Abstract
Reducing fluoroscopic pulse rate, a method used to reduce radiation exposure from Modified Barium Swallow Studies (MBSSs), decreases the number of images available from which to judge swallowing impairment. It is necessary to understand the impact of pulse rate reduction on judgments of swallowing impairment and, consequentially, treatment recommendations. This preliminary study explored differences in standardized MBSS measurements (Modified Barium Swallow Impairment Profile (MBSImP™©) and Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) scores) between two pulse rates: 30 and simulated 15 pulses per second (pps). Two reliable speech-language pathologists (SLPs) scored all 5 MBSSs. Five SLPs reported treatment recommendations based on those scores. Differences in judgments of swallowing impairment were found between 30 and simulated 15pps in all 5 MBSSs. These differences were in six physiological swallowing components: initiation of pharyngeal swallow, anterior hyoid excursion, epiglottic movement, pharyngeal contraction, pharyngeal-esophageal segment opening and tongue base retraction. Differences in treatment recommendations were found between 30 and simulated 15pps in all 5 MBSSs. These findings suggest that there are differences in both judgment of swallowing impairment and treatment recommendations when pulse rates are reduced from 30pps to 15pps to minimize radiation exposure.
Keywords: Deglutition, Deglutition Disorders, Swallowing, Dysphagia, Modified Barium Swallow Study, MBSImP, Fluoroscopy, Videofluoroscopy, Pulse Rate, Radiation Exposure
INTRODUCTION
Swallowing disorders functionally impair an estimated 18 million patients in the United States each year[1] spanning across patient demographics, impacting numerous medical subspecialties, and contributing to over $500,000,000 in yearly government healthcare spending[2]. If untreated, dysphagia can result in malnutrition and aspiration pneumonia. In the United States, it has been estimated that oropharyngeal dysphagia occurs in approximately 10% of all acute hospital inpatients[3], 30% of patients/clients in rehabilitation centers, and half of patients/clients in nursing home facilities[4]. In 2004, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services reported over 203,000 claims for MBSSs (CPT 92611) totaling approximately $21 million in charges.
While the Modified Barium Swallow Study (MBSS) is an important diagnostic tool for the evaluation of swallowing function, it does require caution similar to other medical uses of ionizing radiation[5]. The use of medical techniques that employ ionizing radiation must comply with the As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) principle. ALARA simply means the elimination of all unnecessary radiation exposure, which can be defined as exposure that does not contribute to improved diagnostic performance. Unnecessary radiation should be eliminated because it is associated with cancer risks.
One such strategy that is popularly used to decrease radiation exposure is reducing the pulse rate of the radiation beam emitted during MBSSs[6]. The emitted radiation beam can be either continuous or pulsed. When pulsed, the pulse rate is defined as the number of pulses per second (pps) of the x-ray beam. Pulse rates for fluoroscopy commonly include 30, 15, 7.5, and 4pps. Radiation exposure is reduced as pulse rate is reduced. Specifically, Aufrichtig et al showed average dose reductions of 22% at 15pps and 49% at 7.5pps when compared to doses at 30pps[7].
Decreasing pulse rate also has a direct and proportional effect on the number of unique images in which a swallow is captured. Since the oropharyngeal swallow only lasts approximately 1 second, when pulse rate is decreased from 30 to 15, the number of unique images available to judge swallowing impairment also decreases from 30 to 15. This makes the swallow motion appear less continuous or ‘jerky’. The decrease in number of images in which a swallow is captured, and consequential decrease in the information available from which swallowing impairment can be judged, is not trivial. Specific physiological components occur in tight temporal synchrony and must be accurately assessed to identify the appropriate physiological targets for treatment[8]. These components are only assessable at specific points during the swallow and thus may not be captured when using pulse rates lower than 30.
Although temporal resolution appears to be critical for viewing the swallow in its entirety, it is not known if decreasing fluoroscopy pulse rates as a strategy to reduce radiation dose negatively affects the ability to make judgments of swallowing impairment. This is because we do not know how many unique images are needed to judge swallowing impairment. The effect of a reduction of available diagnostic information could threaten the accuracy of judgments of swallowing impairment and lead to incorrect patient treatment recommendations. The consequences of incorrectly assessing swallowing impairment are serious. If swallowing impairment exists and is un- or under- detected, airway protection and nutrition may be at risk. Inaccurate judgments may also err on the side of overly conservative recommendations of oral intake restriction such as modifications in diet or tube feeding placement that may unnecessarily decrease a dysphagic patient’s health status and quality of life.
Despite the potentially serious implications of using the suboptimal pulse rate, there is only one published study that provides evidence of the effect of pulse rate on judgments of swallowing impairment. Cohen evaluated the impact of pulse rate on the judgment of penetration of thin liquid barium in 10 children ranging in age from one month to two years nine months[9]. He recorded all MBSSs at 30pps and counted the number of unique images in which penetration was visible at full depth and the additional number of frames where partial penetration was visible. The author defined “full penetration” as “a column of barium seen down to the approximate level of the vocal cords” and “partial penetration” as “some barium partially visible in the laryngeal ventricle, but not the full depth of the vocal cords”. In 7 out of 10 children, full penetration was visible in only 1 frame. The other 3 children had 2 frames where full penetration was visible. In 3 of the 7 children where penetration was visible in only 1 frame, there were no additional frames that showed partial penetration. Consequently, any sign of penetration would be missed in 30% of children and the extent of penetration would not be known in 70% of children. Cohen interpreted the results of this novel pilot study to indicate that 15pps is inadequate for judging the incidence of penetration in children.
