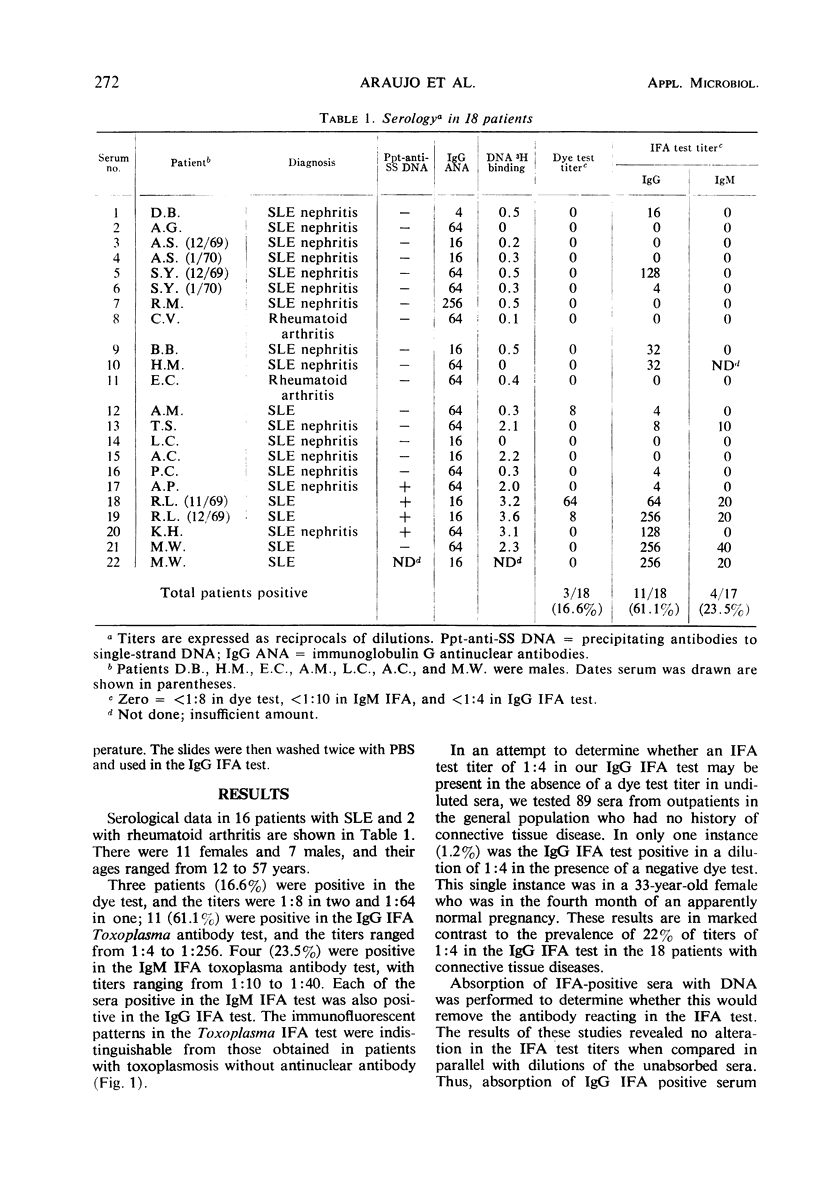
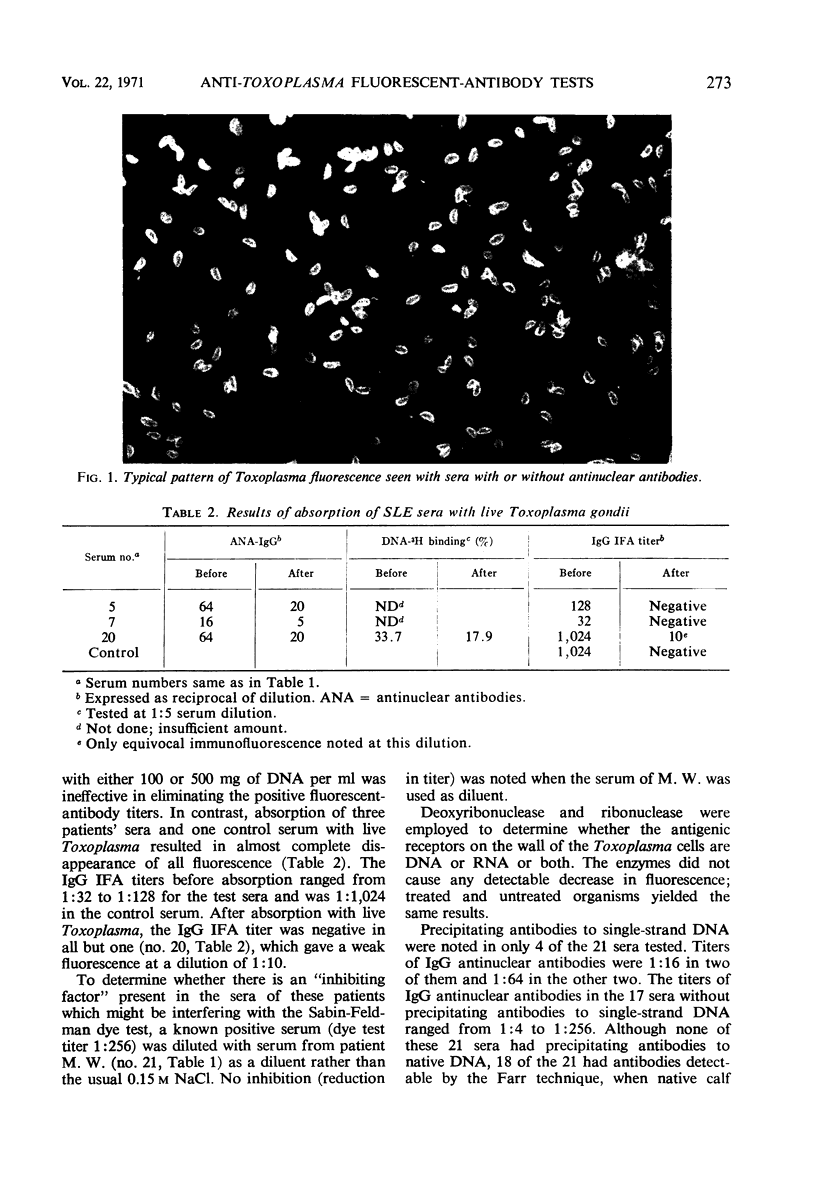
Abstract
The indirect fluorescent-antibody (IFA) method for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis is widely used and is considered to be as specific as the Sabin-Feldman dye test. After observing a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had a positive toxoplasma IFA test but a negative dye test, we studied sera with high titers of antinuclear antibodies from 16 SLE patients and from 2 with rheumatoid arthritis for Toxoplasma antibodies in the immunoglobulin G and M (IgG and IgM) IFA tests and the dye test. Results of these tests were compared with titers of antinuclear antibodies, precipitating antibodies to single-strand deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and binding antibodies by use of DNA labeled with 3H-actinomycin D. Of 18 patients, 11 had IgG and 4 had IgM IFA Toxoplasma antibodies; only 2 had antibodies detectable in the dye test. The immunofluorescence patterns in the Toxoplasma IFA test were indistinguishable from those obtained in patients with toxoplasmosis without antinuclear antibodies. Absorption of SLE sera with DNA did not result in a decrease in Toxoplasma IFA titers. When SLE sera were absorbed with live T. gondii, a marked drop in IgG IFA titer was observed as well as a decrease in titers of antinuclear antibodies and 3H-DNA binding. Treatment of Toxoplasma cells with deoxyribonuclease and ribonuclease did not decrease their fluorescence. These results suggest that T. gondii nuclear antigens can absorb antinuclear antibodies but do not have exposed substrates for deoxyribonuclease. Tests in which organisms containing “nuclear” antigens for IFA detection of antibodies to these organisms are used may result in “false-positives” with sera containing antinuclear antibodies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bickel Y. B., Barnett E. V., Pearson C. M. Immunofluorescent patterns and specificity of human antinuclear antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Sep;3(7):641–656. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr R. I., Koffler D., Agnello V., Kunkel H. G. Studies on DNA antibodies using DNA labelled with actinomycin-D (3H) or dimethyl (3H) sulphate. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 May;4(5):527–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsén N. R., Alspaugh M., Barnett E. V. Precipitating antibodies to DNA induced by heat-denatured DNA-albumin conjugates in the rabbit. Immunology. 1970 Oct;19(4):669–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. L., Van Herle A. J., Barnett E. V. Auto-antibodies of the IgD class. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jun;6(6):951–962. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus S. J., Haserick J. R., Lantz M. A. Fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption test reactions in lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 4;282(23):1287–1290. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006042822303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. I. Diagnostic significance in congenital cases and a method for their rapid demonstration. Pediatrics. 1968 Jun;41(6):1082–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. II. Prevalence and significance in acquired cases. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S. Toxoplasmosis: recent developments. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:201–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Barnett E. V., Leddy J. P. Autosensitivity diseases (concluded). Immunologic and pathogenetic concepts in lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and hemolytic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1966 Dec 29;275(26):1486–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196612292752607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton B. C., Benchoff B. M., Brooks W. H. Comparison of the indirect fluorescent antibody test and methylene blue dye test for detection of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Mar;15(2):149–152. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



