Abstract
Ultraviolet (UV)-irradiated Newcastle disease virus which has lost its infectivity but has the capacity to induce interferon also has the capacity to induce ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis both in vitro and early in infection in vivo. With large doses of UV irradiation, RNA-synthesizing capacity and interferon-inducing capacity are lost in parallel. Limited amounts of base-paired RNA associated with a transcriptive intermediate are involved in this RNA synthesis. These findings suggest the possibility that the single-stranded RNA of the UV-irradiated virus induces interferon by serving as a template for the synthesis of base-paired RNA. UV irradiation of the virus breaks down viral RNA but at a rate which is too slow to be a major cause of the loss of RNA-synthesizing capacity. Evidence is presented which suggests that less of the template RNA of the UV-irradiated virus is copied and that the product which is synthesized is smaller than that synthesized by nonirradiated virus.
Full text
PDF

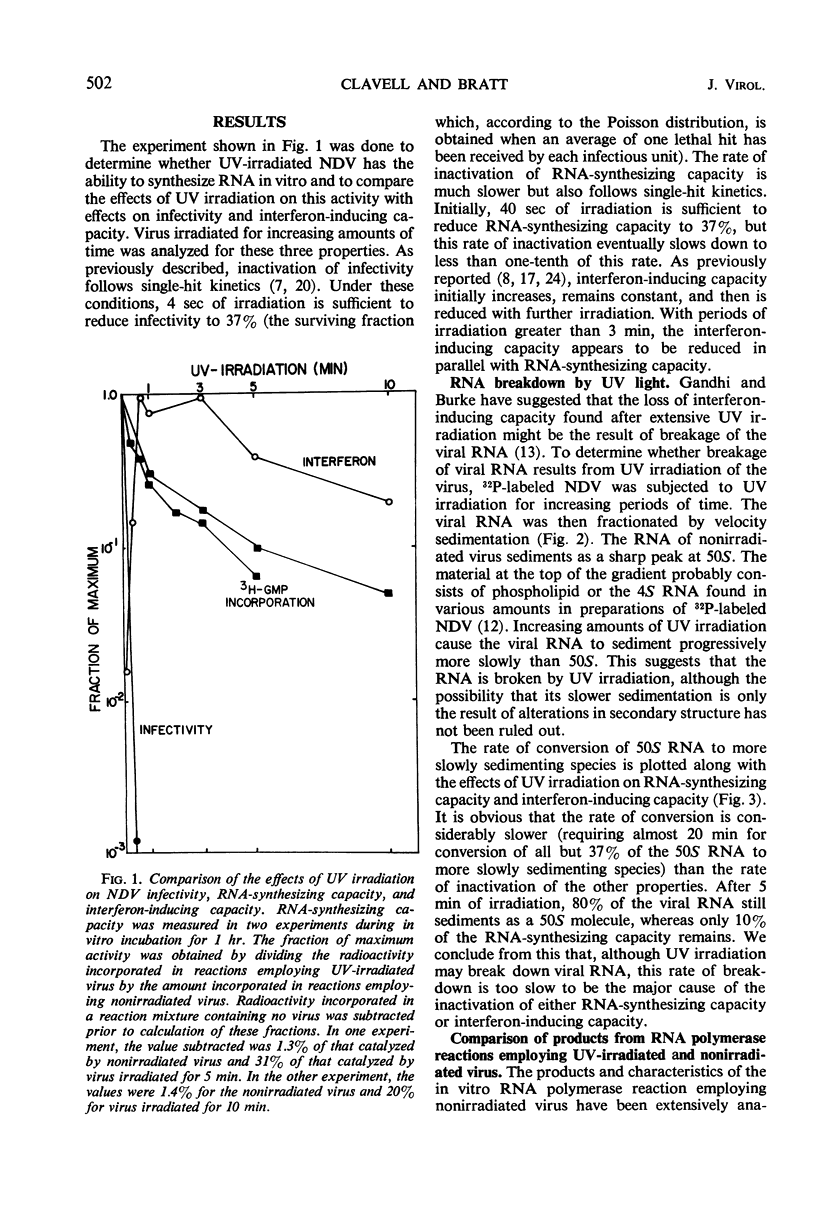
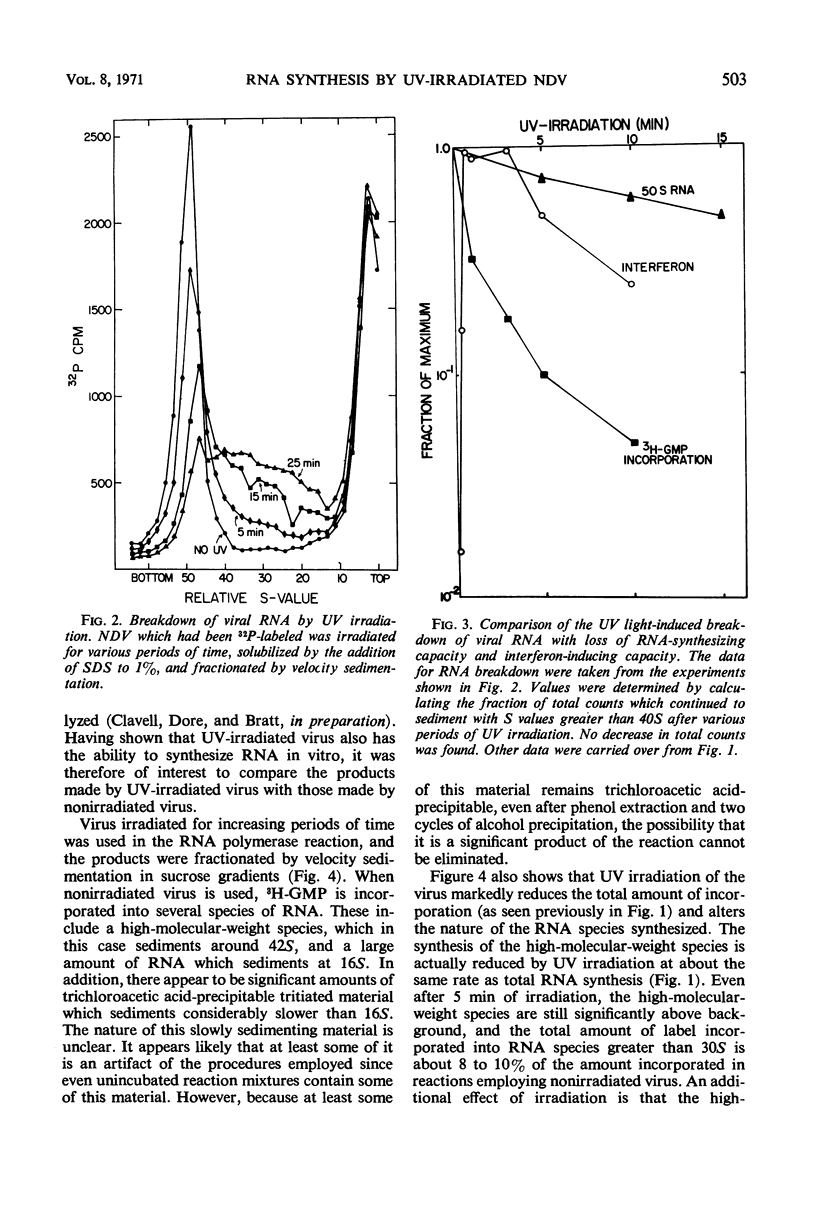
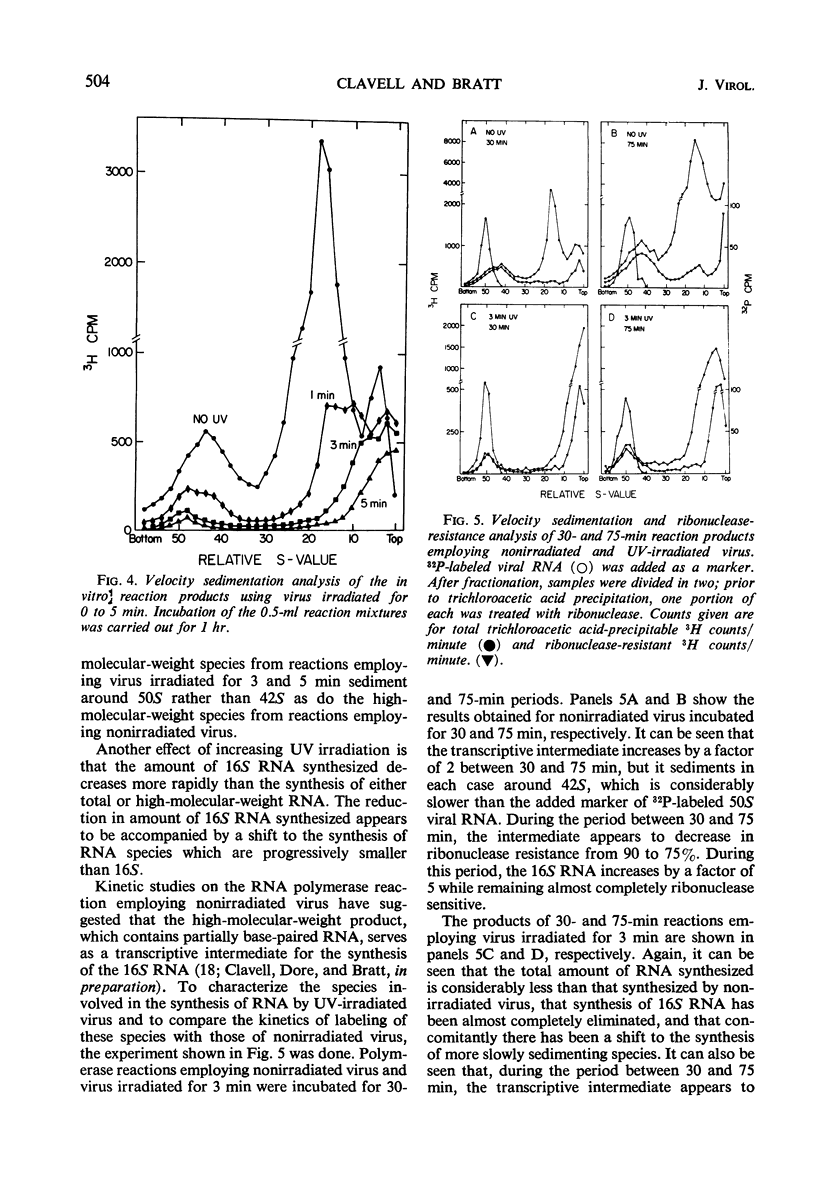
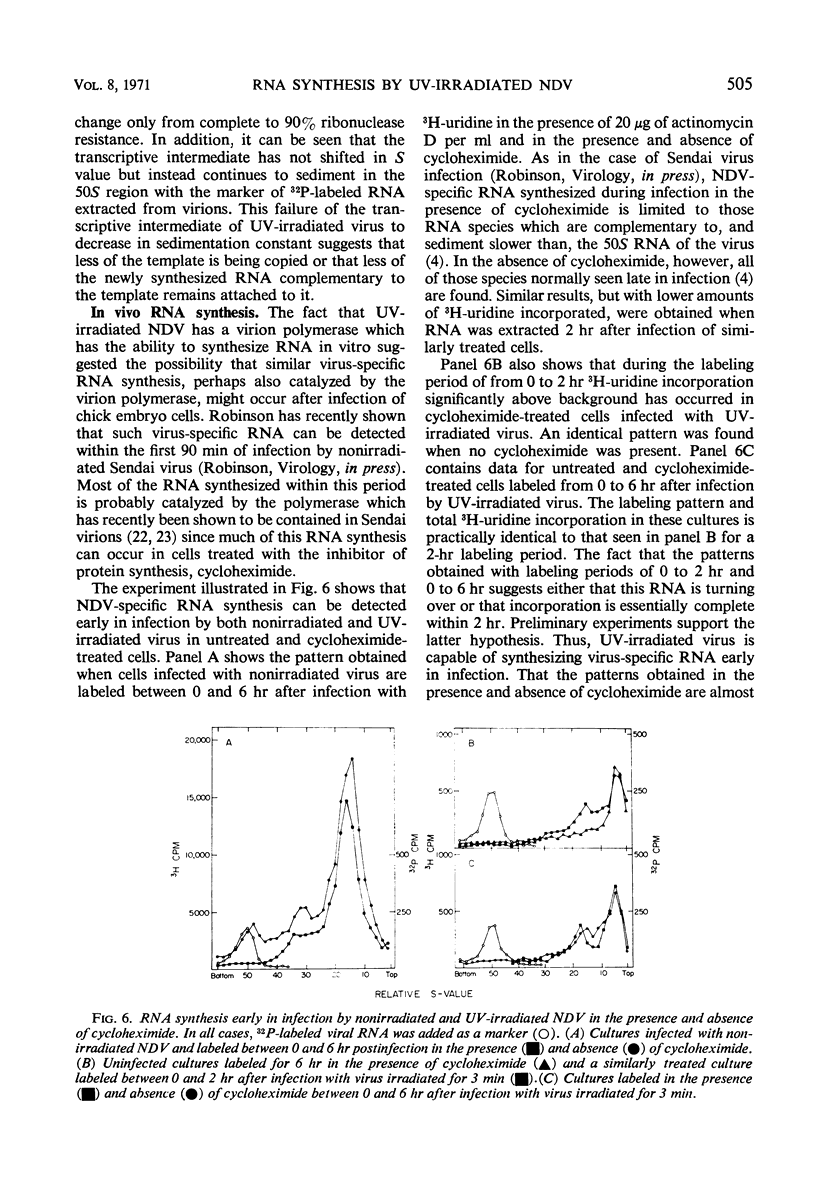