Furthermore, there is no evidence available on the treatment implications of judging swallowing impairment from pulse rates lower than 30. If the reduction in diagnostic yield does not change the treatment plan for a patient it could be argued that it is not a clinically-relevant reduction in yield. Thus, it is also important to investigate the impact of pulse rate on treatment recommendations from the MBSSs. Our experiments were aimed at improving our understanding of the clinical implications of pulse rate on diagnostic yield and treatment recommendations. Knowledge of how diagnostic performance and treatment recommendations are affected by pulse rate will permit practitioners to perform a risk/benefit analysis to decide whether a reduction in fluoroscopy pulse rate is warranted.
METHOD
Experiment 1: Influence of pulse rate on judgments of swallowing impairment
Swallow Studies
Retrospectively 5 swallow studies were randomly selected for inclusion in this study. The demographics of the study patients are found in Table 1. The Modified Barium Swallow Impairment Profile (MBSImP™©, Northern Speech Services, Gaylord, MI) standards were used for the clinical MBSS[10]. Eleven single swallows of standardized, commercial preparations of barium contrast agents (Varibar® E-Z-EM, Inc.) (thin liquid barium (two trials of 5-ml cup sip, sequential swallows from cup); nectar-thick liquid barium (5-ml cup sip, sequential swallows from cup), honey-thick liquid barium (5 ml), pudding-thick barium (5 ml), and a one-half portion of a Lorna Doone shortbread cookie coated with 3-ml pudding-thick barium) were completed for each patient according to the MBSImP™© protocol. Each of the five MBSSs was recorded at 30pps. The protocol allows flexibility to tailor trial compensatory and rehabilitative strategies and alterations in bolus characteristics according to the demonstrated need of the patient. These intervention swallows were not part of the scoring analysis included in the current study. The 30pps recordings were downsampled to 15pps by deleting every other frame and replacing the deleted frames with copies of the preceding frames to emulate a lower pulse rate while maintaining the recording length. The methodology for duplicating frames when converting MBSSs from higher to lower frame rates directly replicates the process used by fluoroscopy machines as set by the manufacturers [6]. This process was accomplished using the VirtualDub 1.9.10 freeware by Avery Lee. The files were all saved in MPEG1 format prior to scoring.
Table 1.
Patient demographics: age, gender, primary diagnosis category and diet at time of MBSS for Experiments 1 and 2.
| Patient Number | Age | Gender | Primary Diagnosis Category | Diet at Time of MBSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | Male | Left lower lobe ventilator-associated pneumonia | NPO, Percutaneous Gastrostomy Feeding Tube |
| 2 | 3 | Male | Knife wound to chest resulting in right pneumothorax and left hemothorax | NPO, Nasogastric Feeding Tube |
| 3 | 7 | Male | Base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma with metathesis to neck | Thin liquid diet |
| 4 | 3 | Male | Gunshot wound to left face | NPO, Percutaneous Gastrostomy Feeding Tube |
| 5 | 6 | Female | Papillary thyroid cancer | Regular diet with Thin liquids |
MBSImP™©Scoring
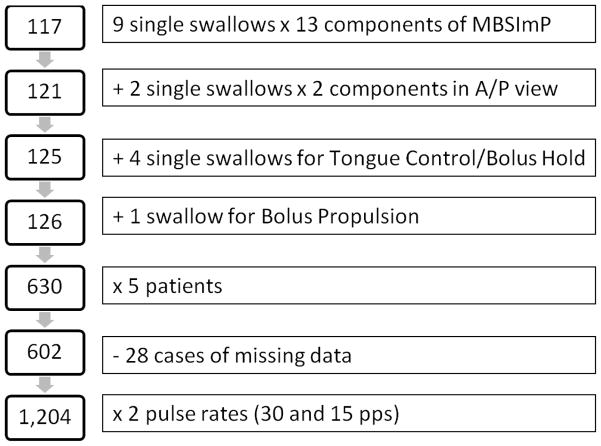
Two reliable (80%) SLPs scored all files individually and in consensus using the MBSImP©™ methodology. Eighty percent reliability of the judges (SLP clinicians) refers to the MBSImP©™ required training. At the end of the MBSImP©™ training, clinicians are tested for their accuracy in detecting the 17 specific aspects of swallowing impairment using the MBSImP©™ scoring system. The clinicians that were judges in this study passed that test. For the purposes of MBSImP™©, videos are viewed in slow motion and at times frame-by-frame. This viewing speed is supported by preliminary findings that slow motion viewing of MBSS improves rating accuracy[11]. The videos were viewed on 23-inch monitors with a resolution of 1920 × 1080. There were 602 judgments of the 17 components of swallowing impairment physiology made for both the 30pps and simulated 15pps recordings (Figure 1). The 17 components of swallowing impairment physiology are defined in Table 2. The purpose of the MBSImP©™ is to detect swallowing impairment. The clinician is instructed to rate what is seen. After the MBSImP is completed and impairments are detected, the clinician interprets the impairment scores in light of other clinical information. Any differences in the judgments were settled by consensus scoring. Consensus scoring involved both SLPs reviewing the MBSS recording at the same time on the same computer screen and agreeing on a score for each component of swallowing impairment physiology for each swallow. If a consensus could not be reached, that judgment was not included in the analysis. Twenty-eight possible judgments were either not made or not used in this study due to missing data points for comparison between pulse rates and swallow types, or poor image quality. Overall Impression (OI) impairment scores were calculated for each component capturing the most severe impairment across all bolus consistencies and volumes. The Penetration and Aspiration Scale (PAS) was scored for each swallow[12]. After consensus, the two SLPs reviewed and reported the specific differences between the 30pps and simulated 15pps recordings. This information was used for interpreting the reasons for differences between the pulse rates.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of components scored (right side) and number of resulting scores (left side) for comparisons between 30 and simulated 15pps.
Table 2.
