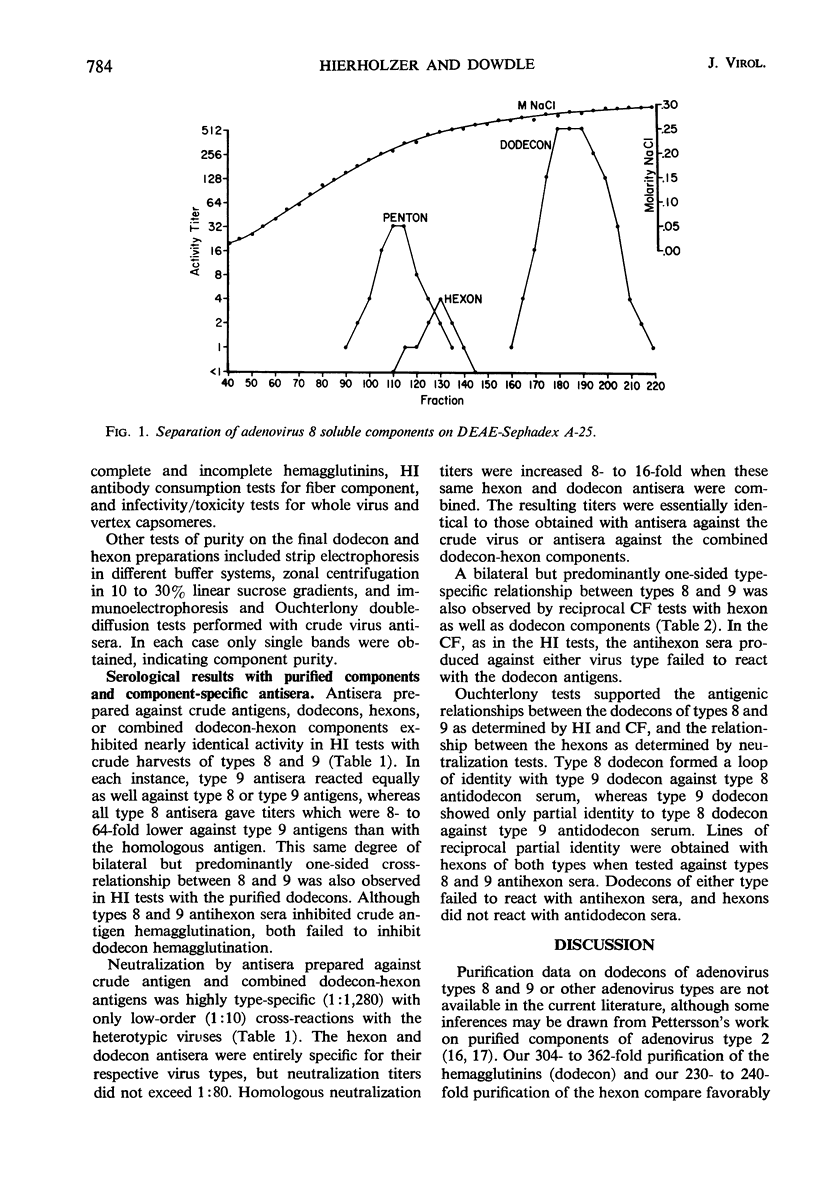
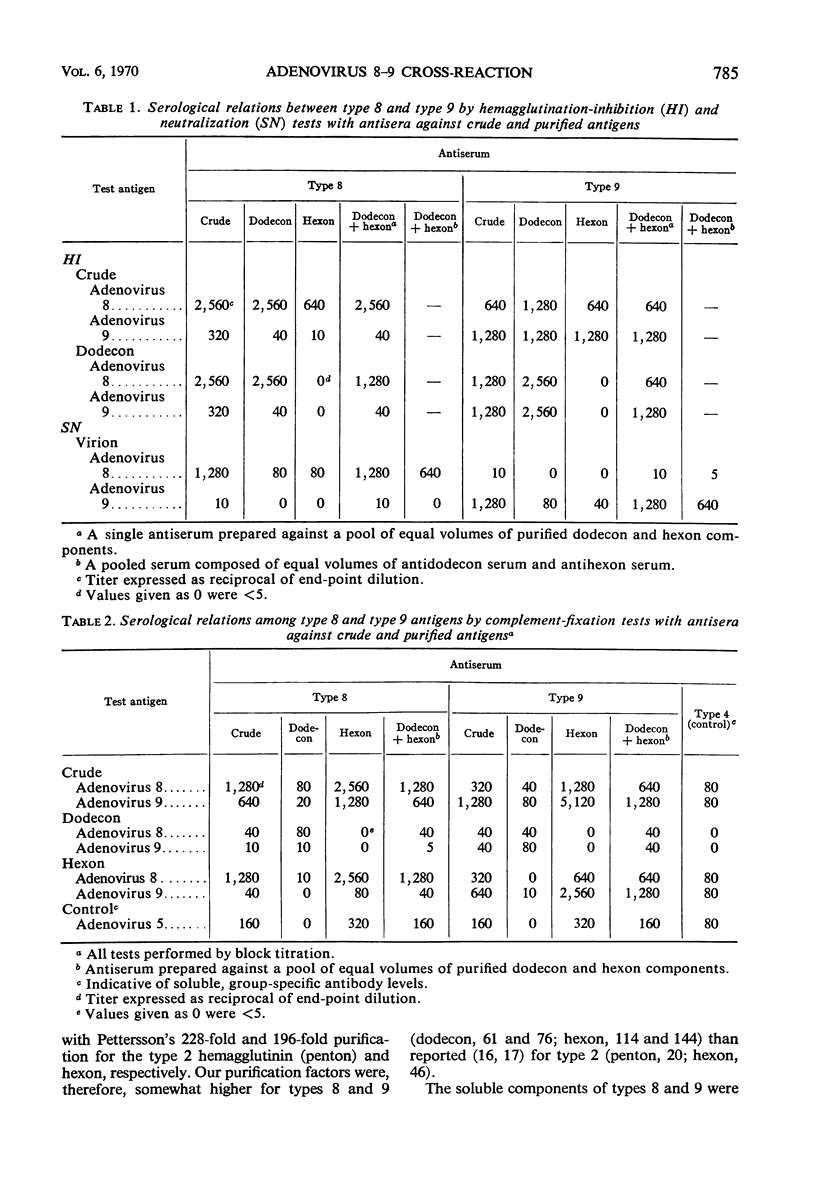
The dedecon and hexon components of adenovirus types 8 and 9 have been extensively purified for use in establishing the basis of the cross-reaction between these types. Dodecons, the complete hemagglutinins, were purified 304- to 362-fold by fluorocarbon extraction, calcium phosphate batch chromatography, and ion-exchange column chromatography. Hexons, the group complement-fixation (CF) antigens, were purified 230- to 240-fold by erythrocyte adsorption, ion-exchange chromatography, and exclusion chromatography. Component antisera prepared in rabbits were tested in reciprocal fashion with crude virus and dodecon and hexon components. By hemagglutination-inhibition (HI), the dodecons of types 8 and 9 demonstrated the same predominantly one-sided relationship characteristic of the crude antigens. Some neutralizing activity was associated with both dodecons and hexons of each type. However, combining anti-dodecon and anti-hexon sera or producing antisera against the combined dodecon-hexon components resulted in neutralizing titers which were identical to titers obtained with antisera against the crude virus harvests. Dedecons of each type appear to share at least one antigenic determinant with hexons of the same type, and this determinant may reside on the vertex capsomere. Hexons possess group- and type-specific determinants, as shown by CF, neutralization, and immunodiffusion tests, and may exhibit some minor relationship between types 8 and 9. The results with the purified components are consistent with the predominantly one-sided antigenic relationship between types 8 and 9 in the conventional HI tests and the largely type-specific relationship by neutralization tests.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GESSLER A. E., BENDER C. E., PARKINSON M. C. A new and rapid method for isolating viruses by selective fluorocarbon deproteinization. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Jun;18(8):701–703. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1956.tb00497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H., Bauer H., Frank H., Wigand R. The structure of group II adenoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1967 Oct;1(4):553–560. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-4-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H., Meiser W., Lengyel A., Wigand R. The serological relationship of the soluble antigens of adenovirus type 19. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):331–340. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Suggs M. T., Hall E. C. Standardized viral hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition tests. II. Description and statistical evaluation. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):824–833. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.824-833.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén L., Pereira H. G. Role of adenovirus antigens in the induction of virus neutralizing antibody. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):177–185. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-1-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiser W., Lange J., Loytved D., Wigand R. Typenspezifische Adenovirus-Antigene. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1969;26(4):355–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norby E. Comparative studies on the soluble components of adenovirus types 9 and 15 and the intermediate strain 9-15. