Abstract
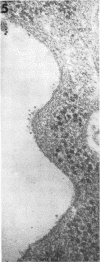
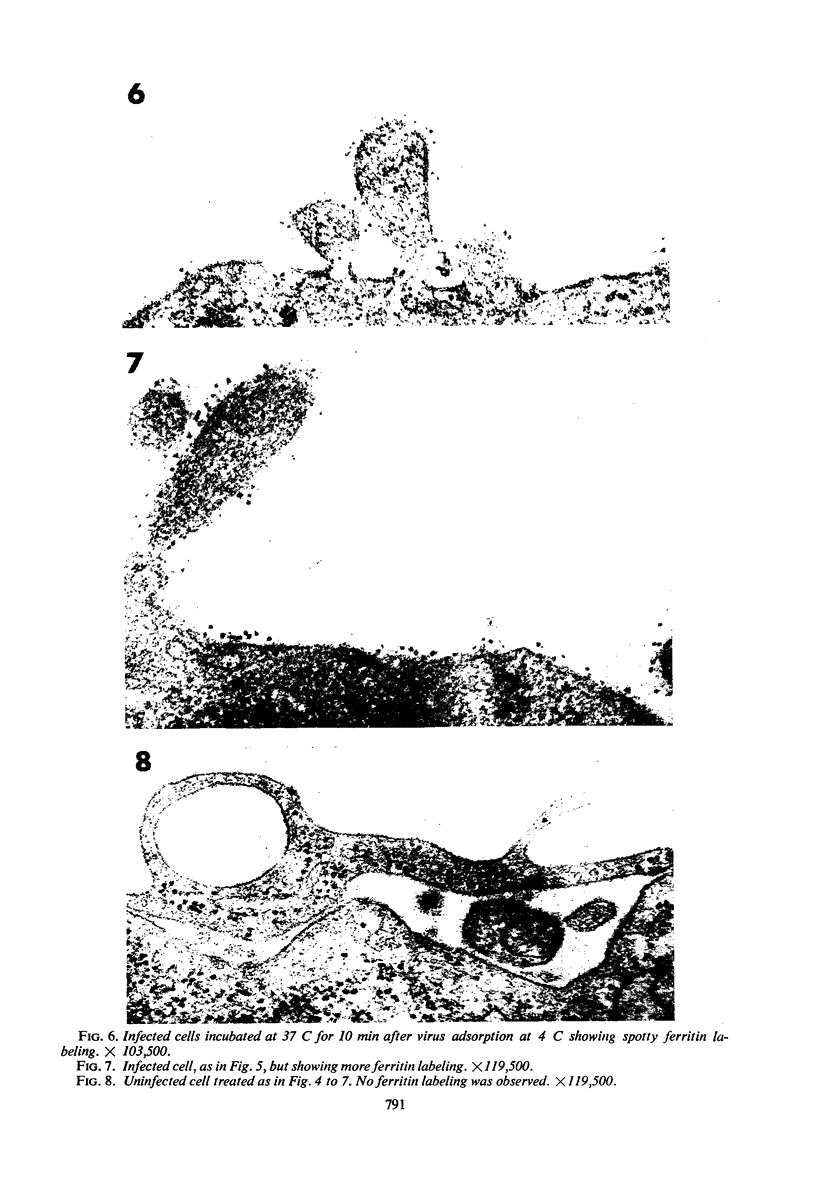
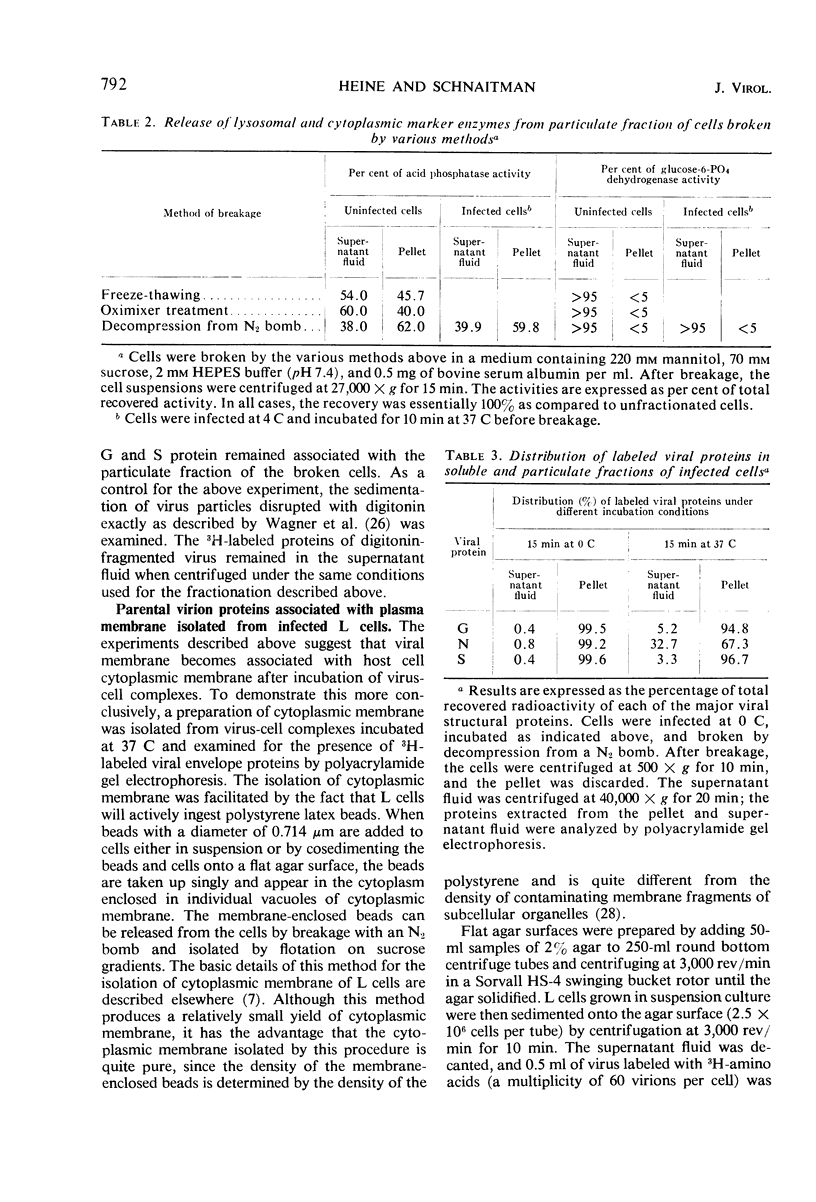
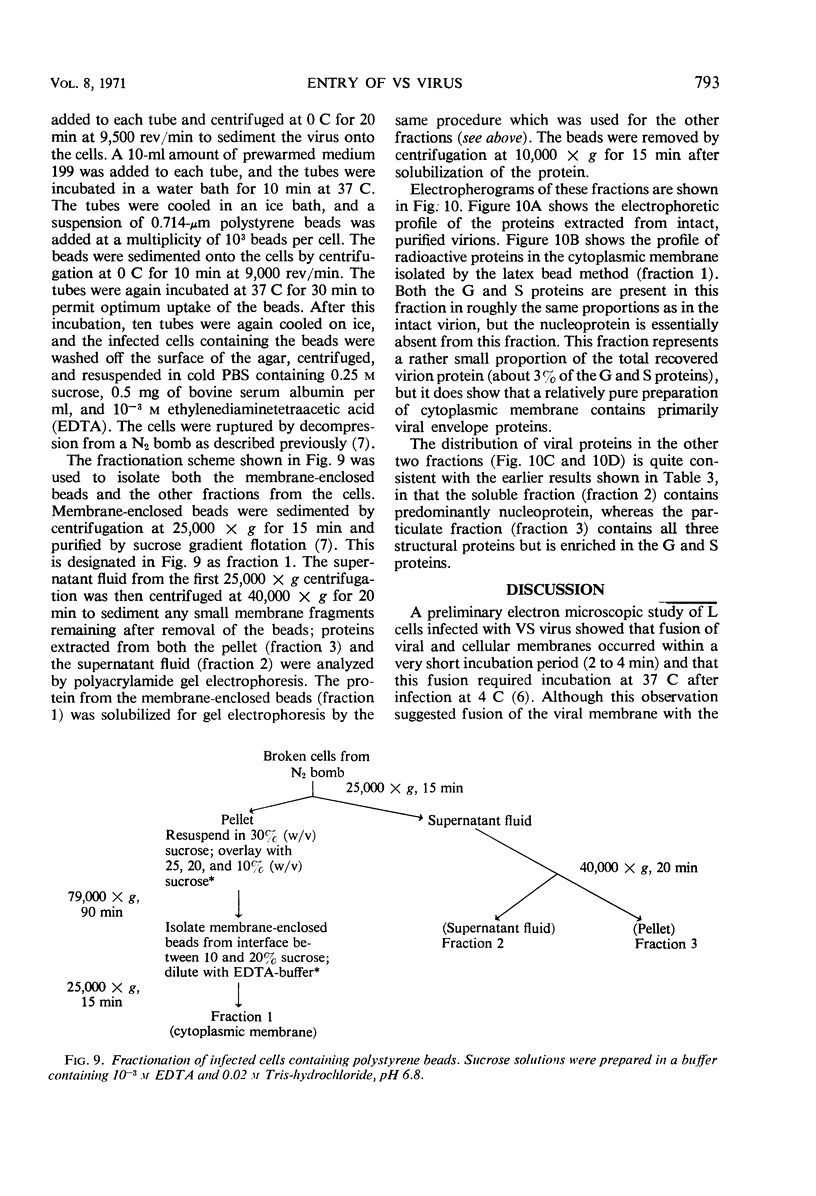
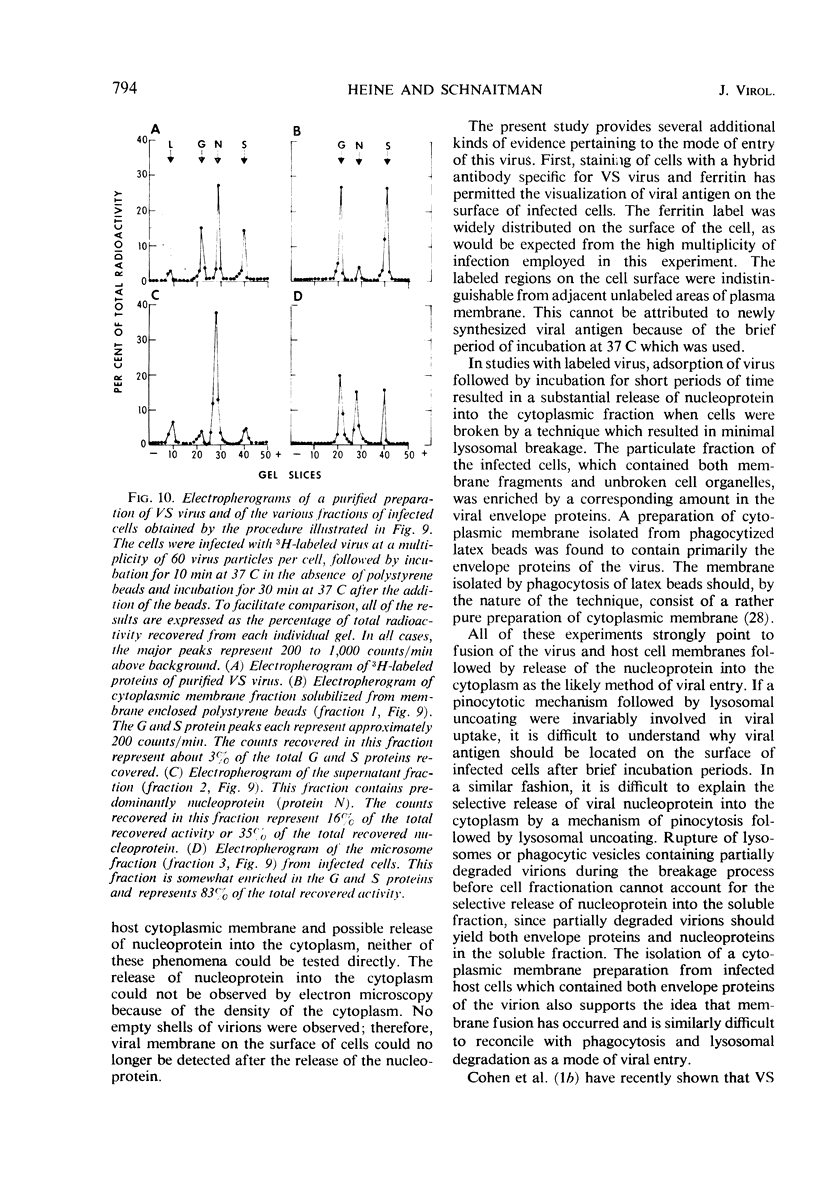
Early stages of the entry of vesicular stomatitis (VS) virus into L cells were followed by electron microscopy with the aid of ferritin antibody labeling. Cells which were infected at 0 C and incubated for 10 min at 37 C were reacted first with antiviral-antiferritin hybrid antibody and then with ferritin or fluorescein-labeled apoferritin. Extensive ferritin labeling of the cell surface was detected by both electron and fluorescence microscopy. The labeled regions of the cell surface were continuous with and indistinguishable from the rest of the host cell membrane, suggesting incorporation of viral antigens into the cell surface during viral penetration. Fusion of parental viral membrane with host cell membrane was further demonstrated by examining the localization of 3H-labeled viral structural proteins in cells infected at 0 C and incubated for short periods at 37 C. Viral nucleoprotein was found in a soluble fraction of the cells which was derived primarily from the cytoplasm, whereas a particulate fraction from the cells was enriched in viral envelope proteins. Cytoplasmic membrane was isolated from these cells, and this membrane contained viral envelope proteins. These results suggest that penetration by VS virus occurs by fusion of the viral and cellular membranes followed by release of nucleo-protein into the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basch R. S. An improved method for counting tritium and carbon-14 in acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 10;26(1):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Atkinson P. H., Summers D. F. Interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus structural proteins with HeLa plasma membranes. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 26;231(21):121–123. doi: 10.1038/newbio231121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN W. H., LERNER F. A method for estimating serum acid phosphatase of prostatic origin. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):89–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galasso G. J. Enumeration of VSV particles and a demonstration of their growth kinetics by electron microscopy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):43–48. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Galasso G. J. Effects of x-irradiated aqueous solutions on vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1147–1153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1147-1153.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Schnaitman C. A. A method for the isolation of plasma membrane of animal cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Mar;48(3):703–707. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Schnaitman C. A. Fusion of vesicular stomatitis virus with the cytoplasmic membrane of L cells. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):619–622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.619-622.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Morgan C. Interactions between Sendai virus and human erythrocytes. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):70–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.70-81.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling U., Aoki T., de Harven E., Boyse E. A., Old L. J. Use of hybrid antibody with anti-gamma-G and anti-ferritin specificities in locating cell surface antigens by electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1461–1473. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Wagner R. R. Lipid composition of purified vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):59–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.59-70.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J., Benzinger R. Concentration and purification of vesicular stomatitis virus by polyethylene glycol "precipitation". Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):745–746. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Howe C. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. IX. Entry of parainfluenza I (Sendai) virus. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1122–1132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1122-1132.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rose H. M. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. 8. Entry of influenza virus. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):925–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.925-936.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., RIVERS M. M. Recombination of a mixture of univalent antibody fragments of different specificity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:460–462. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90296-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOLTMANN E. A., GUBLER C. J., KUBY S. A. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (Zwischenferment). I. Isolation of the crystalline enzyme from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1225–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Howatson A. F. The fine structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):268–281. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif A. E. Batch preparation of rabbit gammaG globulin with deae-cellulose. Immunochemistry. 1969 Sep;6(5):723–731. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Examination of the protein composition of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):882–889. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.882-889.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C., Greenawalt J. W. Enzymatic properties of the inner and outer membranes of rat liver mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):158–175. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. W., Hauser R. E., Dales S. Viropexis of vesicular stomatitis virus by L cells. Virology. 1969 Feb;37(2):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Heine J. W., Goldstein G., Schnaitman C. A. Use of antiviral-antiferritin hybrid antibody for localization of viral antigen in plasma membrane. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):274–277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.274-277.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. A., Snyder R. M. Structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):395–403. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.395-403.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. C., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the structural components of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):611–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.611-618.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel M. G., Korn E. D. Phagocytosis of latex beads by Acahamoeba castellanii (Neff). 3. Isolation of the phagocytic vesicles and their membranes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):90–104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]