Definitions of the MBSImP™© components.
| Component | Definition |
|---|---|
| 1. Lip Closure | Presence and location of bolus material seen between or outside of the lip seal |
| 2. Tongue Control during Bolus Hold | Integrity of the patient’s ability to seal the tongue anteriorly, laterally and posteriorly to the hard and soft palate during the oral command, “hold it until I ask you to swallow” |
| 3. Bolus Prep/Mastication | Timely, efficient and organized chewing/mashing of a bolus |
| 4. Bolus Transport/Lingual Motion | Speed and organization of tongue movement during bolus transport |
| 5. Oral Residue | Amount and location of oral residue. |
| 6. Initiation of Pharyngeal Swallow | Position of the bolus head (leading edge) at the time of first initiation of the brisk, superior-anterior hyoid trajectory |
| 7. Soft Palate Elevation | Contact between the soft palate and posterior pharyngeal wall scored at the point of maximal soft palate displacement |
| 8. Laryngeal Elevation | Superior movement of the thyroid cartilage and approximation of the arytenoids to the epiglottic petiole when the epiglottis reaches the horizontal position |
| 9. Anterior Hyoid Movement | Maximal anterior displacement of the hyoid |
| 10. Epiglottic Movement | Position of the epiglottis at the maximal anterior hyoid displacement |
| 11. Laryngeal Vestibular Closure | Laryngeal vestibular closure at maximum anterior hyoid displacement |
| 12. Pharyngeal Stripping Wave | Presence and magnitude of the pharyngeal stripping wave |
| 13. Pharyngeal Contraction | Pharyngeal shortening and compression of the lateral pharyngeal walls against the tail of the bolus, bilaterally |
| 14. PES Opening | Distension, duration and obstruction of the PES opening |
| 15. Tongue Base Retraction | Contact between the tongue base and the posterior pharyngeal wall scored at the point of maximal tongue base retraction |
| 16. Pharyngeal Residue | Amount and location of pharyngeal residue |
| 17. Esophageal Clearance Upright Position | Esophageal clearance of contrast from proximal esophagus through the lower esophageal sphincter |
Experiment 2: Clinical implications of differences in judgments of swallowing impairment due to pulse rate
After the SLPs scored the exams, the scores were de-identified (obscuring the pulse rate and the patient source) and were given to other SLPs who made treatment recommendations from the scores. This allowed for the evaluation of the influence of the judgments from 30pps and simulated 15pps on treatment recommendations. Specifically, the 10 patient profiles (PAS and MBSImP™©), as detailed above (5 at simulated 15pps and 5 at 30pps), were assembled and presented as if they were from 10 separate patients. Based on these profiles alone, we asked 5 SLPs, not involved in the MBSS scoring, who were trained and reliable in scoring MBSImP™© and PAS, about their 1) Diet Recommendations, 2) Compensatory or Treatment Strategies, and 3) Patient Prognosis for Improving Swallowing Function. Diet recommendation categories were: Regular Diet/Thin, Nectar or Honey Liquid; Mechanical Soft Diet/Thin, Nectar, or Honey Liquid; Puree/Thin, Nectar, or Honey Liquid; All liquids; Thin liquids only; Nectar liquids only; Honey liquids only; or NPO. Compensatory or treatment strategy categories were: Mendelsohn maneuver[13], Supraglottic swallow/super supraglottic swallow[14], Chin tuck[15], Effortful swallow[16], Cough[17], Masako maneuver[18], Clearance of oral residue[19], Range of motion exercises[20], Shaker chin lifts[21], Additional swallows per bolus[22], Use of straw[23], Head turn[24], and Bolus hold[10]. Prognostic categories for recovery of swallow function included: Good, Fair, or Poor. The dietary recommendations and prognostic categories were exclusionary (only one could be chosen), whereas several compensatory and treatment strategies could be selected for each profile.
Experiment 3: Further testing of the influence of pulse rate on judgments of penetration and aspiration
Swallow Studies
Retrospectively 15 swallow studies were selected for inclusion in this study based on having been previously judged and determined to have PAS scores over the entire range of the scale. The demographics of the study patients are found in Table 3. The MBSImP™© standard protocol was used to conduct the clinical MBSS[10]. Similar to Experiment 1, clinical recordings were made at 30pps and downsampled. For Experiment 3, four pulse rates were used 30, simulated 15, simulated 7.5, and simulated 4pps. The PAS was judged for each recording at each of the four pulse rates[12]. The same two SLPs who participated in Experiment 1 provided the PAS scores for this experiment. The SLPs were blinded to the pulse rate of the recordings. The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test was used to evaluate the differences in PAS scores between pulse rates with an alpha level set at 0.05.
Table 3.
Patient demographics: age, gender, primary diagnosis category and diet at time of MBSS for Experiment 3.