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1200–1210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1200-1210.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E. Capsid mosaics of intermediate strains of human adenoviruses. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):657–662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.657-662.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Nyberg B., Skaaret P., Lengyel A. Separation and characterization of soluble adenovirus type 9 components. J Virol. 1967 Dec;1(6):1101–1108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.6.1101-1108.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Skaaret P. The relationship between soluble antigens and the virion of adenovirus type 3. 3. Immunological identification of fiber antigen and isolated vertex capsomer antigen. Virology. 1967 Jul;32(3):489–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E. The relationship between the soluble antigens and the virion of adenovirus type 3. IV. Immunological complexity of soluble components. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E. The structural and functional diversity of Adenovirus capsid components. J Gen Virol. 1969 Sep;5(2):221–236. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Wadell G. Immunological relationships between hexons of certain human adenoviruses. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):663–670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.663-670.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Höglund S. Sructural proteins of adenoviruses. 3. Purification and characterization of the adenovirus type 2 penton antigen. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):90–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90351-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Philipson L., Höglund S. Structural proteins of adenoviruses. I. Purification and characterization of the adenovirus type 2 hexon antigen. Virology. 1967 Dec;33(4):575–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAFAJKO R. R. PRODUCTION AND STANDARDIZATION OF ADENOVIRUS TYPES 1 TO 18 REFERENCE ANTISERA. Am J Hyg. 1964 May;79:310–319. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON M. Chromatography of adenoviruses on calcium phosphate columns. Acta Virol. 1962 Jul;6:302–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortridge K. F., Biddle F. The proteins of adenovirus type 5. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):1–24. doi: 10.1007/BF01253875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. A., Schaeffer M., Fox J. P., Brandt C. D., Romano M. Standardization and certification of reference antigens and antisera for 30 human adenovirus serotypes. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Nov;86(3):617–633. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILCOX W. C., GINSBERG H. S. PRODUCTION OF SPECIFIC NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY WITH SOLUBLE ANTIGENS OF TYPE 5 ADENOVIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Oct;114:37–42. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigand R., Meiser W. Neutralization and adenoviruses by component antisera. (Brief report). Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1969;27(1):112–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01250320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigand R. Serologische Beziehungen der Adenoviren der Gruppe II. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;23(1):40–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