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt M. A., Gallaher W. R. Preliminary analysis of the requirements for fusion from within and fusion from without by Newcastle disease virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):536–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt M. A., Robinson W. S. Evidence for an RNA replicative intermediate in cells infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1971 Feb;10(2):139–145. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-10-2-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt M. A., Rubin H. Specific interference among strains of Newcastle disease virus. 3. Mechanisms of interference. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt M. A., Rubin H. Specific interference among strains of Newcastle disease virus. II. Comparison of interference by active and inactive virus. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):381–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90217-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby C., Jr The induction of interferon by natural and synthetic polynucleotides.hs. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1971;11:1–32. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dianzani F., Gagnoni S., Buckler C. E., Baron S. Studies of the induction of interferon system by nonreplicating Newcastle disease virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):324–328. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Robinson W. S. Isolation of the nucleic acid of Newcastle disease virus (NDV). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):794–800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi S. S., Burke D. C. Interferon production by myxoviruses in chick embryo cells. J Gen Virol. 1970 Jan;6(1):95–103. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi S. S., Burke D. C., Scholtissek C. Virus RNA synthesis by ultraviolet-irradiated Newcastle disease virus and interferon production. J Gen Virol. 1970 Oct;9(1):97–99. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-9-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M., BREINIG M. K. METABOLIC DETERMINANTS OF INTERFERON FORMATION. Virology. 1965 Mar;25:331–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Interferon induction and utilization. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Feb;71(1):43–59. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040710107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Bratt M. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase in virions of Newcastle disease virus: comparison with the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.389-394.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert J., Hillova J., Gresland L. Viral RNA synthesis in chicken cells infected with ultraviolet irradiated Newcastle Disease Virus. Nature. 1969 Sep 6;223(5210):1015–1017. doi: 10.1038/2231015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Rubin H. Radiation studies of avian tumor viruses and of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. Ribonucleic acid polymerase activity in Sendai virions and nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1971 Jul;8(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.1.81-86.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. O., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Ribonucleic acid transcriptases in Sendai Virions and infected cells. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):174–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.174-180.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Scott A. W., Hallum J. V., Stinebring W. R. Interferon production by inactivated Newcastle disease virus in cell cultures and in mice. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):862–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.862-868.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhdanov V. M., Kingsberi D. U. Replikativnaia promezhutochnaia forma RNK v kletkakh, zarazhennykh virusom bolozni N'iukasla VB. Vopr Virusol. 1969 Sep-Oct;14(5):537–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