| Patient Number | Age | Gender | Primary Diagnosis Category | Diet at Time of MBSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | M | R MCA occlusion | NPO, Percutaneous Gastrostomy Feeding Tube |
| 2 | 1 | F | L Pontine infarct | NPO, Nasogastric Feeding Tube |
| 3 | 6 | M | L Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage | Puree diet with nectar thick liquids |
| 4 | 8 | F | Large R MCA infarction | NPO, Percutaneous Gastrostomy Feeding Tube |
| 5 | 4 | M | Lacunar infarct within R internal capsule | NPO, Percutaneous Gastrostomy Feeding Tube |
| 6 | 8 | M | R caudate lacunar infarct | Regular diet, Nectar Thick Liquids |
| 7 | 8 | F | Infarcts within L pre and post central gyri | NPO, Nasogastric Feeding Tube |
| 8 | 5 | F | R basil ganglia infarct | NPO, Percutaneous Gastrostomy Feeding Tube |
| 9 | 3 | M | Infarction of R insula and subcortical areas of R frontoparietal region | NPO, Nasogastric Feeding Tube |
| 10 | 6 | M | Infarctions within R parietal and frontal lobes | NPO, Extubated prior to MBSS |
| 11 | 8 | F | Infarctions bilateral MCA territories | NPO, IV |
| 12 | 4 | F | Infarctions within L ACA and MCA territories | NPO, Nasogastric Feeding Tube |
| 13 | 7 | F | Infarcts within R MCA territory involving posterior frontal/parietal/temporal/occipital lobes and insular | NPO, Dobhoff tube |
| 14 | 9 | M | Infarction within pons | NPO, IV |
| 15 | 7 | F | Small infarctions within cerebellum, brainstem and L MCA territory. | NPO, IV |
Skin entrance air kerma measurements
Skin Entrance Air Kerma (EAK) measurements were made on the GE Precision RF unit that is used in our department for performing barium swallow examinations. All Entrance Air Kerma measurements were obtained using a Radcal 9010 exposure meter with a 6cc ionization chamber. The chamber was placed on the table top and the image intensifier positioned 30 cm above the chamber. Source to table top distance for this unit is fixed at 55 cm. Lucite blocks were used for the attenuating material and supported over the ionization chamber using blocks, so that our measurements include backscatter radiation. EAK measurements in the normal II mode (40 cm diameter) were made using 10cm and 20 cm of Lucite to simulate the range of patient size(s) that are expected to be encountered in clinical practice. Entrance Air Kerma rates were obtained in mGy/minute at continuous fluoroscopy (30 frames per second), as well as pulsed fluoroscopy operated at rates of 15 and 7.5 pulses/s. The EAK per pulse was obtained by dividing the EAK rate (mGy/min) by the corresponding number of images generated in a minute for each of the three imaging rates investigated.
RESULTS
Experiment 1: Influence of pulse rate on judgments of swallowing impairment
Difference in OI scores from the MBSImP™©
The OI score on the MBSImP™© is the worst score for each of the 17 physiological components across all of the boluses. The OI score differed in three out of five patients (patients 2, 3, and 5) depending on the pulse rate associated with the recording. In patient 2, pharyngoesophageal segment opening (PESO) appeared to have complete distension and full duration with no obstruction of flow in the 30pps recording, but partial distension and duration in the simulated 15pps recording. In patient 3, pharyngeal contraction (PC) appeared incomplete due to the presence of a pulsion pseudodiverticulum on the 30pps recording and complete on the simulated 15pps recording. In patient 5, initiation of pharyngeal swallow (IPS) was judged as occurring earlier, when the bolus head was at the posterior lateral surface of epiglottis at the onset of anterior hyoid excursion on the 30pps recording compared to the simulated 15pps recording where it was scored as occurring when the bolus head was at the pit of the pyriforms.
Difference in Individual Swallow scores from the MBSImP™©
Differences between judgments from 30pps and simulated 15pps recordings were identified in six MBSImP™© swallowing physiology components: IPS, anterior hyoid excursion (AHE), epiglottic movement (EM), PC, PESO, and tongue base retraction (TBR) (Table 4). IPS was the component most influenced by pulse rate evidenced by different ratings between 30pps and simulated 15pps recordings in 15 swallows from 4 patients. For the other components, differences were less prevalent, seen in one of the five patients.
Table 4.
Percent of scores that differed when judged from 30pps and simulated 15pps recordings for each of the six physiological components where differences were found. For example, 56% of the scores for Initiation of Pharyngeal Swallow scores were different when comparing 30 vs simulated 15pps for Patient 1.
| Component | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation of Pharyngeal Swallow | 56% | 0 % | 38% | 11% | 67% |
| Anterior Hyoid Excursion | 0% | 0% | 0% | 22% | 0 % |
| Epiglottic Movement | 0% | 0% | 13% | 0% | 0% |
| Pharyngeal Contraction | 0% | 0% | 50% | 0% | 0% |
| PE Segment Opening | 0% | 13% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Tongue Base Retraction | 0% | 0% | 0% | 11% | 0% |
In general, the direction of the discrepancies, whether 30 or simulated 15pps recordings were more likely to result in a judgment of increased impairment, varied within and between components. However, a trend in direction was noted in scoring differences for IPS. Recordings at 30pps were associated with lower impairment judgments for IPS than simulated 15pps recordings. Twelve of the 15 (80%) swallows with IPS discrepancies had lower (better) scores from the 30pps recordings than the simulated 15pps recordings. For the majority of discrepancies (60%), the discrepancy was between a rating of 2, indicating a bolus head at posterior laryngeal surface of the epiglottis, for 30pps recordings and 3, indicating a bolus head in the pyriform sinus, for simulated 15pps ratings. Other instances where IPS was rated as less impaired between 30pps than simulated 15pps occurred in 3 cases for ratings of 0 and 1, 0 and 2, and 1 and 2 each. For the three instances when IPS was rated as being more impaired from simulated 15pps than 30pps, the ratings changed between 2 and 0 in one instance and between 3 and 2 in two instances.
The other components of swallowing impairment as scored by the MBSImP™© where discrepancies occurred were seen in one out of five patients. The judgments of three components, EM, PC, and PESO, were indicative of less impairment from 30pps than from simulated 15pps. EM was scored as partial movement in the 30pps recording but absent in the simulated 15pps recording. PC appeared incomplete due to the presence of a pulsion pseudodiverticulum on the right side of pharynx on the 30pps recording and complete contraction on the simulated 15pps recording because the pseudodiverticulum was not appreciated in the latter recording. PESO was judged as having complete distension and full duration with no obstruction of flow in the 30pps recording, but only partial distension and duration in the simulated 15pps recording. Judgments for two components, AHE and TBR, revealed less impairment for the simulated 15pps than 30pps recordings. AHE was judged as partial anterior movement in two 30pps recordings and complete anterior movement in the simulated 15pps recordings. TBR was judged as 3, wide column of contrast or air between the tongue base and the pharyngeal wall, from the 30pps recording and 2, trace column of contrast or air between the tongue base and the pharyngeal wall, from the simulated 15pps recording.
