Figure 1.
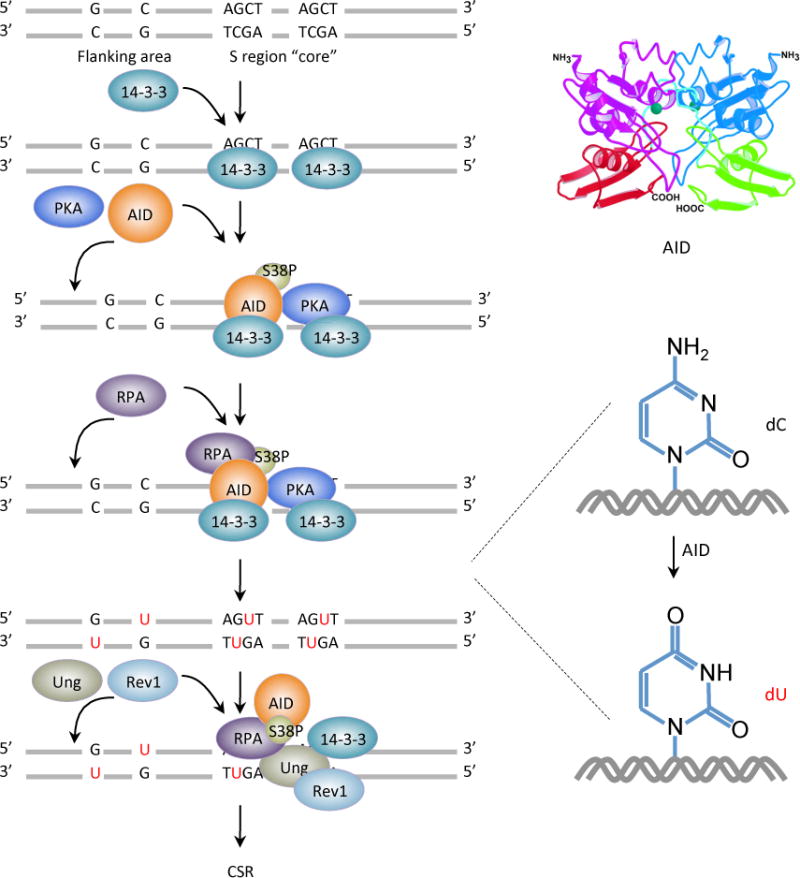
AID initiates CSR by deaminating dCs into dUs yielding dU:dG mismatches. AID is targeted to S regions by 14-3-3 adaptor proteins that specifically bind to 5′-AGCT-3′ repeats in S region core and recruit AID and PKA to S region DNA. PKA phosphorylates AID at serine 38 in its amino-terminal region, generating a binding site for RPA. RPA enhances AID-mediated deamination of dCs in transcribed S region DNA. The resulting dUs are removed by Ung, which could be recruited to and stabilized on S regions by the scaffold functions of 14-3-3 adaptors, RPA and the translesion DNA polymerase Rev1. Ung is also stabilized by AID, which indirectly interacts with Ung (possibly through 14-3-3), within a putative macromolecular complex.