Detailed Analysis Using Frame Counts
Based on the discrepancies found, a detailed analysis of frame counts was conducted for a subset of 4 of the 17 components of swallowing impairment: AHE, laryngeal vestibular closure (LVC), PESO, and TBR. These four components were chosen because the onset and offset of the component behavior can be clearly delineated. AHE, PESO, TBR were chosen because differences in judgments for these components from 30pps and simulated 15pps fluoroscopy were identified. LVC (scored at the point of maximum laryngeal vestibular closure at the height of anterior hyoid displacement) was chosen as a control comparison component because there were no differences seen in this component between 30pps and simulated 15pps. The number of frames required to judge the component were counted for each of these four components across nine swallows in each of the five patients. The frame counts were averaged from the five patients. The three components that had discrepancies in judgments between 30pps and simulated 15pps fluoroscopy were visible in fewer frames than the control component (LVC) that was not associated with such discrepancies (Table 5). When averaged across bolus types and volumes, LVC had the highest number of frames available for scoring, average of 18, while the other components could be scored in less than 11 frames on average.
Table 5.
Number of frames from which a physiological component could be scored for three components with differences between 30 and simulated 15pps recordings and one component without such differences (laryngeal vestibule closure).
| Component | Paient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior Hyoid Excursion – static | 11.89 | 7.75 | 11.80 | 8.89 | 14.67 | 11.00 |
| Laryngeal Vestibule Closure | 22.67 | 23.38 | 14.43 | 10.56 | 19.00 | 18.01 |
| PE Segment Opening | 12.00 | 6.50 | 5.00 | 5.22 | 10.44 | 7.83 |
| Tongue Base Retraction | 9.11 | 9.25 | 7.75 | 9.11 | 12.22 | 9.49 |
Difference in the Penetration/Aspiration Scale (PAS) scores
The PAS score differed in one out of the five patients between judgments from 30pps and simulated 15pps recordings. For that patient, the judgments differed on two separate swallows: 5ml thin and cup sip thin. In both cases, PAS was judged as worse on the 30pps recording compared to the simulated 15pps recording. These differences were both between PAS scores of 2 for 30pps recordings and scores of 1 for simulated 15pps recordings.
Experiment 2: Clinical implications of differences in judgments of swallowing impairment due to pulse rate
Sixty percent (3/5) of patients would be put on a different diet if their swallowing impairment was judged solely on MBSImP™© and PAS scores from a 30pps vs. a simulated 15pps MBSS. Differences in diet recommendations were between: Regular diet/thin liquid and Mechanical soft/thin liquid, Mechanical soft/thin liquid and Puree/Nectar thick liquid, Regular/thin liquid and Regular/nectar liquid, Mechanical soft/thin liquid and Puree/thin liquid, and Regular diet/nectar liquid and Mechanical soft/nectar liquid. When the 25 (5 patients × 5 SLPs) diet recommendation differences were combined, 36% (9/25) of recommendations were different between 30pps and simulated 15pps. All of the patients (5/5) had a different recommended treatment plan when their swallowing impairment was judged from a 30pps vs. a simulated 15pps MBSS. When the 25 (5 patients × 5 SLPs) recommended treatment plans differences were combined, 80% (20/25) of recommendations were different between 30pps and simulated 15pps.
All treatment strategies differed between 30pps and simulated 15 due to the differences in the swallowing severity scores. An example of this difference in treatment recommendations is an SLP indicating chin tuck as a recommended strategy based on information from a 30pps recording but not when using information from a simulated 15pps recording. Similarly, prognostic judgments for each patient (5/5) were different when judged from a simulated 15pps vs. a 30pps MBSS. When the 25 (5 patients × 5 SLPs) prognostic differences were combined, 36% (9/25) of prognostic judgments were different between 30pps and simulated 15pps. Differences in prognosis were between Good Prognosis vs. Fair Prognosis.
Experiment 3: Further testing of the influence of pulse rate on judgments of penetration and aspiration
PAS scores were different between recordings at 30pps and those at lower pulse rates in 80% of (12/15) patients studied. When analyzing the data for individual swallows, the highest agreement was between 30 and 15pps while the lowest agreement was between 7.5 and 4pps (Table 6). Difference in agreement occurred with a frequency between 24% to 33% (Table 6). Differences were statistically significant for all comparisons except 30 and 15 pps and 15 and 7.5pps at p<0.05 (Table 6).
Table 6.
Results from Experiment 3 evaluating the differences in the pulse rates using the scores from the PAS. Statistical significance for the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test was set at p=0.05.
| Comparison | Number of Disagreements | Percentage of Disagreements | P-value from Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 vs 15 | 27 | 0.24 | 0.0754 |
| 30 vs 7.5 | 28 | 0.25 | 0.0332 |
| 30 vs 4 | 37 | 0.33 | 0.0003 |
| 15 vs 7.5 | 30 | 0.27 | 0.5716 |
| 15 vs 4 | 28 | 0.25 | 0.0173 |
| 7.5 vs 4 | 35 | 0.31 | 0.0196 |
Skin EAK measurements
Table 7 shows the results obtained in this study. The data show that reducing the image acquisition rate to 15 frames per second increased the average dose/frame by 76% but resulted in a reduction in the patient (phantom) Entrance Air Kerma of 12%. Reducing the image acquisition rate to 7.5 frames per second increased the average dose/frame by nearly 220% but resulted in a reduction in the patient (phantom) Entrance Air Kerma of 46%.
Table 7.
Measured Entrance Air Kerma rates (including backscatter) as a function of acrylic thickness obtained at three fluoroscopy image acquisition rates.
| Phantom Thickness (cm) | Measured Dose Rate | Image Acquisition Frame Rate (frames/second) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 | 15 | 30 | ||
| 10 | μGy/Frame | 2.8 | 2.2 | 1.7 |
| mGy/minute | 1.3 | 2.0 | 3.0 | |
| 20 | μGy/Frame | 32.1 | 26.7 | 12.2 |
| mGy/minute | 14.4 | 24.0 | 22.2 | |
DISCUSSION
The MBSS is an evidence-based method that identifies physiologic swallowing impairment, targets direct interventions and contributes to informed prognosis for functional swallowing improvement. Until now, there has been no published report of the impact of fluoroscopy pulse rate on the interpretation and reporting of physiological components of swallowing impairments from the MBSS. Selection of the appropriate pulse rate for MBSSs is a clinical decision that speech-language pathologists and radiologists are required to make without the benefit of evidence to support their decisions. This study sought to provide preliminary evidence on the effect of pulse rate on judgments of swallowing impairment and treatment planning.
OI scores of the MBSImP™© are the scores used for everyday clinical use of the standardized tool. These scores allow for the standardized, objective, reliable and valid assessment of 17 components of swallowing physiology. OI scores capture impairment by reporting the worst score for each physiological component over all bolus consistencies. This initial study revealed that OI scores for 3 out of the 5 patients were different when judged from 30 and 15pps recordings. Since this is an overview measure of impairment, if the results of this study can be generalized, a difference in 60% of patients may indicate potential for the pulse rate to have a significant impact on the diagnosis and treatment of the majority of persons with swallowing impairment.
Individual swallow scores on the MBSImP™© are used for research applications of the standardized tool and when measuring effects of treatment strategies employed during the MBSS. These scores allow for the standardized, reliable, valid and objective assessment of 17 components of swallowing physiology while providing an in-depth analysis for each bolus consistency and volume. Six of these components were scored differently between observations of 30 and simulated 15pps recordings. A hypothesized rationale for the difference in scores for each of these components follows. The component initiation of pharyngeal swallow (IPS) (bolus head position) is judged in 1 frame, the frame where the hyoid begins anterior-superior movement trajectory. The frame selected for scoring of this component in the 30pps recordings would not be available for scoring in some of the simulated 15pps recordings. If the frame prior to or after the frame selected in the 30pps recording is selected in the simulated 15pps, then the position of the bolus head would be different. According to information obtained from the scoring clinicians, the component anterior hyoid excursion was scored as different in 30 and simulated 15pps because the movement appeared more robust and brisk, therefore less impaired, in the simulated 15pps rather than the 30pps recording. Epiglottic movement was noted to be different due to the appearance of greater movement (partial inversion rather than absent inversion) in the 30pps recording when compared with the simulated 15pps recording possibly because frames that demonstrated some horizontal displacement (an indicator of some preservation of laryngeal elevation)[25] were missed in the simulated 15pps recording. Pharyngeal contraction was noted to be different in 30pps recording compared with the simulated 15pps recording, because a small dynamic pulsion psuedodiverticulum, seen only at the height of the swallow and contributed to pharyngeal residue, was observed in the 30pps recording but missed in the simulated 15pps exam. Pharyngoesophageal segment opening scores were worse in the simulated 15pps versus the 30pps recording because of a reduced number of frames were available to appreciate the full extent and duration of the opening. Tongue base retraction was noted to be different between the 30 and the simulated 15pps because maximal tongue base retraction is judged from one frame. If the frame selected to score retraction was not captured in both the 30pps and simulated 15pps recordings, the judgment of tongue base retraction from the two recordings may be different.
The PAS is a valid and reliable measure of airway protection, used to estimate swallowing severity and make oral intake recommendations. This initial study revealed that in one out of five patients PAS scores differed between 30 and simulated 15pps recordings. These discrepancies occurred with thin boluses (5ml and cup sip) and the differences were between a score of 1 and a score of 2. While this is not a robust finding, we consider any difference attributable to pulse rate (e.g. artifact of the exam) versus swallowing function, a potentially significant finding. Given the range of PAS scores for the five randomly selected patients in Experiment 1, it was not possible to draw any meaningful conclusions from this experiment other than that the fact that pulse rate can cause a difference in PAS scores. We completed Experiment 3 to elucidate this topic on a patient population known to have a range of PAS scores. The results of this experiment were significantly more robust and indicate that pulse rate may have a strong impact on PAS scores. Further research with greater numbers of patients across the swallowing impairment severity continuum is warranted before broader conclusions or recommendations can be made.
We included measurements that describe the fluoroscopy system used in our MBS studies (Table 7) to aid the interpretation of our clinically-focused results. It is important to note that these were obtained using the manufacturer’s fluoroscopy Automatic Exposure Control system which varies the x-ray tube voltage (kV) and x-ray beam intensity (mAs) to maintain a nominal Air Kerma at the image receptor. In these exposures, for example, the x-ray tube voltage ranged from 60 to 90 kV, depending on phantom thickness and the image frame acquisition rate. The amount of backscatter, which is an important factor for determining the patient skin dose, is also dependent on the selected x-ray tube voltage. We included backscatter radiation in our measurements because they are essential for the accurate determination of patient skin doses. Any assessment of how the selected pulse rate will impact on the patient dose is a complex undertaking that will depend on how a given manufacturer’s fluoroscopy system AEC system been designed to operate. The data in Table 7 are helpful because they quantitatively illustrate how patient skin doses vary with pulse rate and patient thickness, and quantify dose values likely to be encountered for fluoroscopy units with AEC systems similar to the one used in our study.
The results of this pilot experiment that investigated the clinical implications of pulse rate demonstrated that differences due to pulse rate influenced diet modification, treatment strategies, and judgments of patient prognosis. While the sample sizes for our experiments were limited, the results point to a potential effect of pulse rate on judgments of swallowing impairment severity with implications for patient care. This type of information is necessary to understand the risk/benefit ratio of radiation exposure versus diagnostic accuracy. If the findings of this preliminary study are upheld in a larger well-powered study, they may indicate a significant public health issue.
Limitations
There were 4 main limitations to this study: 1) small sample sizes, 2) the sample was not representative of the severity continuum of swallowing impairments, 3) no evaluation of pulse rates other than 15 and 30pps for the MBSImP™© components and 4) treatment recommendations based only on MBSImP™© and PAS scores. Given the exploratory, preliminary nature of this study, only 5 MBSS recordings were used in Experiment 1 and 15 recordings were used in Experiment 3. Further, the five patients used in Experiment 1 were chosen at random in an attempt to not bias results. These patients had mild to moderate swallowing impairments. It is possible that results would differ in patients with more severe swallowing impairments. This speculation is supported by our results in Experiment 3. Further, Experiment 1 only evaluated differences between recordings at 15 and 30pps. It would likely be important to evaluate other pulse rates to determine a true threshold of temporal resolution necessary for the reliable and accurate scoring of swallowing impairment. The small sample size of Experiments 1 and 2 limited our analysis to descriptive statistics. Lastly, this study asked clinicians to base treatment recommendations only on the MBSS. While the observations of physiologic impairment do and should play a role in accurately targeting treatment of the swallowing mechanism, the clinical circumstances of the patient are integral in treatment planning. While this study did not include such clinical circumstances, the results of the study demonstrate alterations and potentially inaccuracies that may occur if aspects of swallowing impairment are distorted or missed due to pulse rate.
CONCLUSIONS
There are four main conclusions from this study: 1) there were differences in MBSImP™© scores between MBSSs obtained with 30 and simulated 15pps, 2) the differences in scores occurred on physiologic components that are time dependent, 3) the difference in scores influenced treatment recommendations, and 4) there were differences in PAS scores between MBSSs obtained with 30pp and simulated 15, 7.5 and 4pps. 1) The difference in MBSImP™© scores between recordings at 30 and simulated 15pps provide initial evidence of the impact of pulse rate for the diagnosis of swallowing impairment. Further research is needed to better understand these differences and their clinical implications between the 30 and 15pps recordings. In the interim, these preliminary findings and recent data on reasonably low fluoroscopy exposure times when using a standardized protocol, support the practice of using 30pps rate during MBSS[26]. A larger study is needed before a conclusion regarding supremacy of 30 or 15pps can be made. Further investigation into the clinical implications of the scoring differences would also strengthen the evidence available to make recommendations regarding the clinical implications of pulse rate. 2) The difference between scores from recordings of 30pps and recordings of simulated 15pps were most obvious for IPS. We hypothesize that IPS was the component most influenced by pulse rate because scoring accuracy of this component is time dependent and occurs on one specific frame of the video record. Differences were also seen in judgments of five other individual physiologic components of swallowing function: anterior hyoid excursion, epiglottic movement, pharyngeal contraction, pharyngeal-esophageal segment opening and tongue base retraction. 3) The difference in MBSImP™© scores between recordings of 30 and simulated 15pps resulted in differences in diet recommendations, treatment strategies and prognosis of returning to a normal diet. This finding demonstrates that pulse rate may have an impact on patient outcomes. 4) Differences between PAS scores for the four pulse rates tested indicate that pulse rate may have a high impact on attributes of the MBSS examination that are used to determine PO status. Given these findings, clinicians and radiologist should be cognizant of the possible judgment differences caused by pulse rate. However, future studies are needed for an evidence-based recommendation. Such studies should thoroughly evaluate the thresholds of pulse rate needed to reliably and accurately score MBSS as well as address the clinical implications of the scoring differences.
Figure 2.
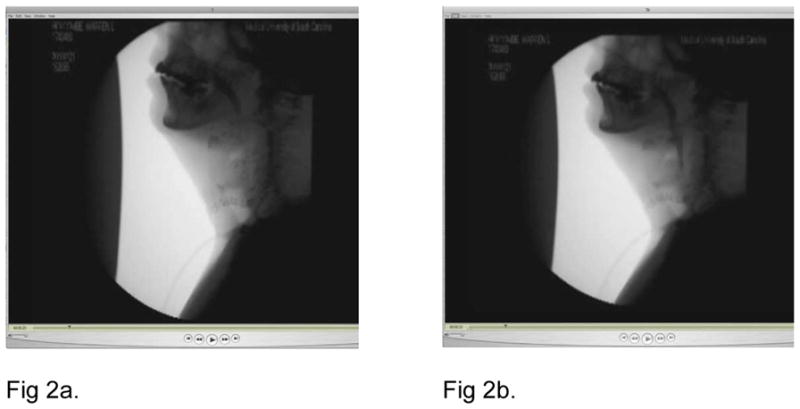
Fluoroscopic images of 30 and simulated 15pps MBSS demonstrating the difference in the scoring of Initiation of Pharyngeal Swallow. Figure 2a is a still image from the 30pps recording and Figure 2b is a still image from the simulated 15pps recording. Both images were captured at 23 seconds into the recording at the beginning of the anterior hyoid excursion.
Acknowledgments
Portions of this study have been presented at the 19th Dysphagia Research Society Annual Meeting, San Antonio, Texas, March 2011; the Medical Image Perception Society meeting, Dublin, Ireland, August 2011; the Annual American Speech-Language-Hearing Association convention, San Diego, California, November 2011; the Association for Clinical Research Training Translational Science 2012 Meeting; and the 20th Dysphagia Research Society Annual Meeting, Toronto, Canada, March 2012.
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
This work was supported by the following grants: grant number K23 DC005764-05 funder NIH/NIDCD, grant number KL2 UL1 RR029880 funder NIH/NCRR, and funder Bracco Diagnostics (no grant number). Other financial or material support was provided by Evelyn Trammell Voice and Swallowing Institute and Northern Speech Services.
References
- 1.Emergency Care Research Institute, Evidence-Based Practice Center. Diagnosis and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia) in Acute Stroke Patients. Rockville MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Altman KW, Yu GP, Schaefer SD. Consequence of dysphagia in the hospitalized patient: impact on prognosis and hospital resources. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;136(8):784–9. doi: 10.1001/archoto.2010.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Groher ME, Bukatman R. The prevalence of swallowing disorders in two teaching hospitals. Dysphagia. 1986;1:3–6. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Logemann JA. Dysphagia: Evaluation and treatment. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 1995;47(3):140–164. doi: 10.1159/000266348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Martin-Harris B, Logemann JA, McMahon S, Schleicher M, Sandidge J. Clinical utility of the modified barium swallow. Dysphagia. 2000;15(3):136–41. doi: 10.1007/s004550010015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mahesh M. Fluoroscopy: Patient radiation exposure issues. RadioGraphics. 2001;21:1003–1045. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.21.4.g01jl271033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Aufrichtig R, Xue P, Thomas CW, Gilmore GC, Wilson DL. Perceptual comparison of pulsed and continuous fluoroscopy. Med Phys. 1994;21:245–256. doi: 10.1118/1.597285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Martin-Harris B, Michel Y, Castell D. Physiologic model of oropharyngeal swallowing revisited. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;133(2):234–40. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.03.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cohen MD. Can we use pulsed fluoroscopy to decrease the radiation dose during video fluoroscopic feeding studies in children? Clinical Radiology. 2009;64(1):70–73. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2008.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Martin-Harris B, Brodsky M, Michel Y, Castell D, Schleicher M, Sandidge J, Maxwell R, Blair J. MBS measurement tool of swallow impairment – MBSImp: Establishing a standard. Dysphagia. 2008;(4):392–405. doi: 10.1007/s00455-008-9185-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Murray J, Johnson A, Hockman E. Slow Motion Affects Accuracy of Interpretation of Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Studies. Dysphagia. 2007;22:357. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rosenbek JC, Robbins J, Roecker EV, Coyle JL, Woods JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia. 1996;11:93–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00417897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Krugler C, Flanagan E. Volitional augmentation of upper esophageal sphincter opening during swallowing. The American journal of physiology. 1991;260:G450–456. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.3.G450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ohmae Y, Logemann JA, Kaiser P, Hanson DG, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of two breath-holding maneuvers on oropharyngeal swallow. The Annals of otology, rhinology, and laryngology. 1996;105:123–131. doi: 10.1177/000348949610500207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shanahan TK, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of chin down posture on aspiration in dysphagic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74:178–181. doi: 10.1016/0003-9993(93)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lazarus CL, Logemann JA, Song CW, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of voluntary maneuvers on tongue base function for swallowing. Folia PhoniatrLogop. 2002;54:171–176. doi: 10.1159/000063192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Groher ME. Dysphagia: Diagnosis and Management. Newton MA: Butterworth-Heineman; 1997. p. 228. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fujiu M, Logemann JA. Effect of a tongue holding maneuver on posterior pharyngeal wall movement during deglutition. American Journal of Speech Language Pathology. 1996;5:23–30. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Logemann JA. Management of dysphagia poststroke. In: Chapey R, editor. Language Intervention Strategies in Adult Aphasia. 3. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins; 1994. pp. 503–512. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Logemann JA, Pauloski BR, Rademaker AW, Colangelo LA. Speech and swallowing rehabilitation for head and neck cancer patients. Oncology. 1997;11:651–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mepani R, Antonik S, Massey B, Kern M, Logemann J, Pauloski B, Rademaker A, Easterling C, Shaker R. Augmentation of deglutitivethyrohyoid muscle shortening by the Shaker Exercise. Dysphagia. 2009;24(1):26–31. doi: 10.1007/s00455-008-9167-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Logemann JA. Behavioral management for oropharyngeal dysphagia. Folia PhoniatrLogop. 1999;51:199–212. doi: 10.1159/000021497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Butler SG, Maslan J, Stuart A, Leng X, Wilhelm E, Lintzenich CR, Williamson J, Kritchevsky SB. Factors influencing bolus dwell times in healthy older adults assessed endoscopically. Laryngoscope. 2011;121(12):2526–34. doi: 10.1002/lary.22372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Logemann J, Kahrilas P, Kobara M, Vakil NB. The benefit of head rotation on pharyngo-esophageal dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989;70:767–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ekberg O, Sigurjónsson SV. Movement of the epiglottis during deglutition: A cineradiographicstudy. Gastrointest Radiol. 1982;7(2):101–7. doi: 10.1007/BF01887619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bonilha HS, Humphries K, Blair J, Hill E, McGrattan K, Carnes B, Martin-Harris B. Radiation exposure time during MBSS: Influence of swallowing impairment severity, medical diagnosis, clinician experience, and standardized protocol use. Dysphagia. doi: 10.1007/s00455-012-9415-z. in press, #DYSP914R1, NIHMSID#386358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]